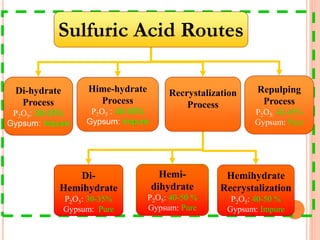
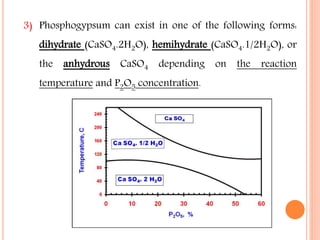
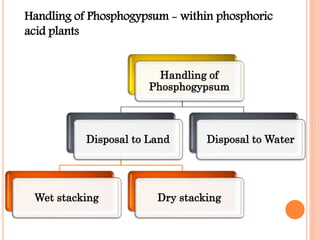
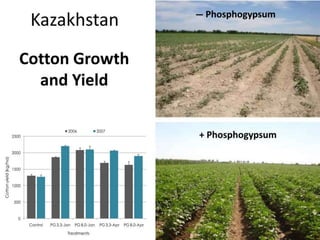
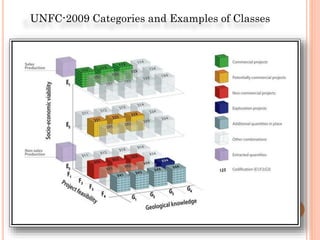
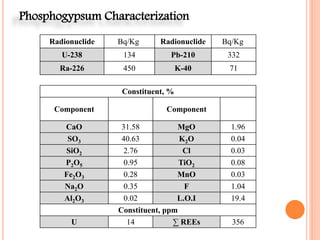
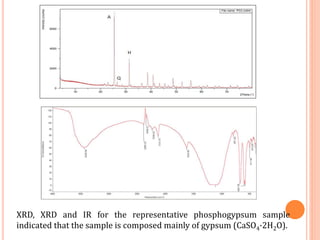
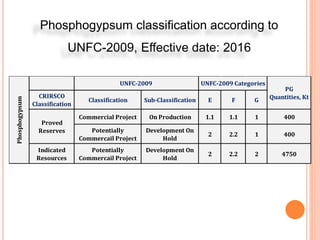
The document discusses the management and application of phosphogypsum, a by-product from phosphoric acid production, highlighting its potential as a resource rather than a waste. It outlines the production statistics in Egypt, with two main companies generating approximately 800-900 kt/year and new complexes expected to produce an additional 4.75 mt/year. The document also emphasizes the economic and environmental implications of phosphogypsum disposal and its utilization in agriculture, cement manufacturing, and road paving.