More Related Content
PDF
General English SI CLASS - 6-1-15_250618_223743.pdf PPTX
Grammar Essentials - Core grammatical structures.pptx PDF
Word classes / Part of speech PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
partsofspeech-140707153049-phpapp02.pptx DOCX
PPTX
Similar to all important English GRAMMAR.ppt
PPT
Parts of speech in English PPTX
Complete grammar UNIT III Vocabulary with example PDF
partsofspeech-140707153049-phpapp02-29-Oct-2025.pdf PPTX
Recognizing use of verbalsPPT-15056.pptx PPTX
ADVANCED GRAMMAR 2 - PARTS OF SPEECH.pptx PPTX
003 seven PARTS OF SPEECH english subject.pptx PPTX
Parts of speech lecture 2.pptx ,8 parts of speech PDF
27 - 8 Parts of Speech - Complete.pdf PDF
PDF
English Grammar Shortcut Rules.pdf PDF
PDF
English grammar a short guide PDF
English grammar made easy by chandra shekar pendoti PPTX
PDF
Business grammar __practice_(new_edition) PPTX
English Language Terminology: Word Classes PPTX
BS-BE Parts of Speech, Types of Nouns and its Uses.pptx PPTX
PDF
PDF
English grammar a short study Recently uploaded
PPTX
ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION (UNIT 2) .pptx PDF
Unit-III pdf (Basic listening Skill, Effective Writing Communication & Writin... PDF
Nutrients & Role in Horticulture.pdf, Dr. Sharad Bisen Horticulture PDF
BỘ TEST KIỂM TRA CUỐI HỌC KÌ 1 - TIẾNG ANH 6-7-8-9 GLOBAL SUCCESS - PHIÊN BẢN... PDF
Orchard Floor Managment.pdf Orchard Floor Management DOCX
TOXICITY AND ITS MANAGEMENT 6th sem unit 5, PHARMACOLOGY-III B. PHARMACY PPTX
CLASS -9 POLITICAL SCIENCE PPT CHAPTER -5 DEMOCRATIC RIGHTS.pptx PPTX
Hypothesis. its definition and typrs pptx PDF
The Tale of Melon City poem ppt by Sahasra PPTX
Unit I — General Physiology: Basic Concepts PDF
The Pity of War: Form, Fragment, and the Artificial Echo | Understanding War ... PDF
DHA OPTOMETRY MCQ Question /HAAD/MOH.pdf PPTX
15 December 2025 Education for human flourishing Michael Stevenson .pptx PDF
Projecte de la porta d'i5B: Els animals marins PDF
Projecte de la porta de primer B: L'antic Egipte PDF
The Tale of Melon City poem ppt by Sahasra PPTX
ICH Harmonization A Global Pathway to Unified Drug Regulation.pptx PDF
All Students Workshop 25 Yoga Wellness by LDMMIA PPTX
Pain. definition, causes, factor influencing pain & pain assessment.pptx PPTX
Unit I — Introduction to Anatomical Terms and Organization of the Human Body all important English GRAMMAR.ppt
- 1.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Professional
Professional
Communication,
Communication,
(UPTU), 2e
(UPTU), 2e
Meenakshi Raman
Meenakshi Raman
Sangeeta Sharma
Sangeeta Sharma
- 2.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
MODULE- I
MODULE- I
English Grammar and
English Grammar and
Correct Usage
Correct Usage
- 3.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Agenda
• Introduction
• Nouns
• Pronouns
• Verbs
• Modals
• Gerunds
• Infinitives
• Adjectives and Degree of comparison
• Adverbs
• Conjunctions
• Interjections
• Prepositions
• Articles
- 4.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Introduction
The persons taking part in a conversation should be competent in
both written and spoken communication. If our grammar is not
sound, our technical writing will not make much sense to our
readers
- 5.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Nouns
Noun is defined as a word used for a name of a person, place,
thing, or idea. In English, it is one of the eight parts of speech
Different types of modifiers of a noun are given below:
Determiners: The scientist assembled the machine.
Possessives: She brought the machine’s parts.
Adjectives: The cumbersome machines are kept
underground.
Prepositions: The pedestrians over the bridge …
Clauses: The conference we went to …
- 6.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Pronoun
A pronoun takes place of a noun and is used as a substitute for
nouns. Every pronoun must have a clear antecedent.
- 7.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Verbs
The doer word is called a verb in a sentence. It tells and asserts
something about a thing or a person
- 8.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Modals
Modals are special verbs that give additional information about
the function of the principal verb that follows it.
- 9.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Gerunds
Any verb with the -ing form used as a subject of a verb and acting
like a verb-noun is called a gerund.
- 10.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Infinitives
An infinitive is a kind of noun with some features of the verb,
especially that of taking an object (when the verb is transitive) and
adverbial qualifiers.
When an infinitive is
used as a noun, it
is called the ‘simple
Infinitive’
- 11.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
• The ‘subject’ should agree with the ‘verb’ in number and
person.
Subject Verb Agreement
- 12.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
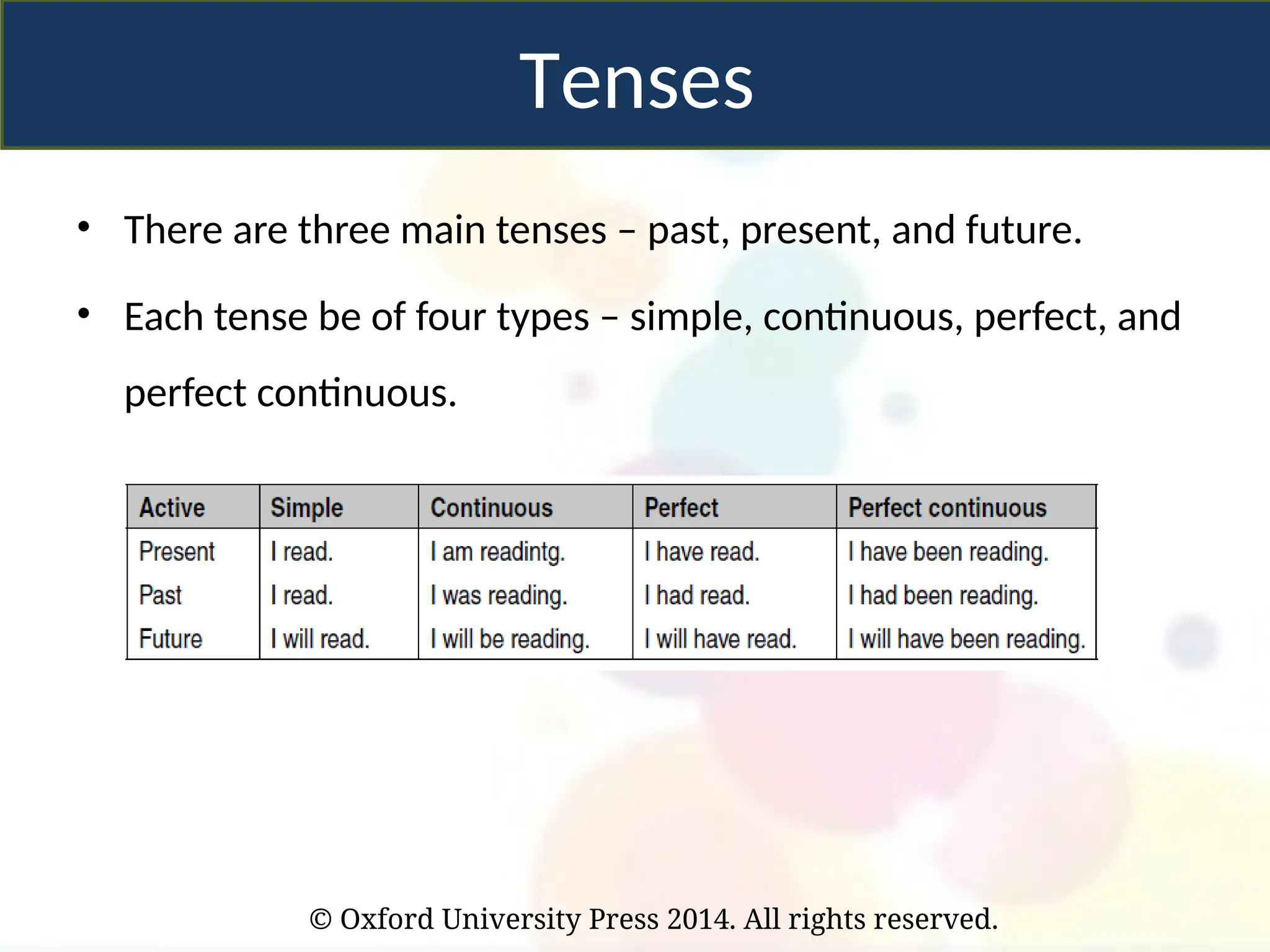
• There are three main tenses – past, present, and future.
• Each tense be of four types – simple, continuous, perfect, and
perfect continuous.
Tenses
- 13.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Adjectives and degrees of comparison
An adjective is a word that qualifies or describes a noun. It can also
give the number by quantifying. It gives extra meaning to the noun
by adding something to it.
- 14.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Comparison of Adjectives
Positive degree: She is smart
Comparative degree: But her sister is smarter
Superlative degree: Their brother, however, is the smartest.
- 15.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Adverbs
An adverb is a word that adds more information about a place,
time, manner, cause, or degree to a verb, an adjective, a phrase, or
another adverb.
- 16.
© Oxford UniversityPress 2014. All rights reserved.
Articles
Articles in English are used to clarify if a noun is specific or not
specific. Basically, articles are adjectives. Like adjectives, articles
also modify nouns and are used before nouns or adjectives. There
are two types of articles:
Definite articles (the): These are used for specific nouns.
Indefinite articles (a, an): These are used for specific nouns