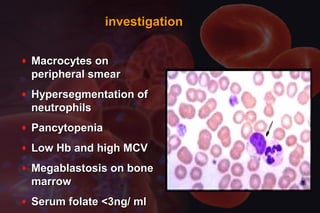
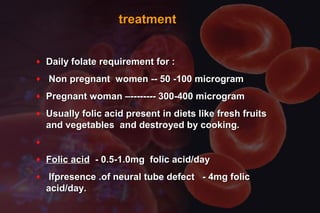
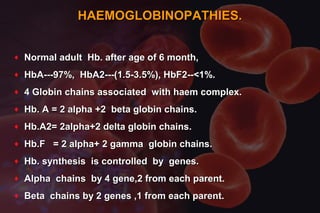
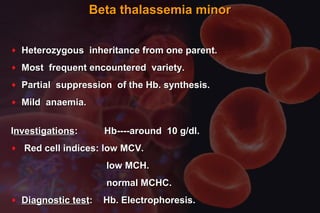
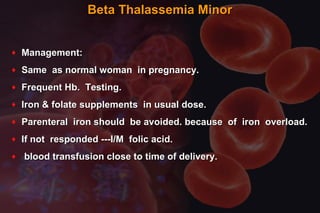
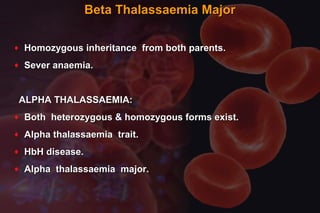
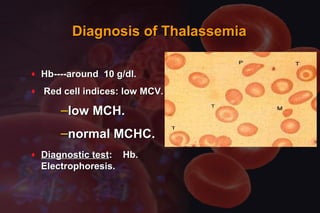
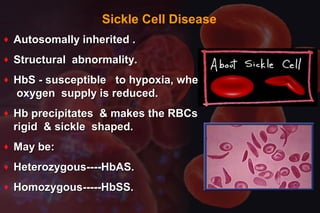
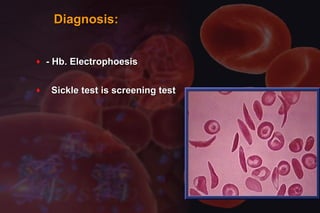
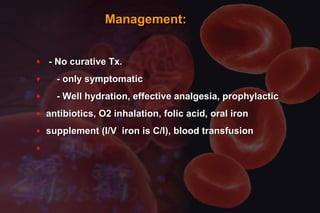
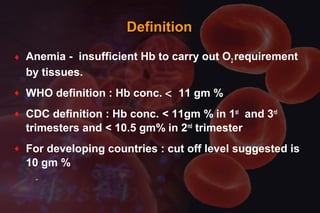
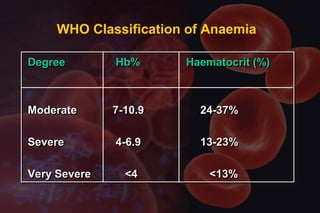
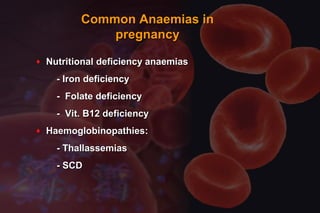
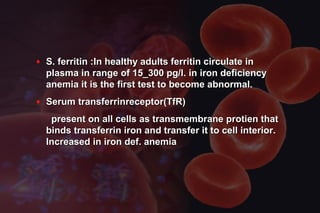
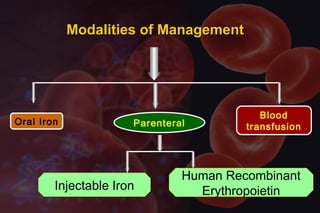
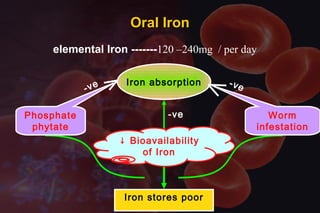
This document discusses anemia in pregnancy. It defines anemia and its classifications according to severity. Anemia affects 30-90% of pregnant women in developing countries and is a major cause of maternal deaths. During pregnancy, plasma volume increases more than red blood cell mass, causing haemodilution. Iron deficiency is the most common type of nutritional anemia in pregnancy. The document outlines iron requirements and absorption during pregnancy, signs and symptoms of anemia, and treatments including oral and parenteral iron supplementation.







![↑ Hb – 0.21 gm %
Fractionated Irondextran
[Iron hydroxide dextran complex]
Les
s
Les
s
Parenteral Therapy
120 mg
elemental Iron
AnaphylacticAnaphylactic
reactionreaction
AnaphylacticAnaphylactic
reactionreaction
I.M. I.V.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anemiawithpregnancy-150222134745-conversion-gate01/85/Anemia-with-pregnancy-27-320.jpg)