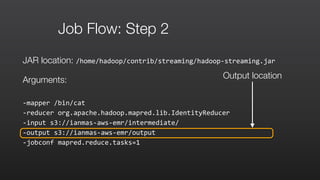
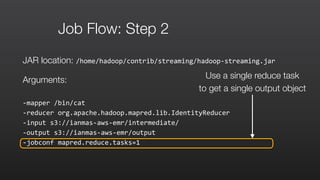
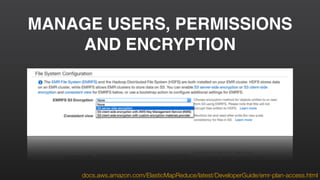
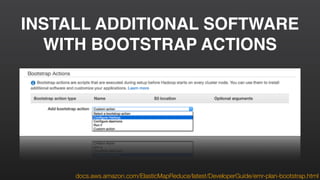
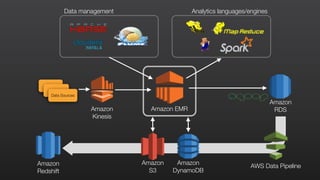
This document provides an overview of Amazon Elastic MapReduce (EMR), including:
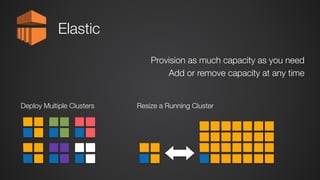
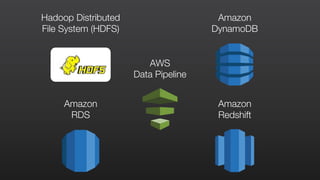
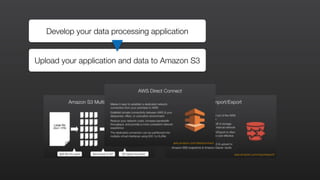
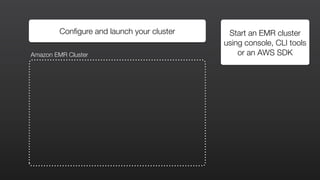
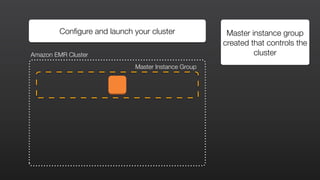
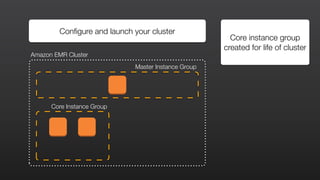
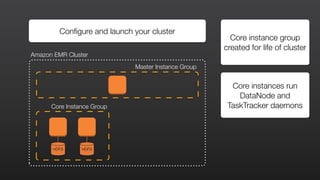
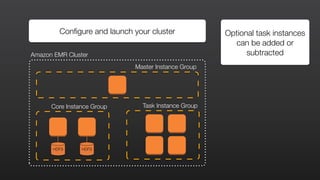
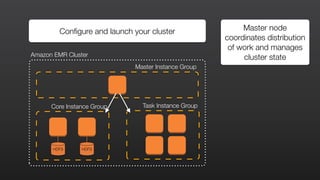
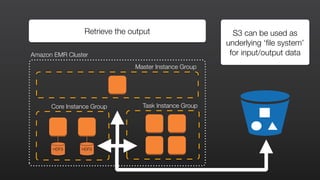
1) EMR allows users to quickly and cost-effectively process vast amounts of data by providing a managed Hadoop framework and supporting popular distributed frameworks like Spark.
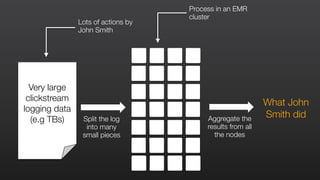
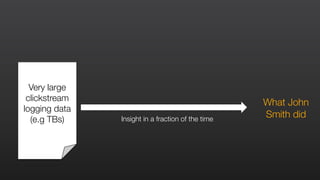
2) The document demonstrates how to use EMR for tasks like clickstream analysis, log processing, and genomic research through example use cases.
3) It outlines the agenda which will cover Hadoop fundamentals, EMR features, how to get started, supported tools, and additional resources.









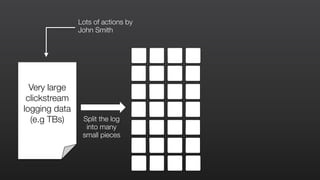
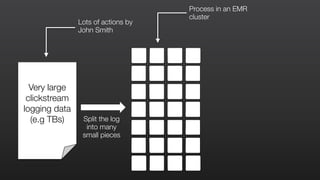
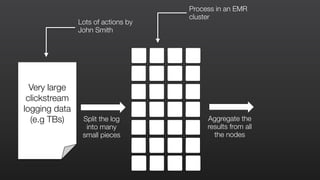
















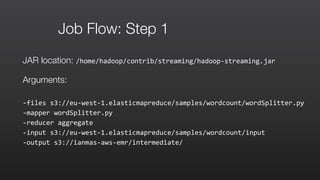
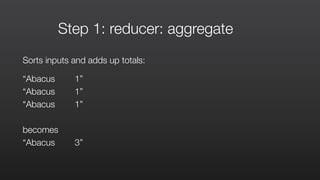
![Step 1: mapper: wordSplitter.py
#!/usr/bin/python
import
sys
import
re
def
main(argv):
pattern
=
re.compile("[a-‐zA-‐Z][a-‐zA-‐Z0-‐9]*")
for
line
in
sys.stdin:
for
word
in
pattern.findall(line):
print
"LongValueSum:"
+
word.lower()
+
"t"
+
"1"
if
__name__
==
"__main__":
main(sys.argv)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amazonemrmasterclass-150630092526-lva1-app6892/85/Amazon-EMR-Masterclass-46-320.jpg)
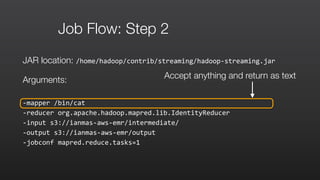
![Step 1: mapper: wordSplitter.py
#!/usr/bin/python
import
sys
import
re
def
main(argv):
pattern
=
re.compile("[a-‐zA-‐Z][a-‐zA-‐Z0-‐9]*")
for
line
in
sys.stdin:
for
word
in
pattern.findall(line):
print
"LongValueSum:"
+
word.lower()
+
"t"
+
"1"
if
__name__
==
"__main__":
main(sys.argv)
Read words from StdIn line by line](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amazonemrmasterclass-150630092526-lva1-app6892/85/Amazon-EMR-Masterclass-47-320.jpg)
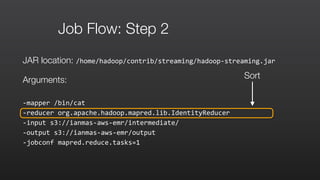
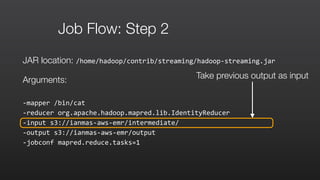
![Step 1: mapper: wordSplitter.py
#!/usr/bin/python
import
sys
import
re
def
main(argv):
pattern
=
re.compile("[a-‐zA-‐Z][a-‐zA-‐Z0-‐9]*")
for
line
in
sys.stdin:
for
word
in
pattern.findall(line):
print
"LongValueSum:"
+
word.lower()
+
"t"
+
"1"
if
__name__
==
"__main__":
main(sys.argv)
Output to StdOut tab delimited records
in the format “LongValueSum:abacus 1”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amazonemrmasterclass-150630092526-lva1-app6892/85/Amazon-EMR-Masterclass-48-320.jpg)