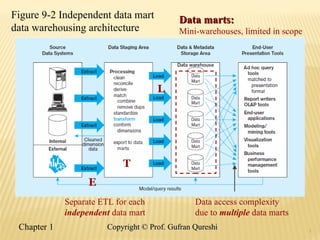
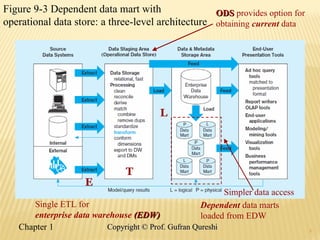
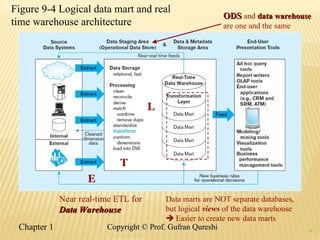
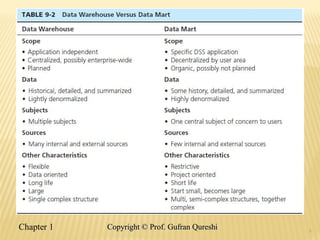
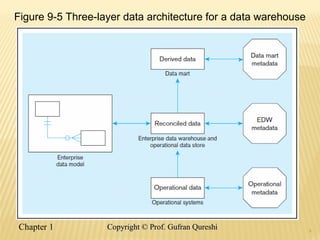
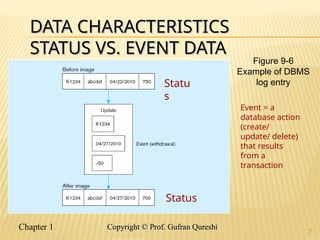
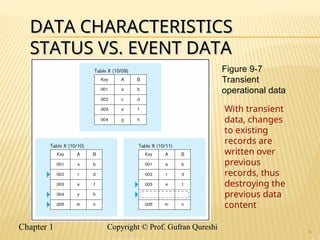
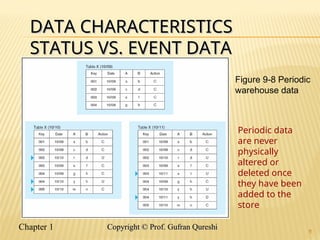
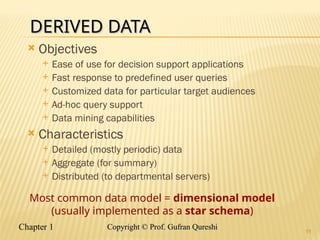
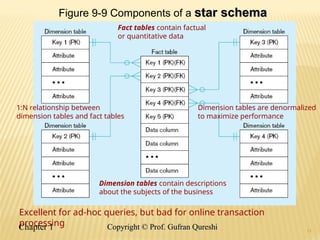
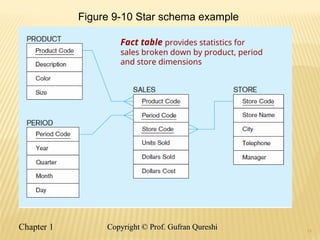
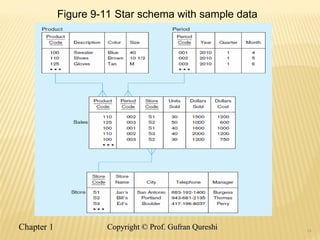
The document discusses various data warehouse architectures, including independent and dependent data marts, as well as logical data marts and real-time data warehouses. It explores the complexities of ETL processes, data characteristics, and the star schema model commonly used in dimensional modeling for decision support applications. Key concepts include managing both transient and periodic data, along with the evolution of descriptive attributes in data warehouses.