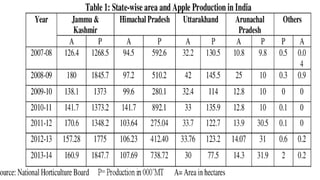
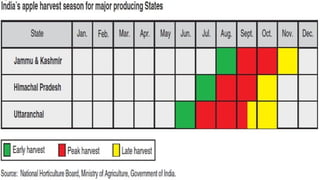
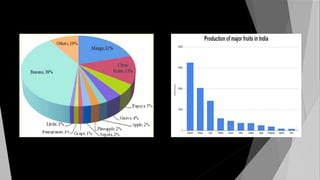
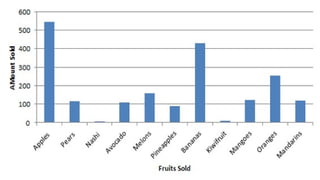
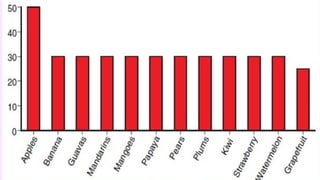
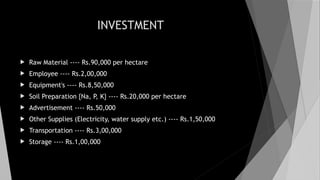
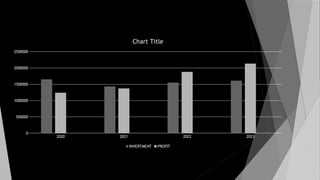
The document provides a comprehensive overview of apple cultivation, focusing on its significance as a leading temperate fruit globally, particularly in India, where it is most extensively grown in Himachal Pradesh. It details the taxonomy, growing conditions, varieties, nutritional benefits, and various uses of apples, as well as economic aspects such as production, trade, and financial support for farmers. Additionally, it highlights modern practices like drone technology in apple farming and the environmental impact of apple cultivation.