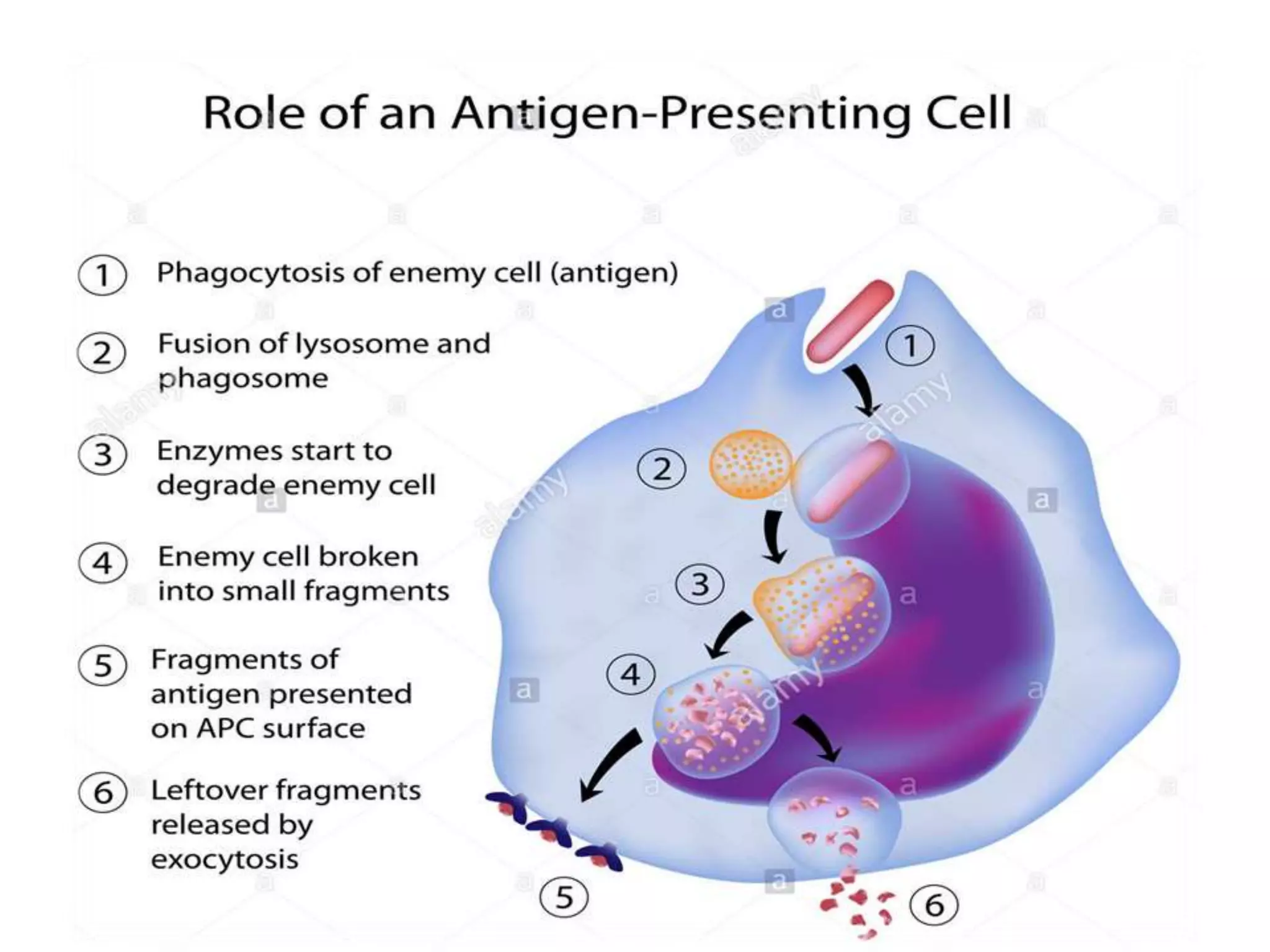
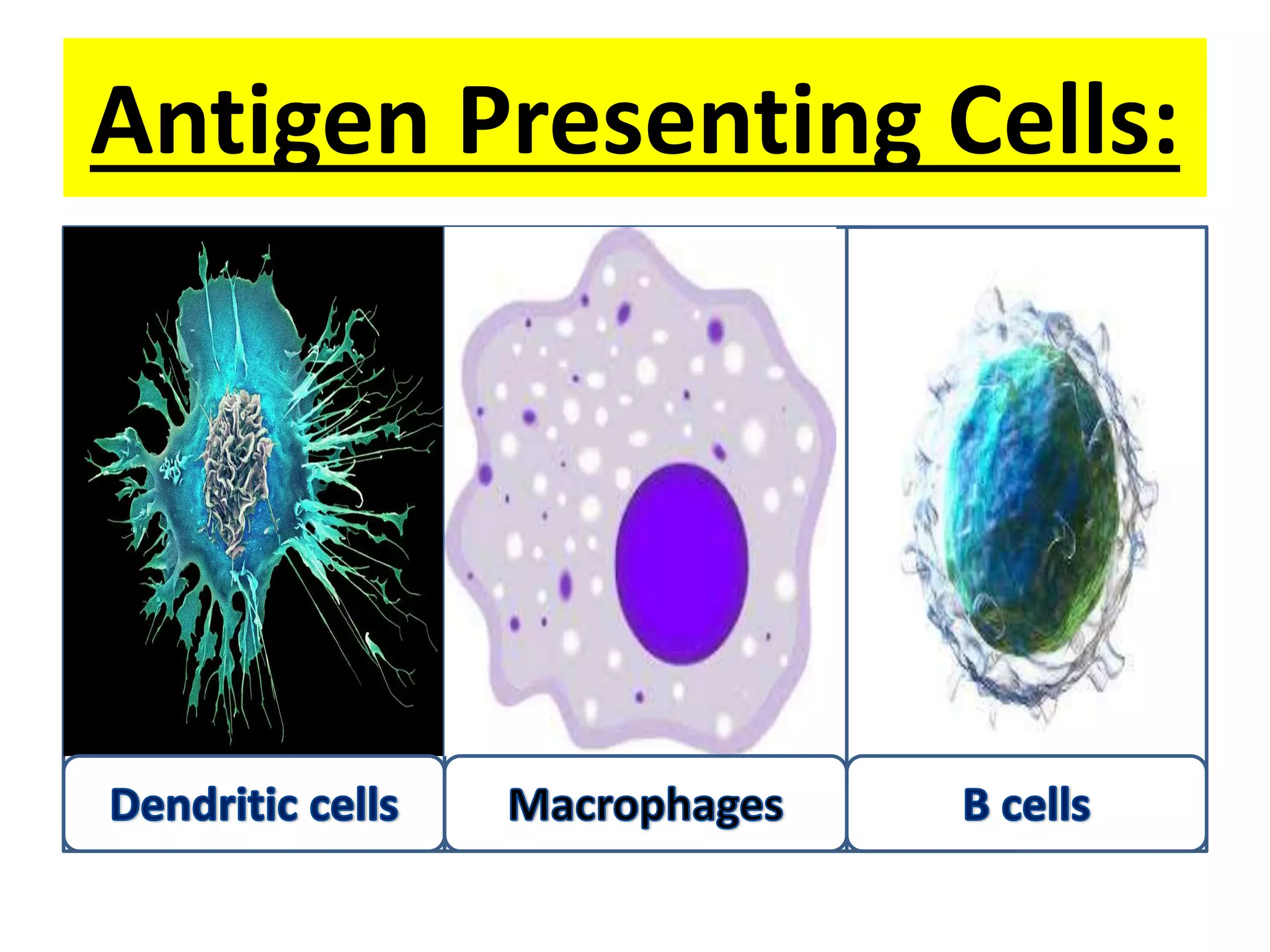
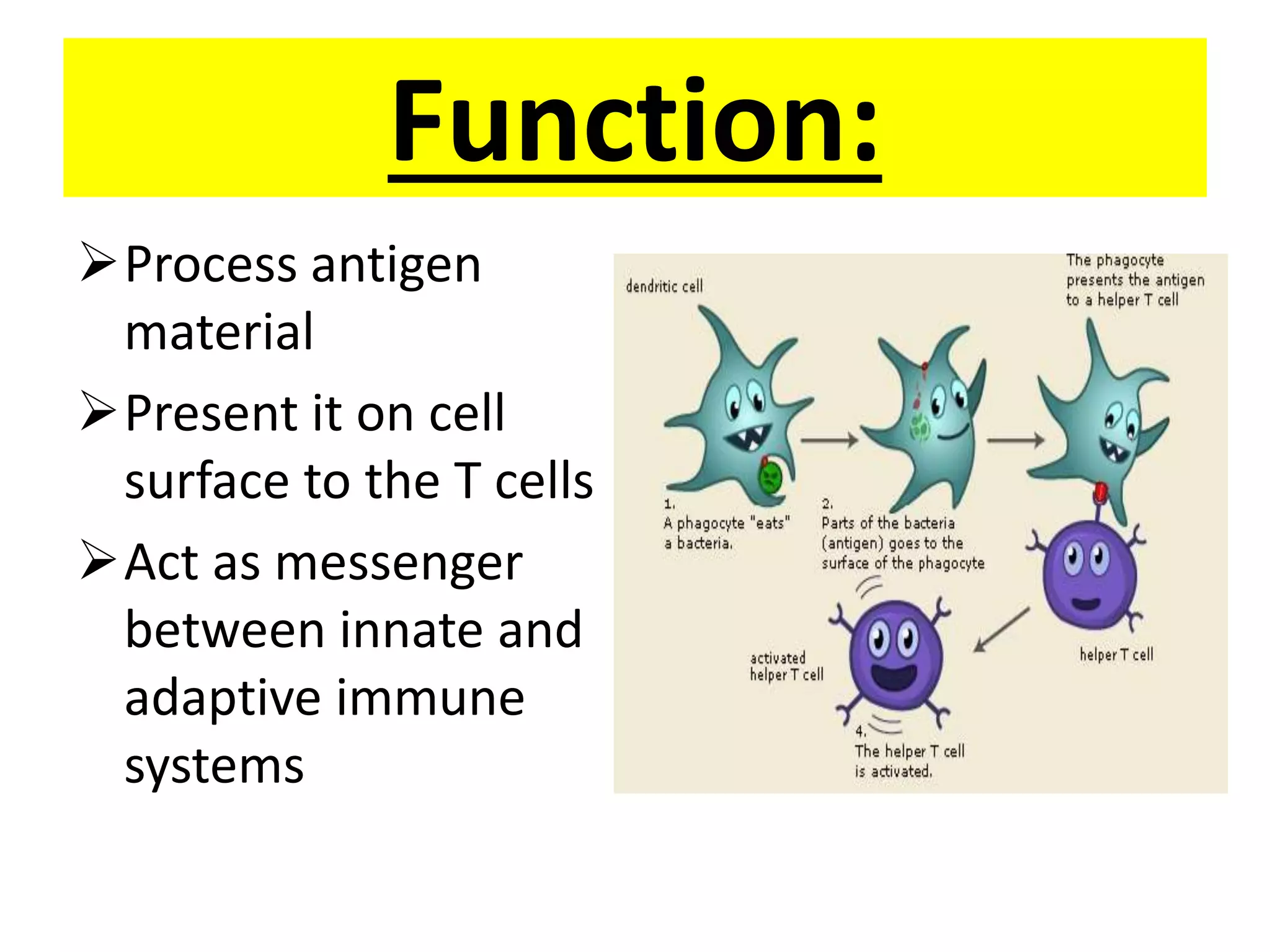
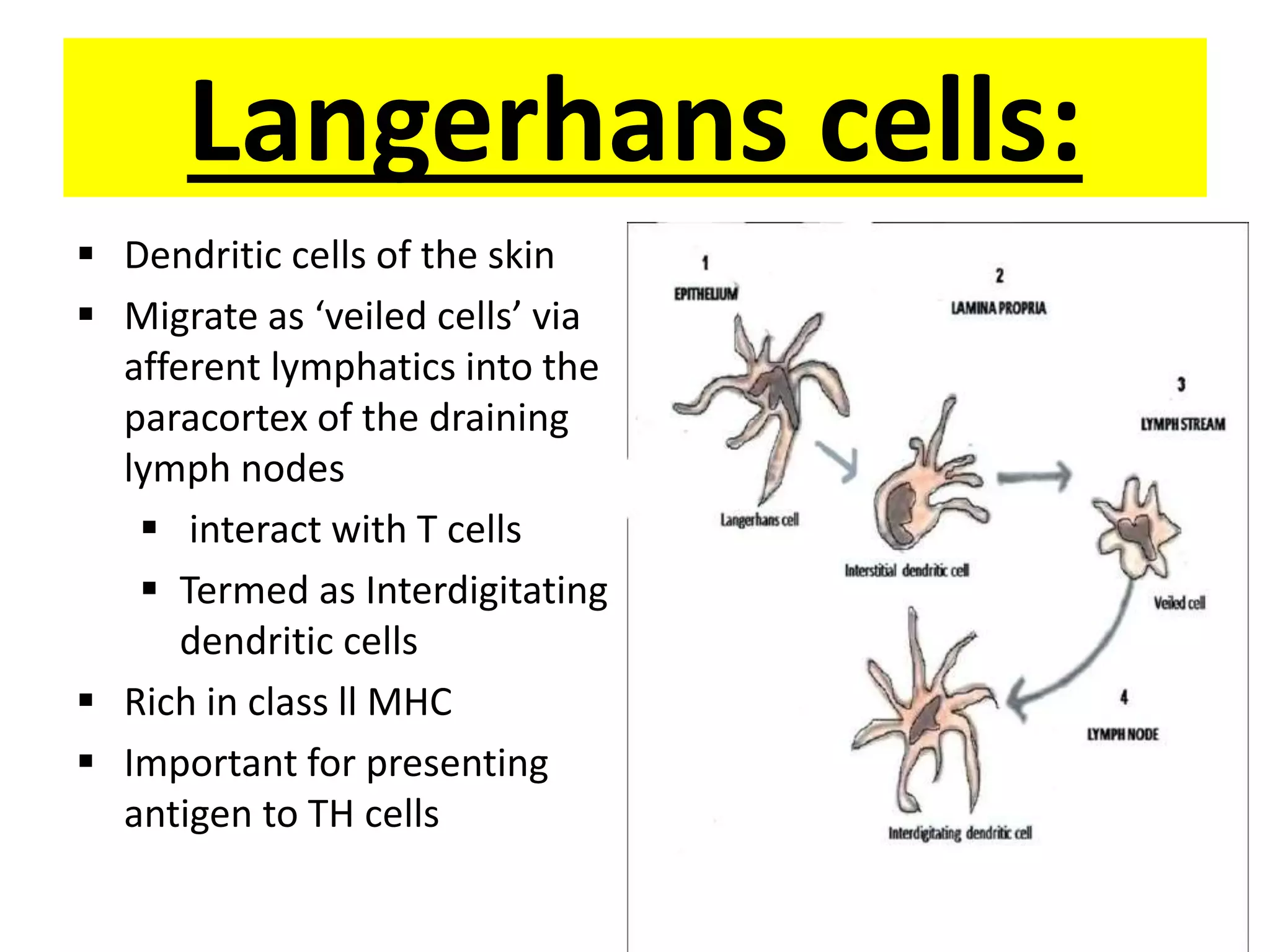
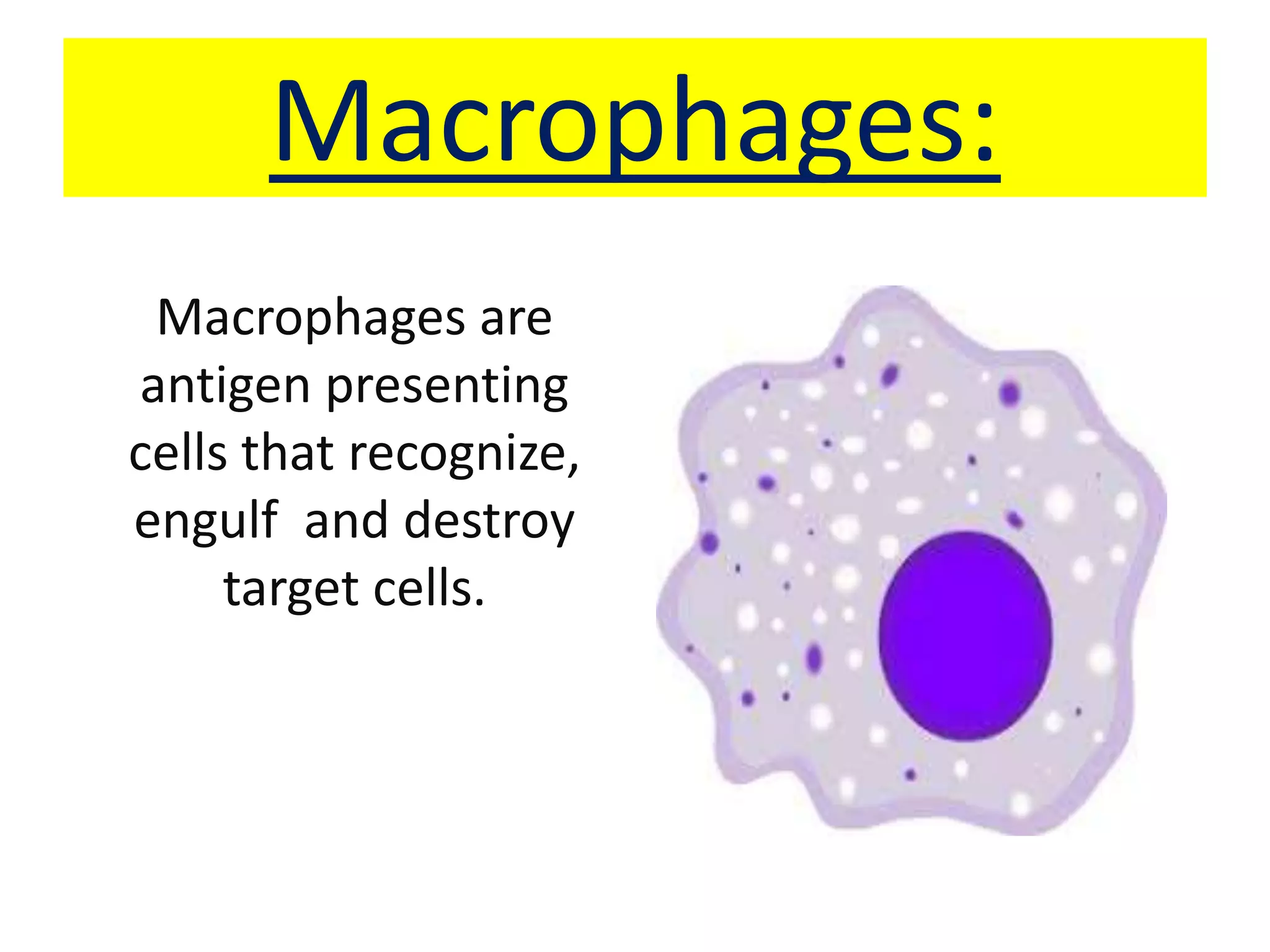
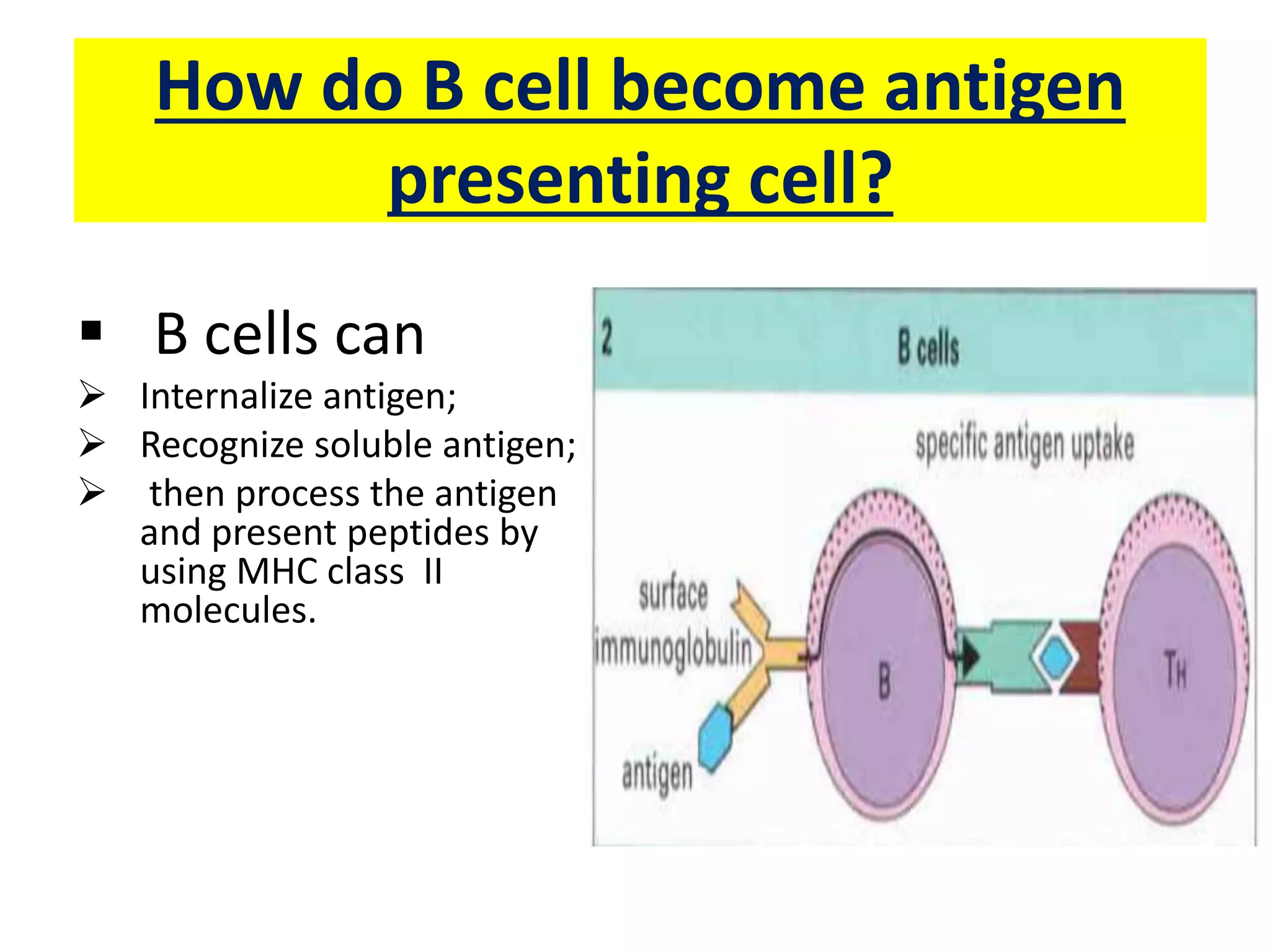
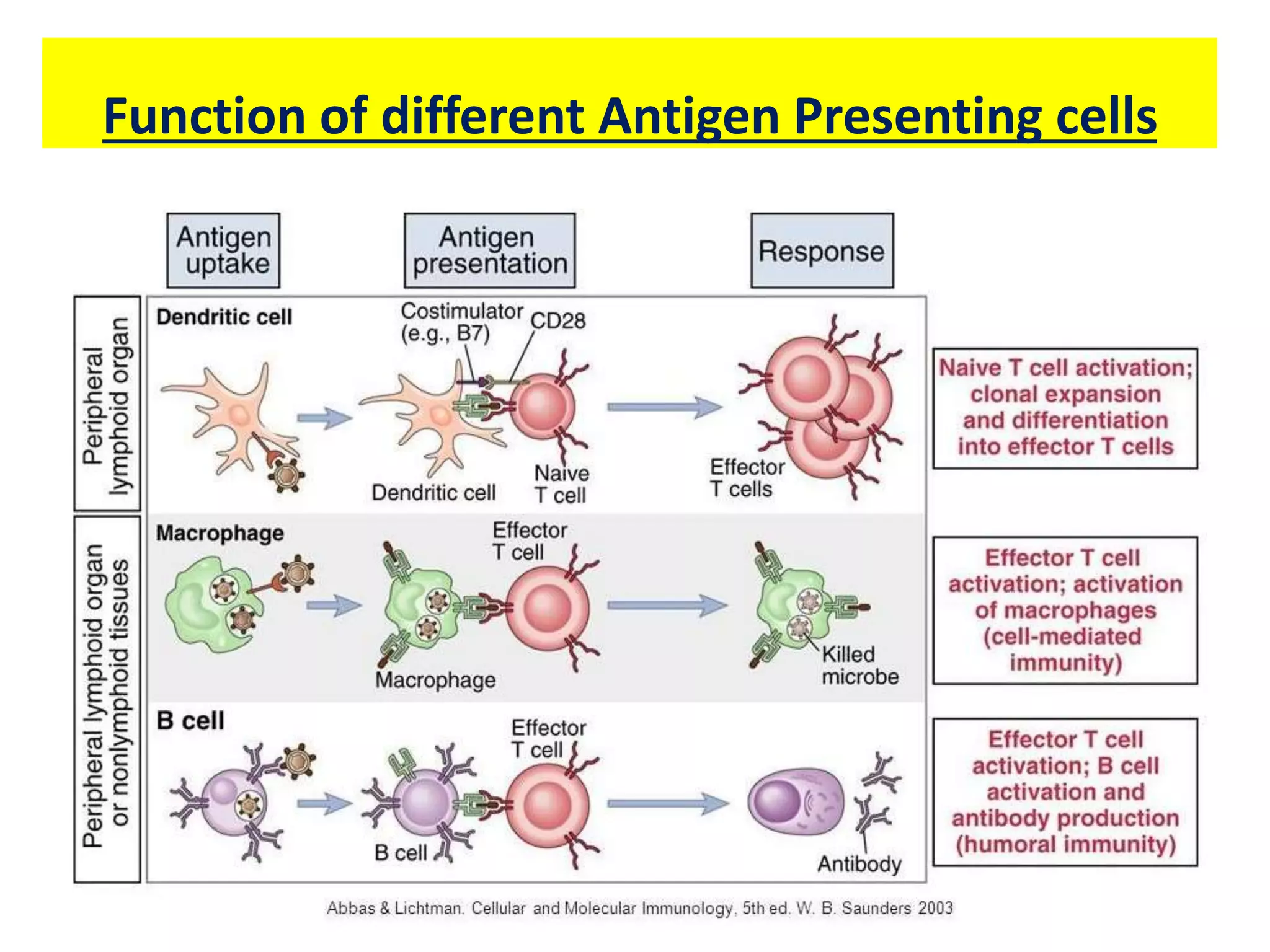
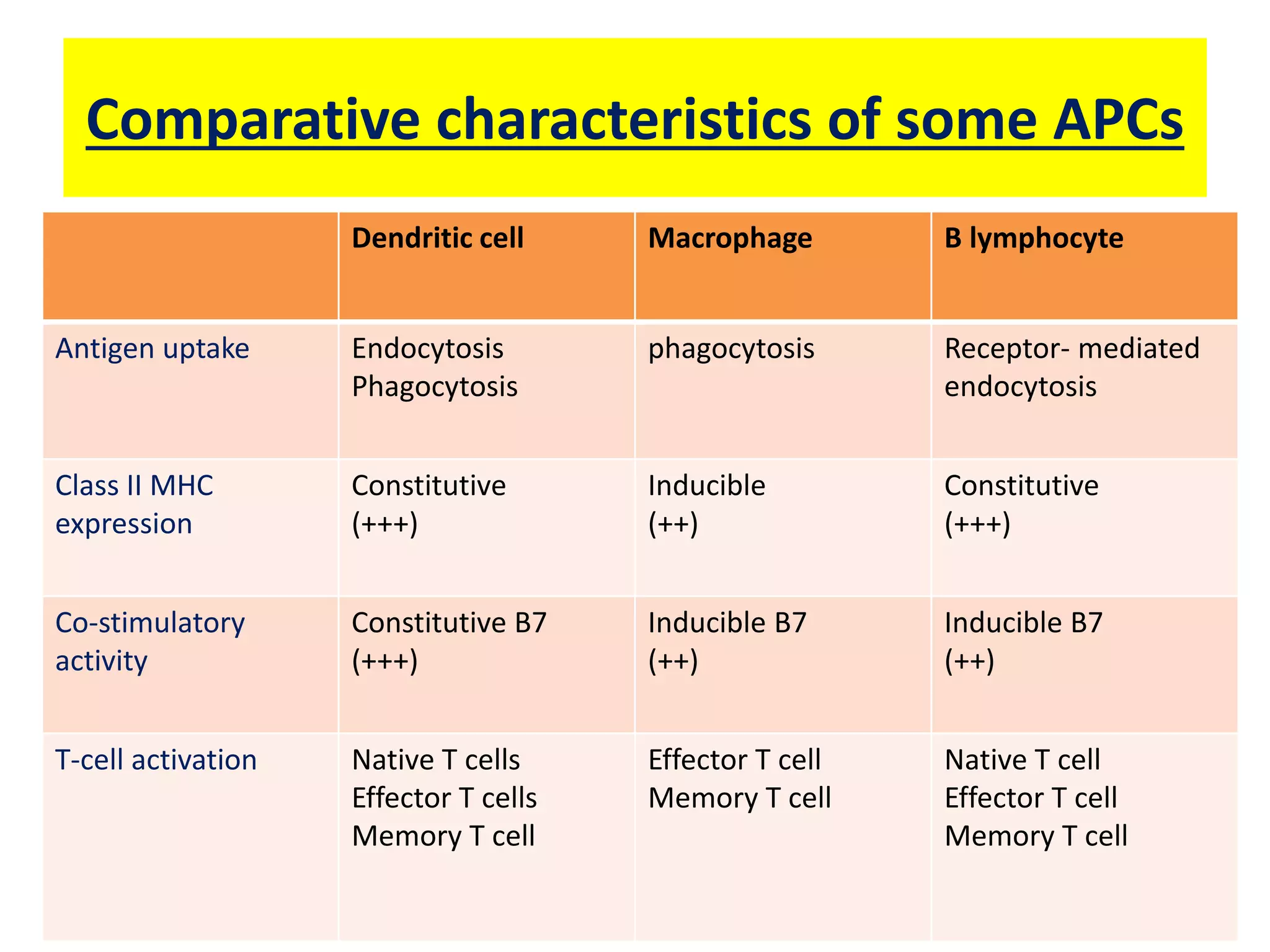
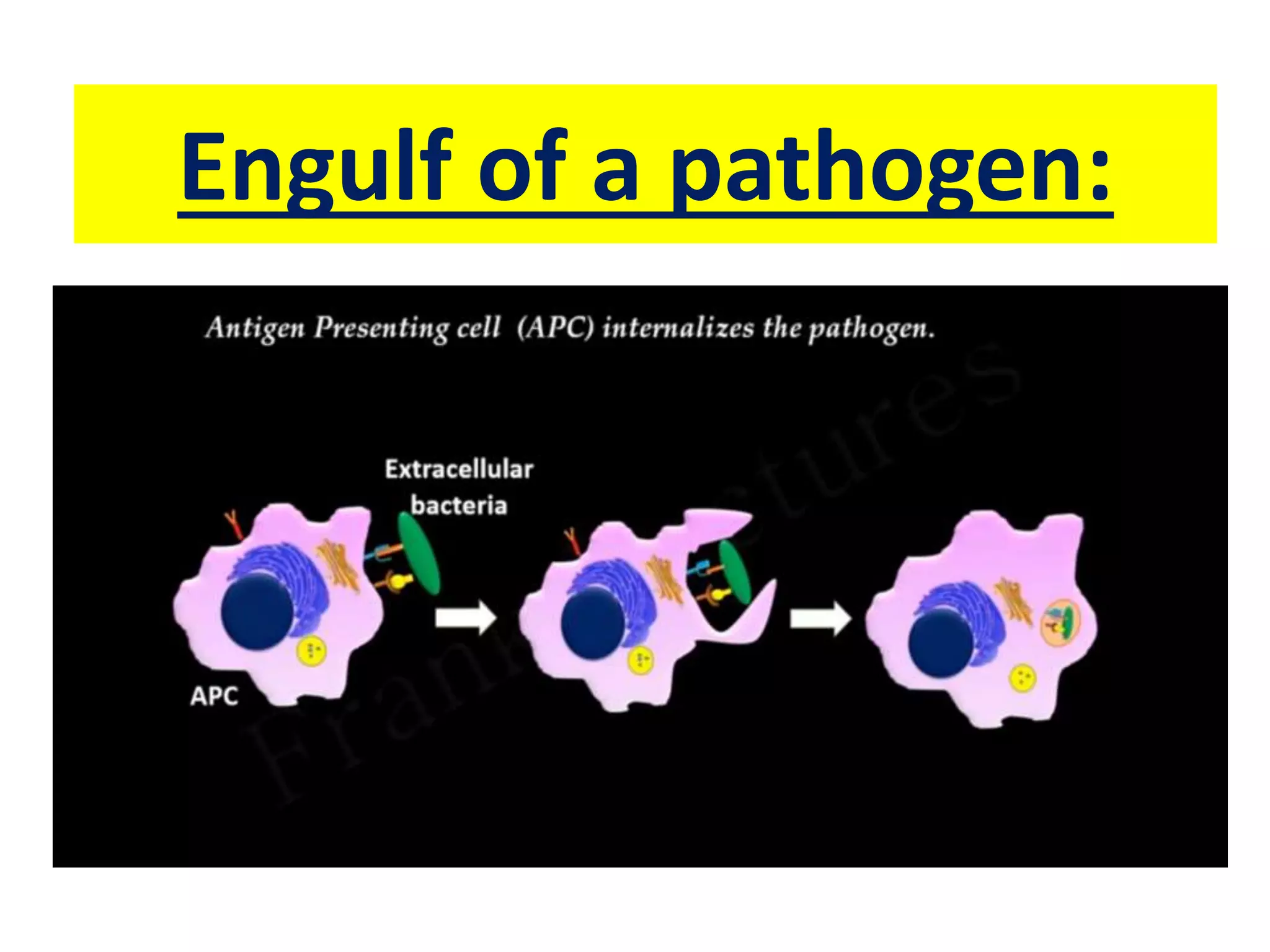
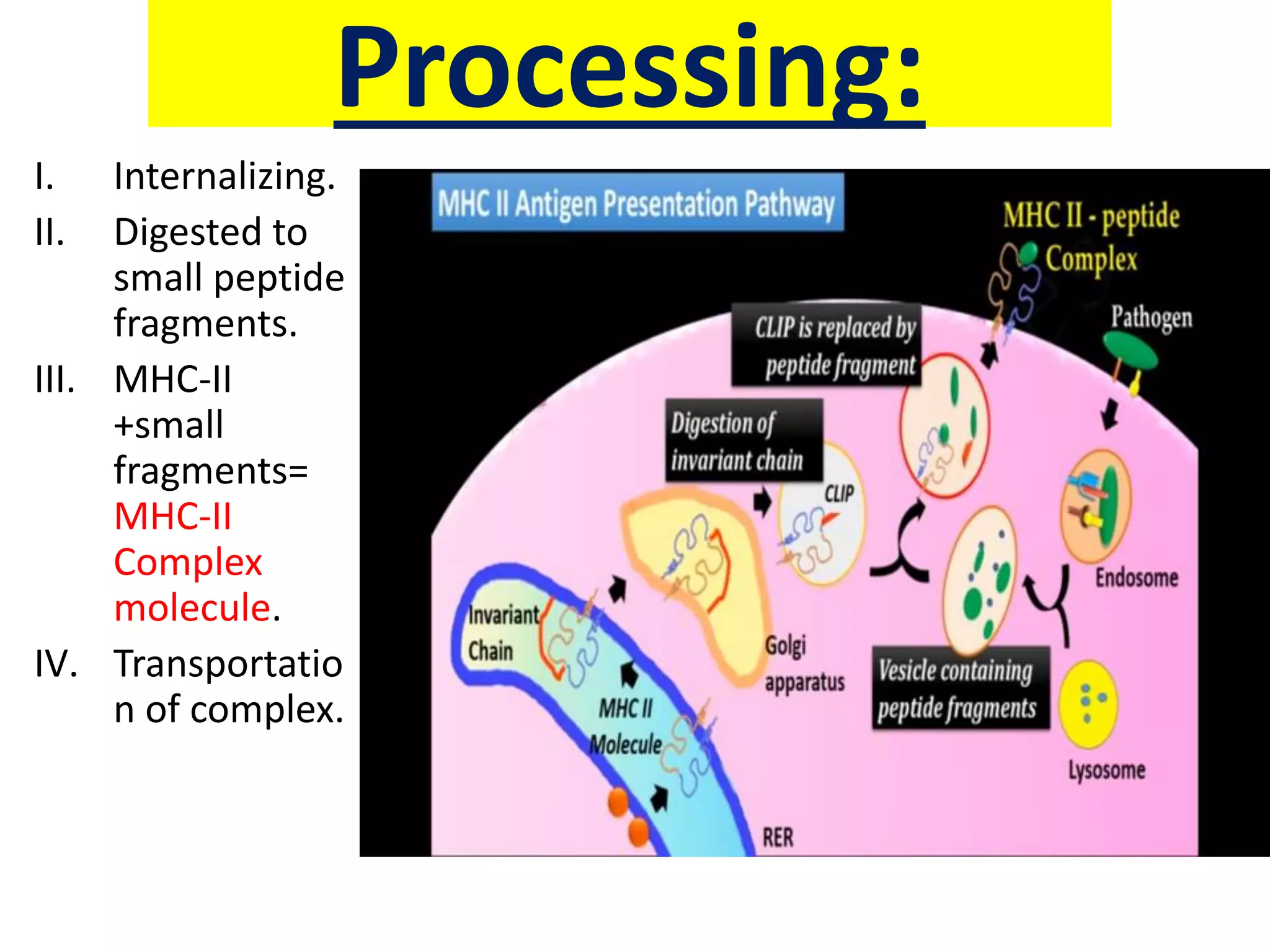
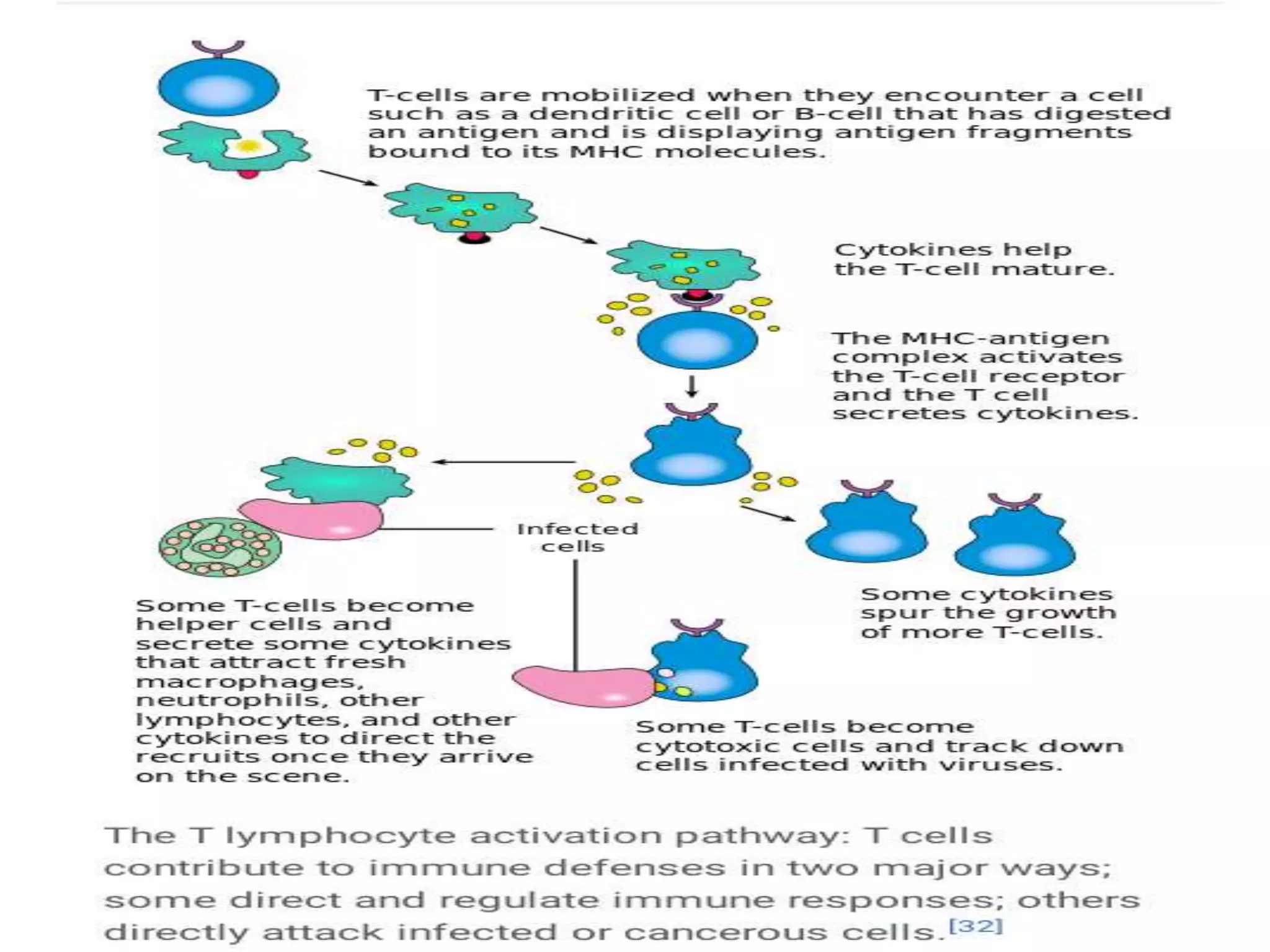
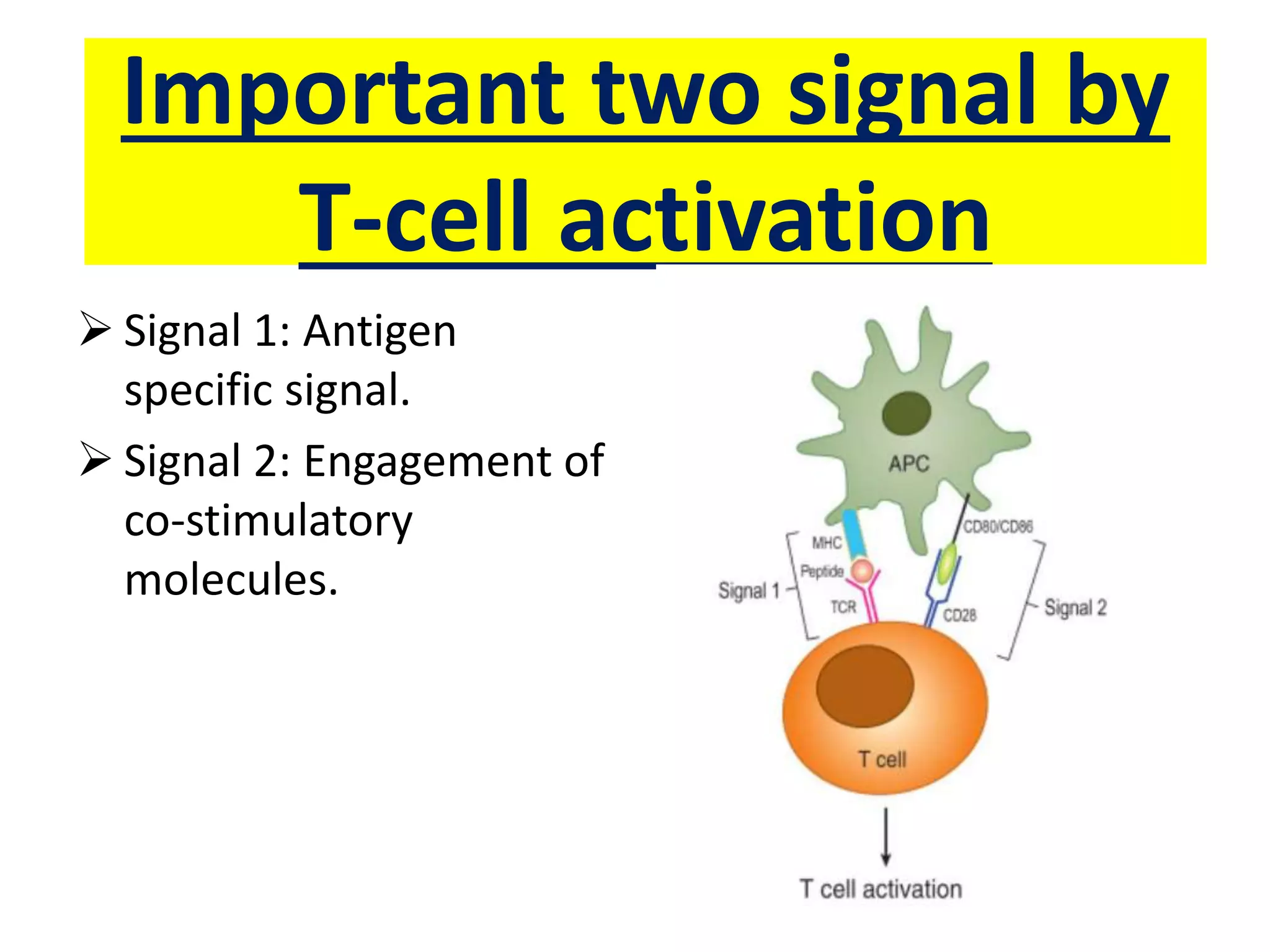
Antigen presenting cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells play a key role in activating T cells during an immune response. They process foreign antigens, display antigen fragments on MHC molecules, and present these to T cells. This initiation of T cell activation requires two signals: 1) antigen recognition by T cell receptors and 2) co-stimulatory signaling between molecules on the antigen presenting cell and T cell. Together, these signals trigger T cells to proliferate and carry out their immune functions in fighting pathogens or cancer cells.