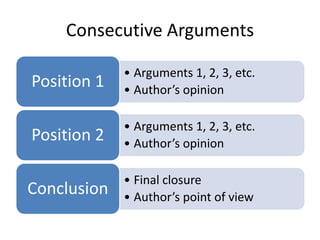
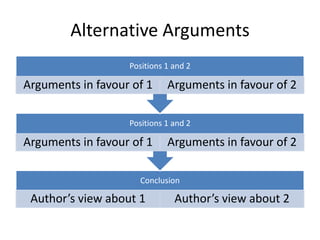
The document defines argumentation as the act of giving reasons for or against something in order to make and present arguments. It discusses three types of arguments: exposition which presents a thesis defended by arguments and concluded, discussion which presents two opposing paradigms argued for over each other, and challenge which attacks a thesis with arguments. The document also describes two ways arguments can be organized - consecutively with opposing positions presented one after another, or alternatively with opposing views contrasted within the same section and the author indicating their preferred view.