Recommended
PPTX
PPTX
ACHD anaesthesia PowerPoint presentation.pptx
PPTX
ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE GUIDELINES - INTRODUCTION
PDF
2018 AHA ACC guideline for the management of adults with congenital heart dis...
PPTX
2018_ACHD_Guideline_Slide_Set.pptx
PPTX
Caring for the Adult with Congenital Heart Disease
PPT
PPTX
Debate: Who should care for GUCH?
PPTX
Adult with congenital heart diseasel.pptx
PDF
3. dr. Bagus Artiko Sp.A(K), M.Kes - Special Needs in Children with Cardiac D...
PPTX
Congenital Heart Disease for Anaesthesia
PPT
Management of congenital heart disease in infants
PPTX
ACYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEARTT DISEASES.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
ACYANOTIC CONGENITALLL HEART DISEASES.pptx
PPTX
Congenital heart disease in adults internal medicine.ppt
PPTX
Approach to cvs disease - Dr. Gunasekaran
PPTX
Update on Outcomes of Neonatal Heart Disease
PDF
Anesthesia for Congenital Heart Disease 4th Edition Dean B Andropoulos Emad B...
PPTX
Pulse oximetry screening in newborns
PPT
Pediatric_Cardiac_Disorders.ppt
PDF
PPT
Congenital heart disease toufiqur rahman NICVD
PPTX
WHEN TO REFER A CHILD TO A PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGIST FOR INTERVENTION
PPTX
WHEN TO REFER TO A PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGIST
PDF
2018 ACC AHA guideline for the management of adults with congenital heart dis...
PDF
PDF
Study of Congenital Heart Diseases in Pediatric Patient
PDF
Lecture 7 Extra oral examination power point.pdf
PDF
Types-of-culture-media; basal,enriched,enrichment,differential and selective ...
More Related Content
PPTX
PPTX
ACHD anaesthesia PowerPoint presentation.pptx
PPTX
ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE GUIDELINES - INTRODUCTION
PDF
2018 AHA ACC guideline for the management of adults with congenital heart dis...
PPTX
2018_ACHD_Guideline_Slide_Set.pptx
PPTX
Caring for the Adult with Congenital Heart Disease
PPT
PPTX
Debate: Who should care for GUCH?
Similar to Approach_to_ACHD_in_Pediatrics population.pptx
PPTX
Adult with congenital heart diseasel.pptx
PDF
3. dr. Bagus Artiko Sp.A(K), M.Kes - Special Needs in Children with Cardiac D...
PPTX
Congenital Heart Disease for Anaesthesia
PPT
Management of congenital heart disease in infants
PPTX
ACYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEARTT DISEASES.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
ACYANOTIC CONGENITALLL HEART DISEASES.pptx
PPTX
Congenital heart disease in adults internal medicine.ppt
PPTX
Approach to cvs disease - Dr. Gunasekaran
PPTX
Update on Outcomes of Neonatal Heart Disease
PDF
Anesthesia for Congenital Heart Disease 4th Edition Dean B Andropoulos Emad B...
PPTX
Pulse oximetry screening in newborns
PPT
Pediatric_Cardiac_Disorders.ppt
PDF
PPT
Congenital heart disease toufiqur rahman NICVD
PPTX
WHEN TO REFER A CHILD TO A PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGIST FOR INTERVENTION
PPTX
WHEN TO REFER TO A PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGIST
PDF
2018 ACC AHA guideline for the management of adults with congenital heart dis...
PDF
PDF
Study of Congenital Heart Diseases in Pediatric Patient
Recently uploaded
PDF
Lecture 7 Extra oral examination power point.pdf
PDF
Types-of-culture-media; basal,enriched,enrichment,differential and selective ...
PPTX
HEMOGLOBIN and Hemoglobin electrophoresis.
PDF
Kaplan and Sadock's Comprehensive Text of Psychiatry 11th Edition PDF
PDF
Vertebrate Animals, reptiles, birds, mammals, amphibian, fish
PDF
MOT , VBT , Ionic Bonding, VSPER Theory BSc 1st Sem Inorganic Chemistry Irfan...
PDF
Neuroscience 6th Edition PDF Textbook by Dale Purves
PDF
International Chemistry Scientist Awards
PDF
Organic Chemistry 3rd Edition By David Klein PDF
PDF
634987849-Class-12-Physics-Formula-Sheet.pdf
PPTX
Physical Science SHS 24.2 Expanding Universe.pptx
PDF
Form 2 Integrated Science -- Electricity.pdf
PDF
A Brief Review on Antibacterial Activity of Citrullus colocynthis
PPTX
UNIT -5 PPT PP-1.pptx buffer second year
PDF
Amino acid cost and supply chain analysis for cultivated meat
PDF
Multiple outflows and delayed ejections revealed by early imaging of novae
PDF
Introduction to Genomics lecture note.pdf
PPTX
Determination of Permanent Wilting Point (PWP) by Sunflower pot culture techn...
PPTX
UNIT 3 - Surface and interfacial tension ppt.pptx
PDF
Rock Types and Formations: Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic
Approach_to_ACHD_in_Pediatrics population.pptx 1. Approach to ACHD in Pediatrics
• Understanding the continuum of congenital
heart disease care
• Presented by: [Your Name / Institution]
• Date: [Date of Presentation]
2. 3. Epidemiology
• - ~90% of children with CHD now survive into
adulthood
• - Estimated 1.4 million adults with CHD in the
US
• - Common defects: TOF, TGA, Fontan, etc.
4. Why Pediatricians Should Know
About ACHD
• - Early planning for transition
• - Coordination with cardiologists
• - Identifying red flags and complications early
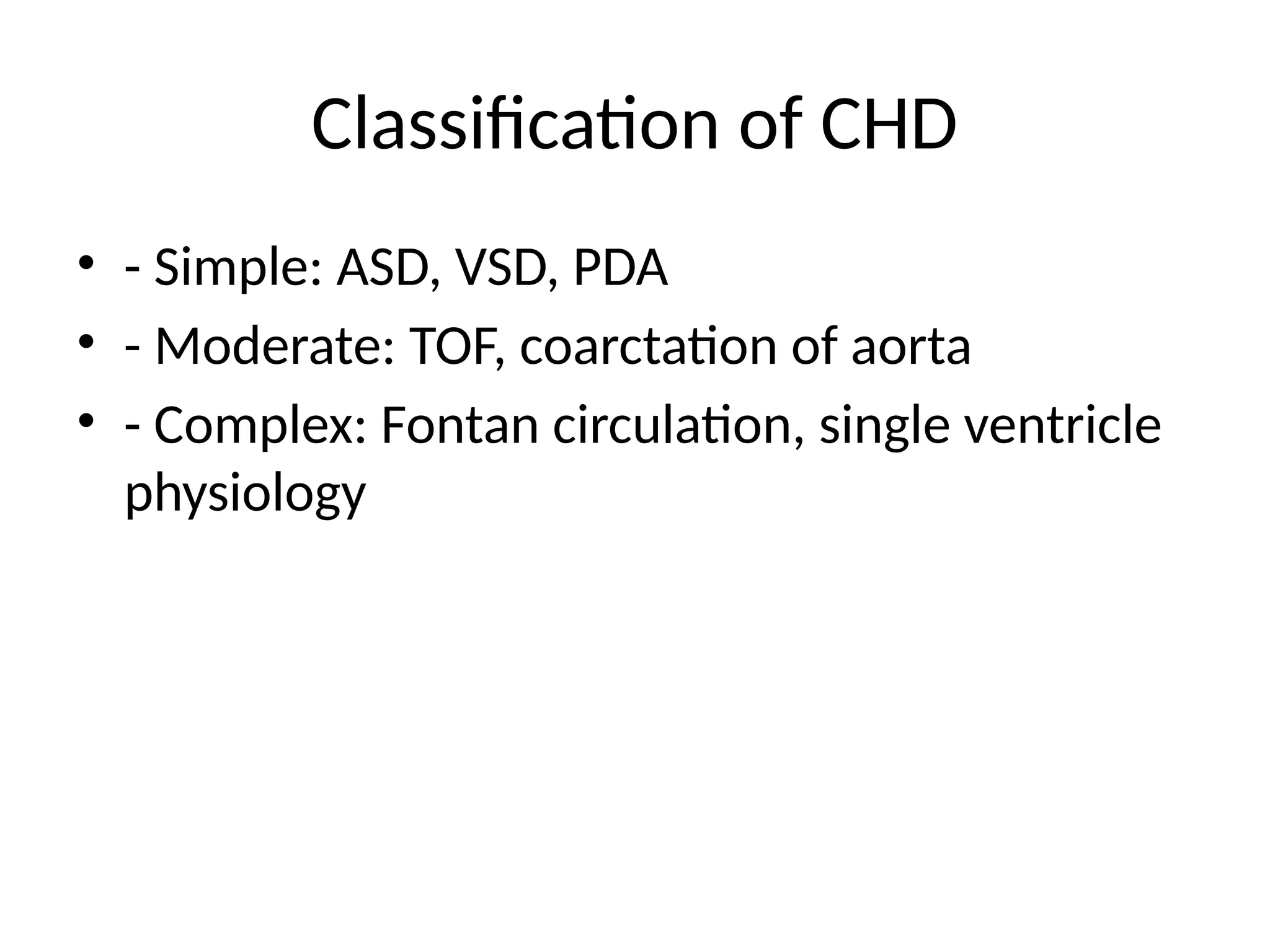
5. Classification of CHD
• - Simple: ASD, VSD, PDA
• - Moderate: TOF, coarctation of aorta
• - Complex: Fontan circulation, single ventricle
physiology
6. Clinical Approach
• - Detailed history: surgery, interventions,
complications
• - Growth and development assessment
• - Cardiac exam and vitals
• - Functional capacity (NYHA class)
• - Screening for complications
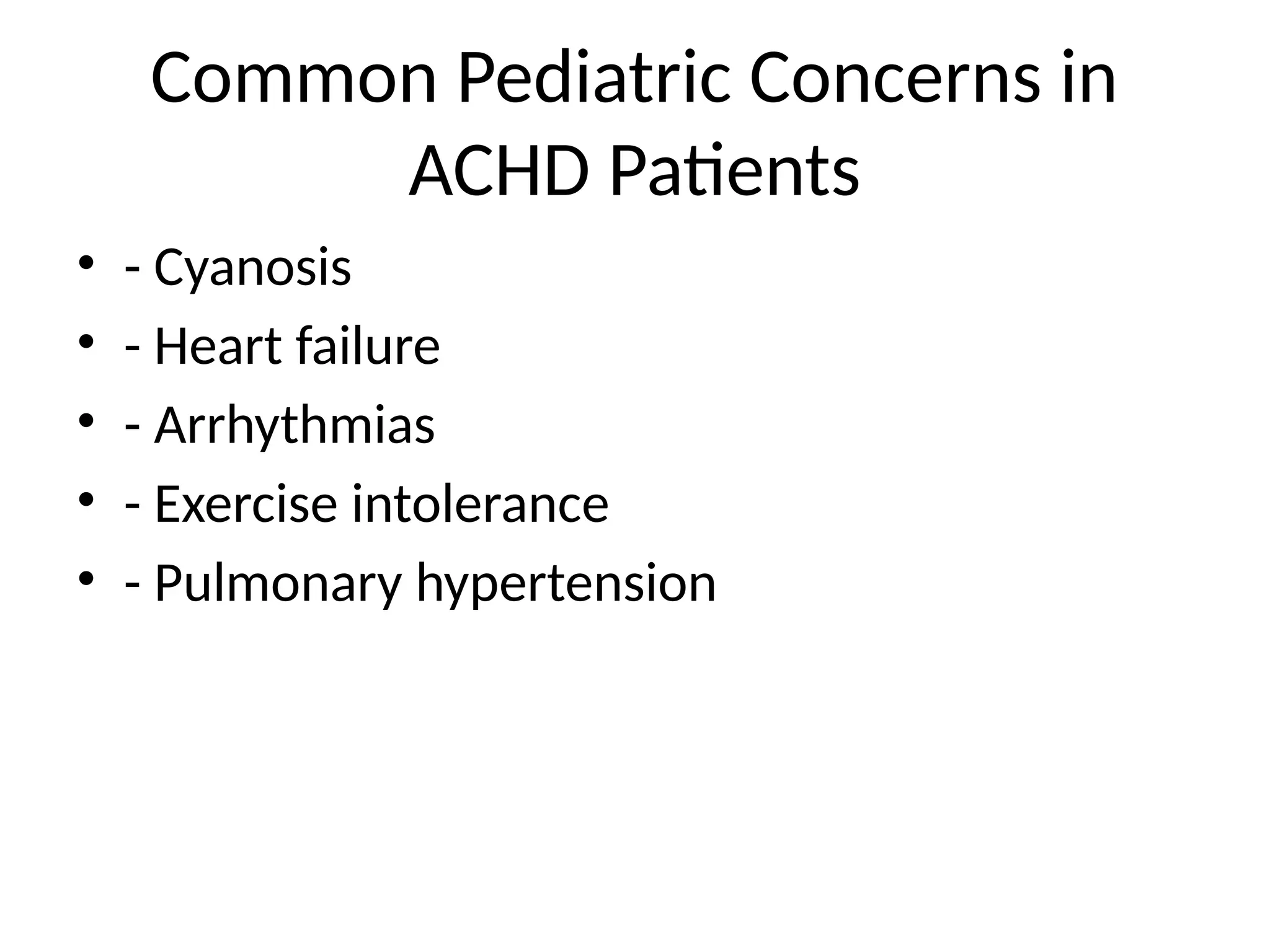
7. Common Pediatric Concerns in
ACHD Patients
• - Cyanosis
• - Heart failure
• - Arrhythmias
• - Exercise intolerance
• - Pulmonary hypertension
8. Investigations
• - ECG
• - Echocardiography
• - Cardiac MRI/CT
• - Holter monitoring
• - Cardiac catheterization (if needed)
9. Transition of Care
• - Age-appropriate education
• - Gradual shift of responsibility
• - Transition clinics: joint care with ACHD
specialists
10. Psychosocial Aspects
• - Neurodevelopmental issues
• - Mental health (depression, anxiety)
• - School/work challenges
• - Family and peer support
11. Preventive Care
• - Endocarditis prophylaxis
• - Immunizations (e.g., influenza, RSV,
pneumococcus)
• - Reproductive counseling (adolescents)
• - Lifestyle modifications
12. Coordination with ACHD Team
• - Role of pediatric cardiologist
• - When to refer to adult CHD center
• - Multidisciplinary approach
13. 14. Summary
• - ACHD begins in pediatrics
• - Identify risk, plan care, educate family
• - Support smooth transition to adult care
15. 16.
![Approach to ACHD in Pediatrics
• Understanding the continuum of congenital
heart disease care
• Presented by: [Your Name / Institution]
• Date: [Date of Presentation]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtoachdinpediatrics-250716042221-e56c7c99/75/Approach_to_ACHD_in_Pediatrics-population-pptx-1-2048.jpg)