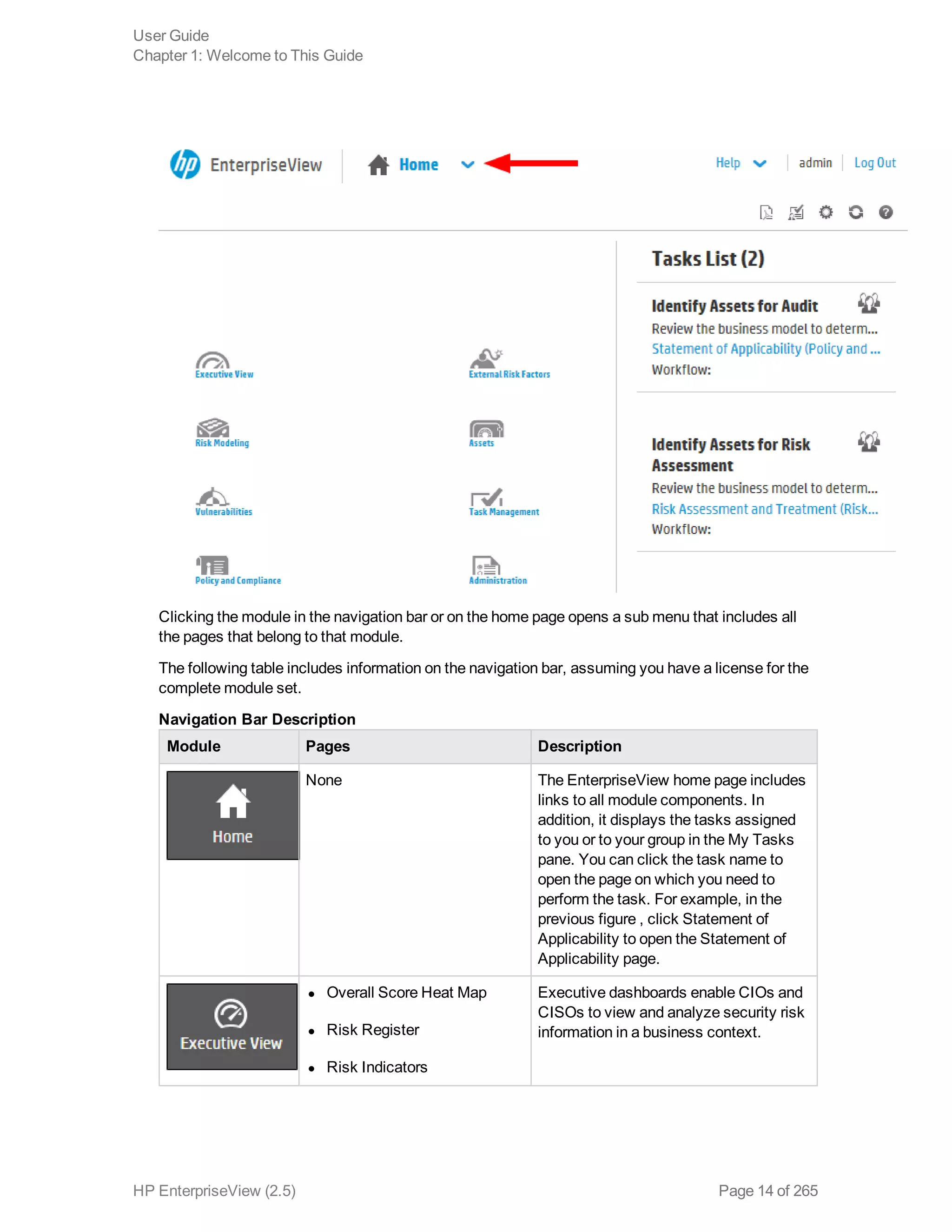
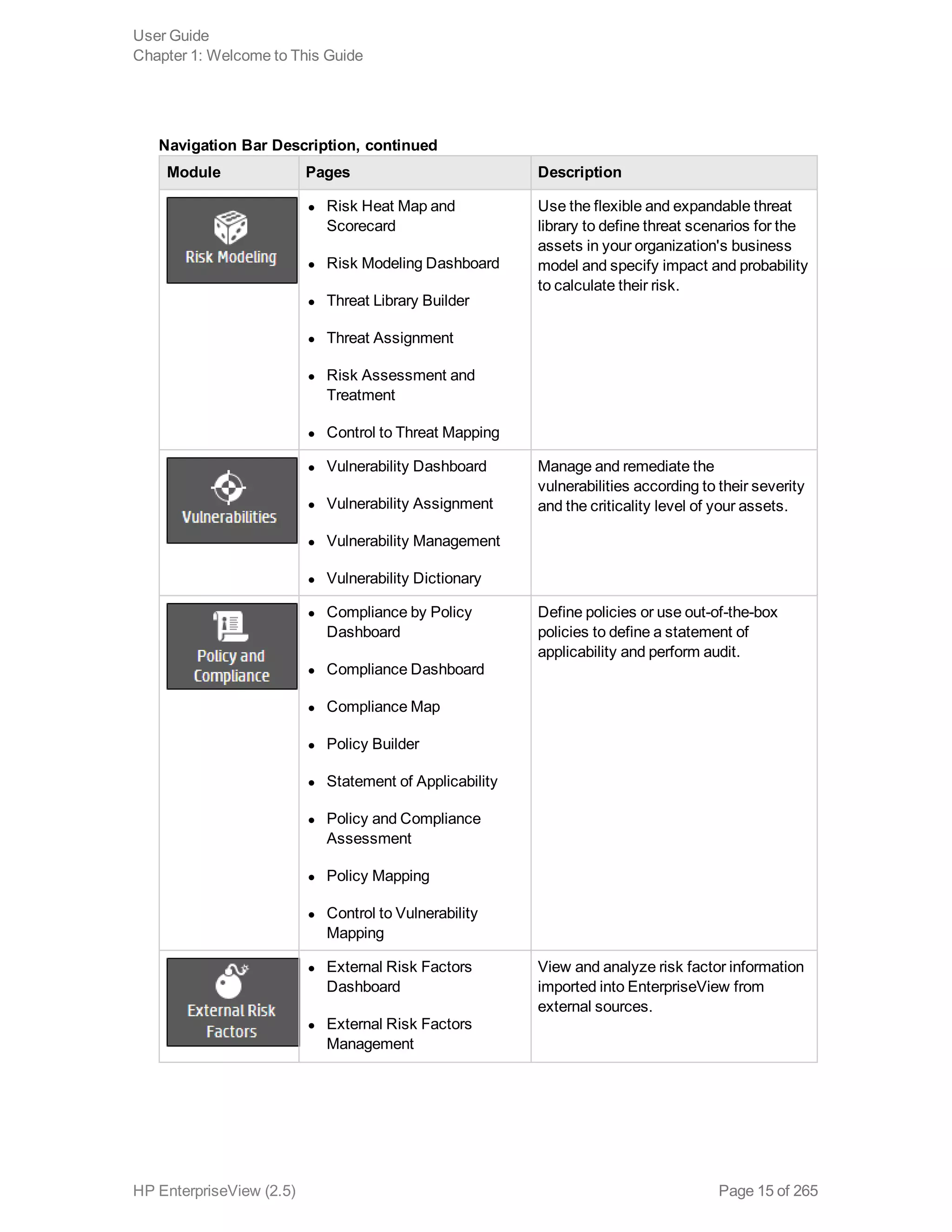
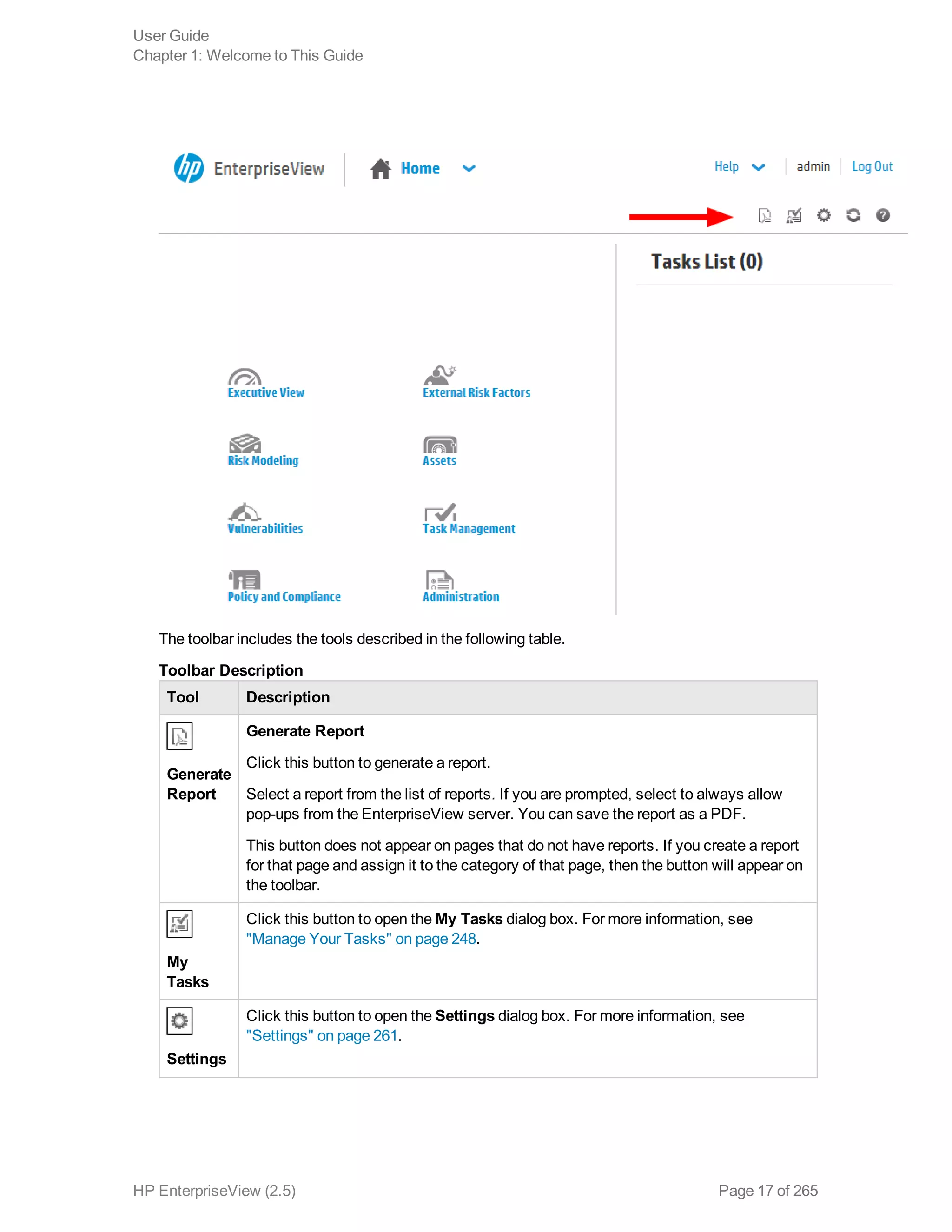
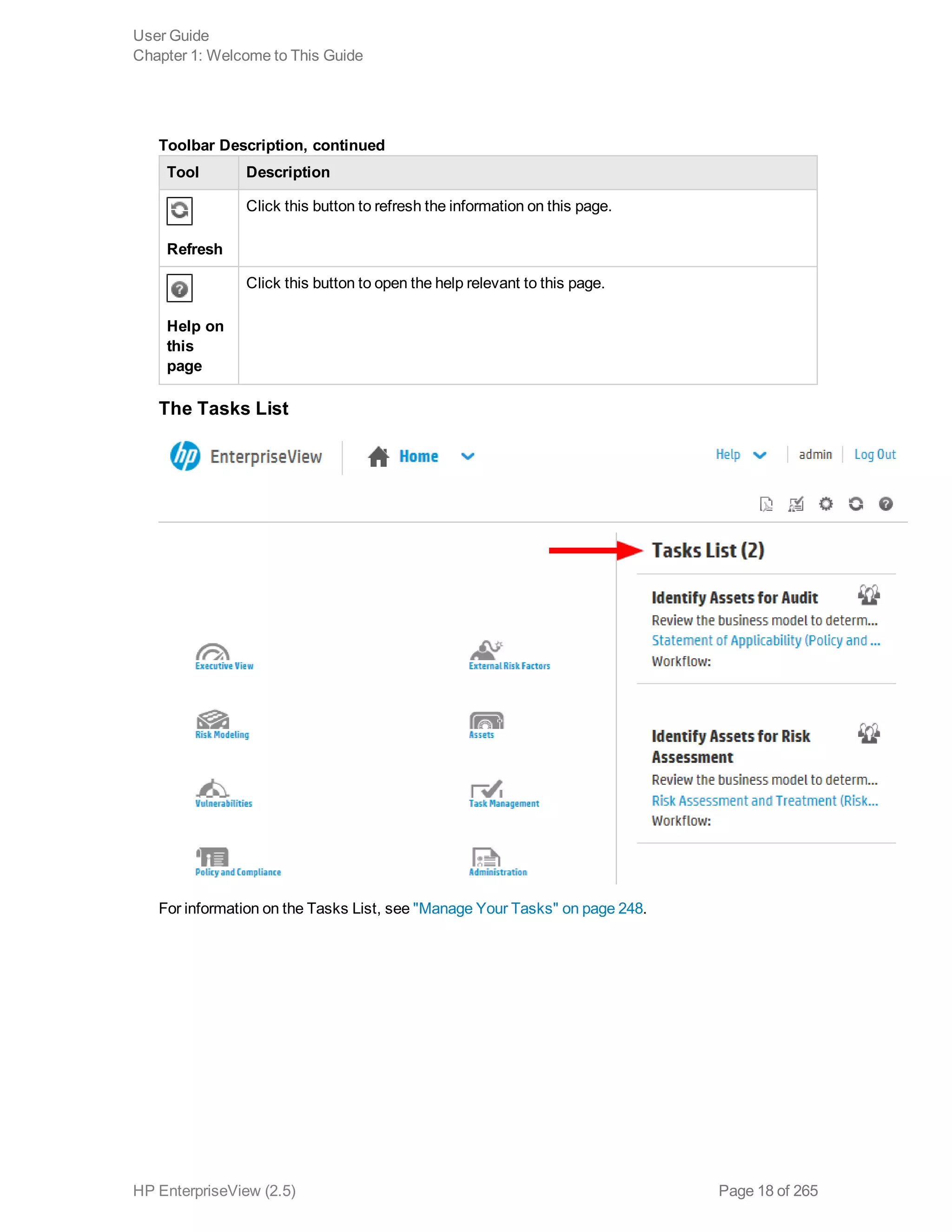
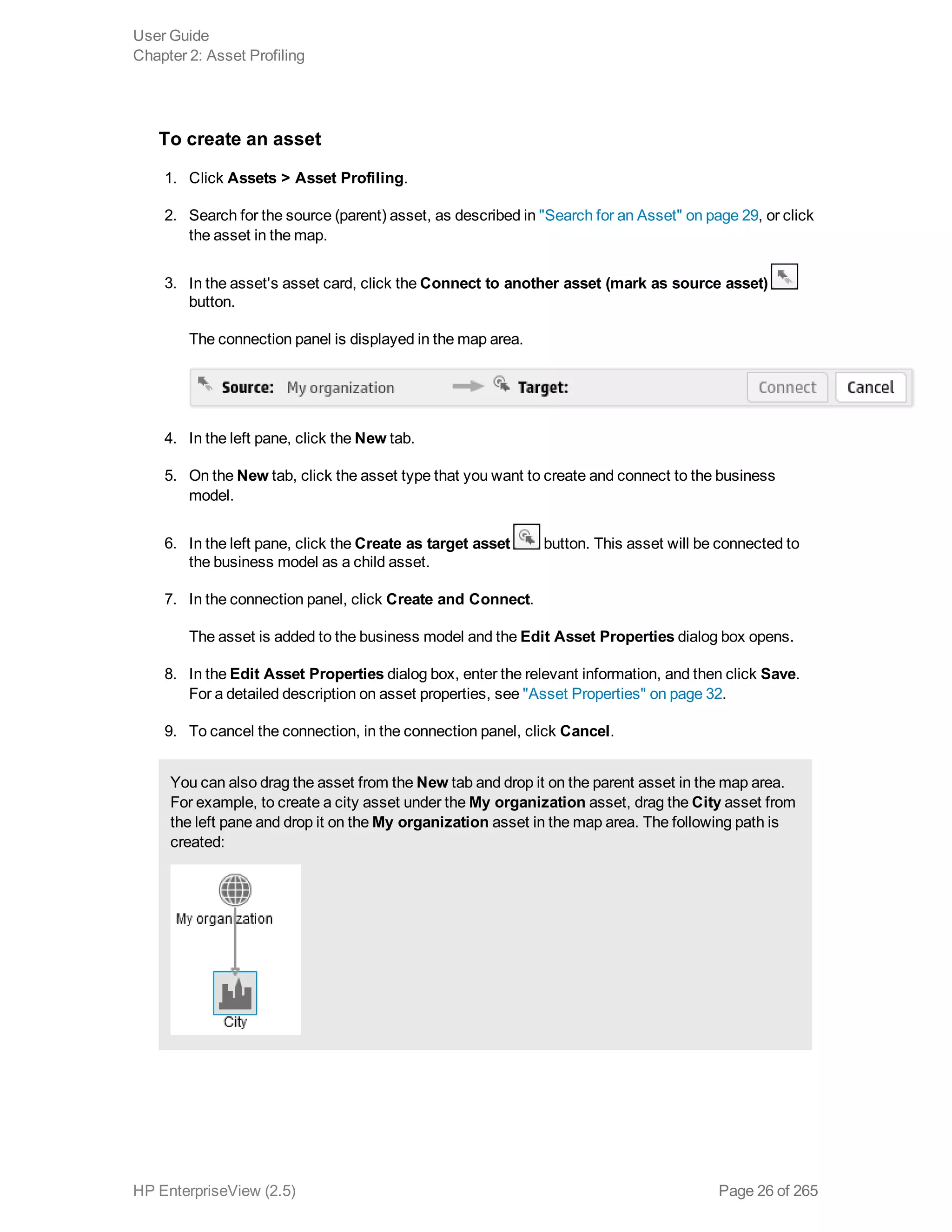
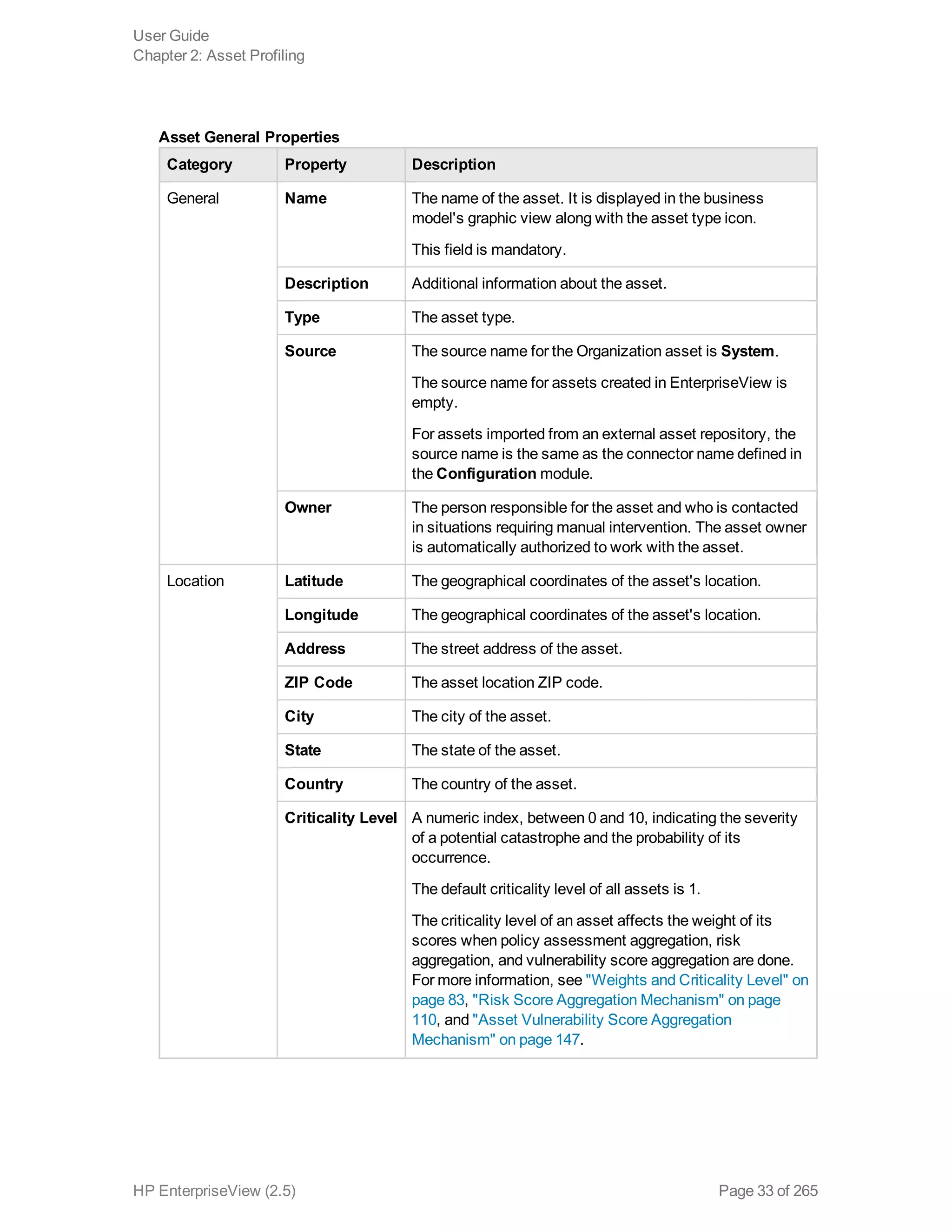
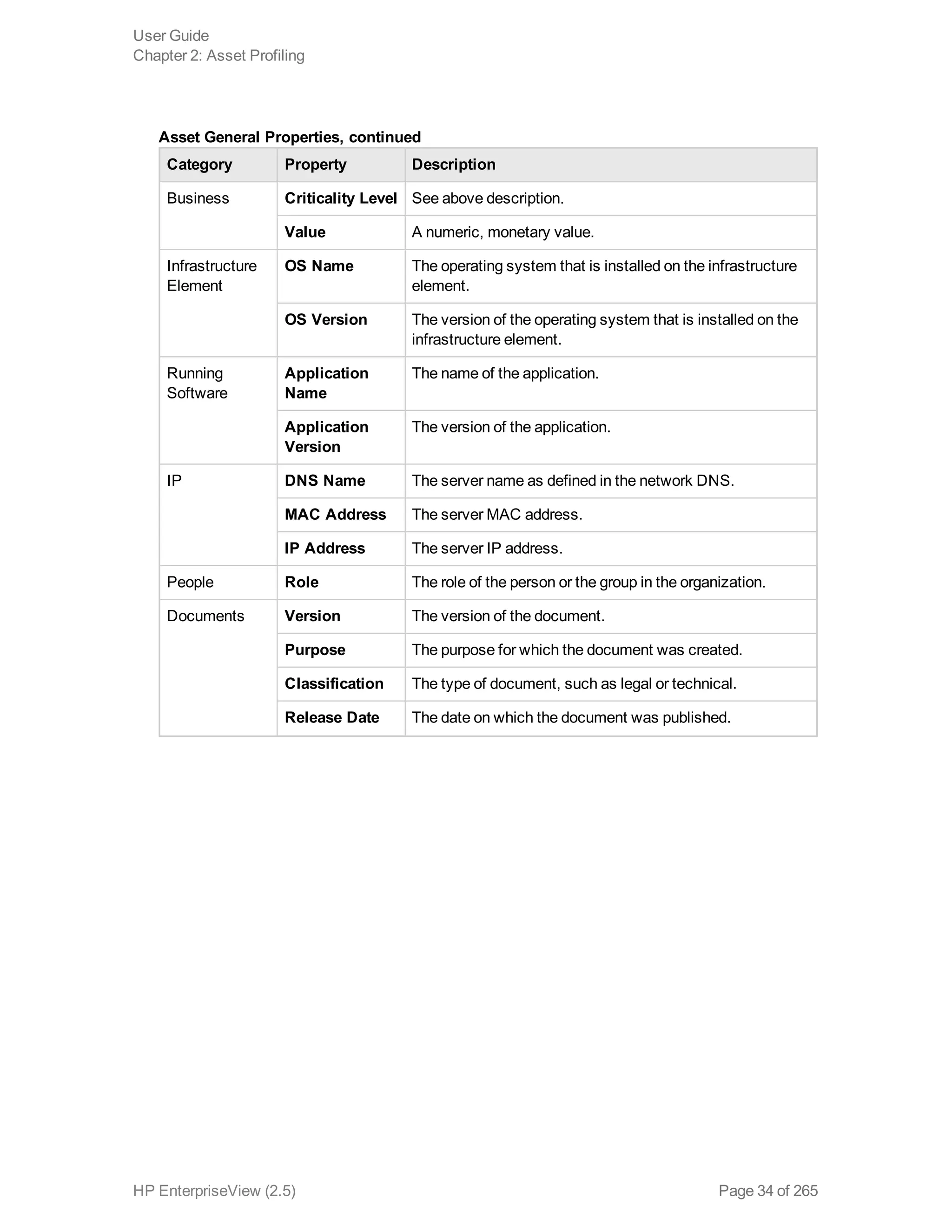
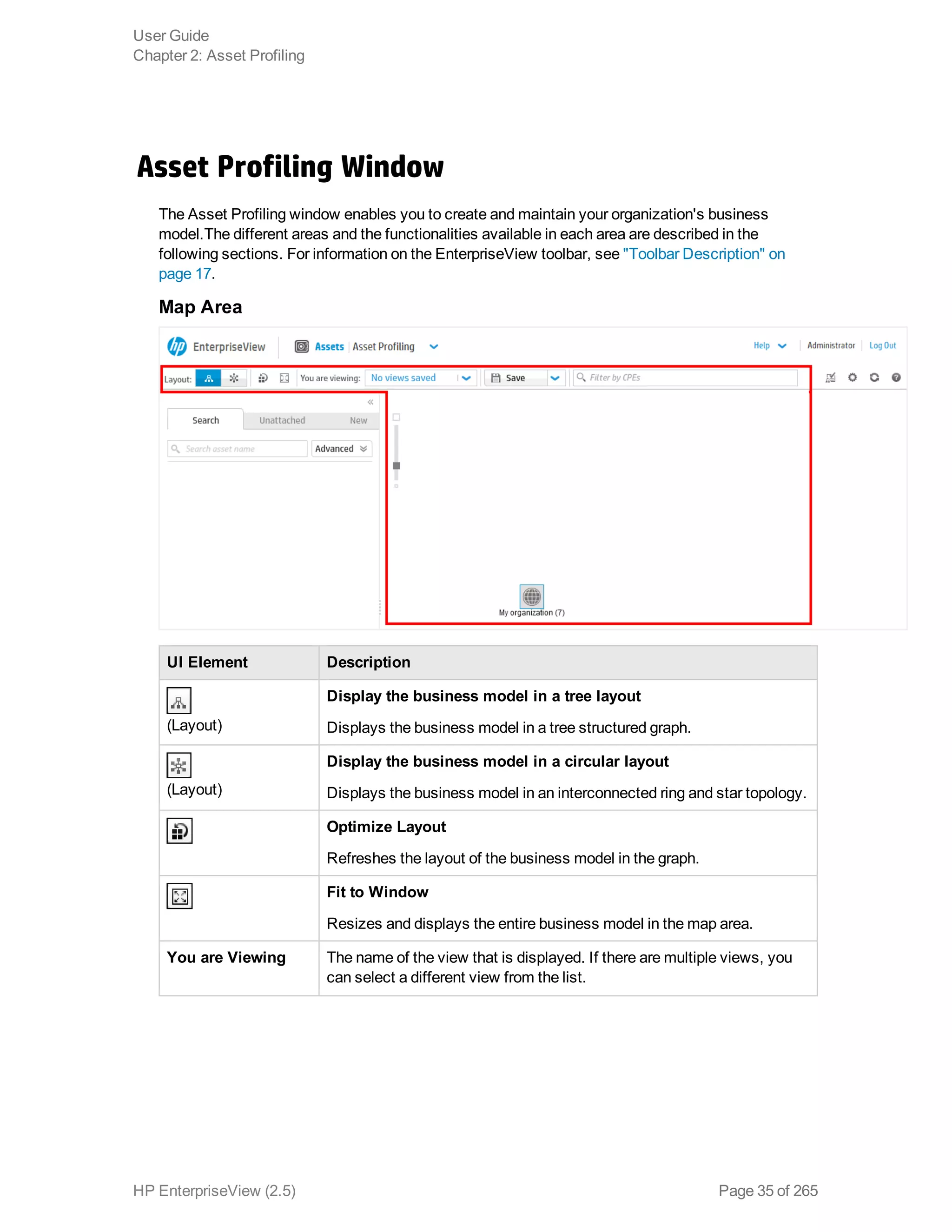
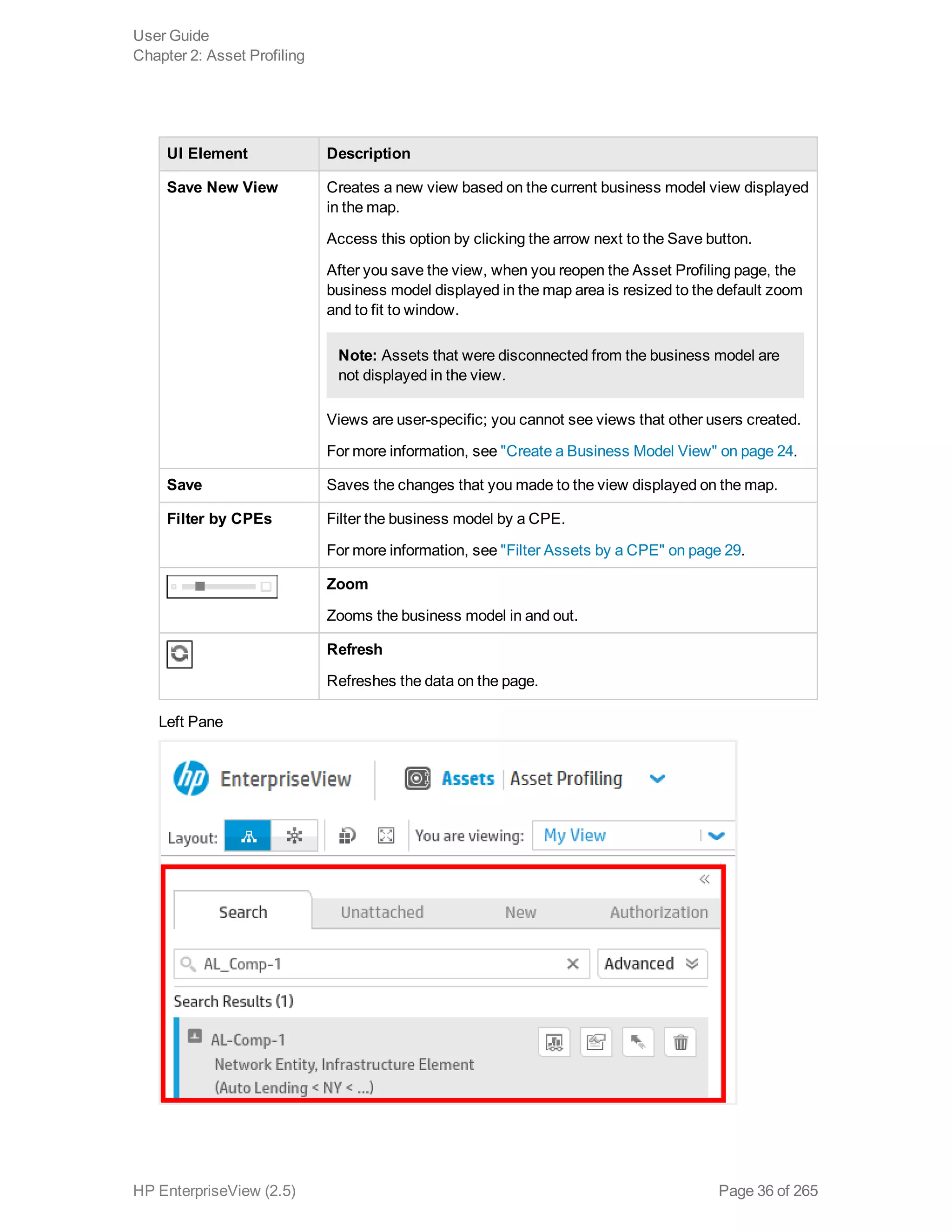
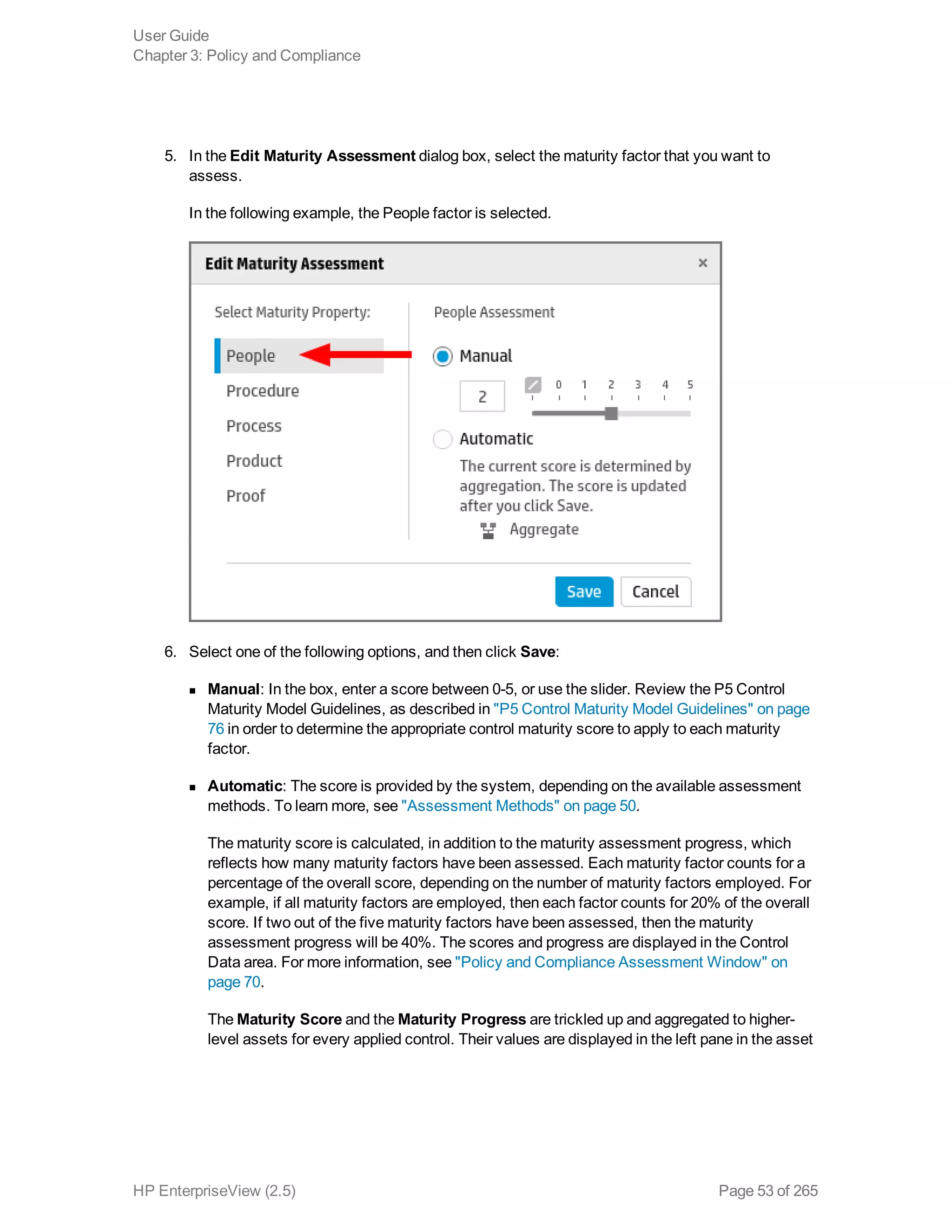
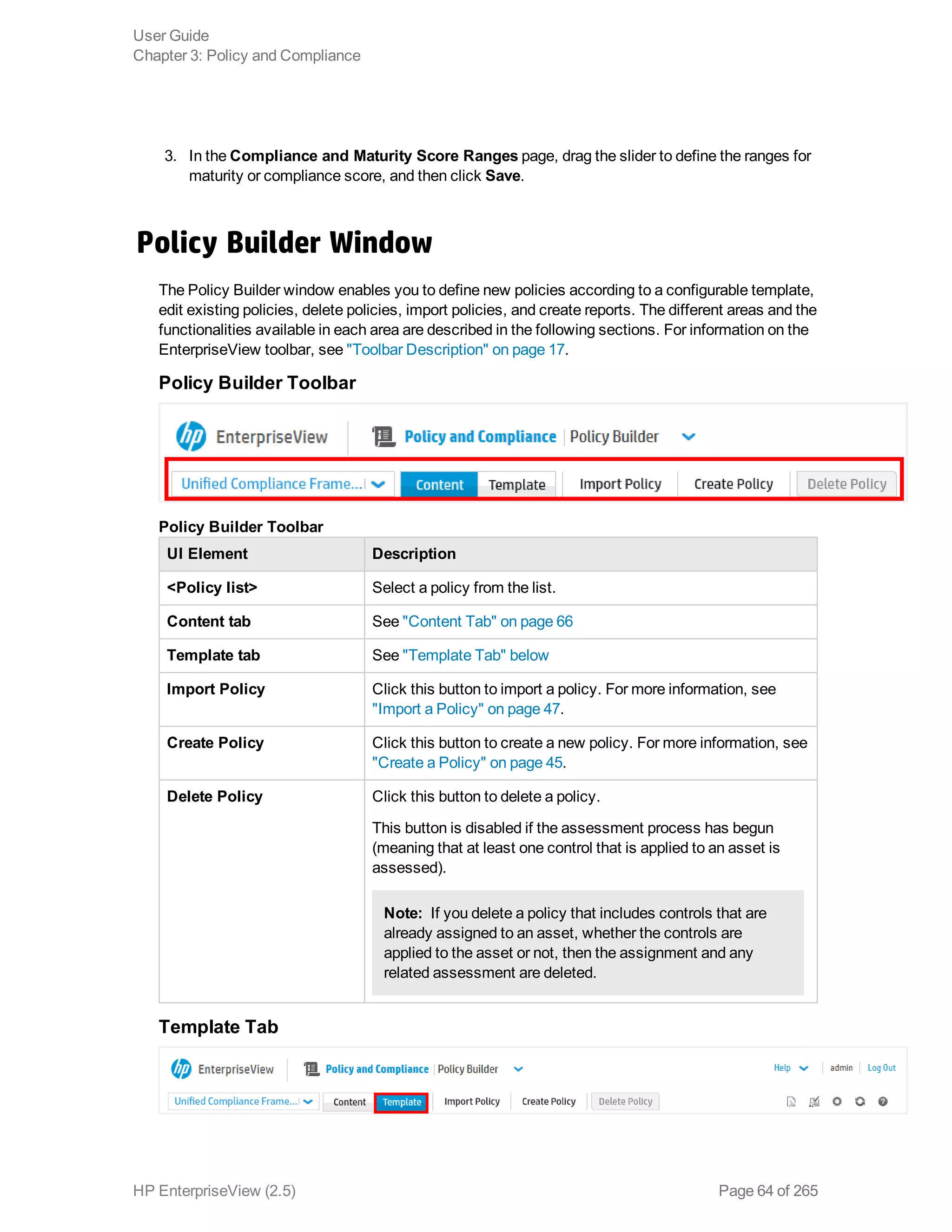
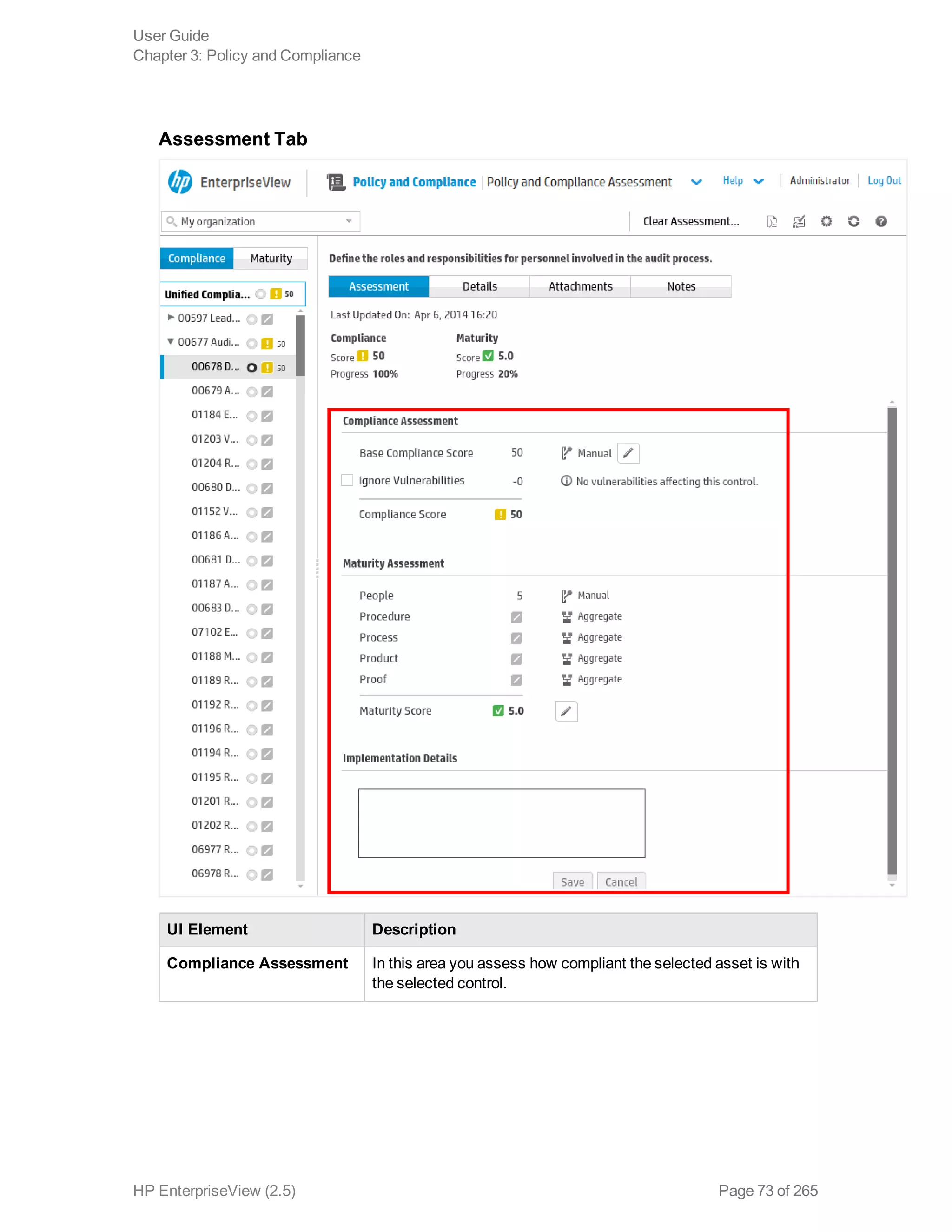
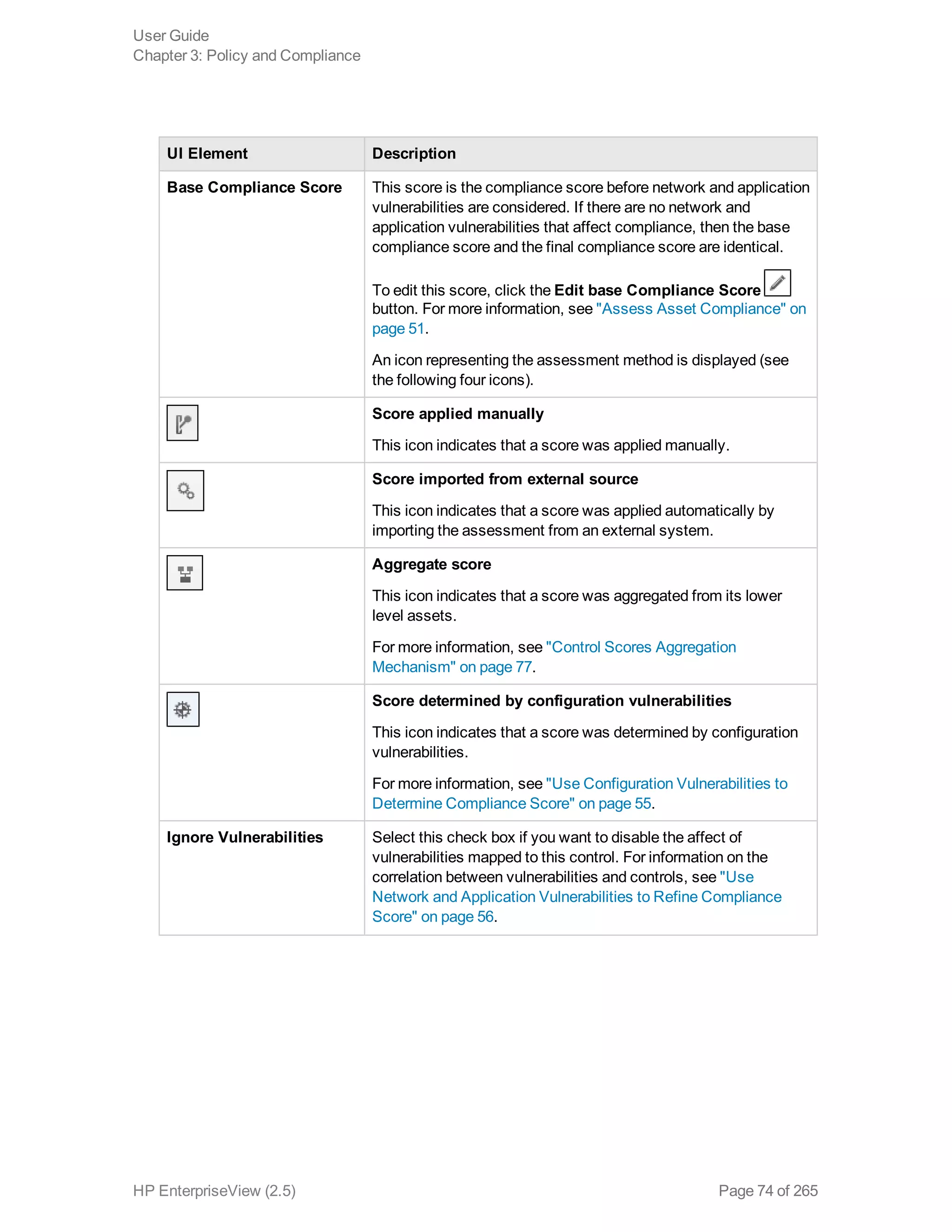
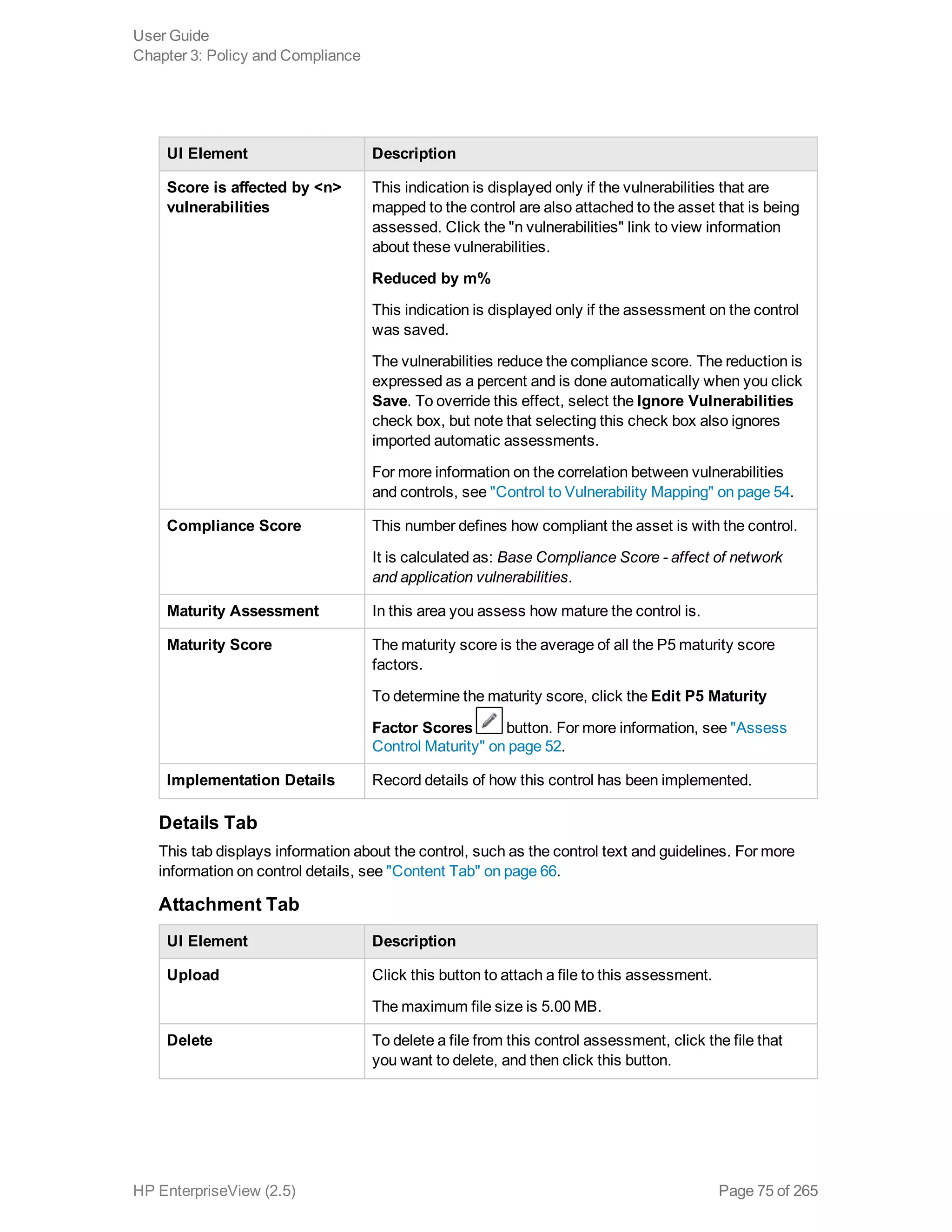
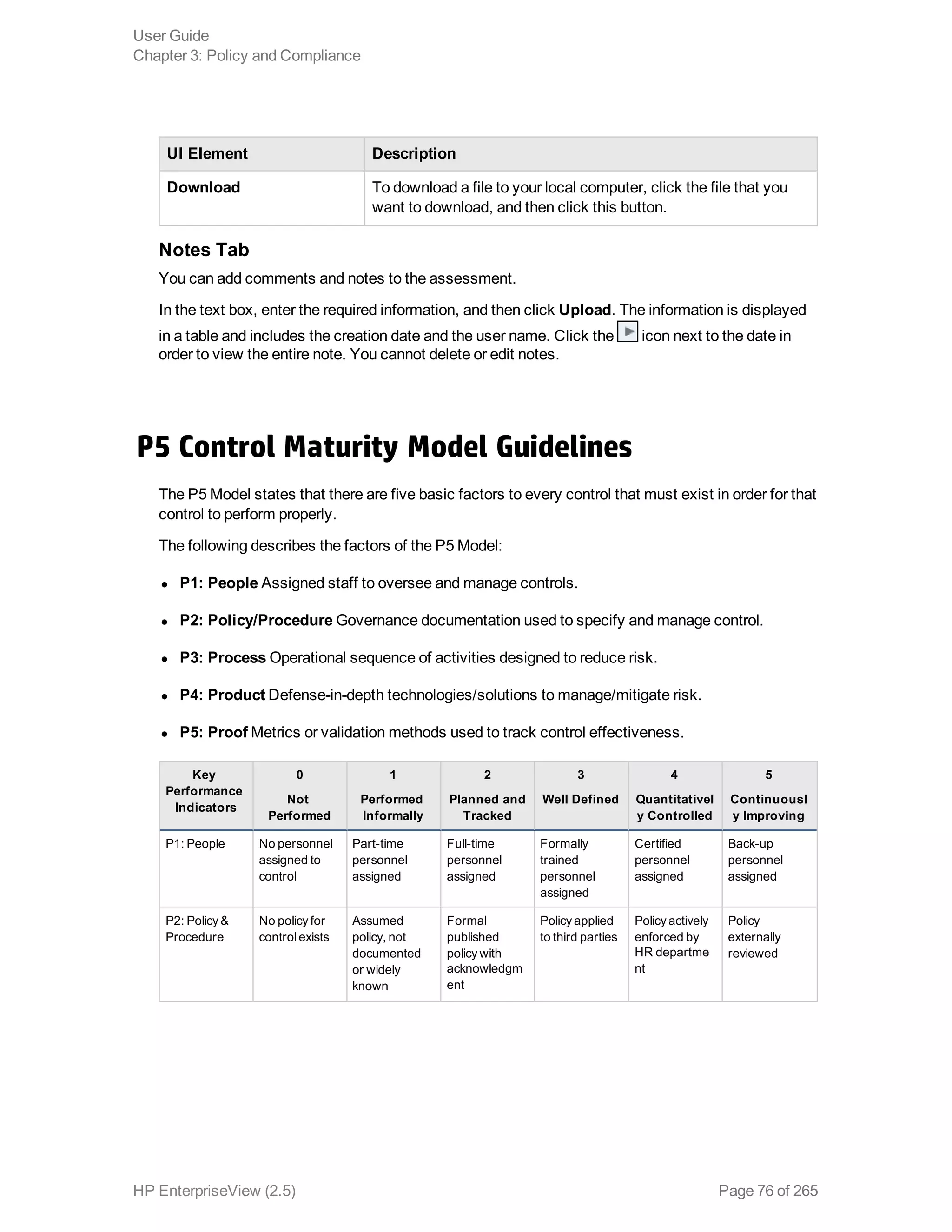
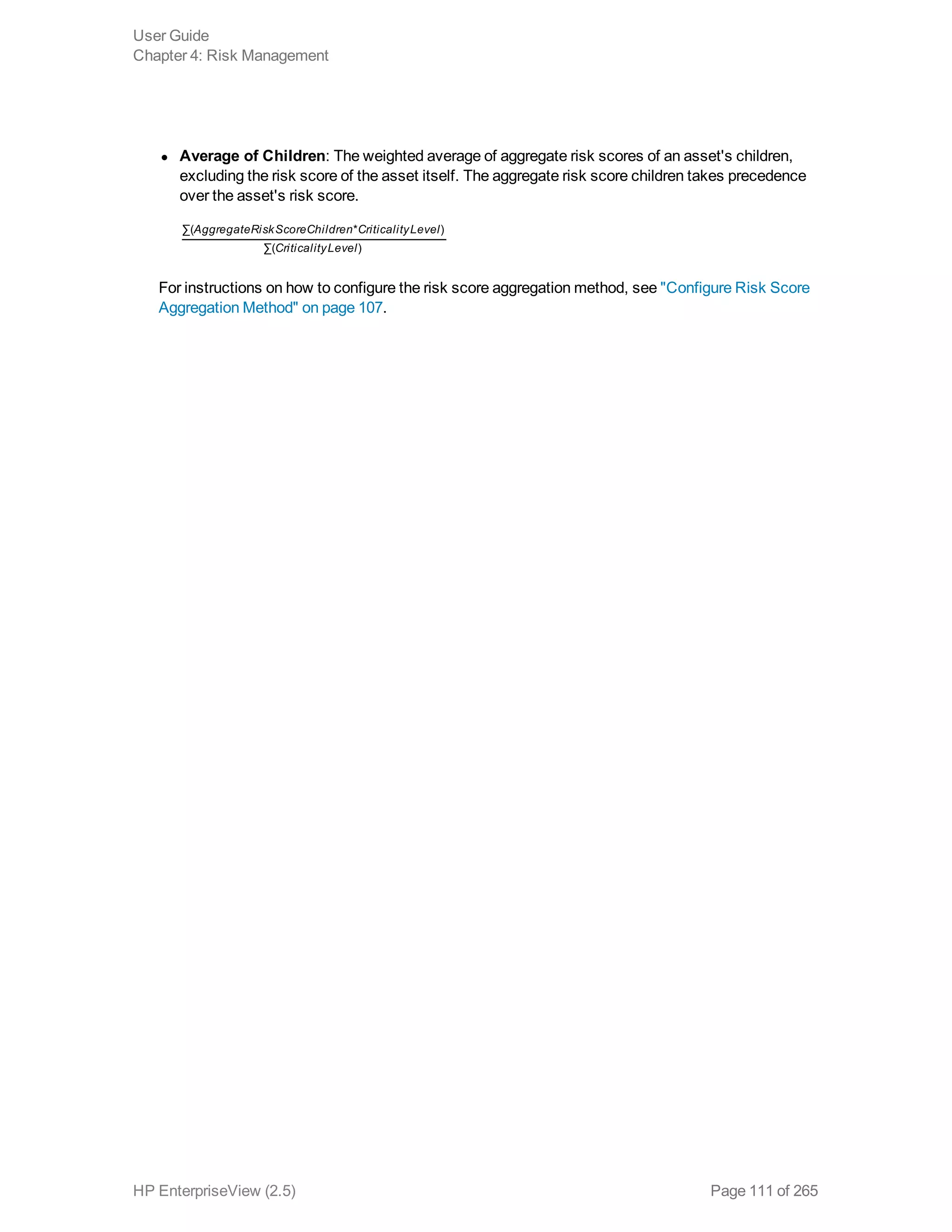
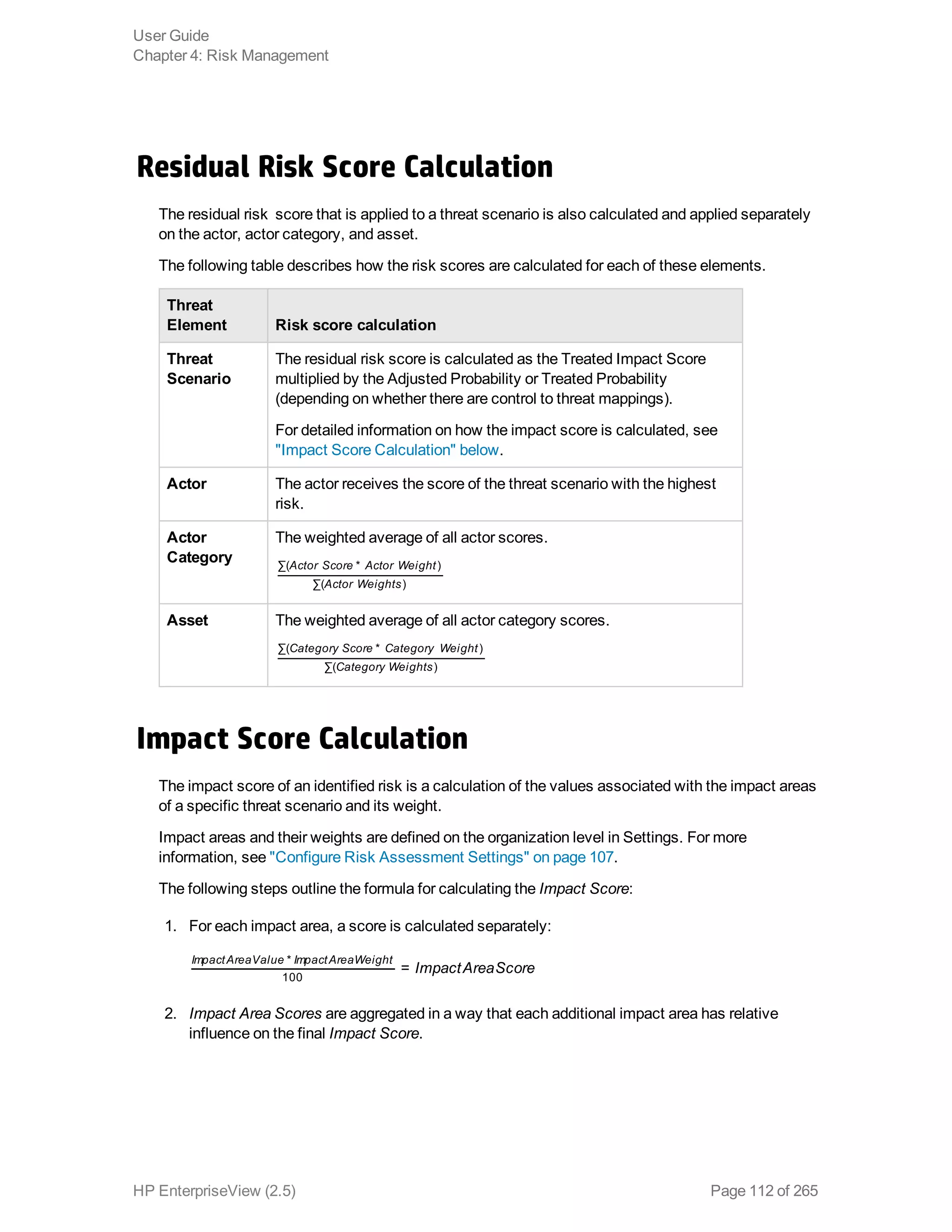
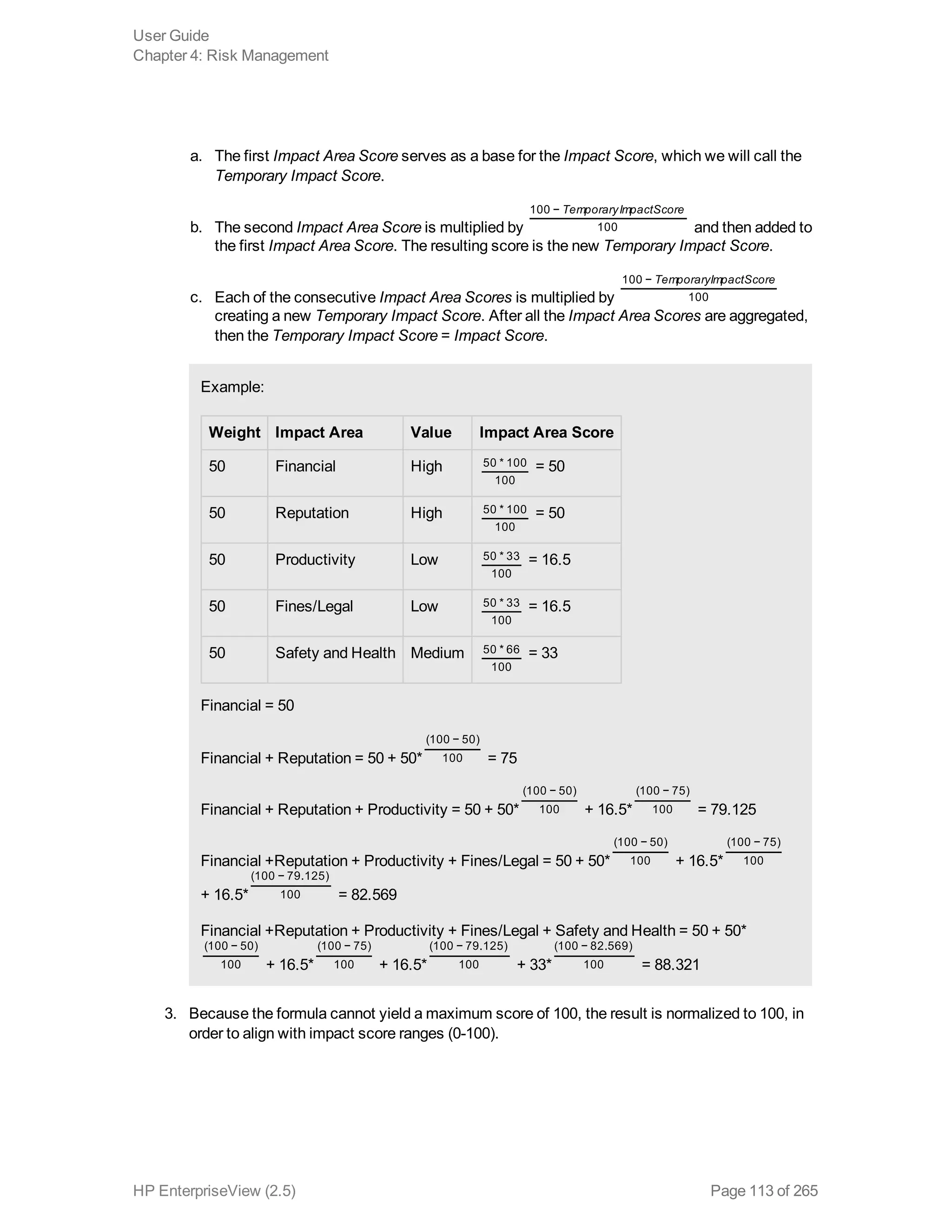
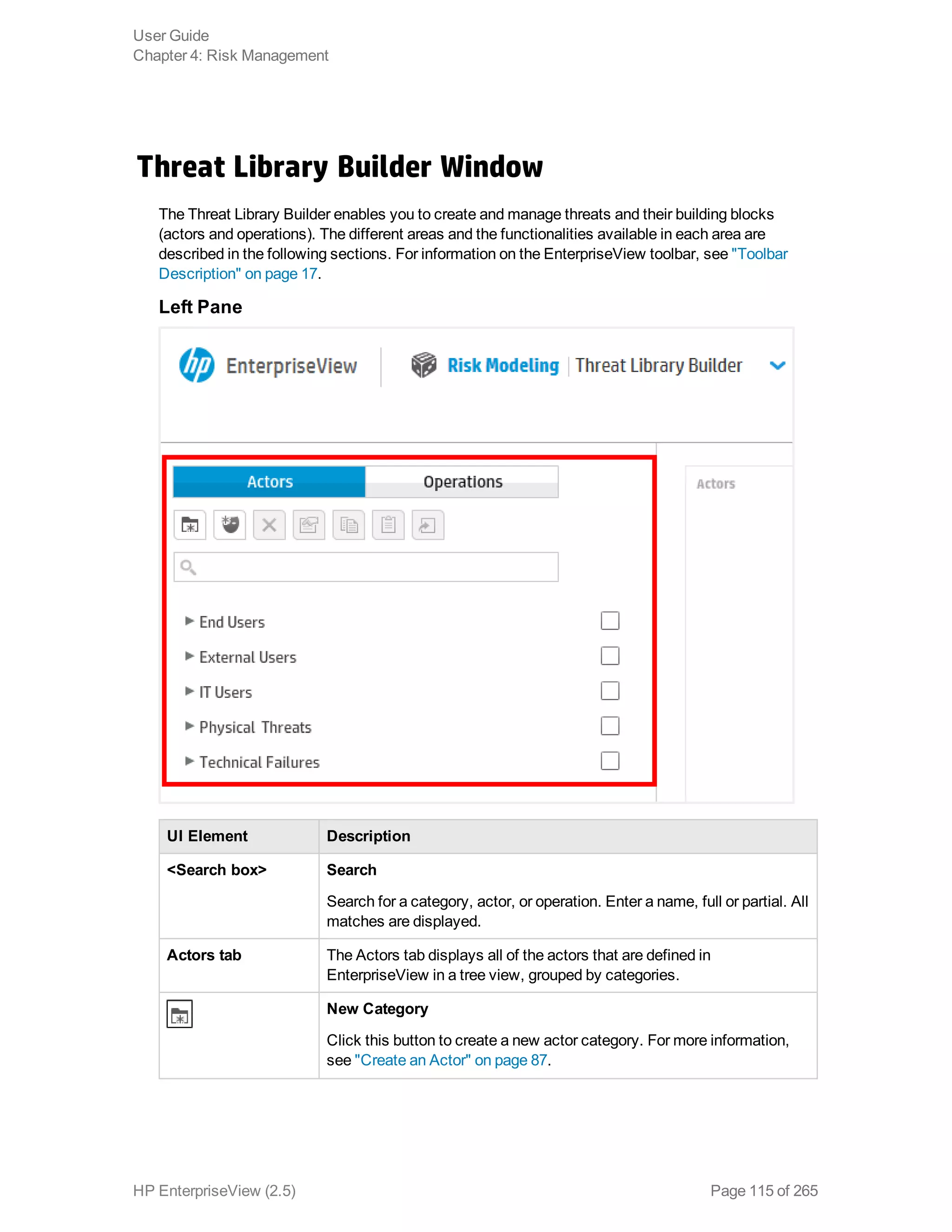
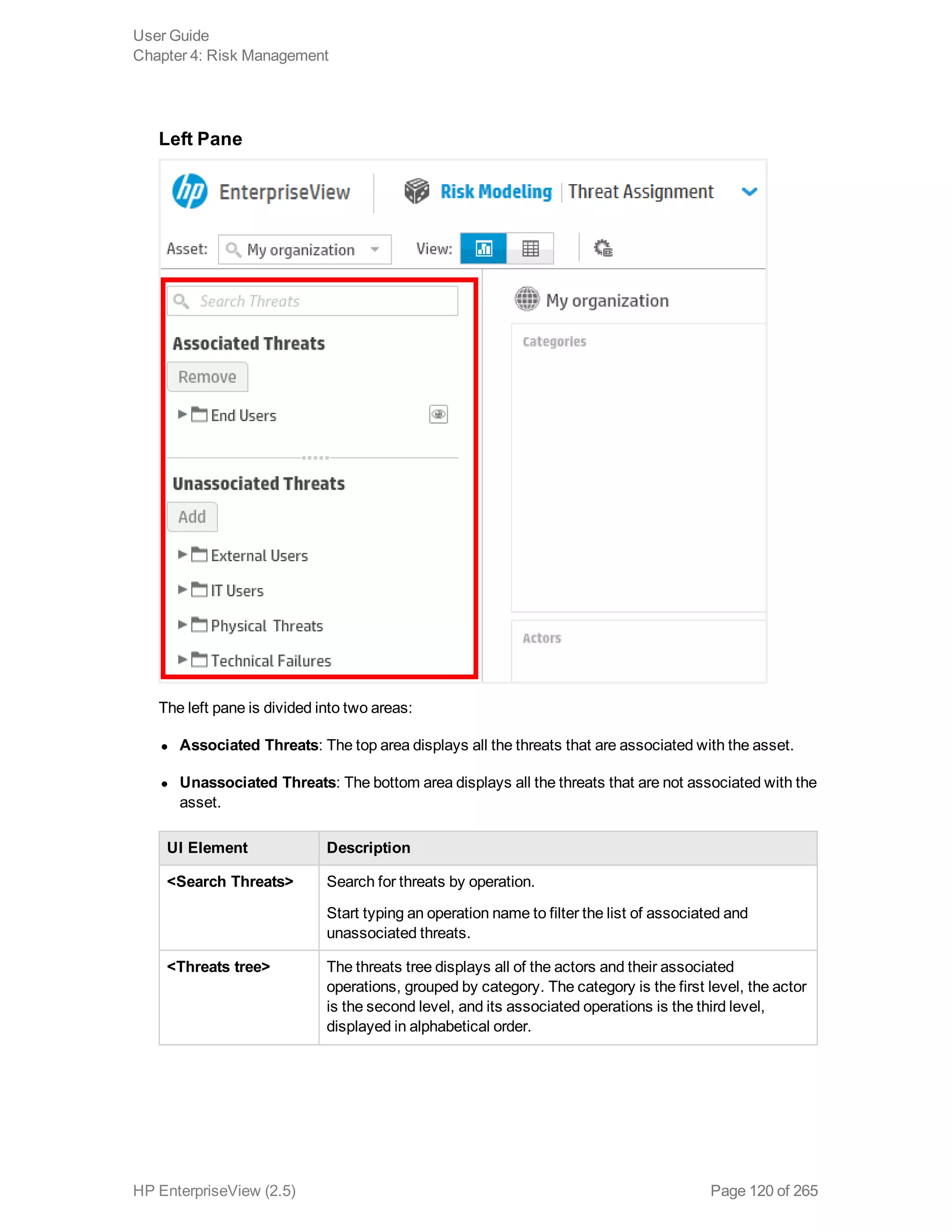
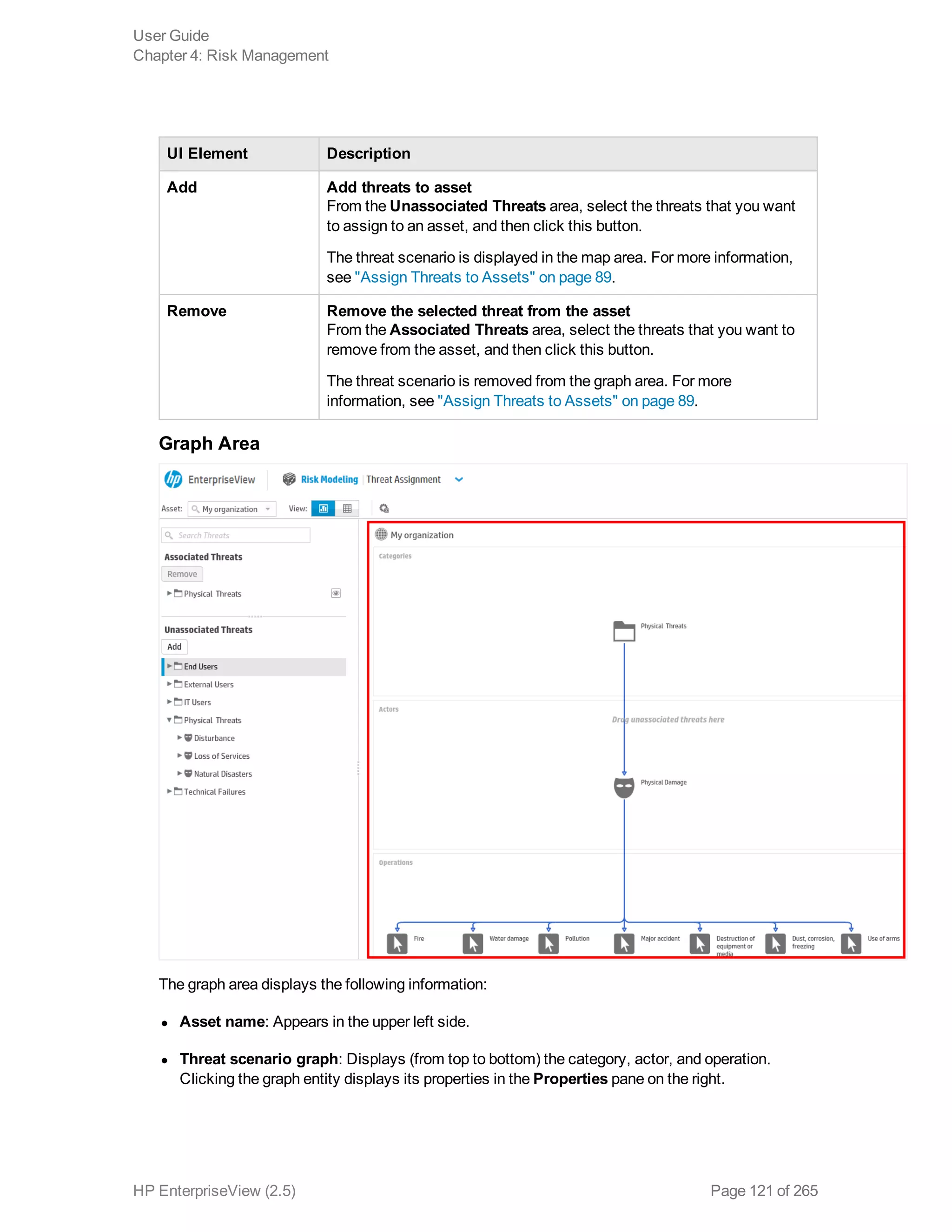
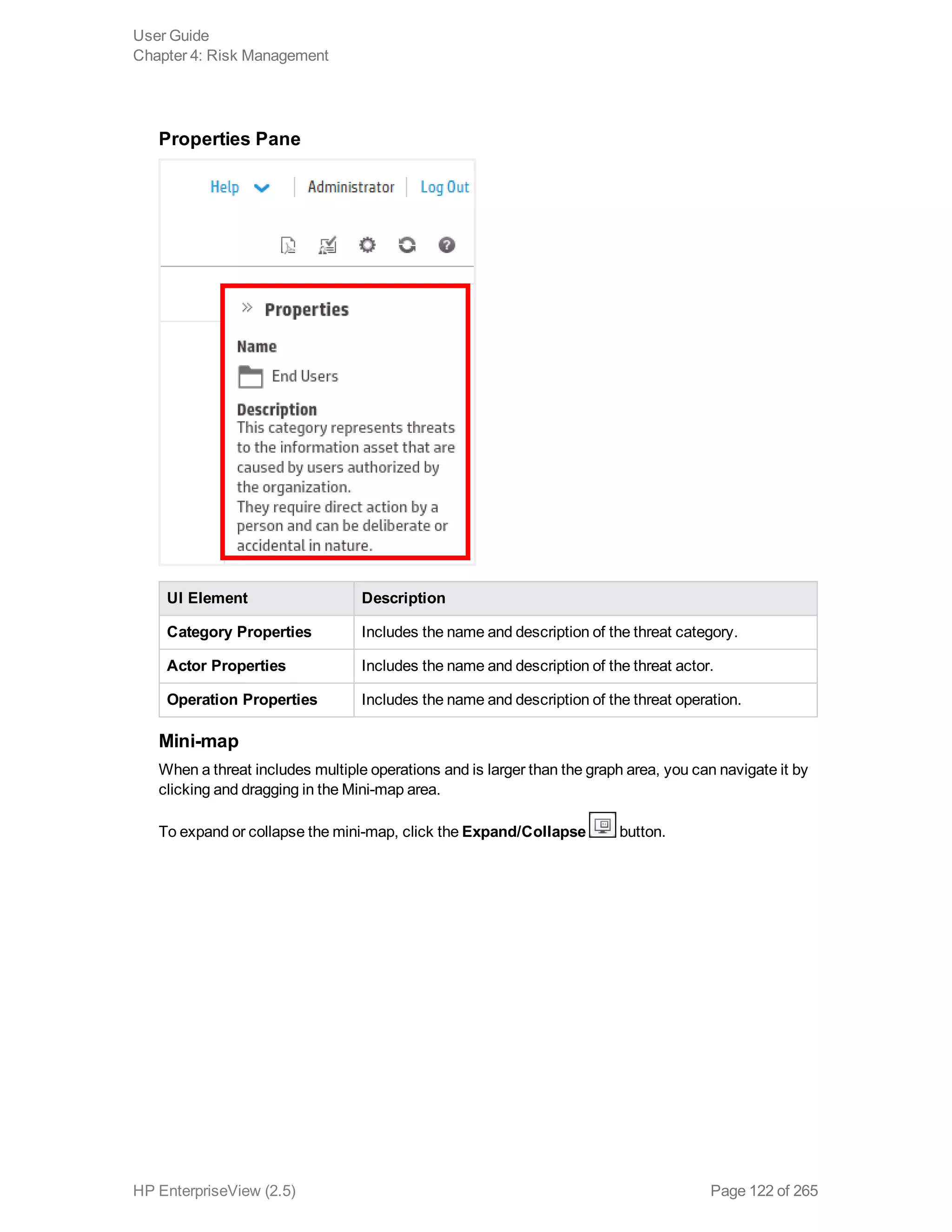
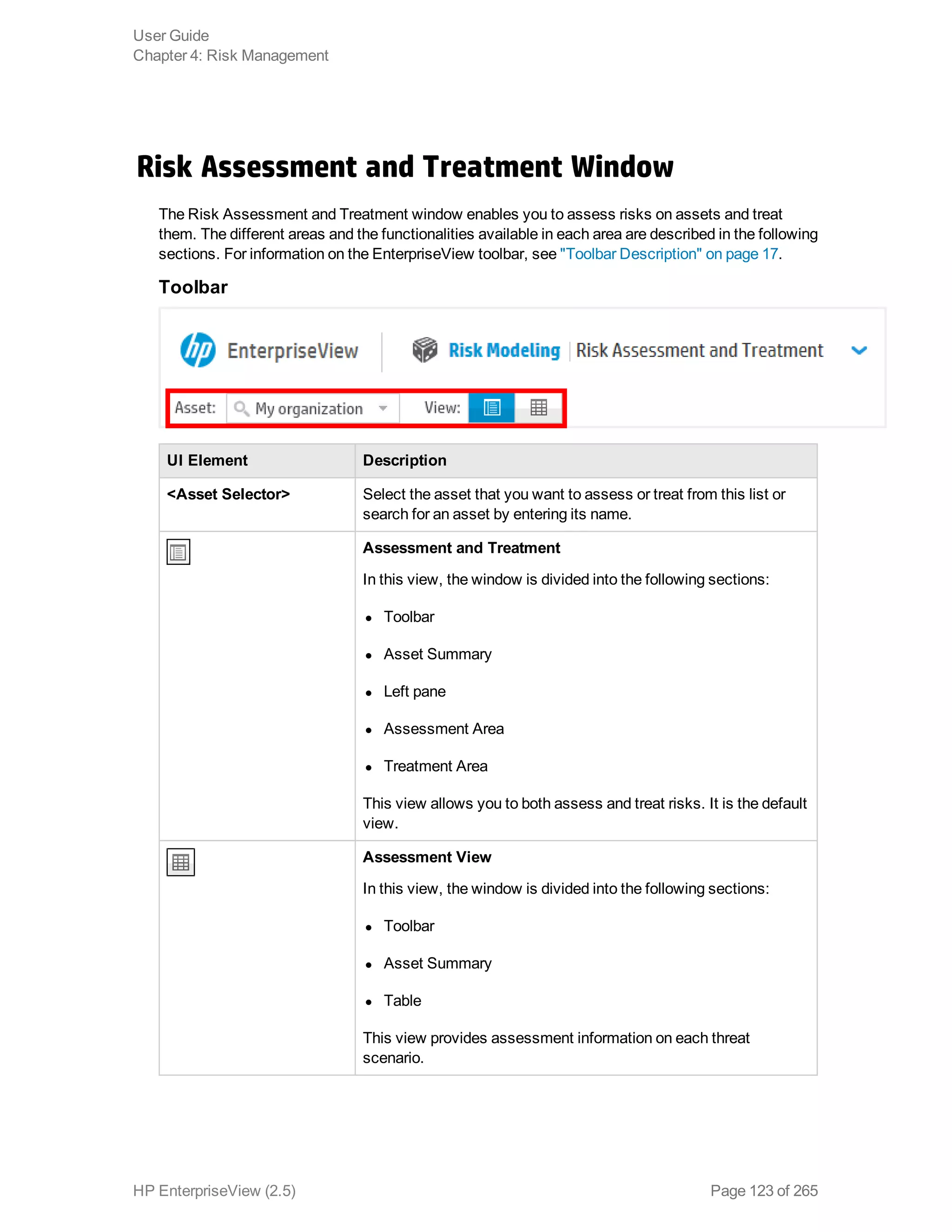
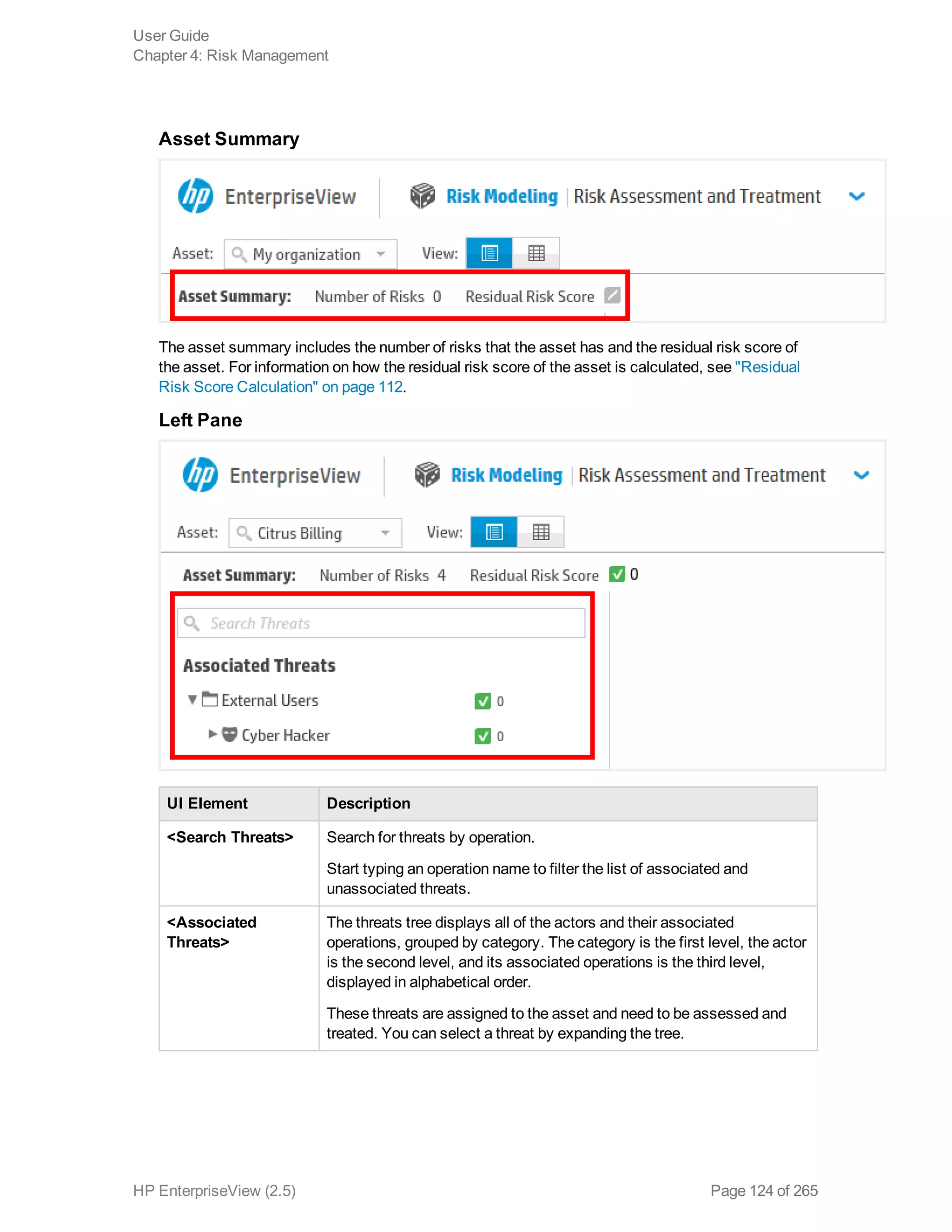
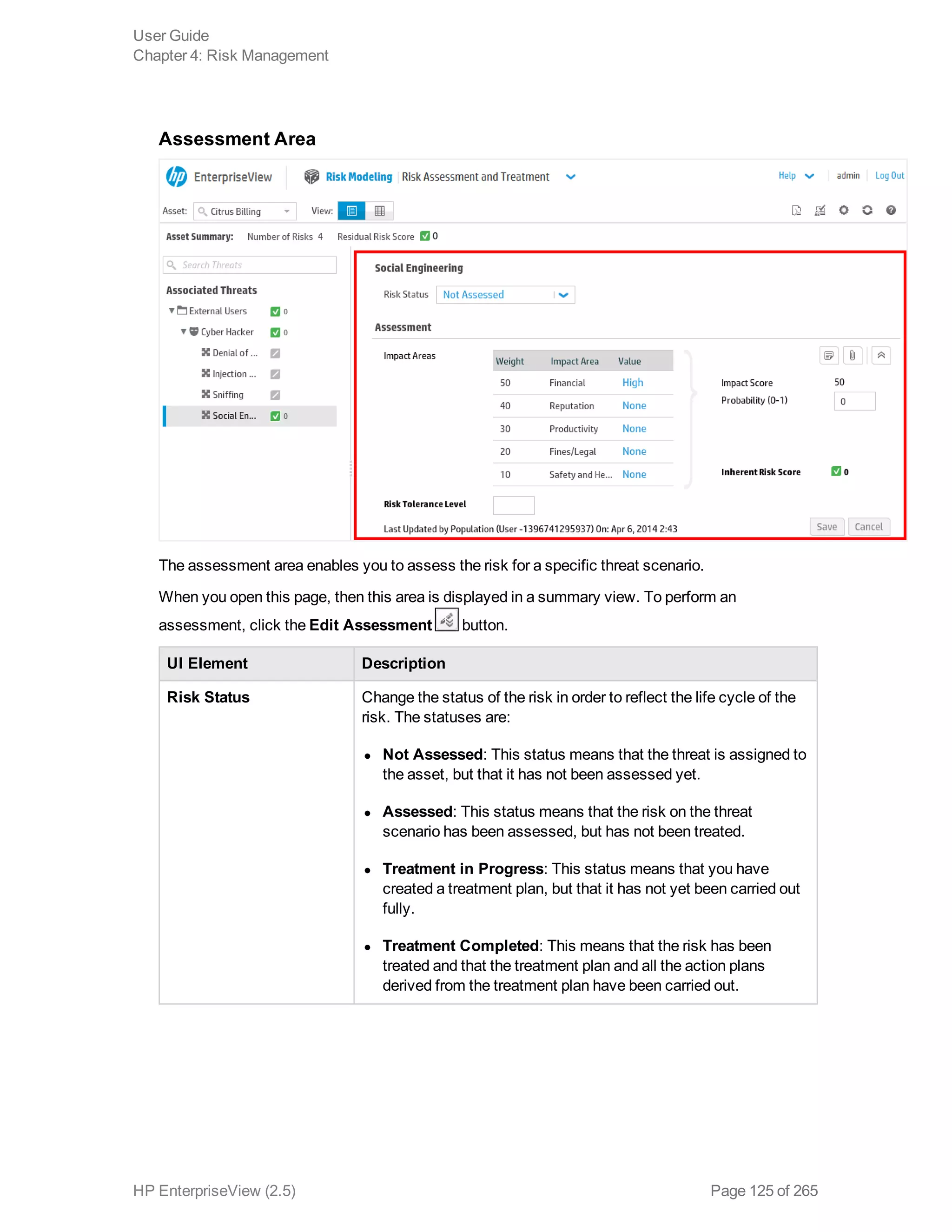
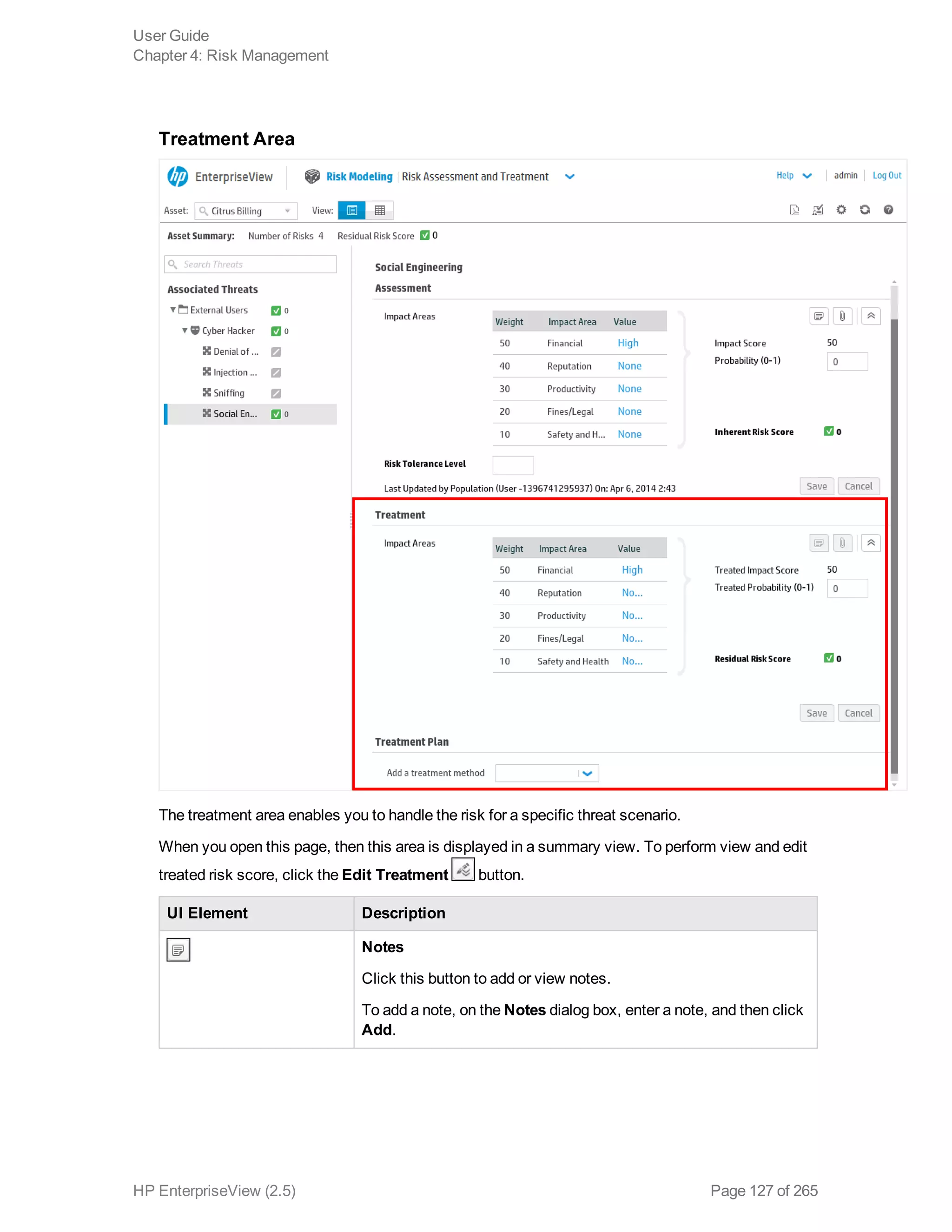
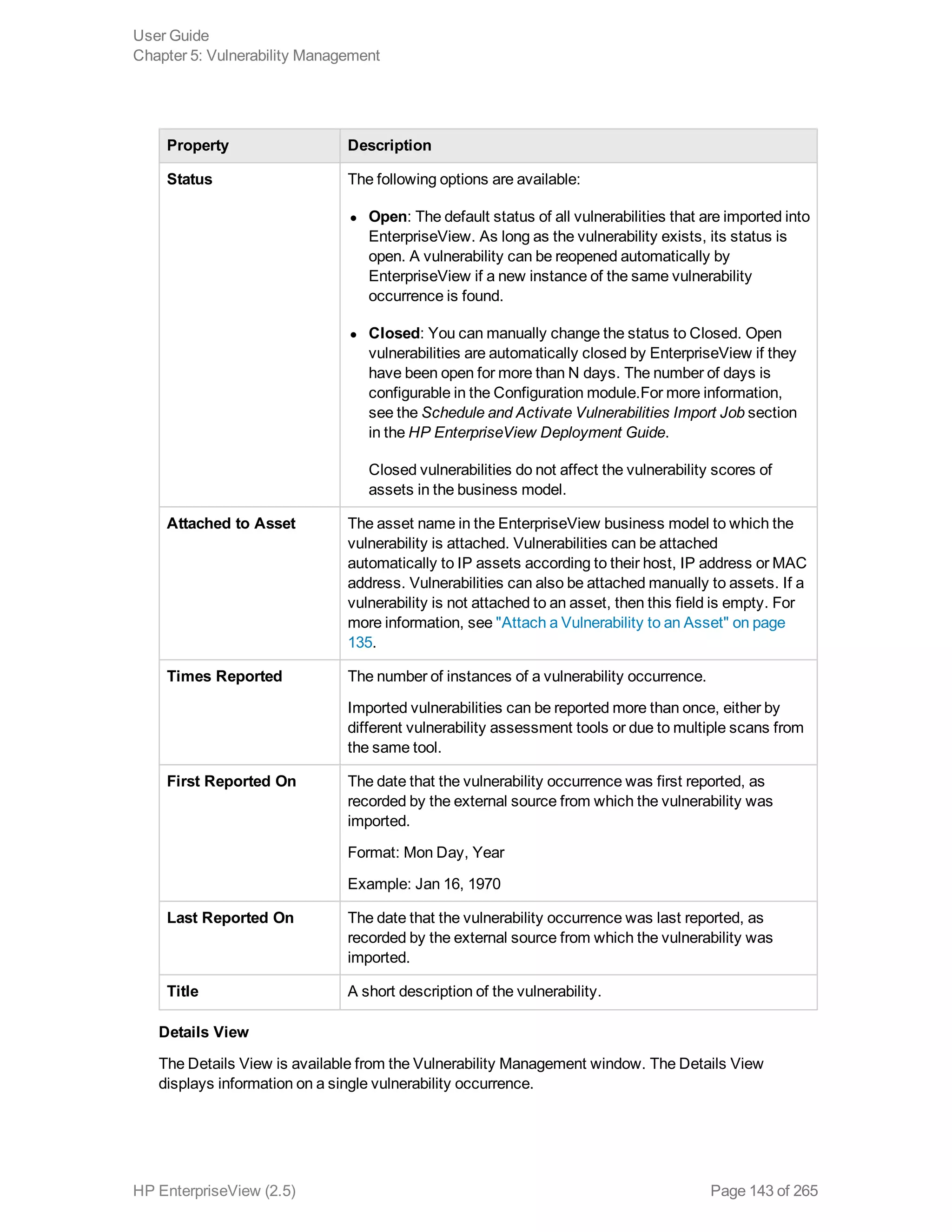
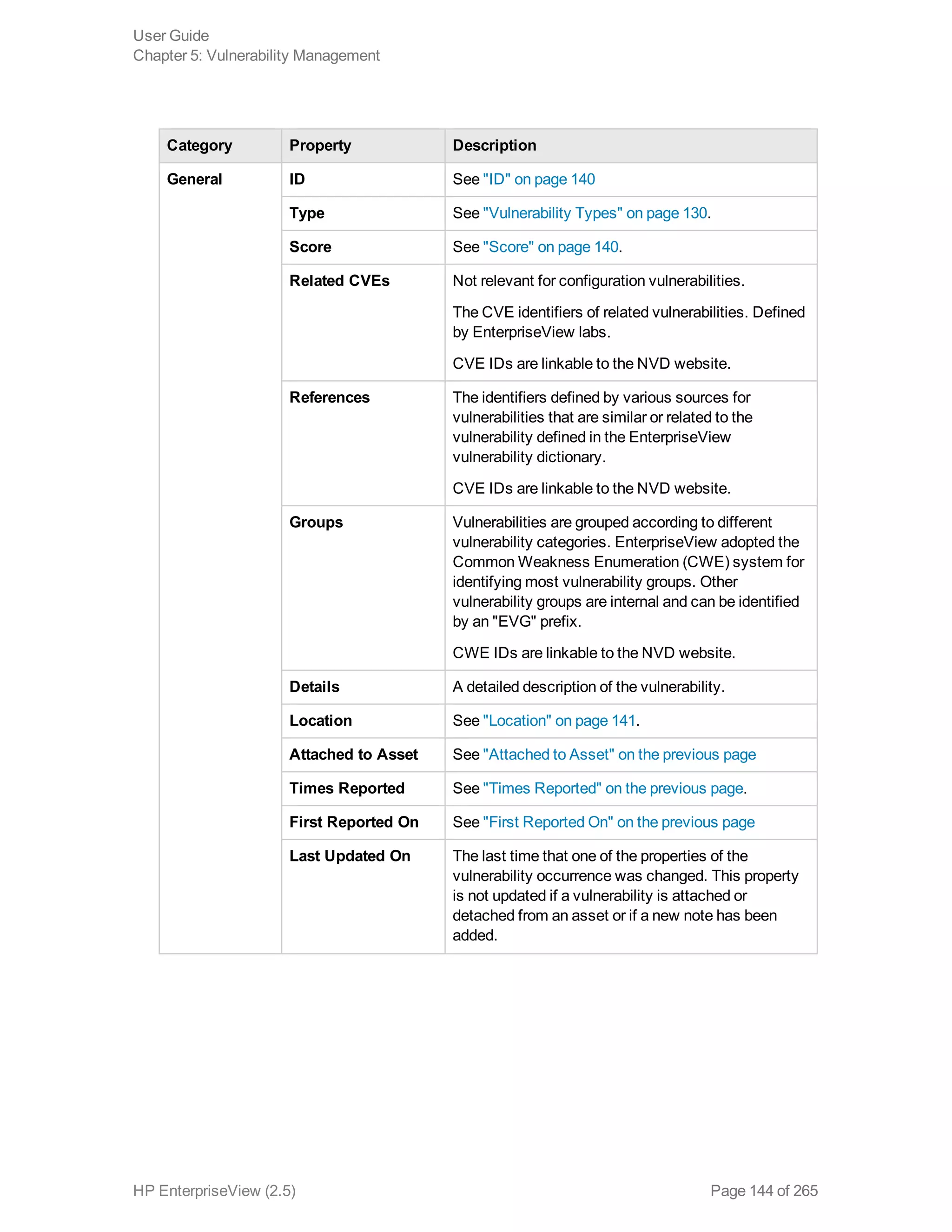
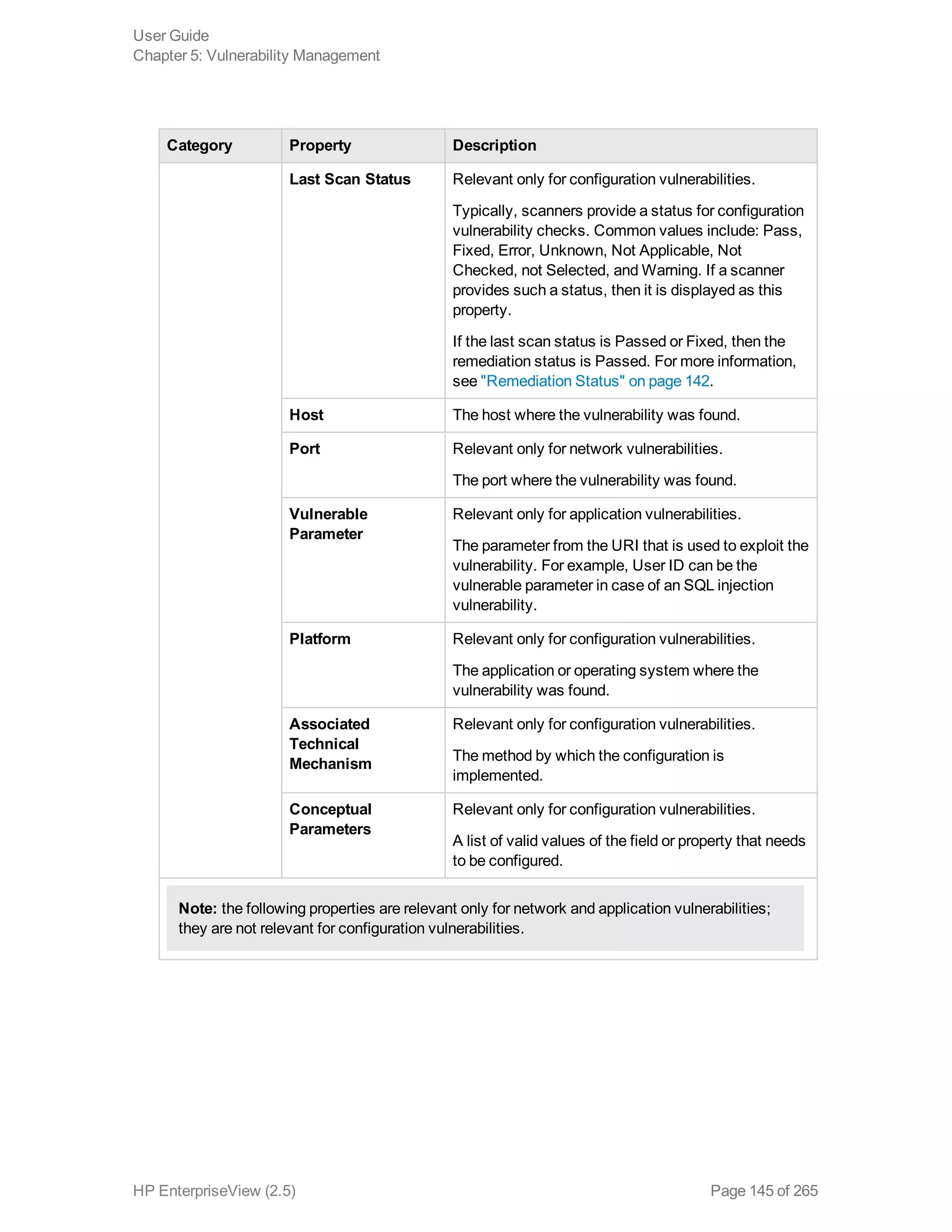
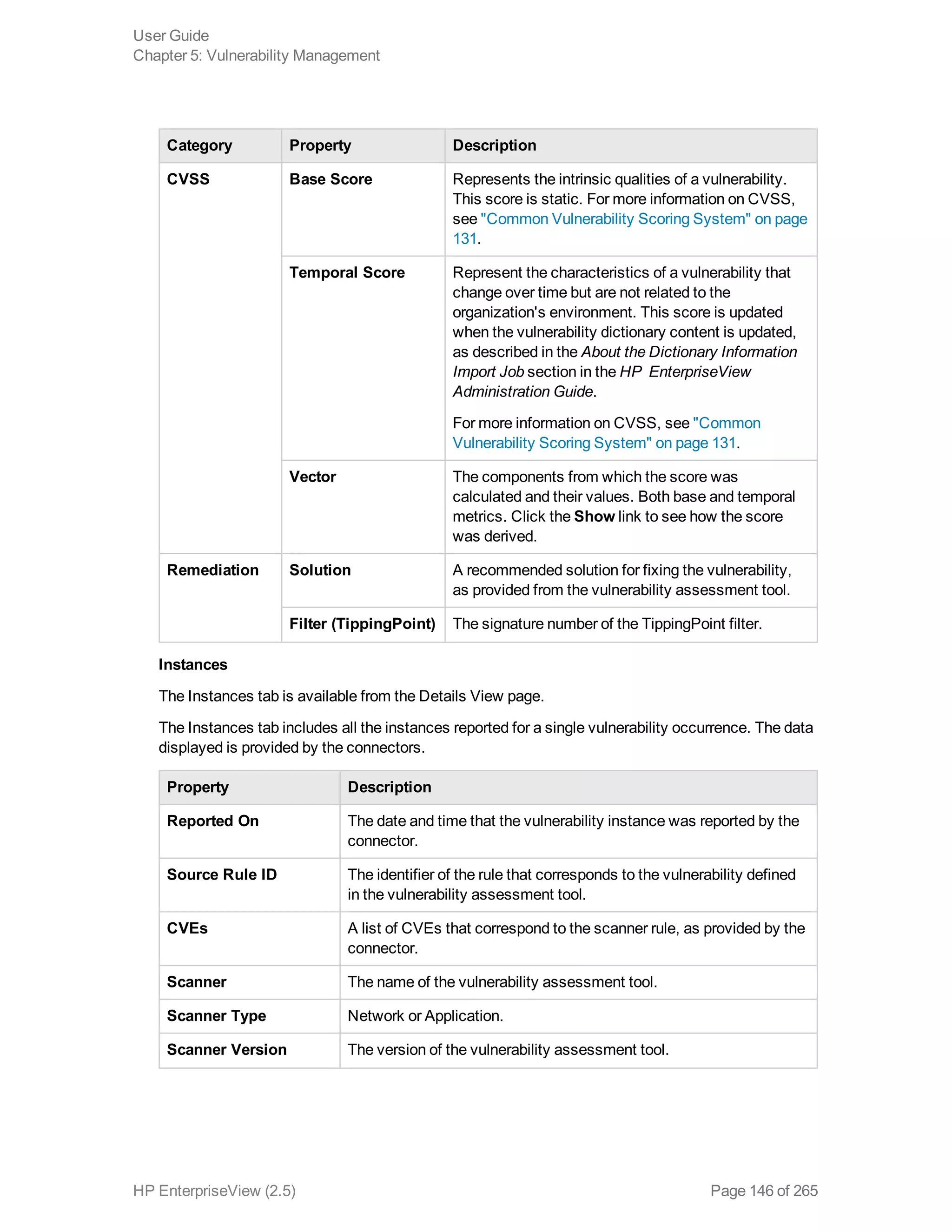
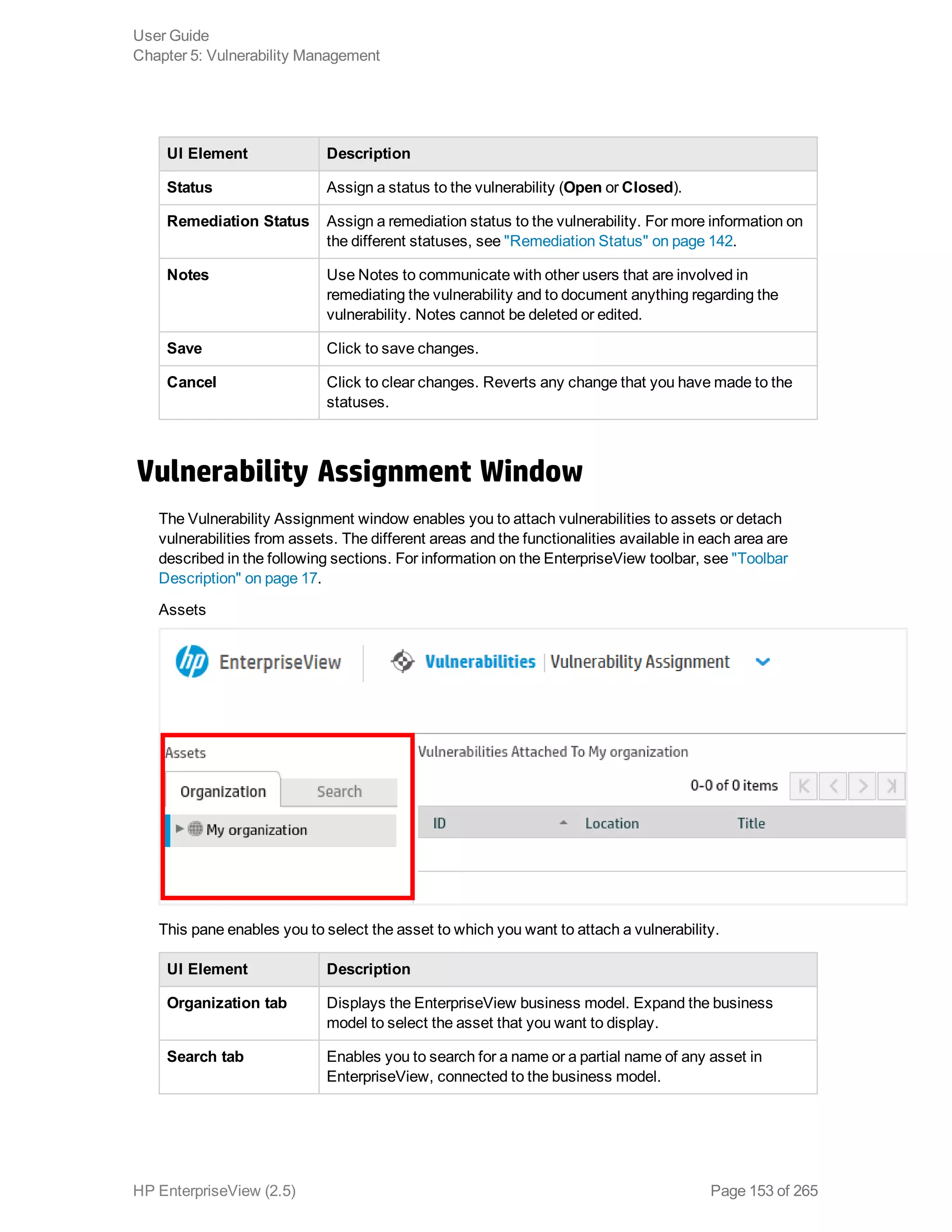
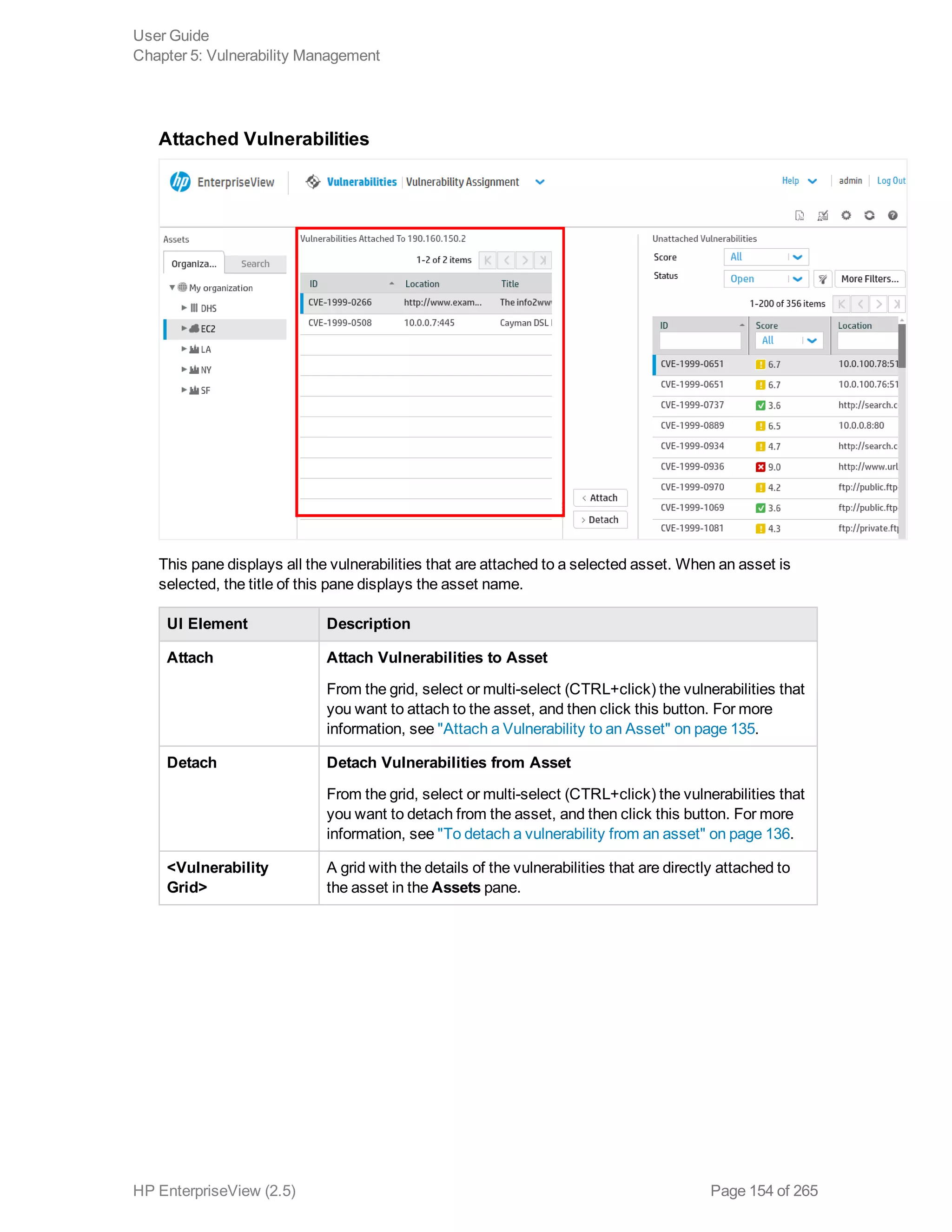
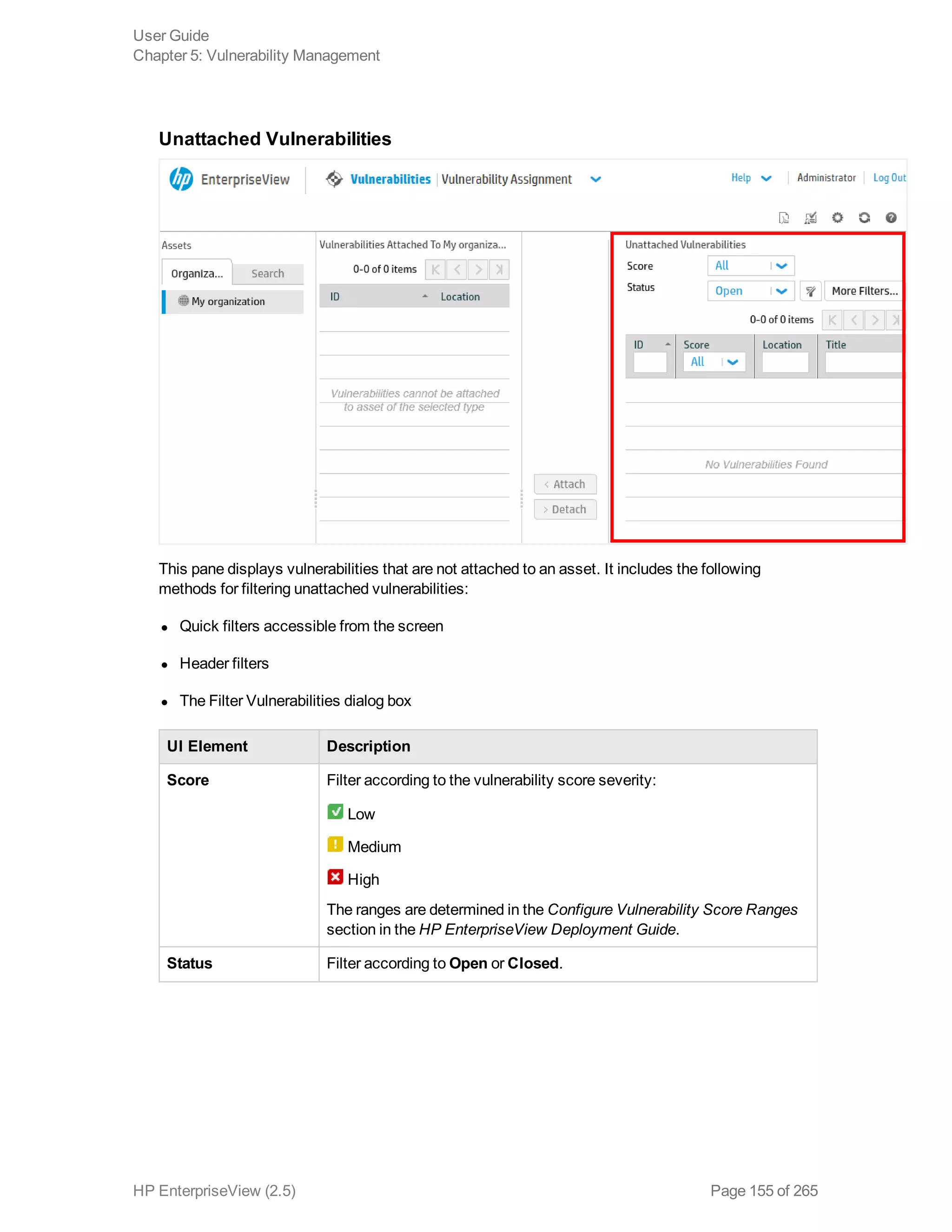
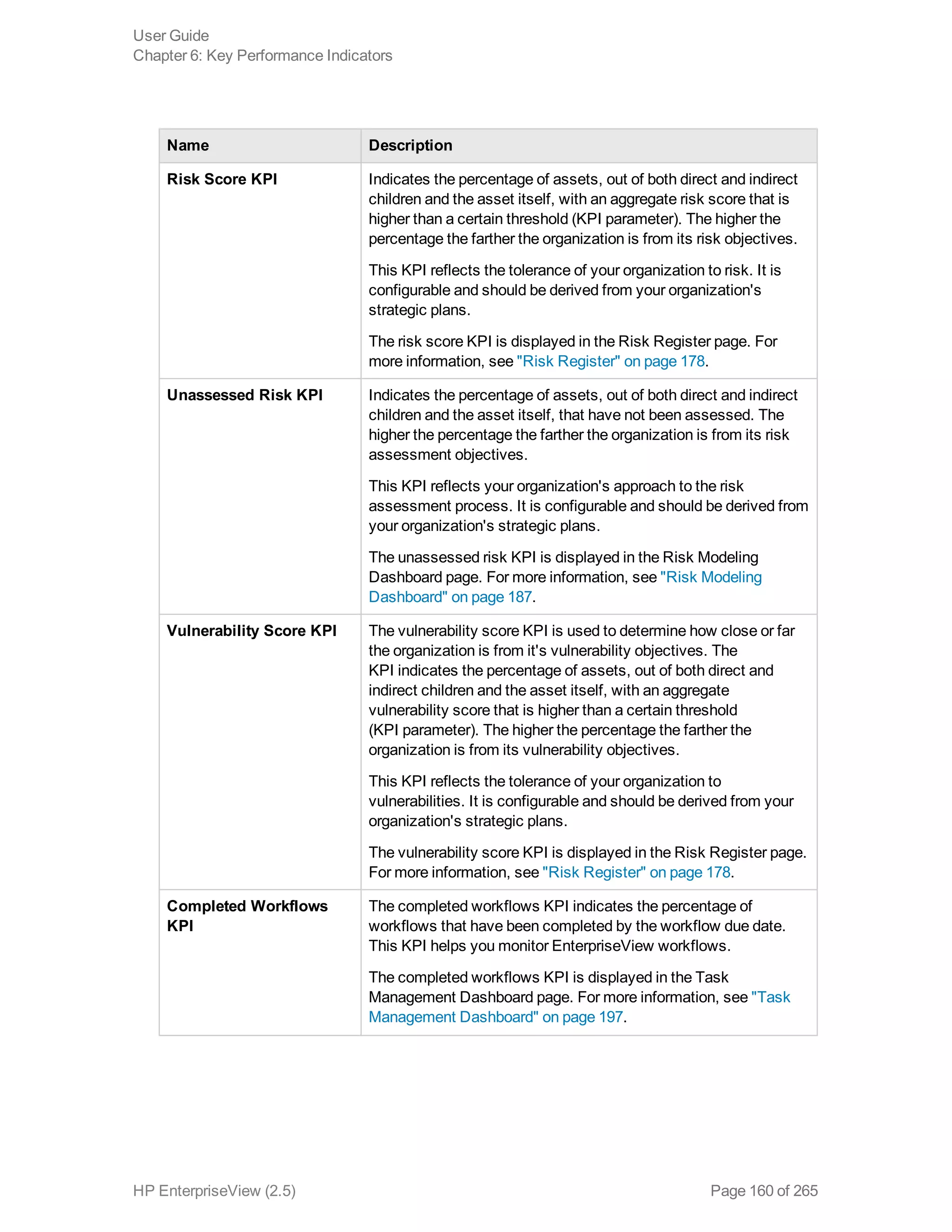
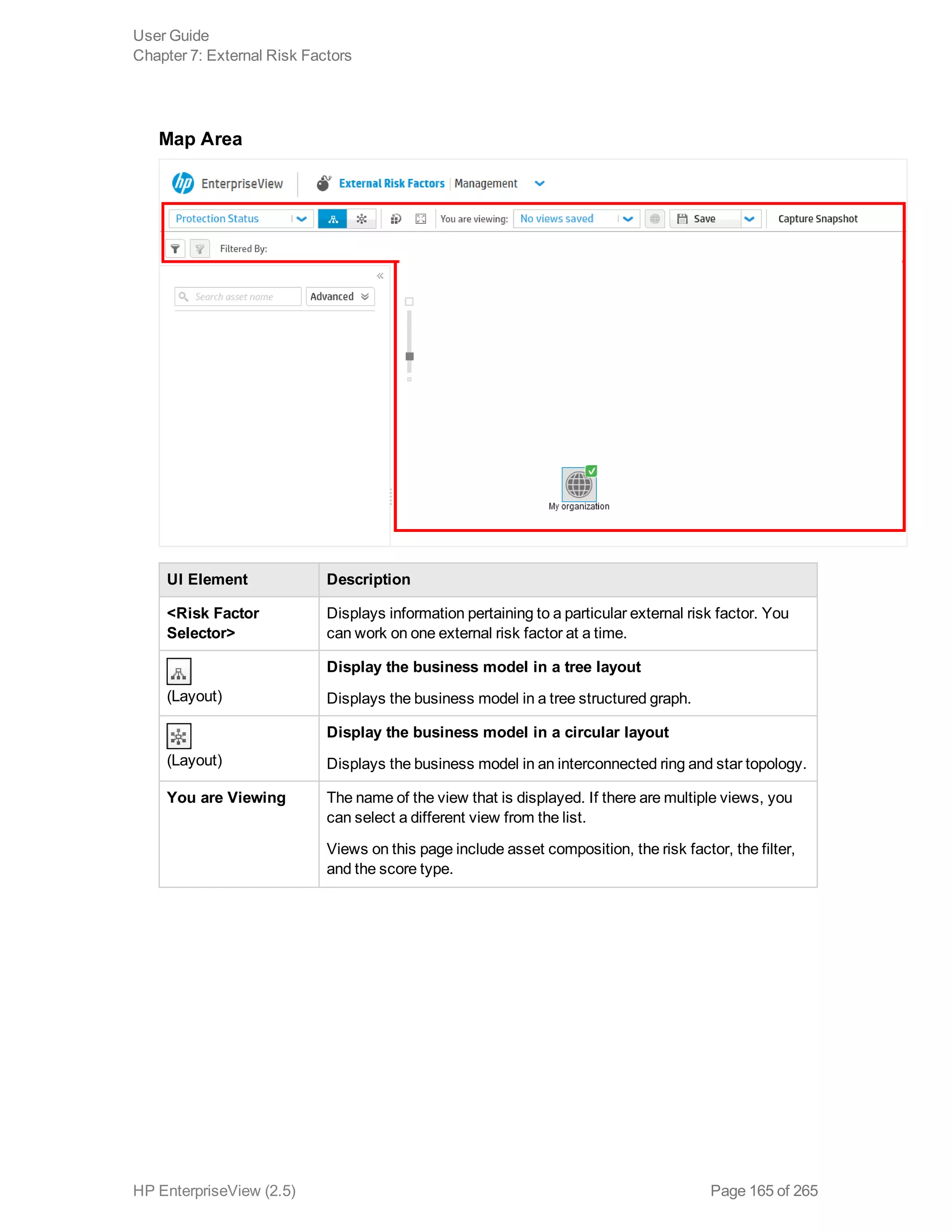
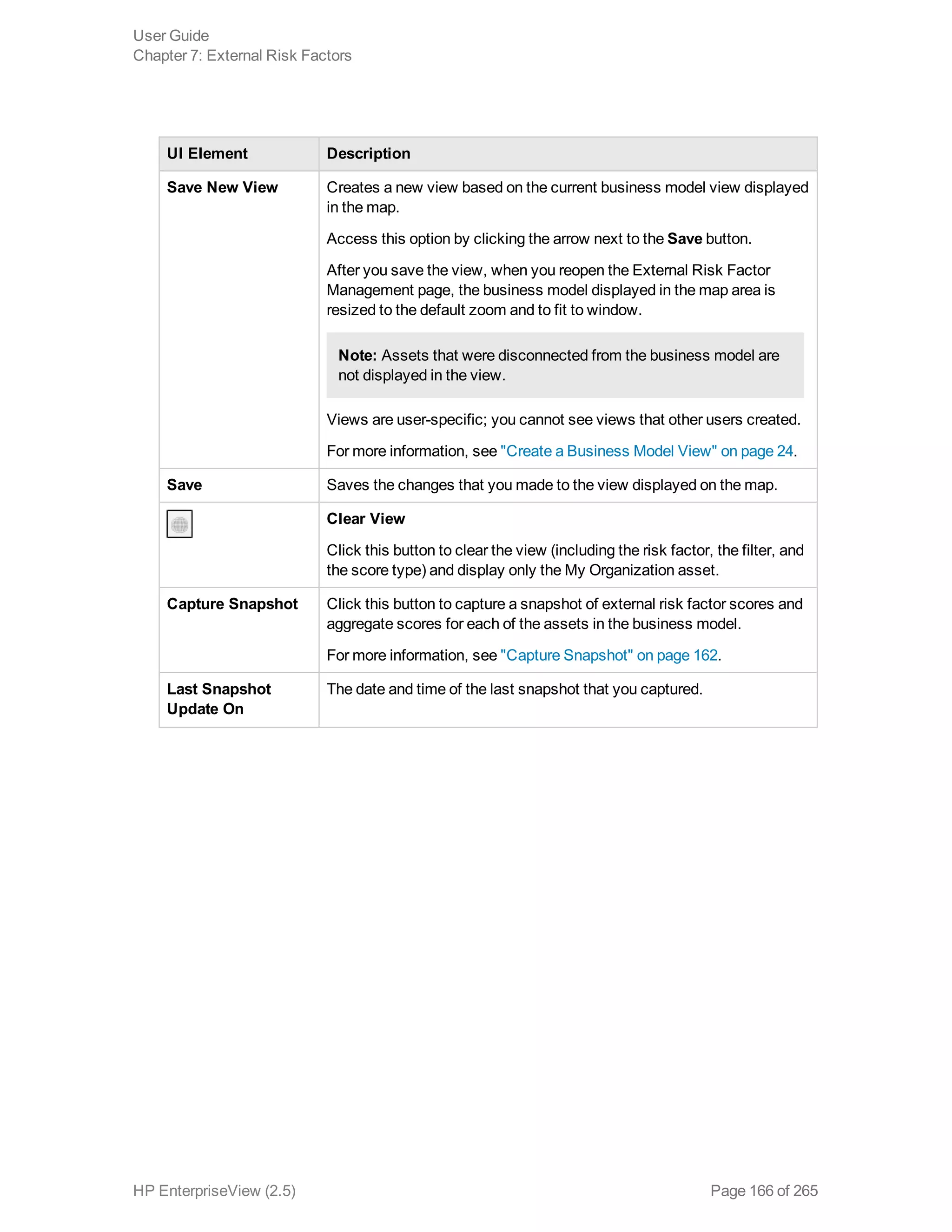
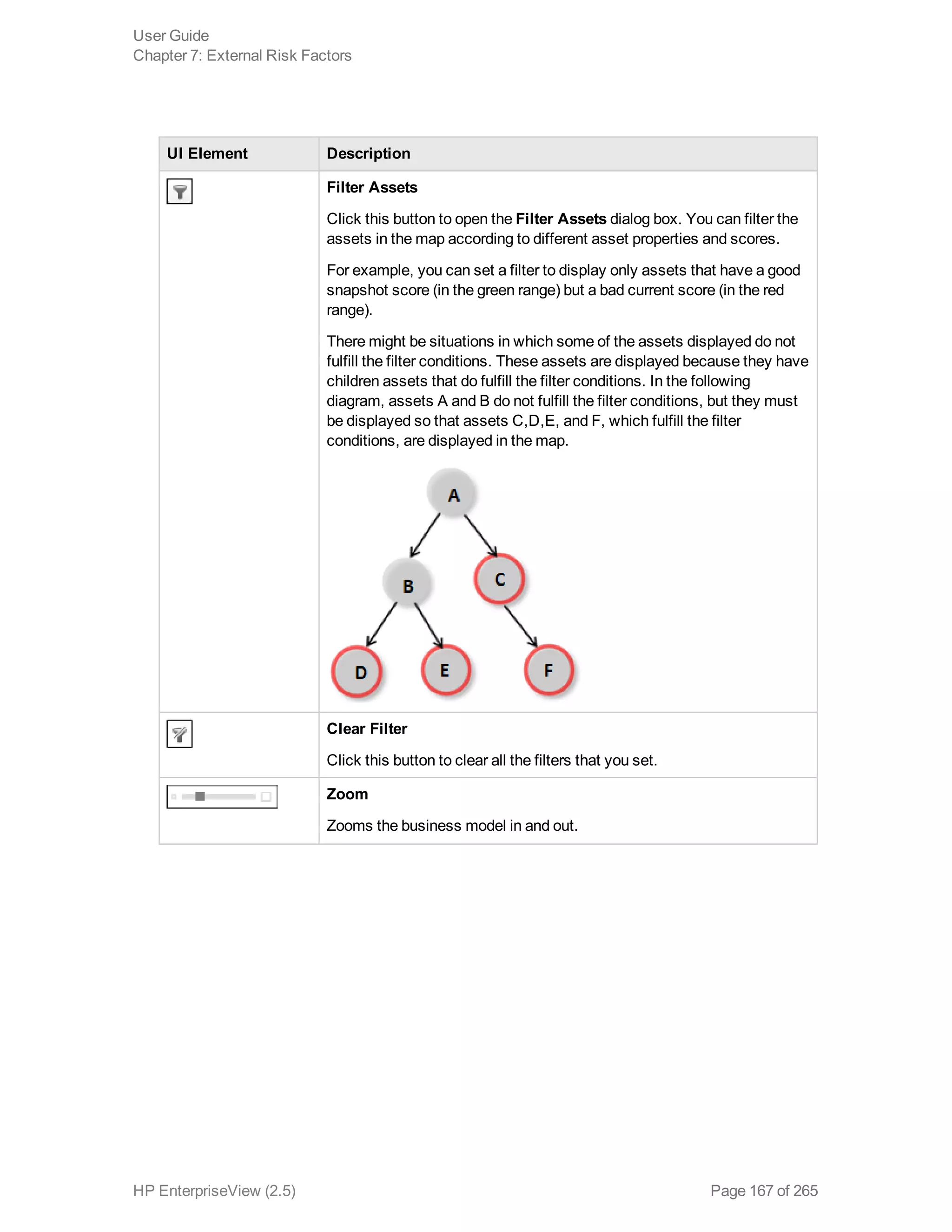
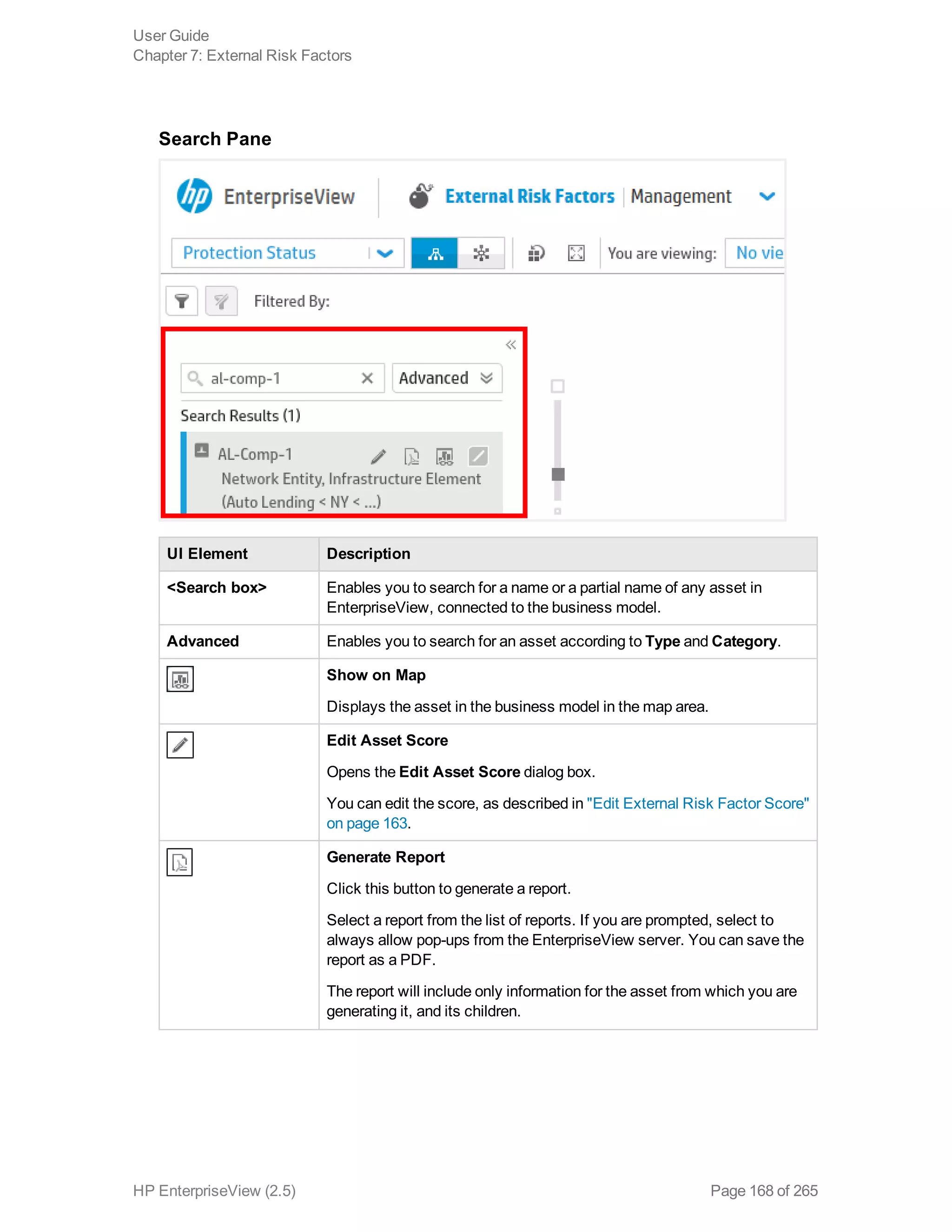
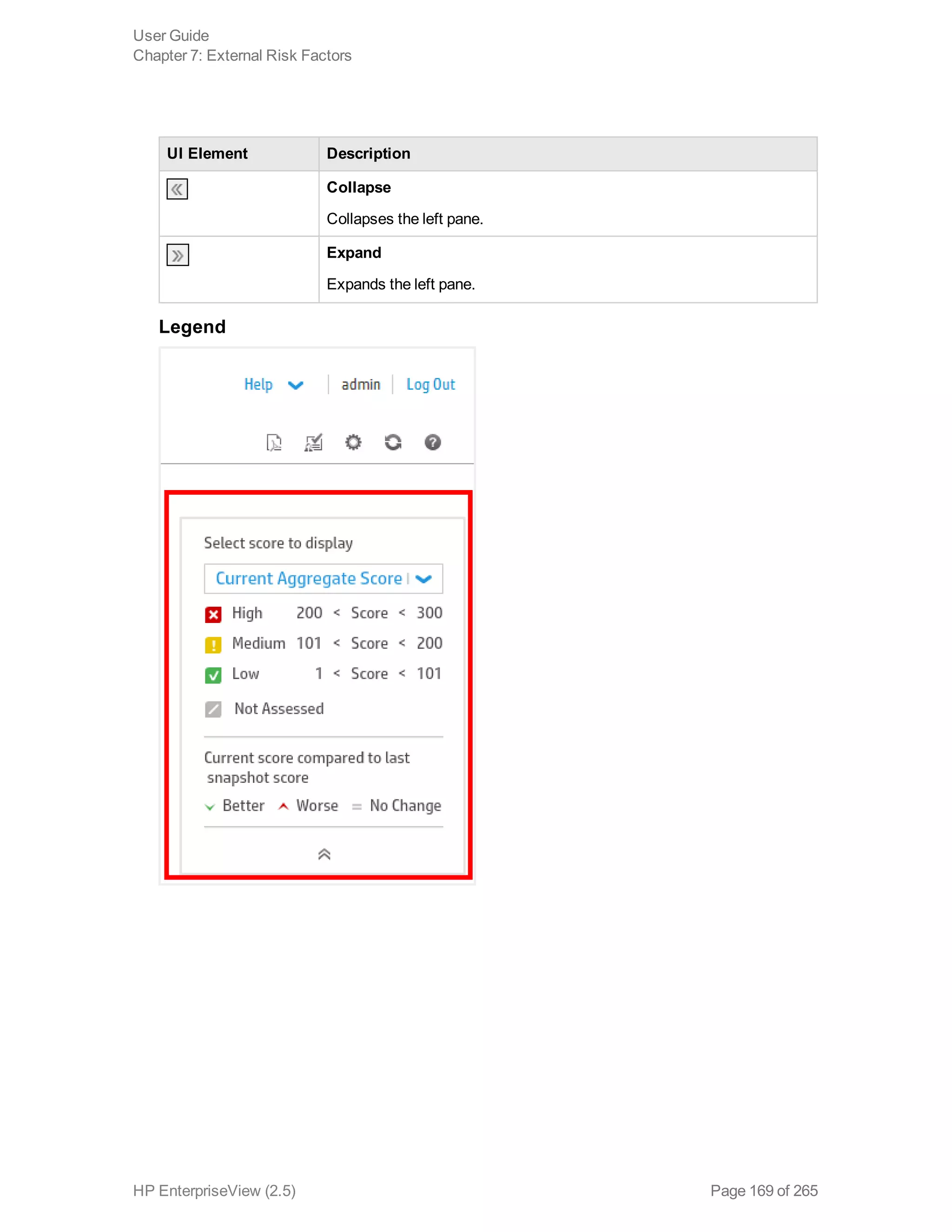
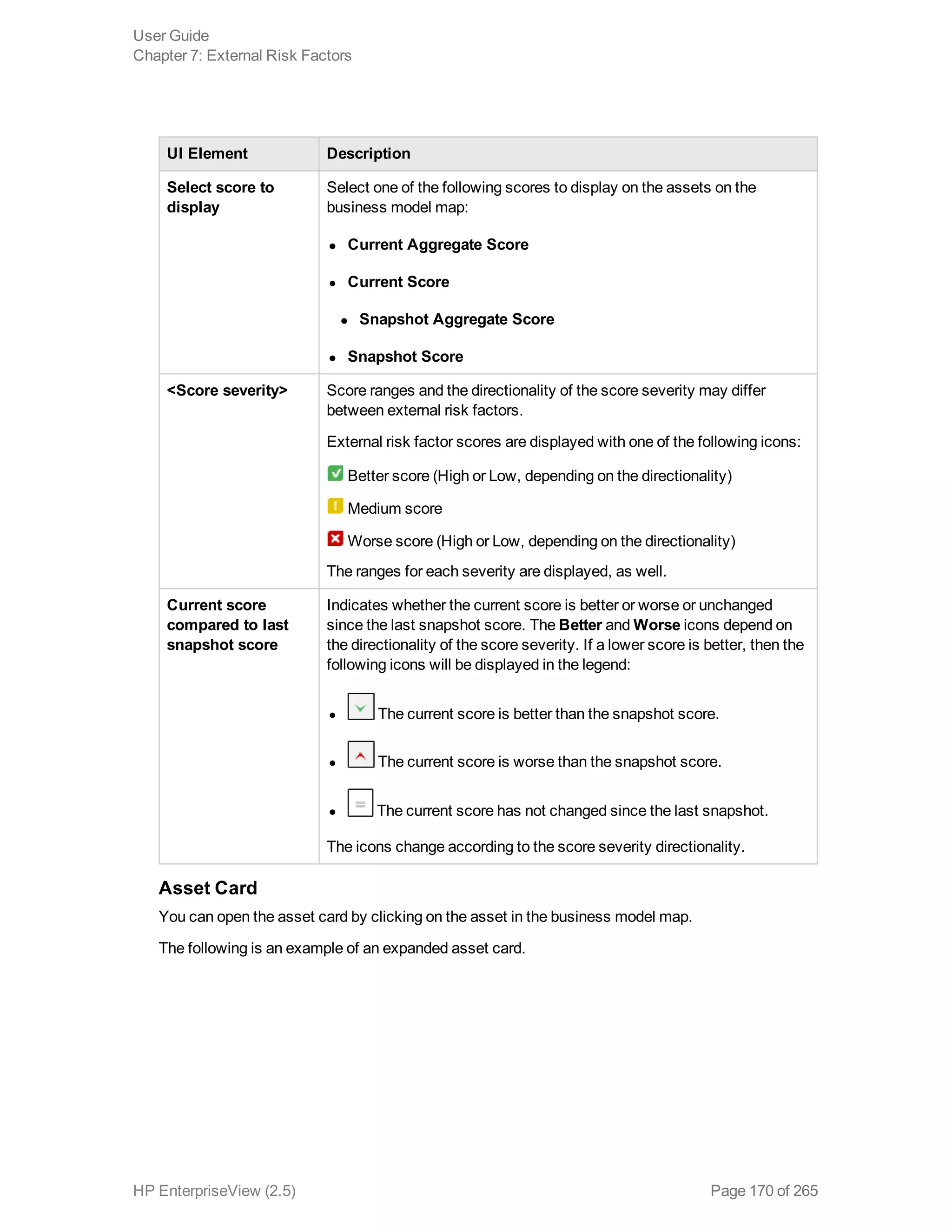
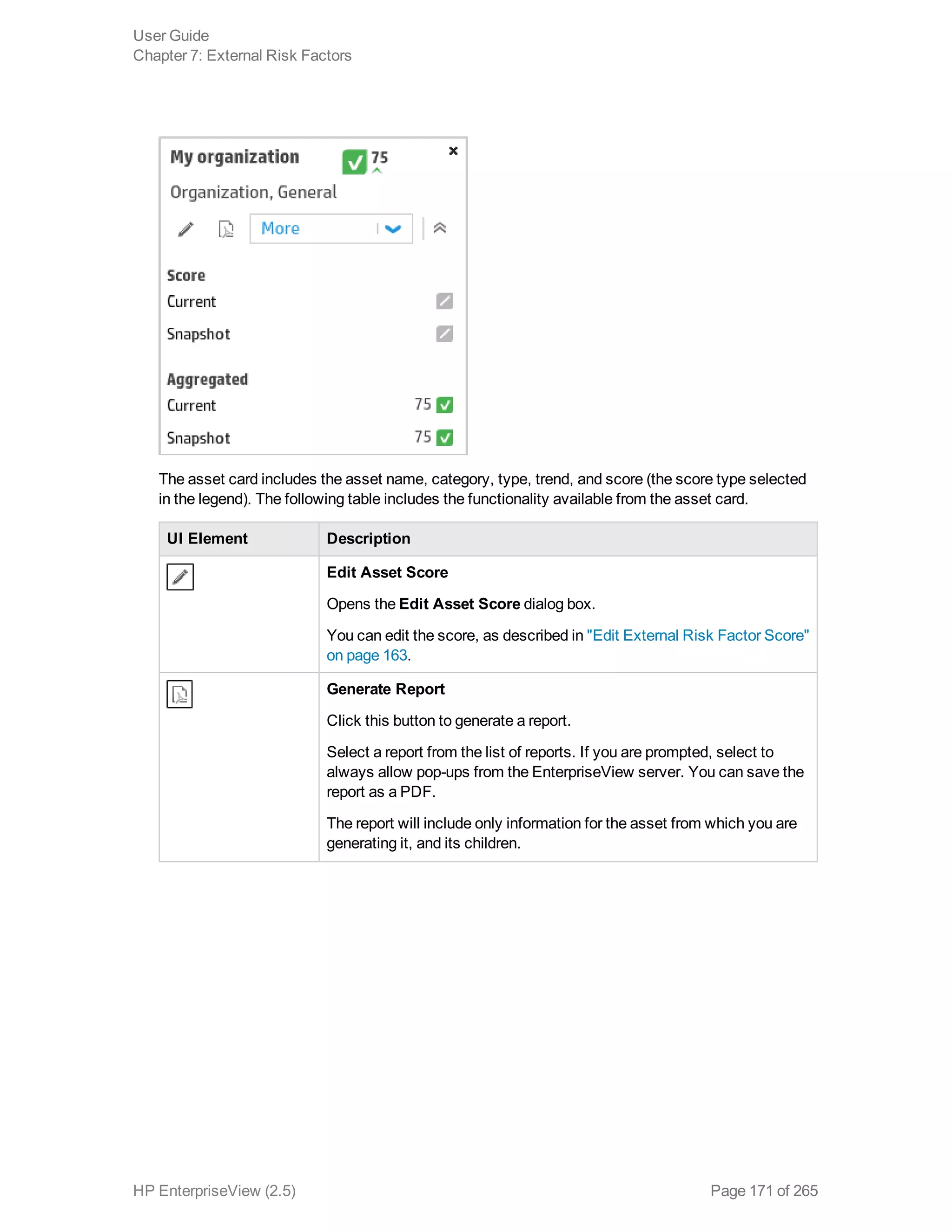
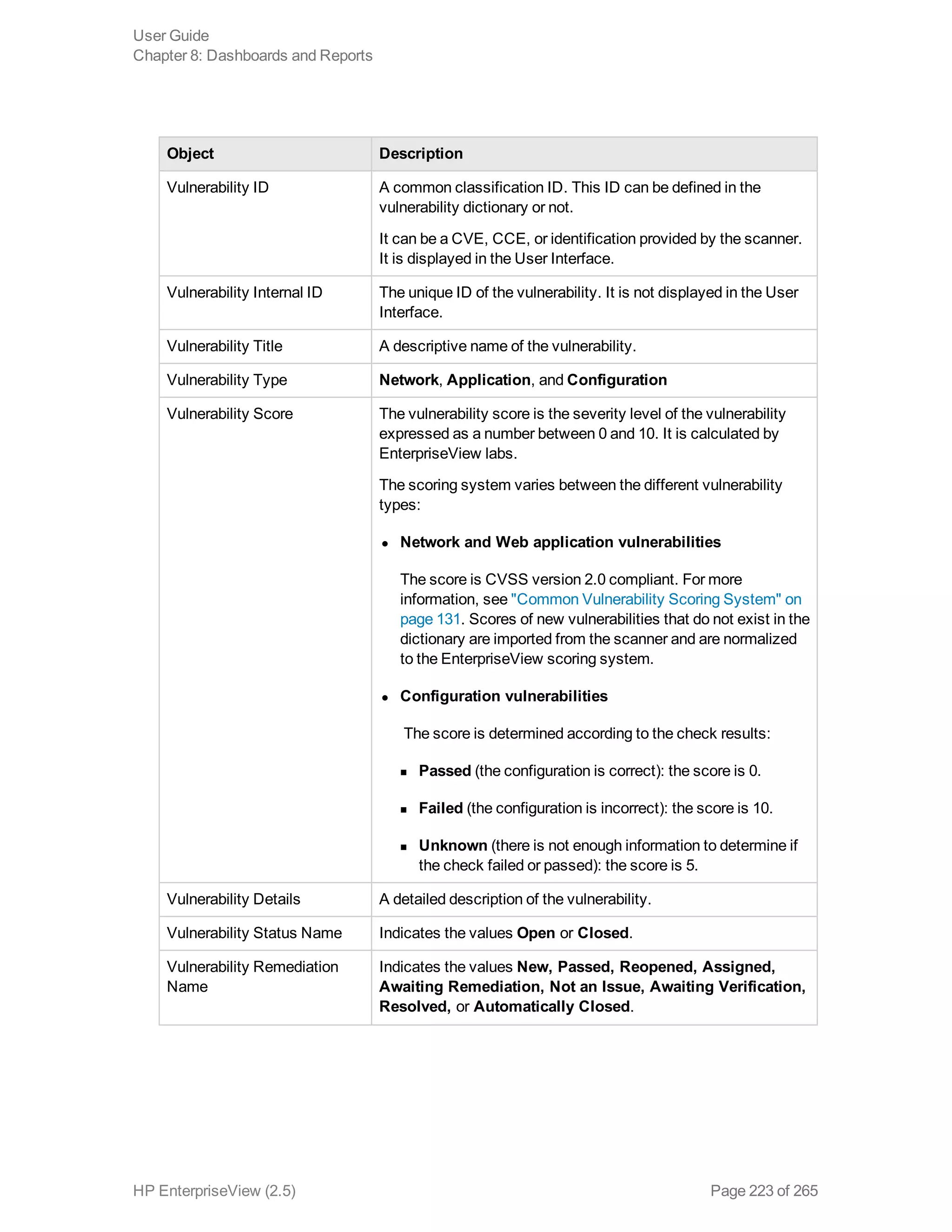
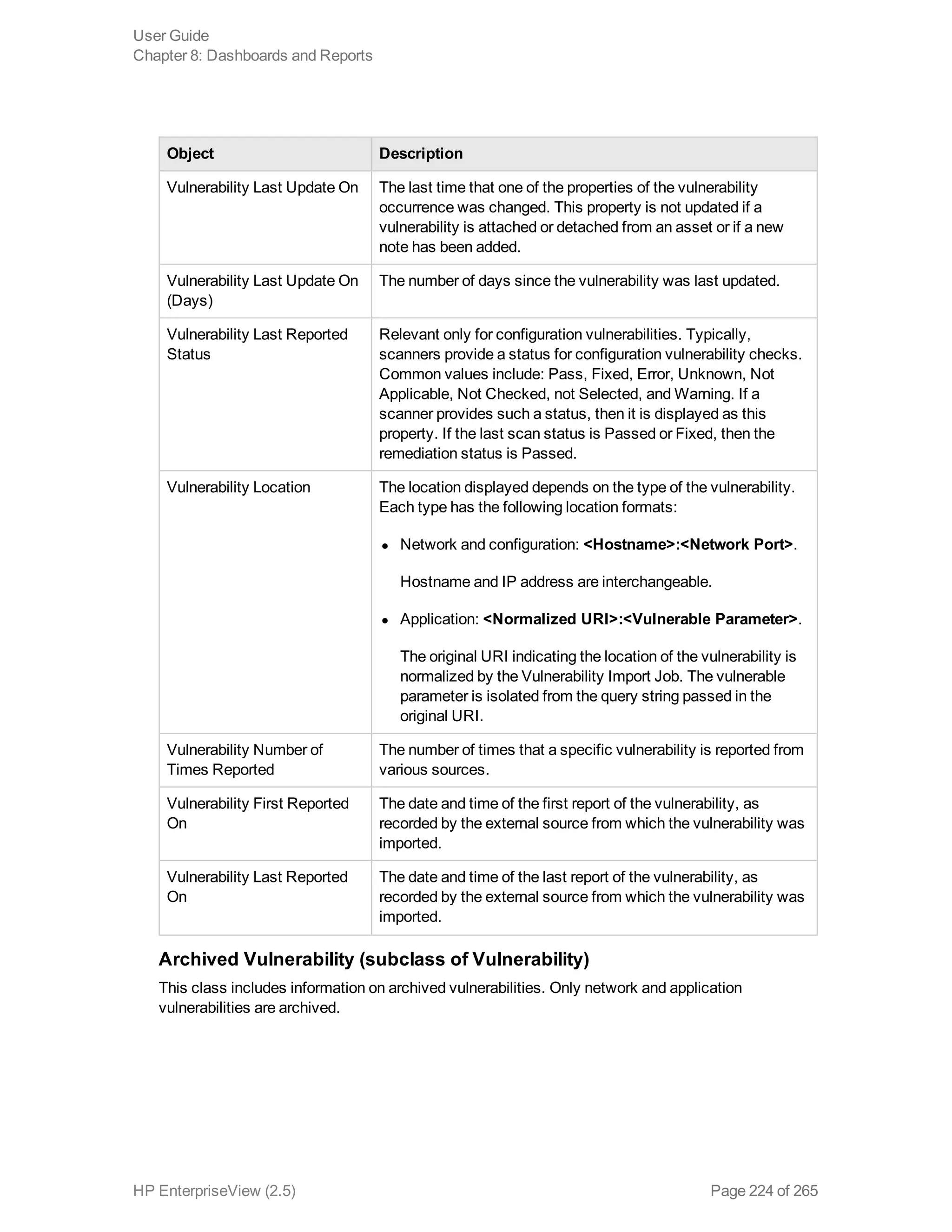
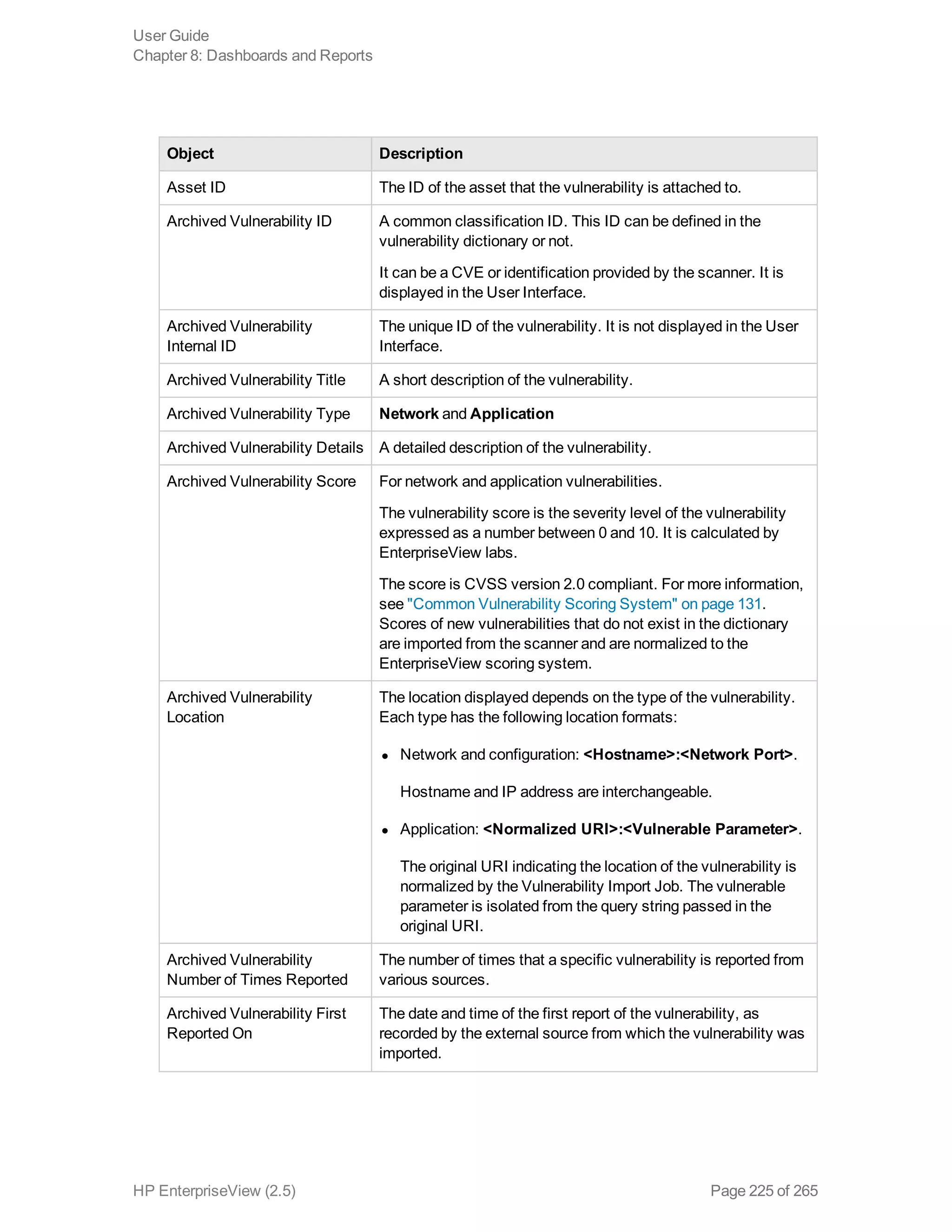
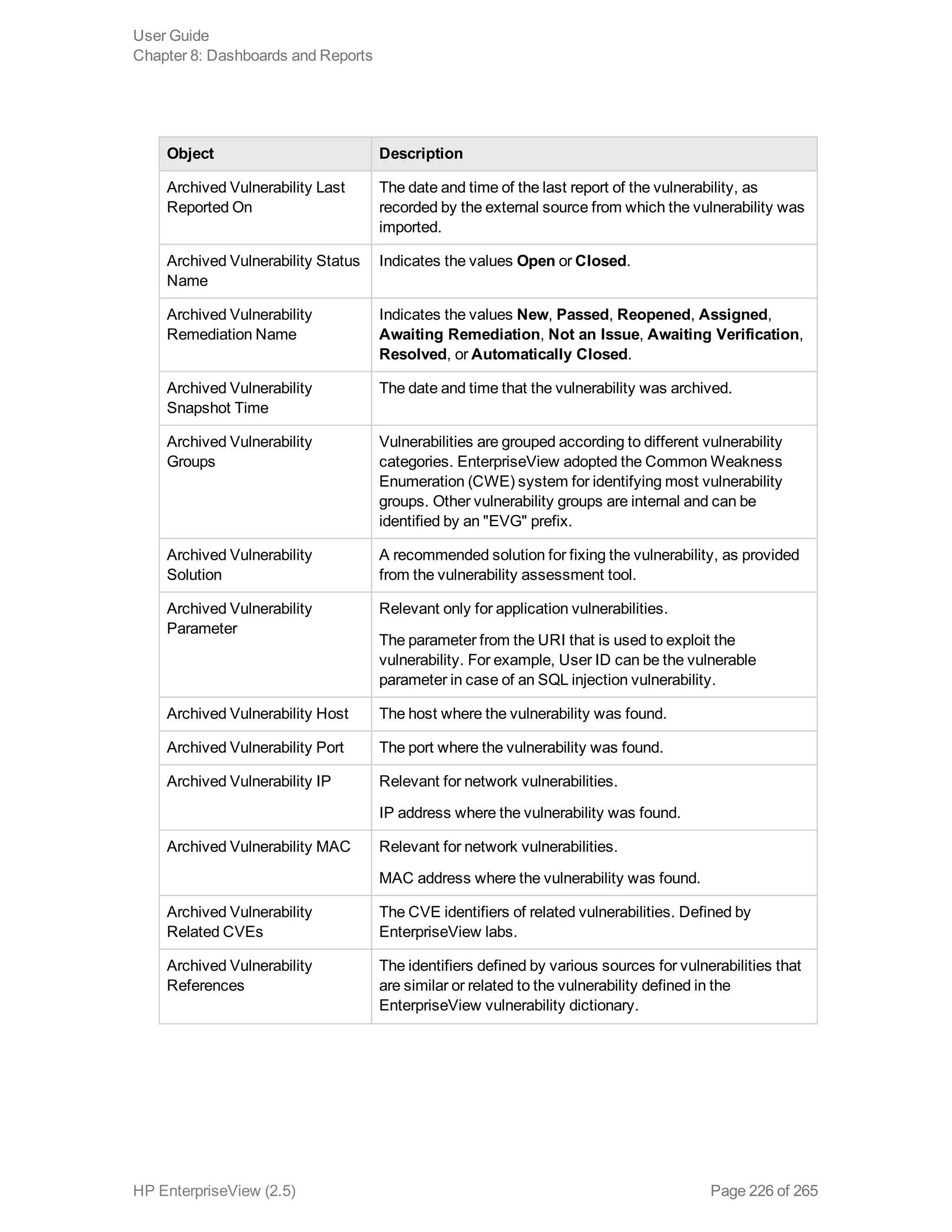
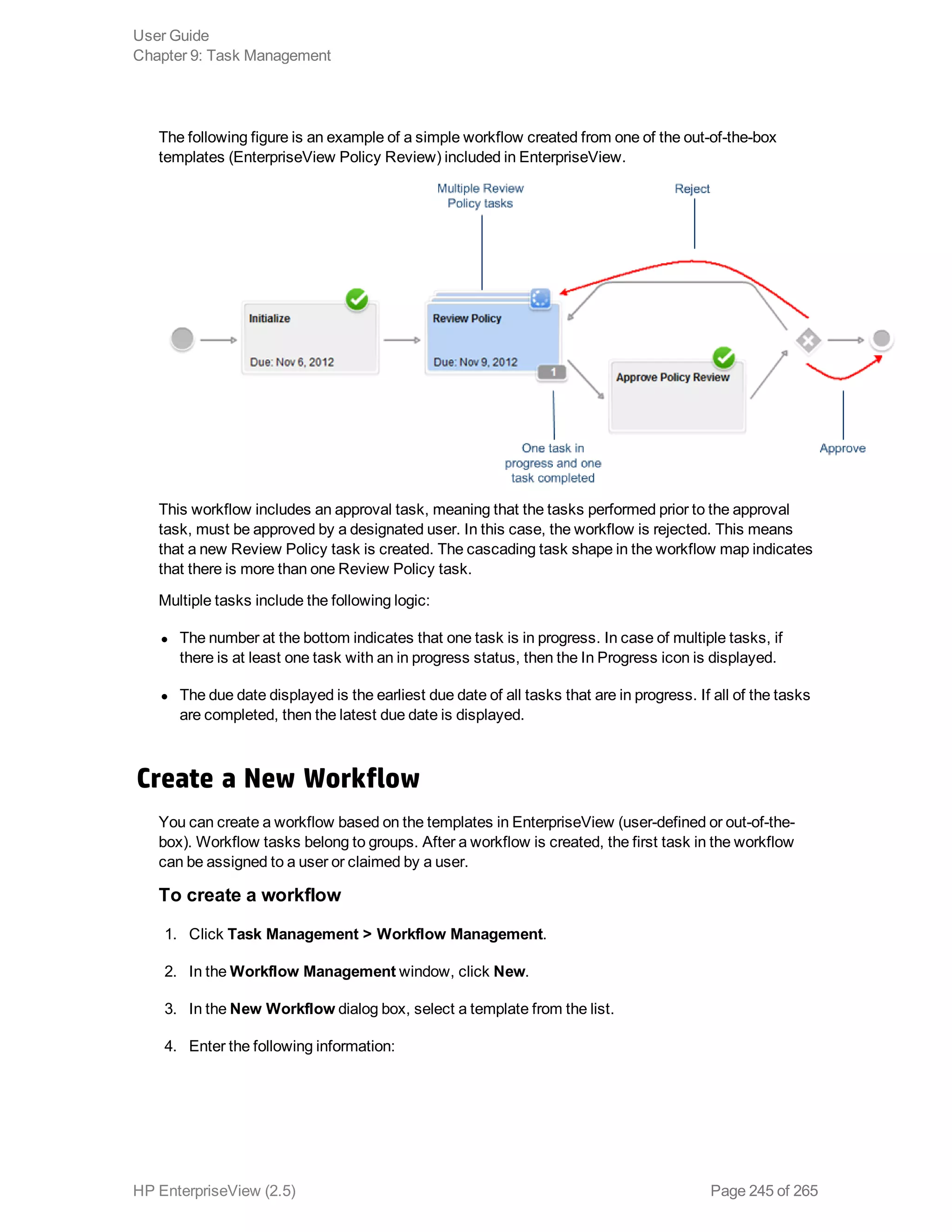
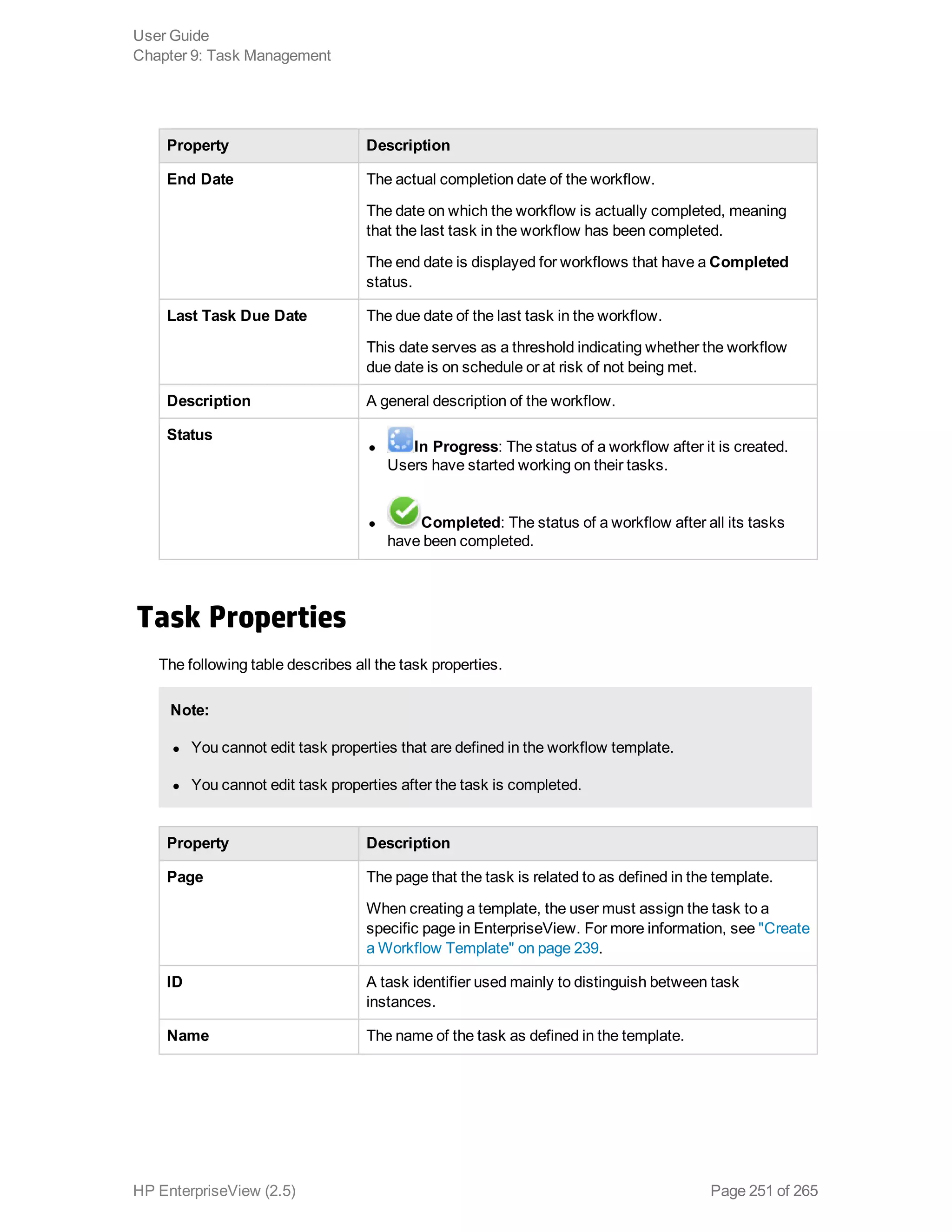
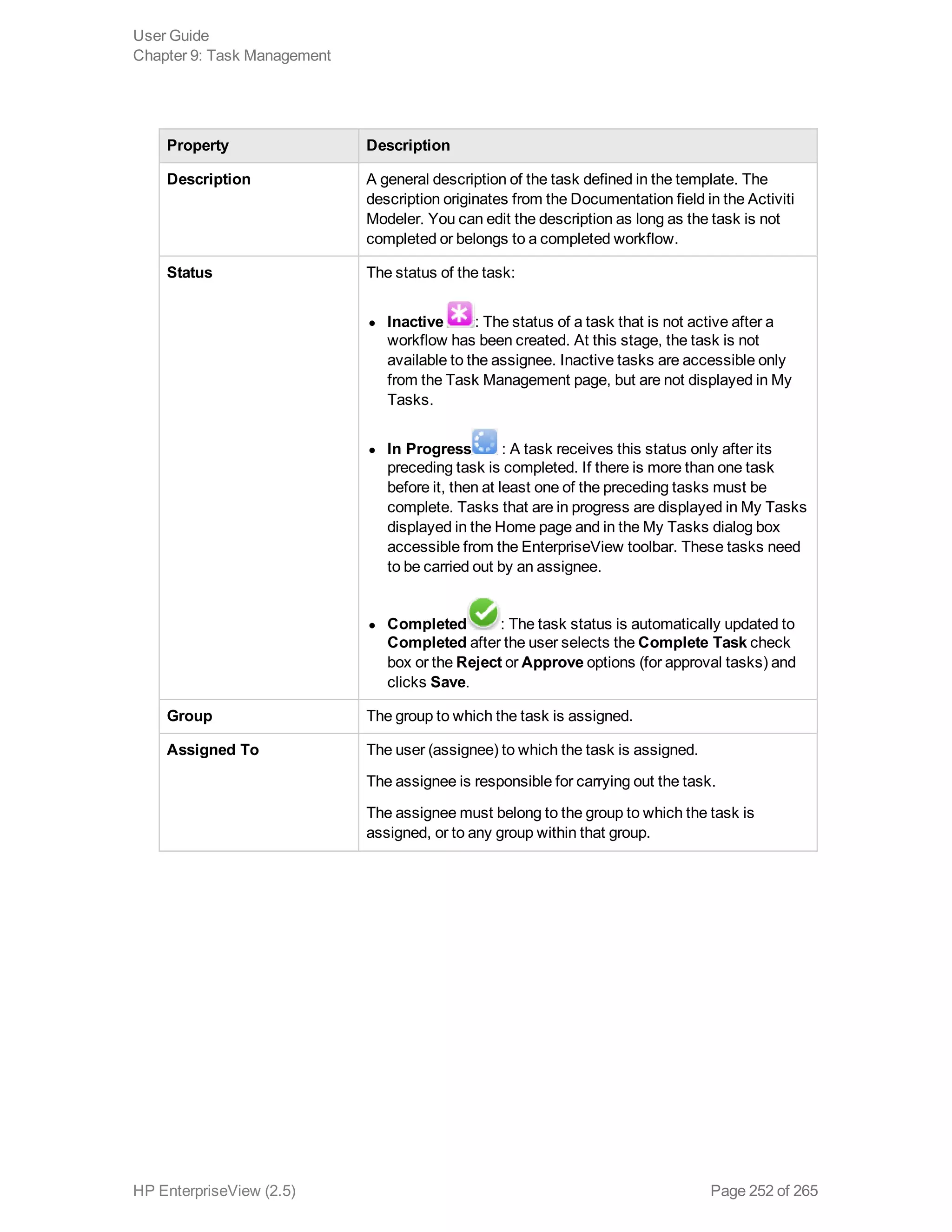
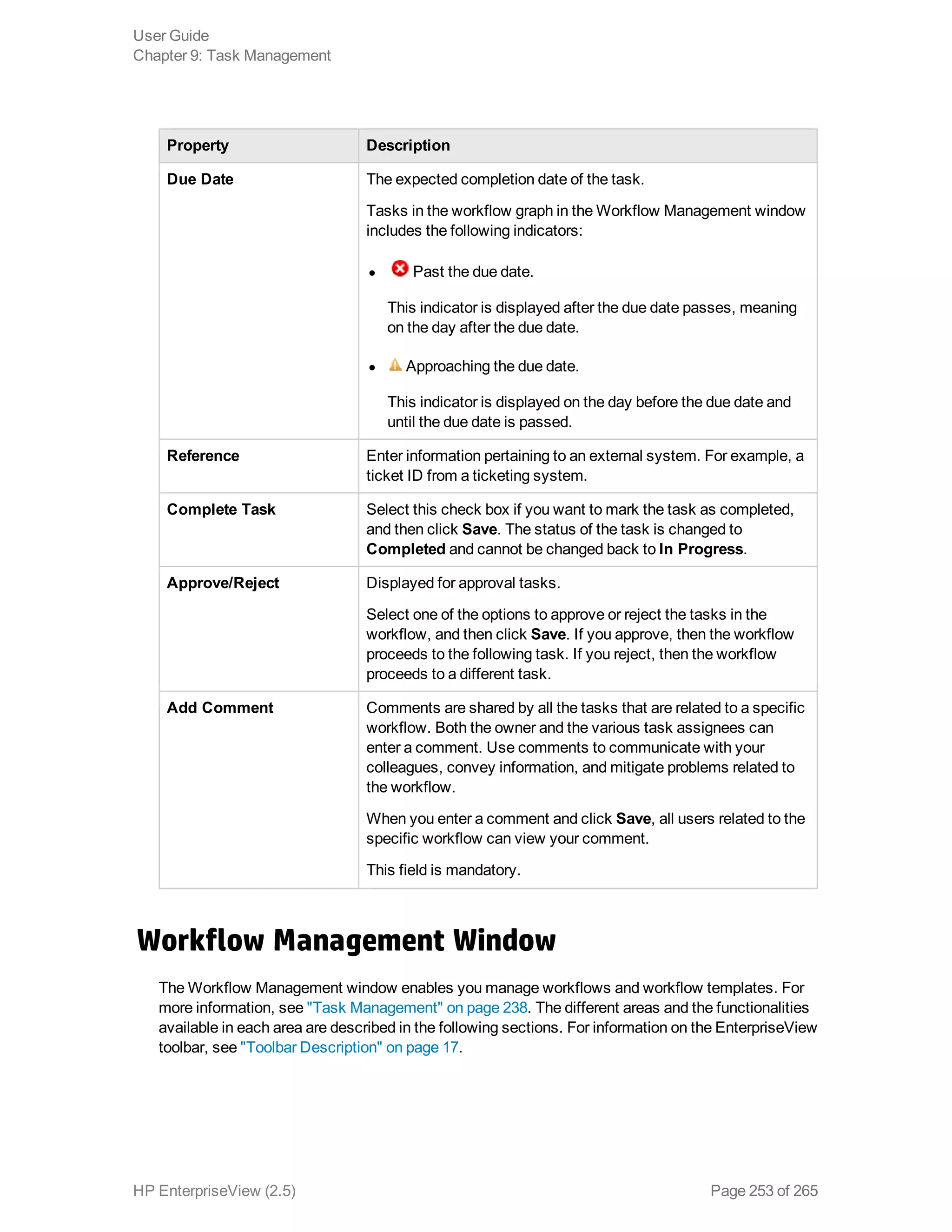
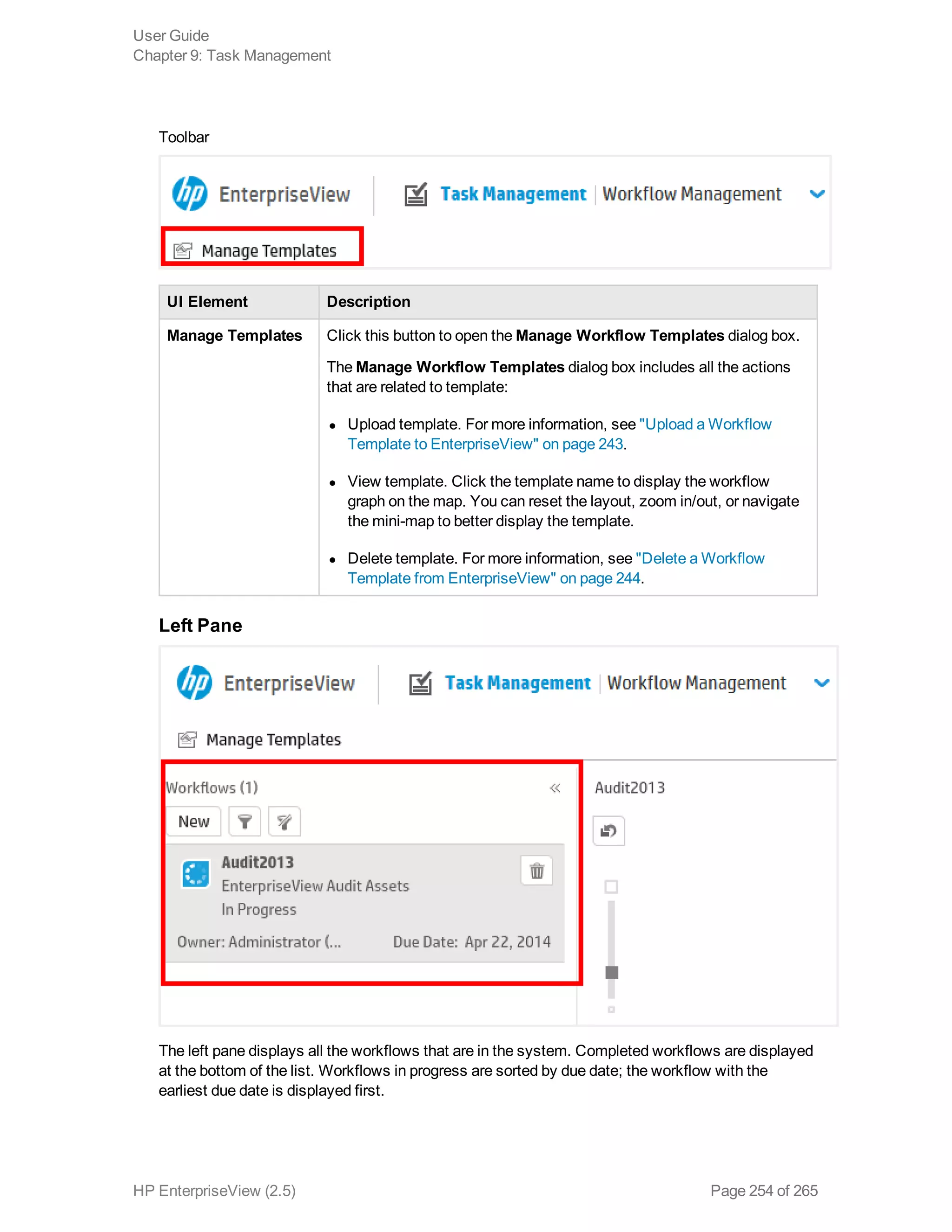
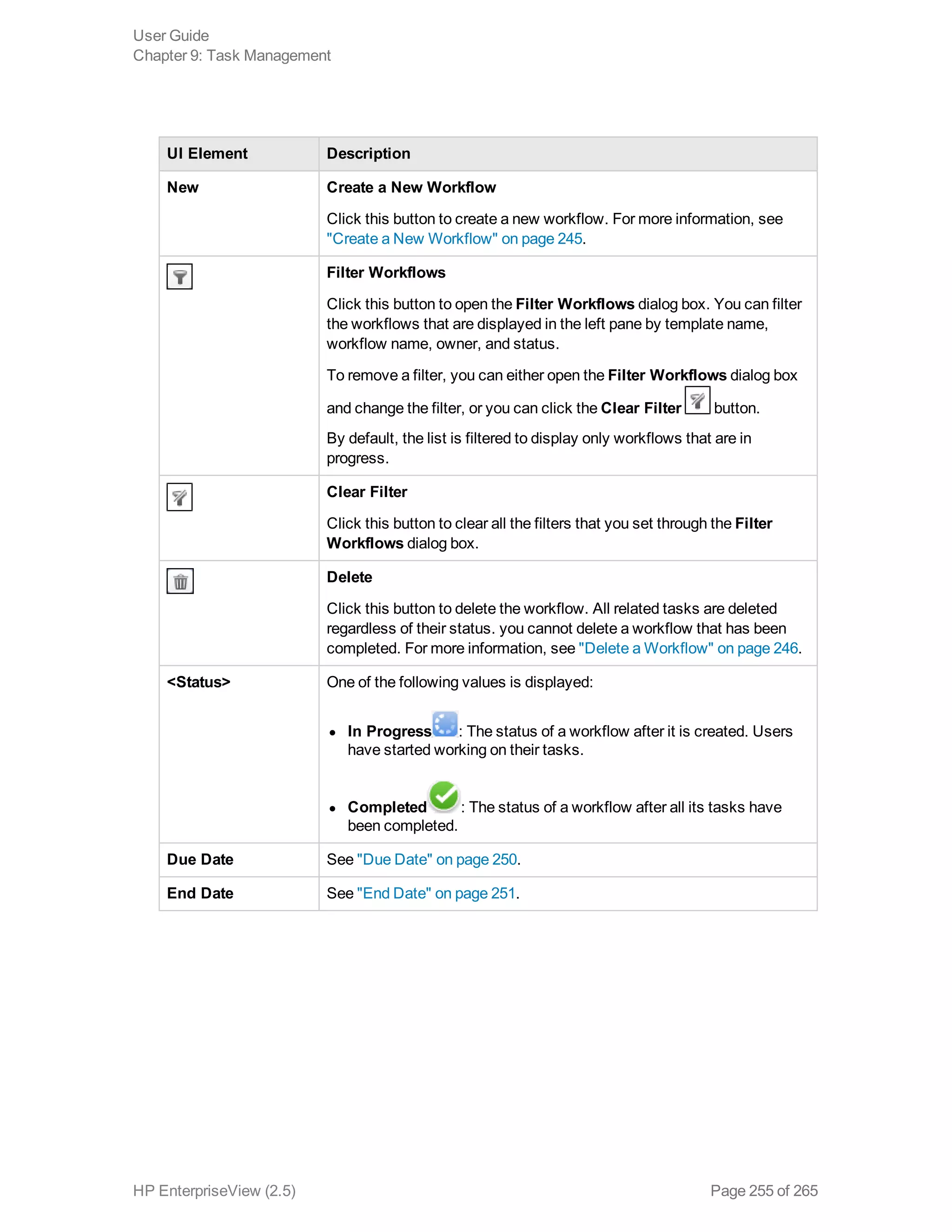
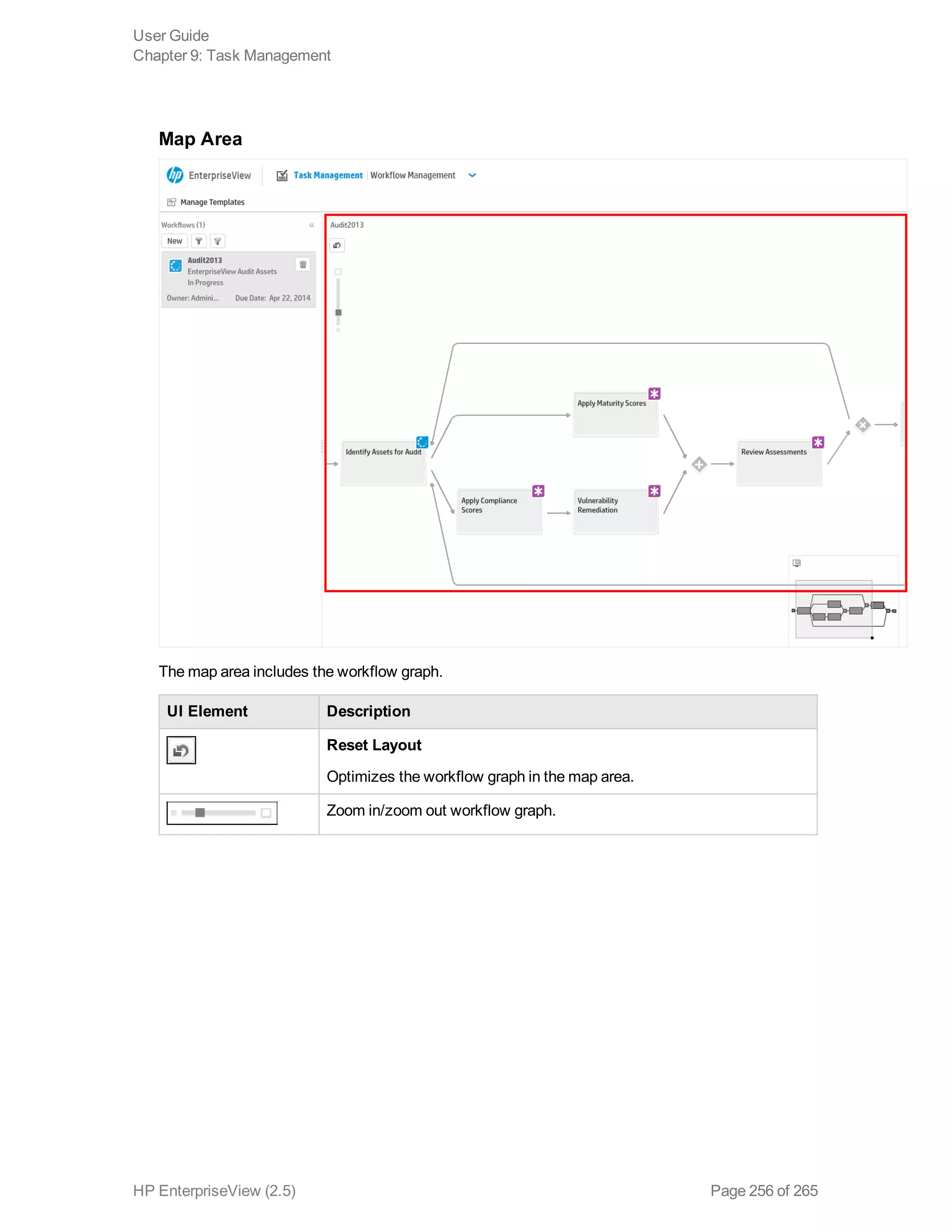
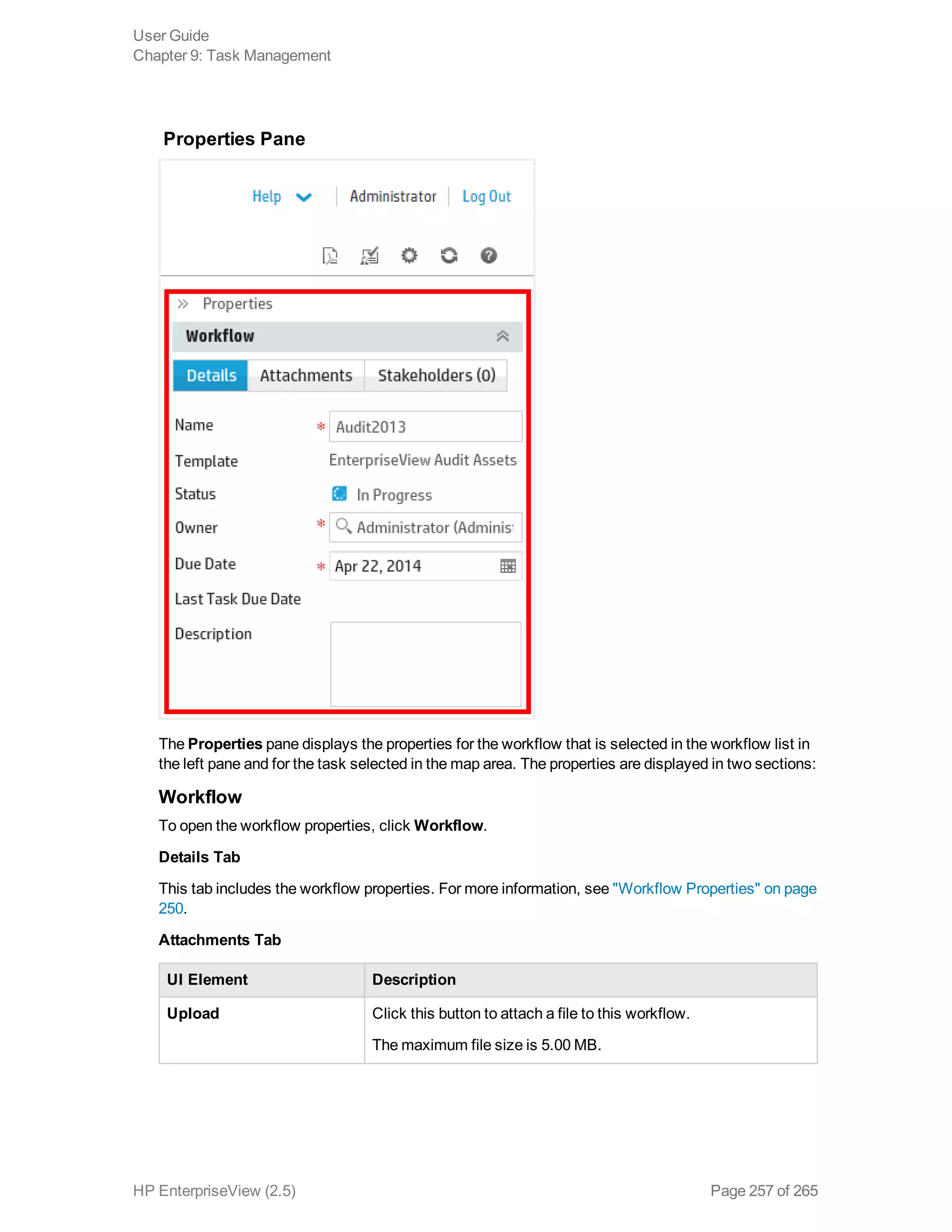
EnterpriseView is a software that enables organizations to manage risk, compliance, vulnerabilities and other security-related information on a business model. This user guide provides information about using EnterpriseView's modules for asset profiling, policy and compliance management, risk management, vulnerability management, dashboards and reports, and task management. It also describes navigating the EnterpriseView interface using the navigation bar and home page.