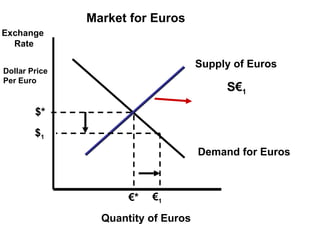
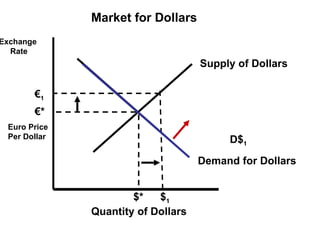
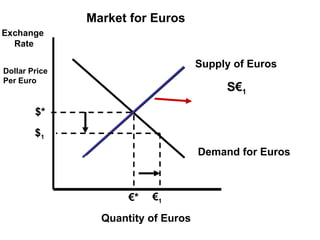
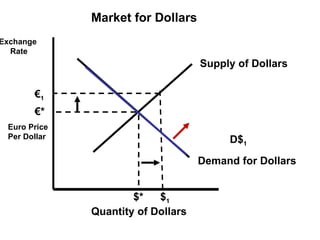
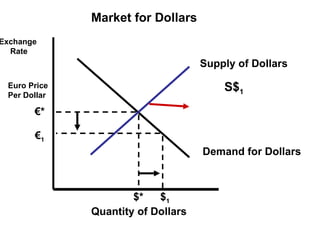
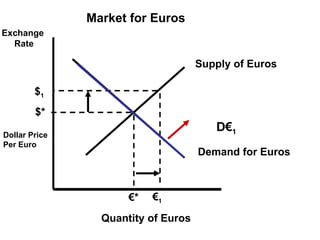
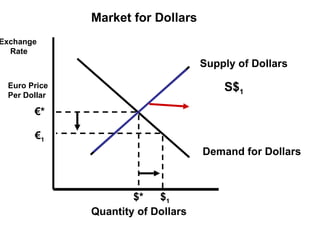
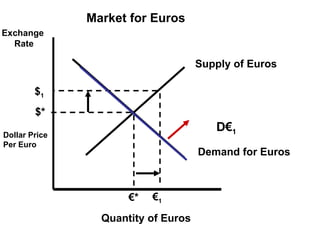
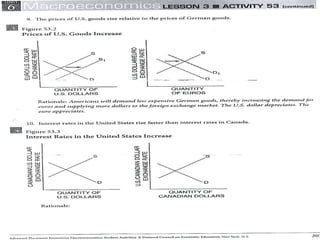
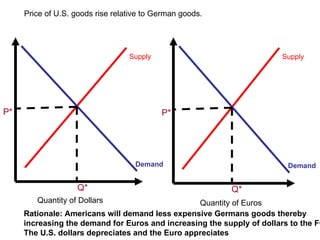
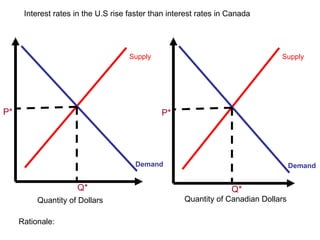
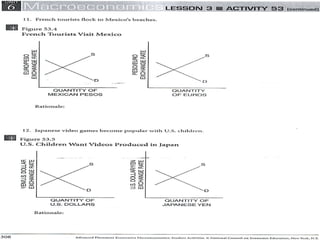
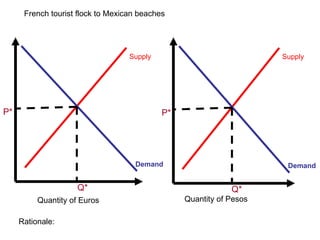
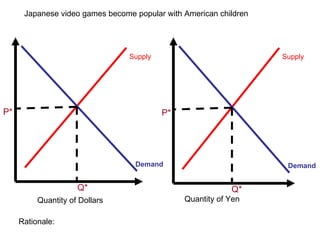
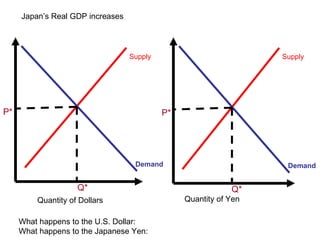
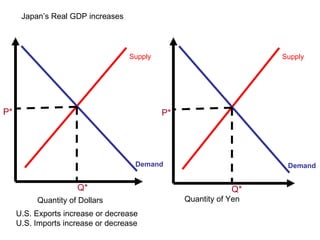
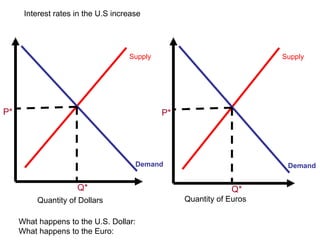
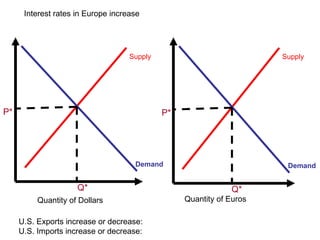
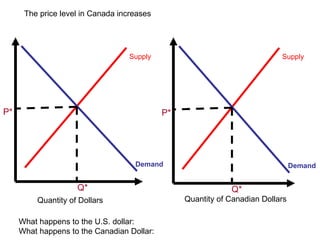
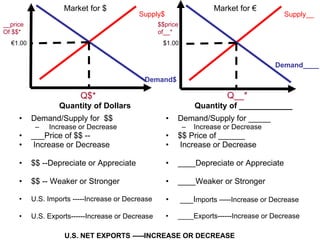
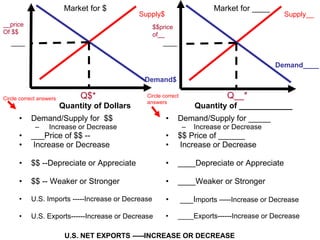
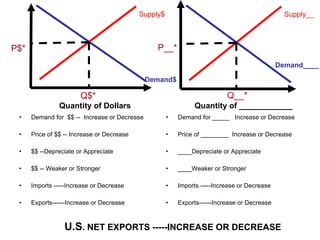
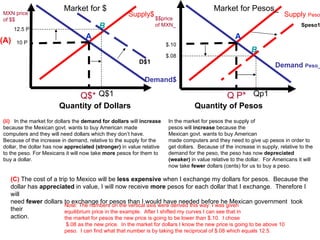
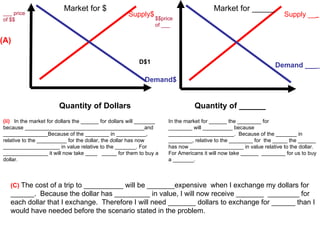
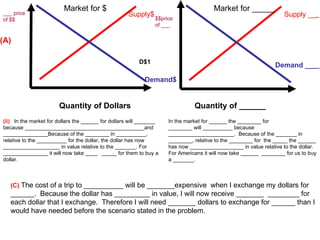
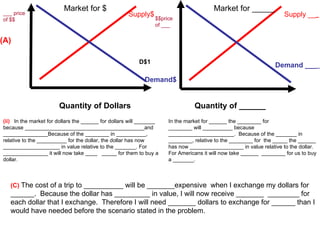
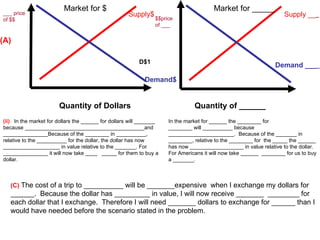
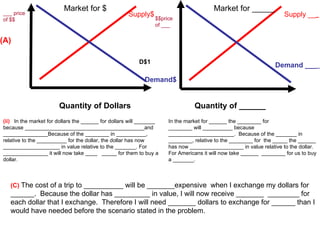
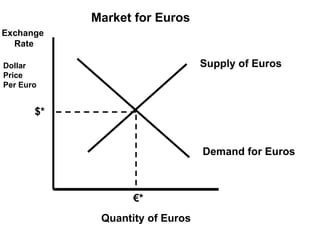
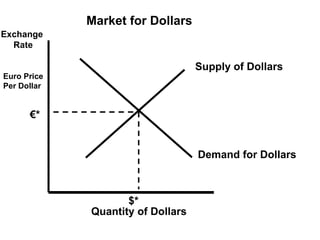
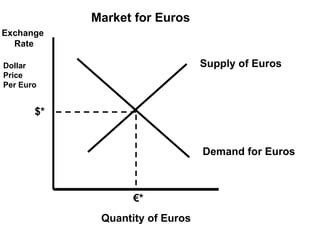
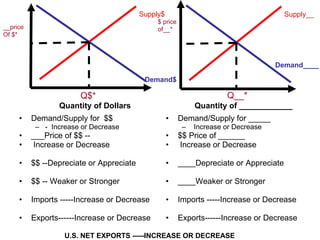
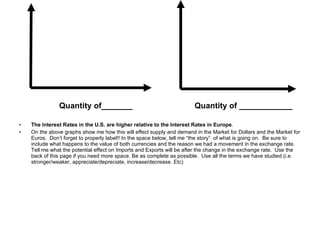
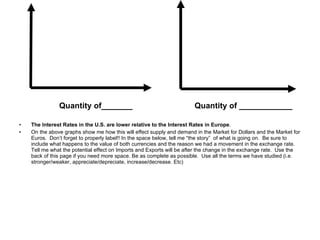
The document discusses how exchange rates between currencies are determined by the forces of supply and demand in foreign exchange markets. There are two main reasons for exchanging currencies: to purchase goods/services from another country or relative changes in interest rates between countries. If demand for a currency increases due to a change in tastes, interest rates, or other economic factors, its value will appreciate as its price in the foreign exchange market rises. An appreciating currency makes imports less expensive and exports more expensive, decreasing exports and increasing imports.