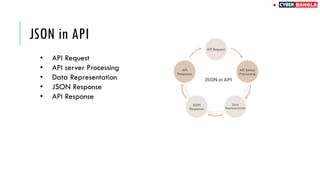
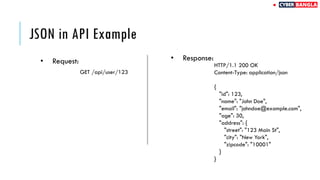
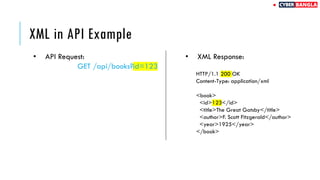
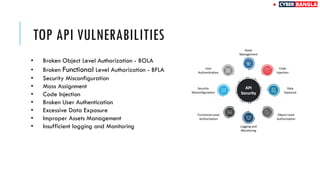
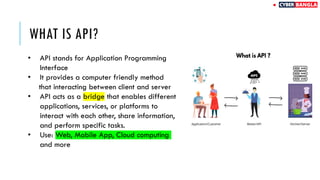
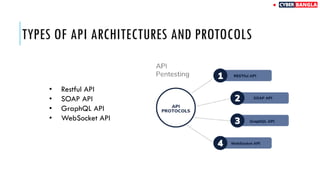
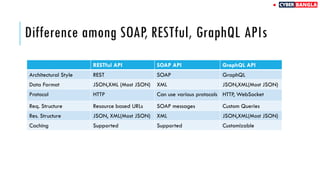
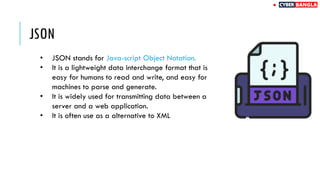
The document outlines achievements in cybersecurity competitions and provides an extensive overview of API penetration testing, discussing its importance, methodologies, and common vulnerabilities. It details various types of APIs, including RESTful, SOAP, and GraphQL, along with their architectural styles, protocols, and data formats. The text also includes examples of API requests and responses in both JSON and XML formats.














![JSON Structure
• Objects and Arrays are the main components of
JSON data structure.
• Objects:
• Arrays:
{
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"city": "New York"
}
[ "apple", "banana", "orange"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apipenetrationtesting-250129112230-d39694f1/85/Api-Penetration-Testing-and-web-app-pentesting-23-320.jpg)
![JSON Structure
{
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"address": {
"street": "123 Main St",
"city": "New York",
"zipcode": "10001"
},
"hobbies": ["reading", "traveling", "photography"],
"isEmployed": true,
"spouse": null
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apipenetrationtesting-250129112230-d39694f1/85/Api-Penetration-Testing-and-web-app-pentesting-24-320.jpg)