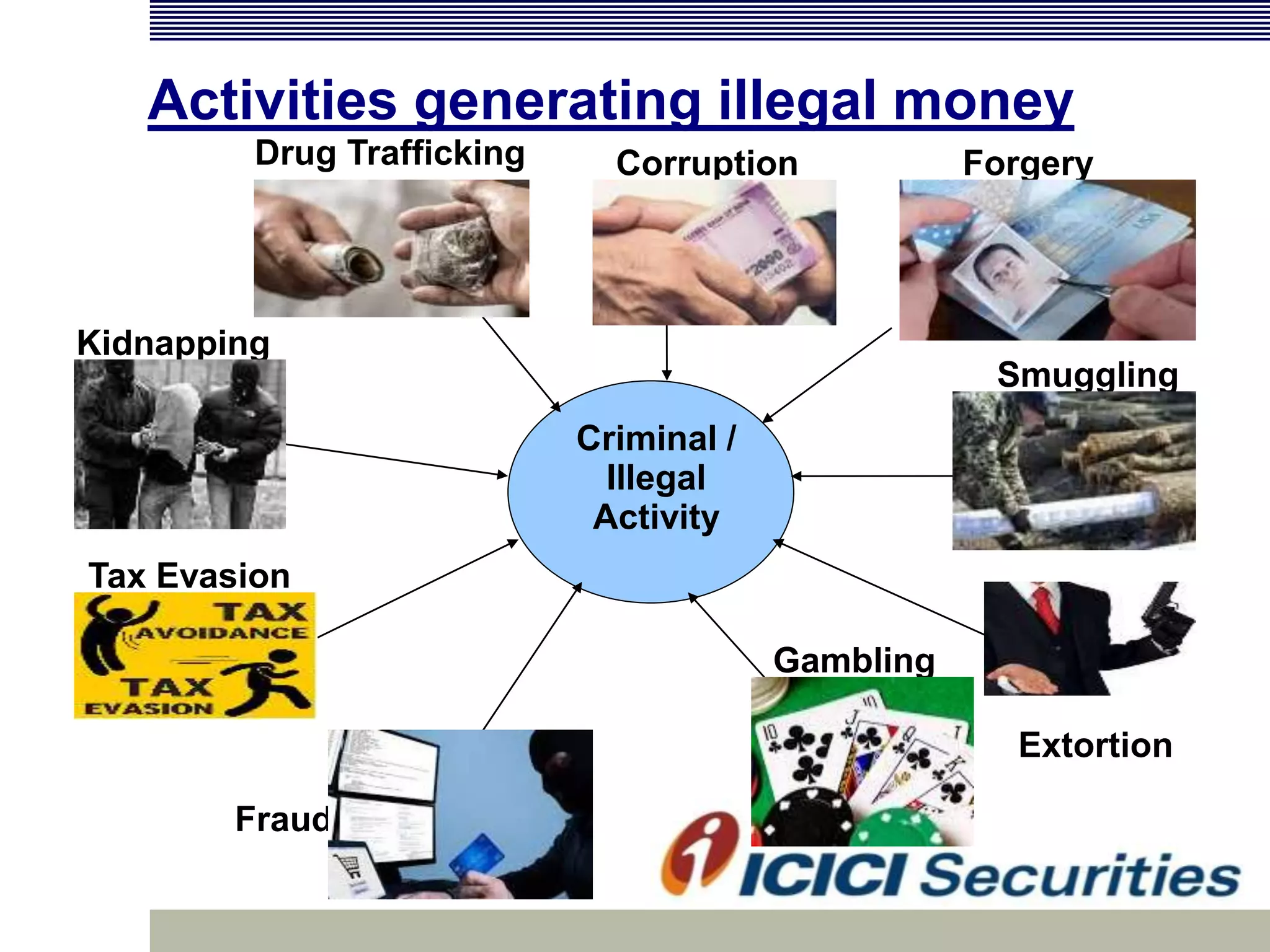
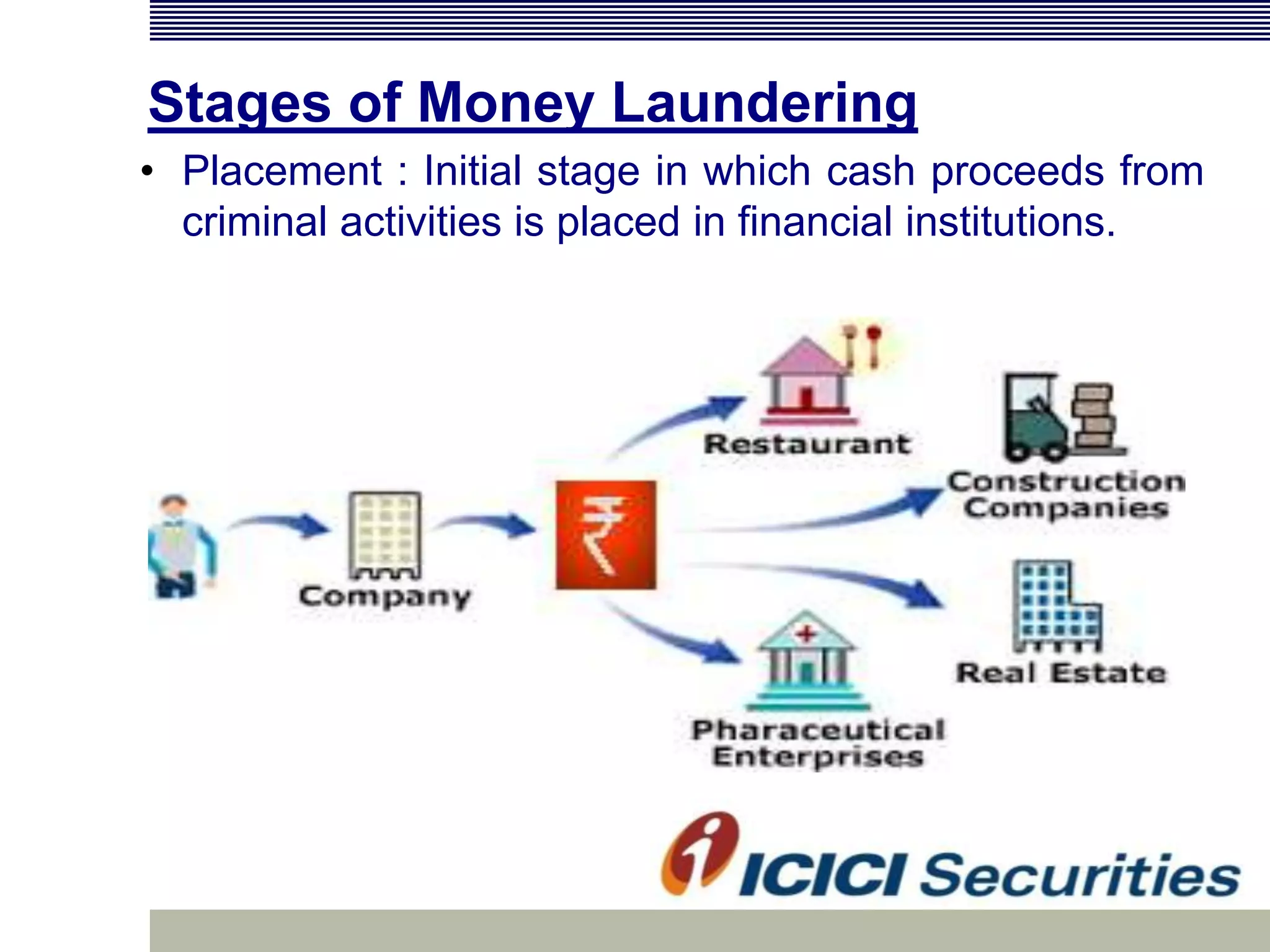
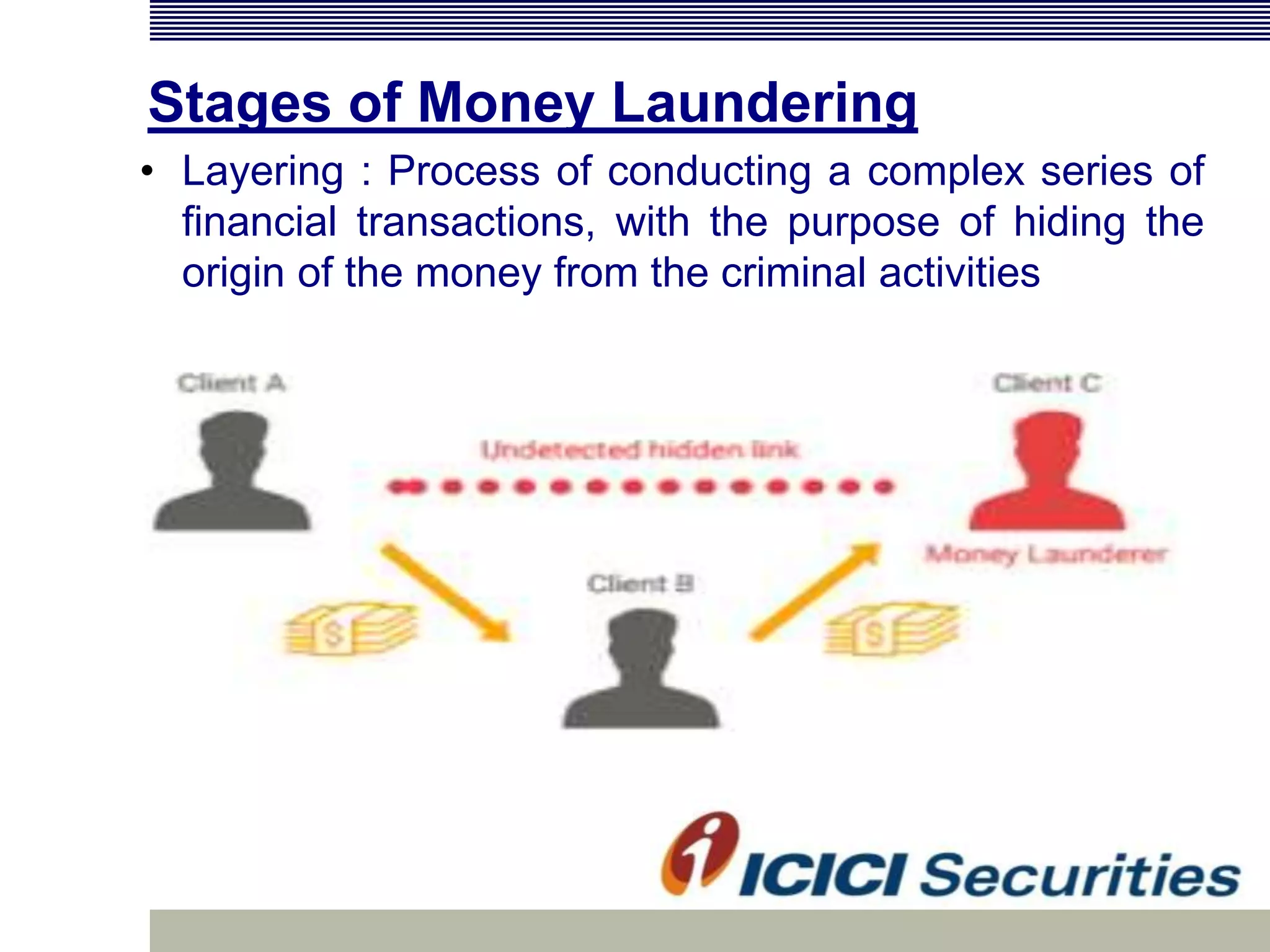
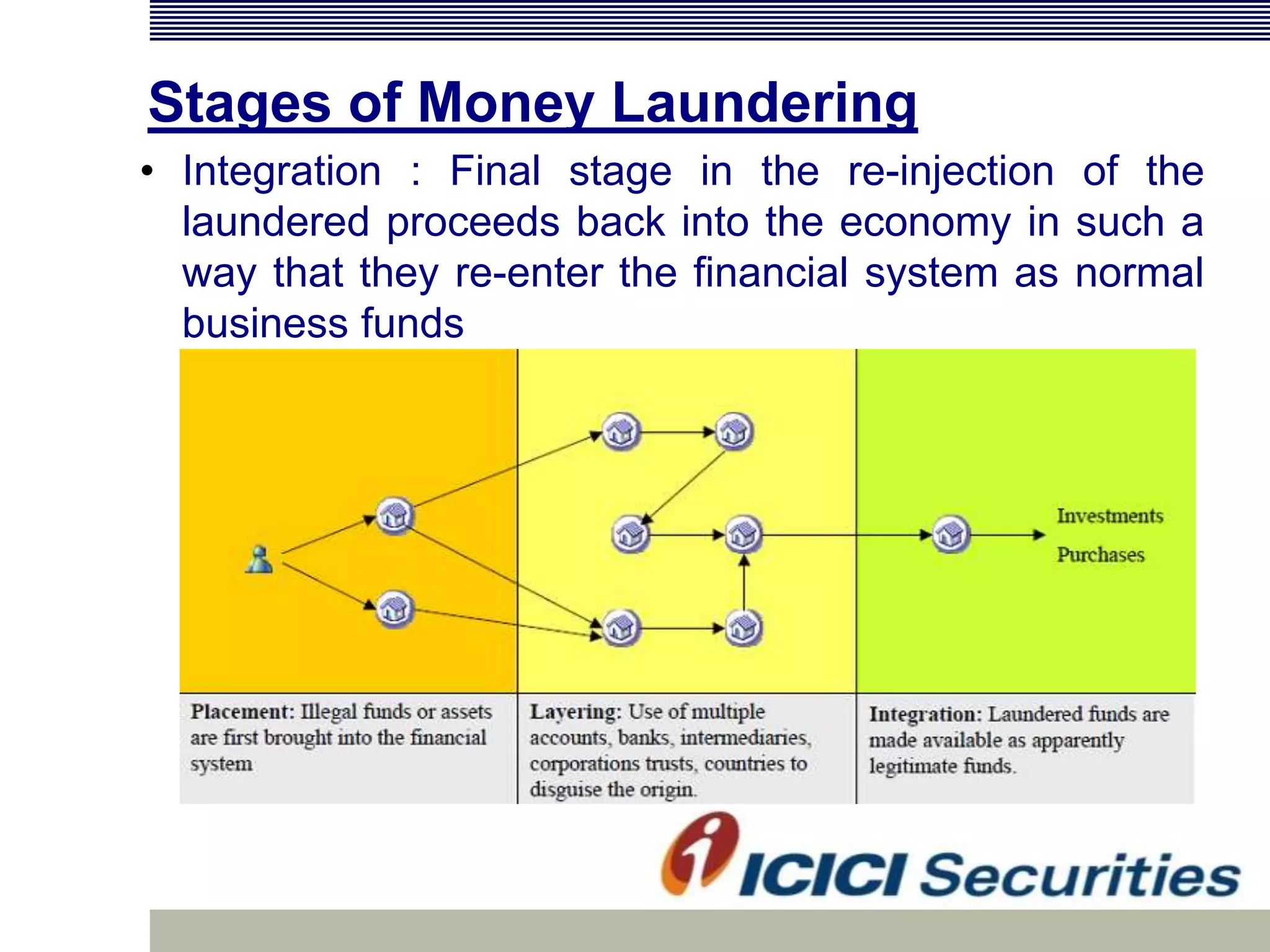
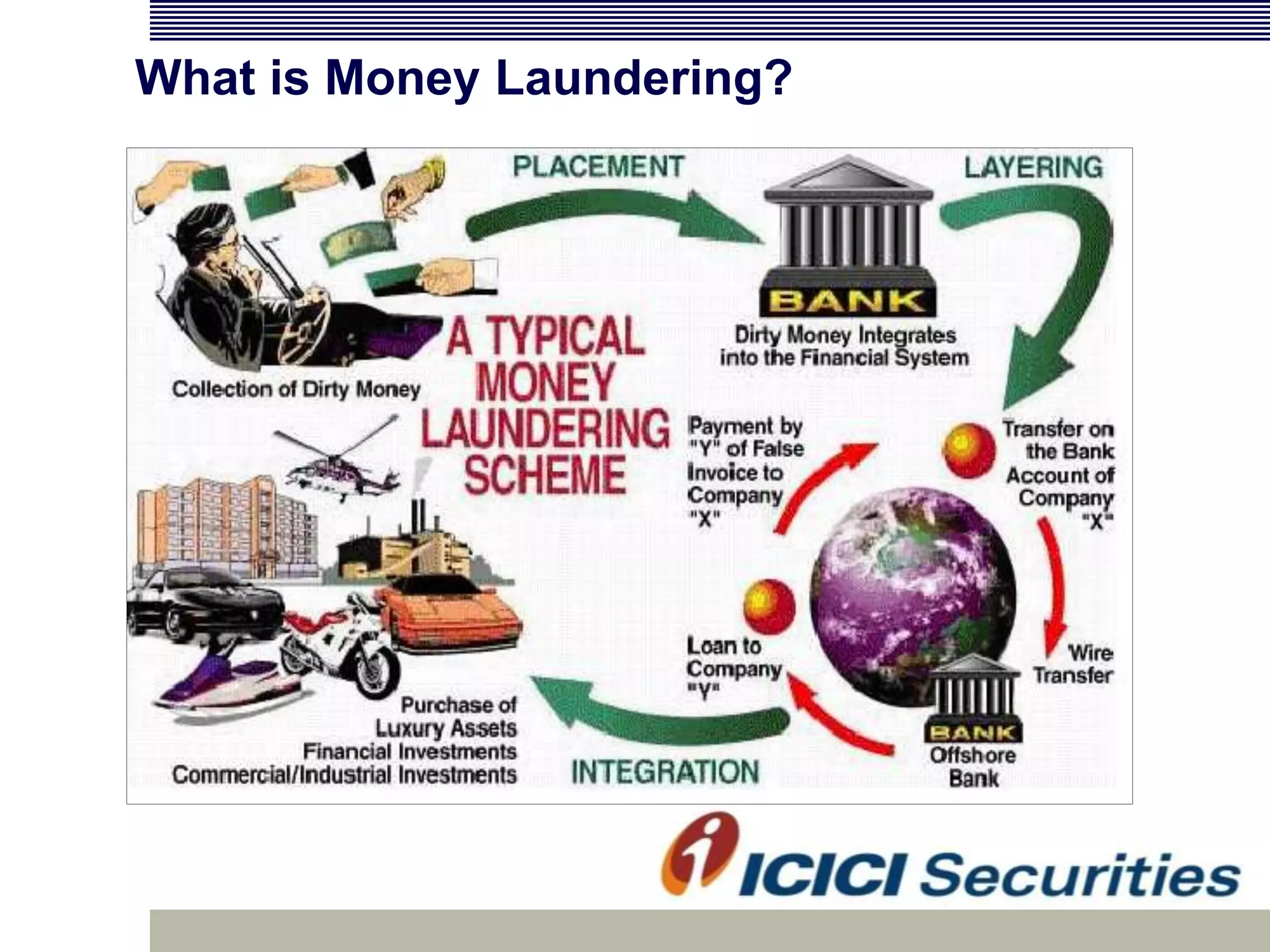
Money laundering involves disguising illegally obtained money to make it appear legitimate. It occurs in three stages: placement, layering, and integration. In India, money laundering is prevented by the Prevention of Money Laundering Act of 2002, which defines related offenses and allows for seizure of criminal proceeds. Financial institutions must implement anti-money laundering procedures like customer due diligence, suspicious transaction monitoring and reporting, and employee training to comply with regulatory requirements.