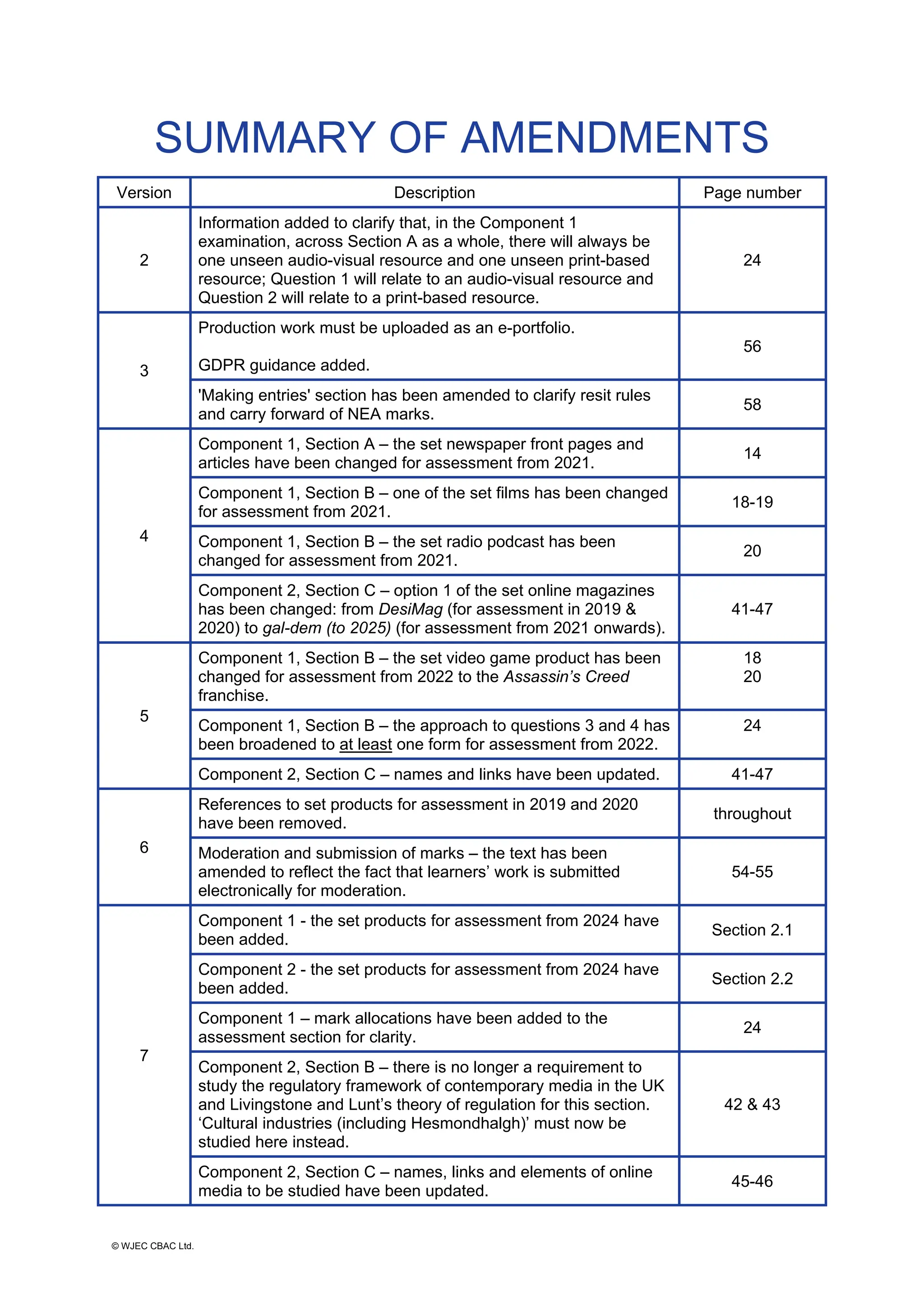
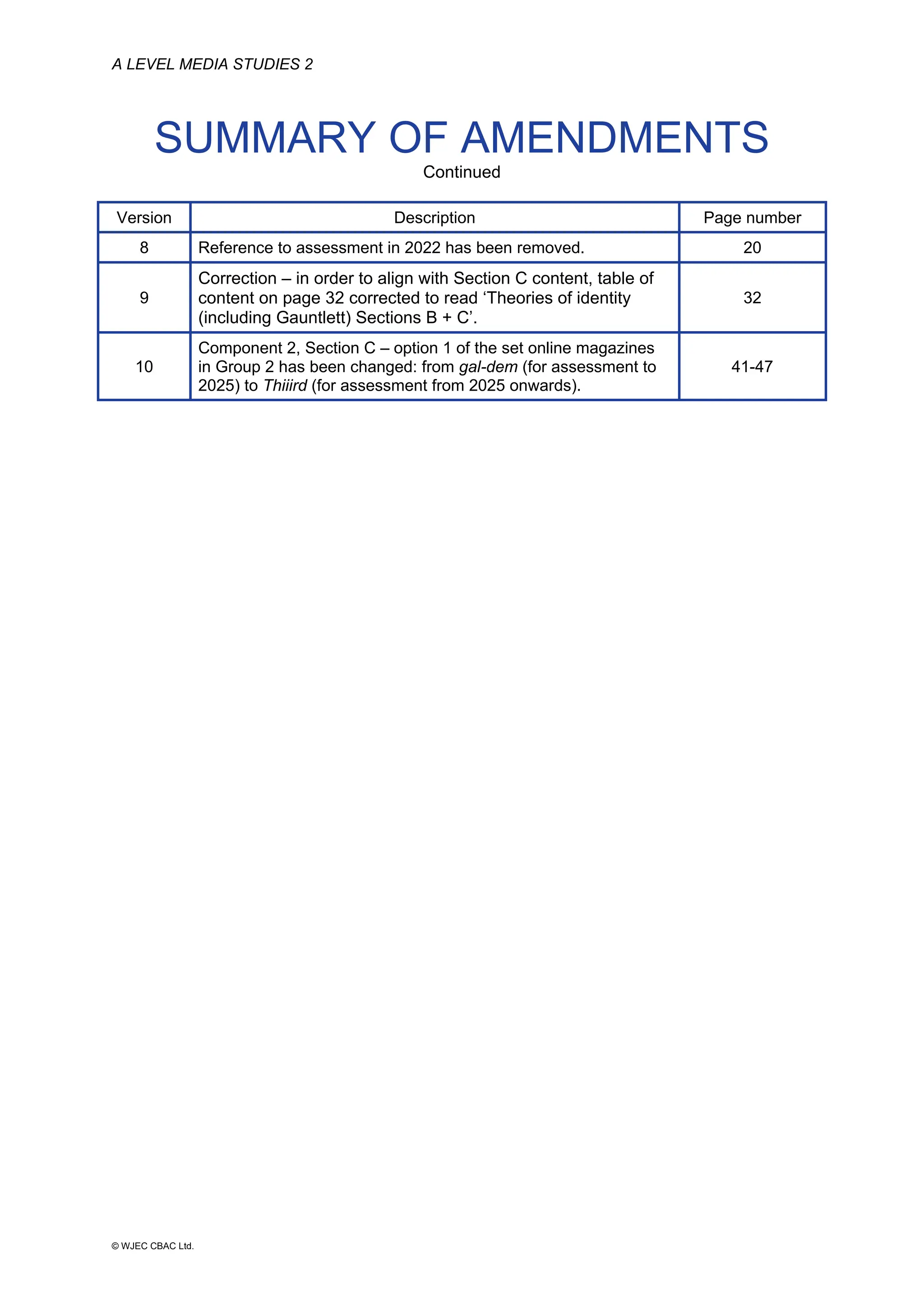
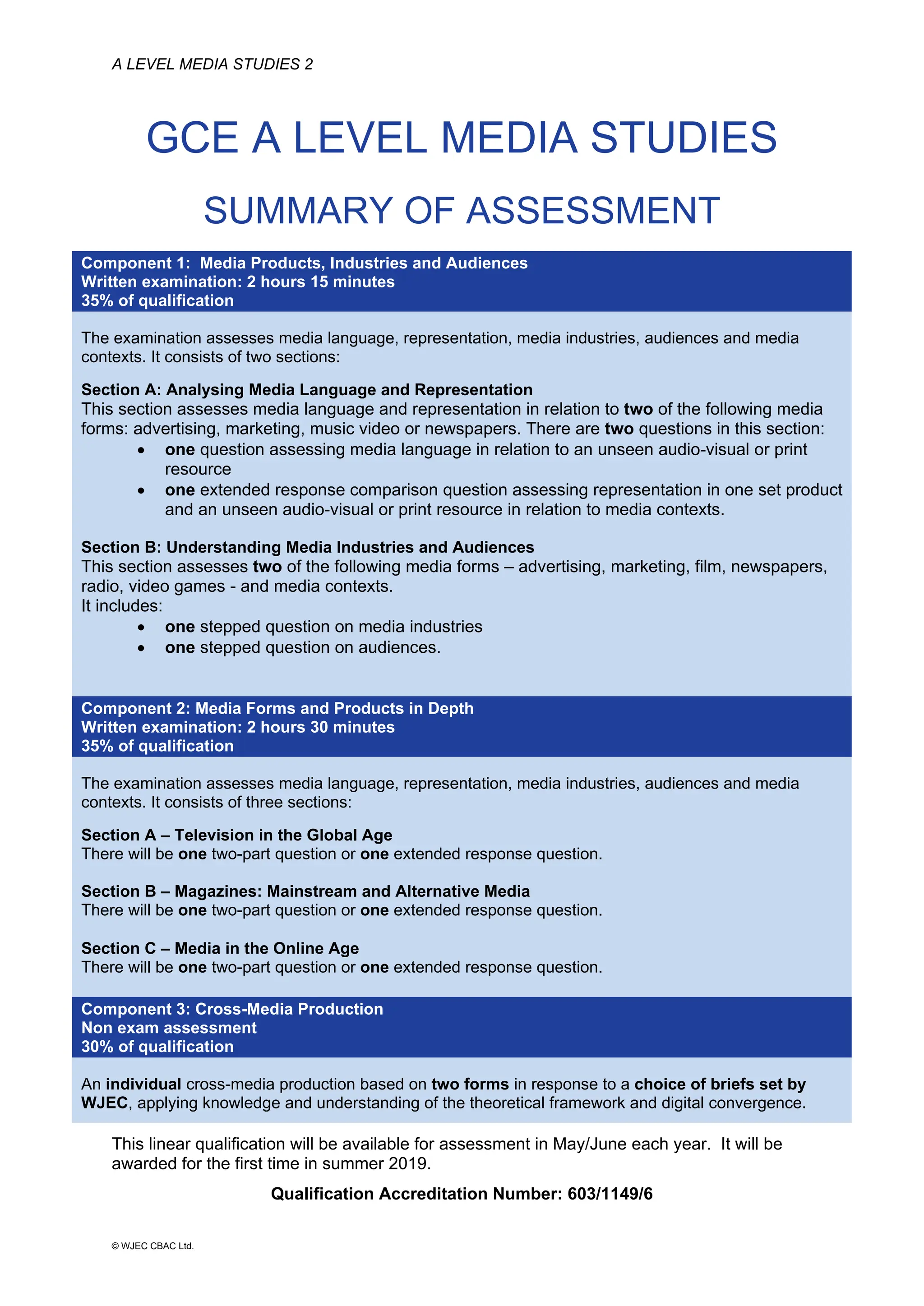
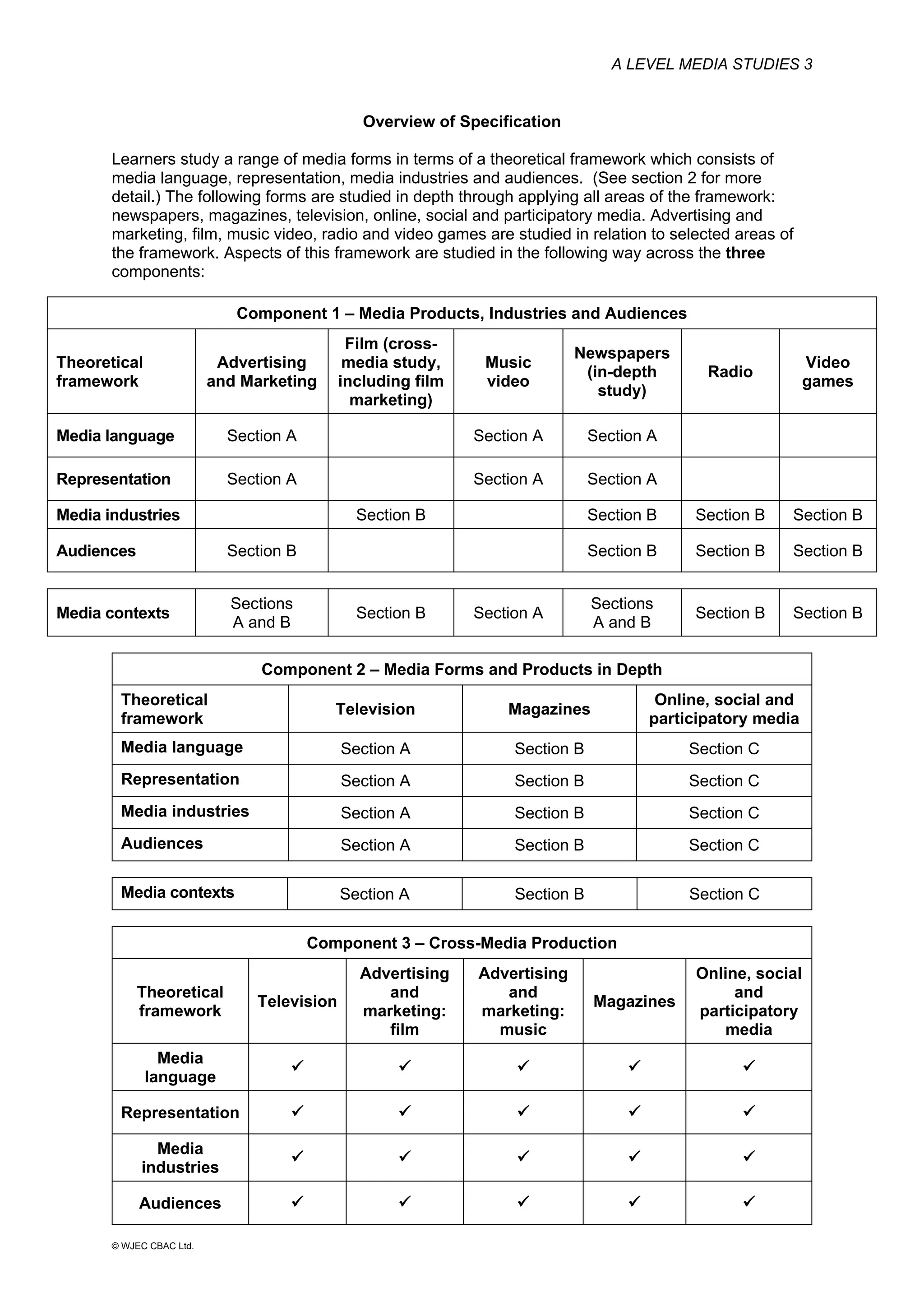
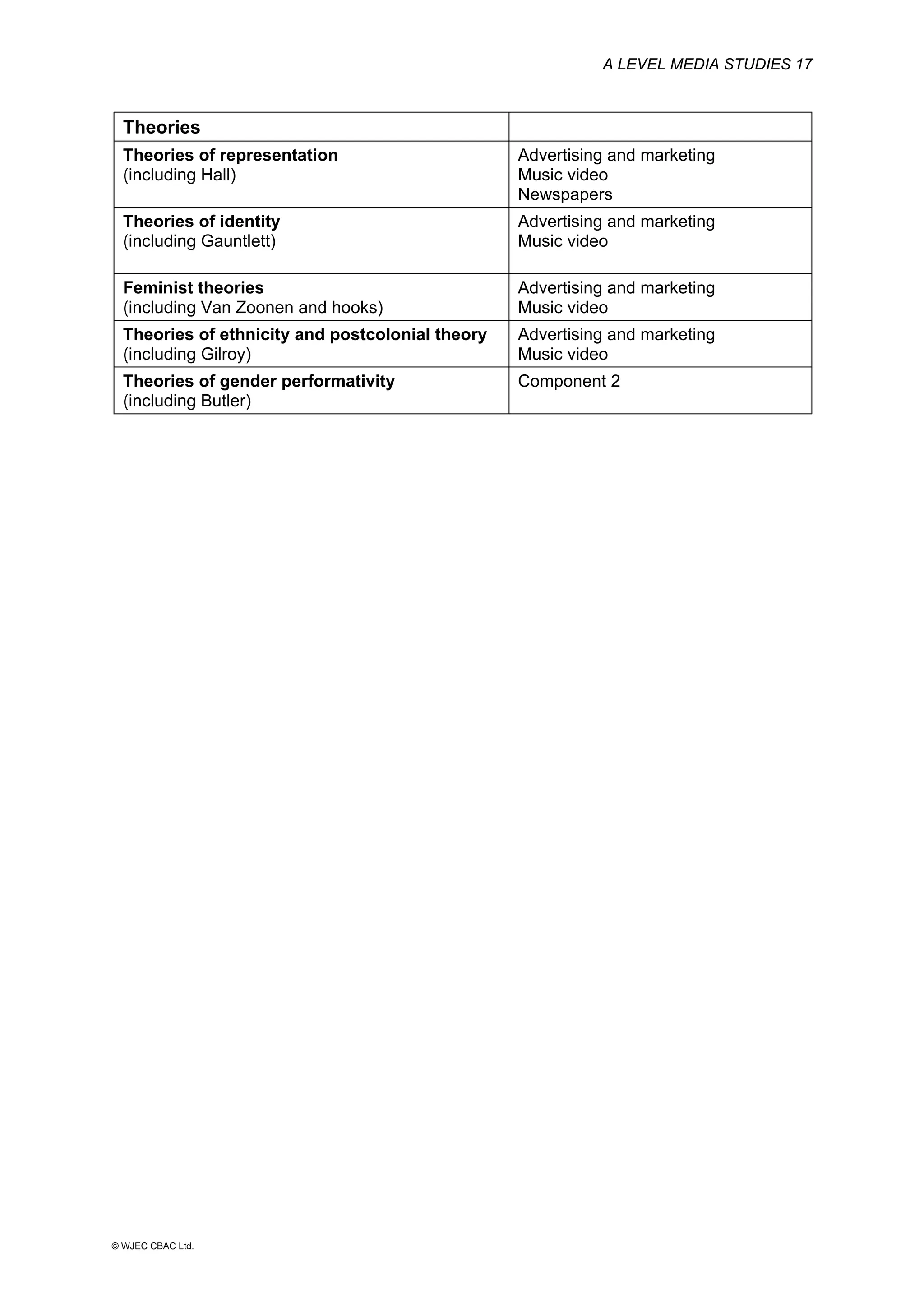
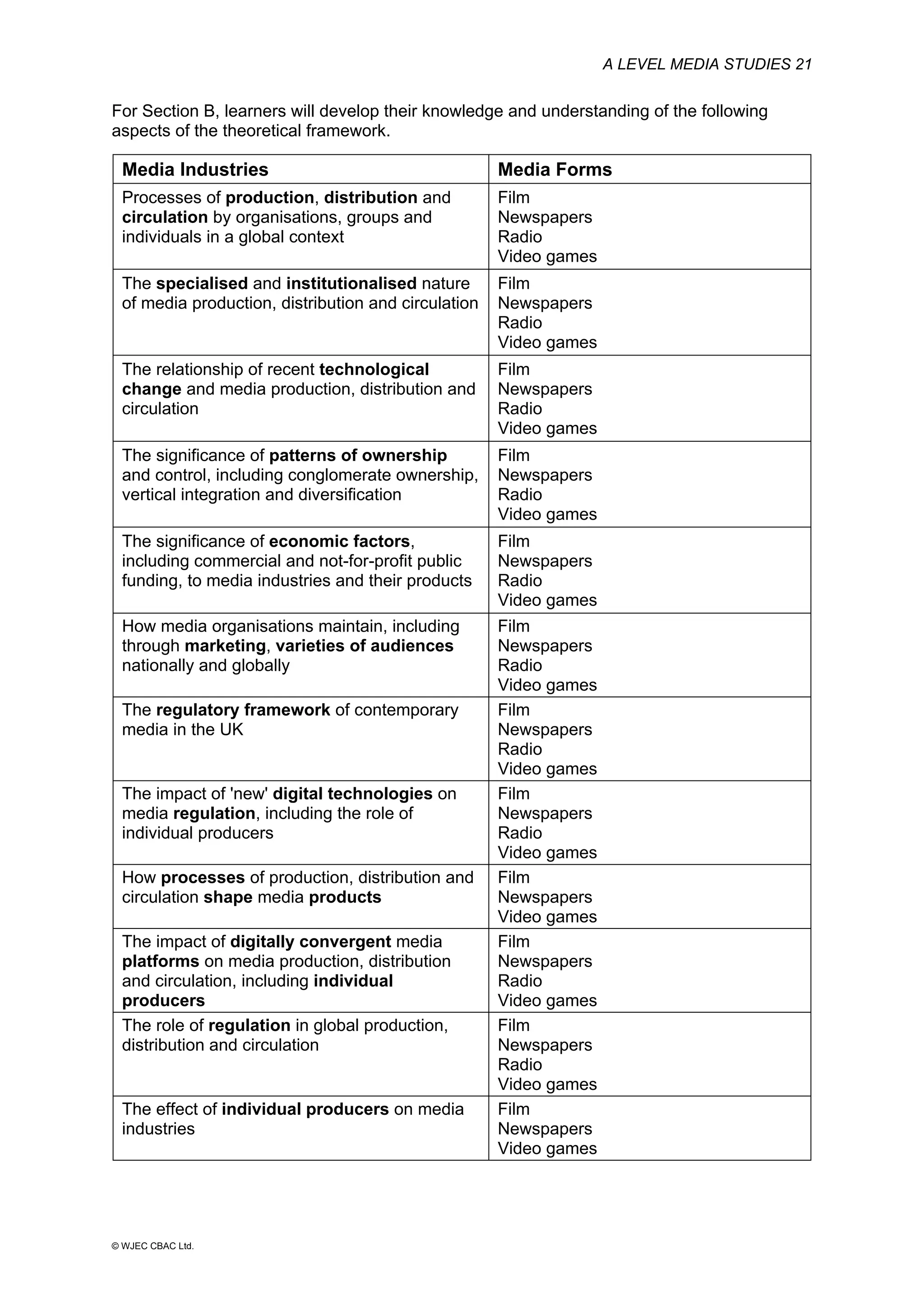
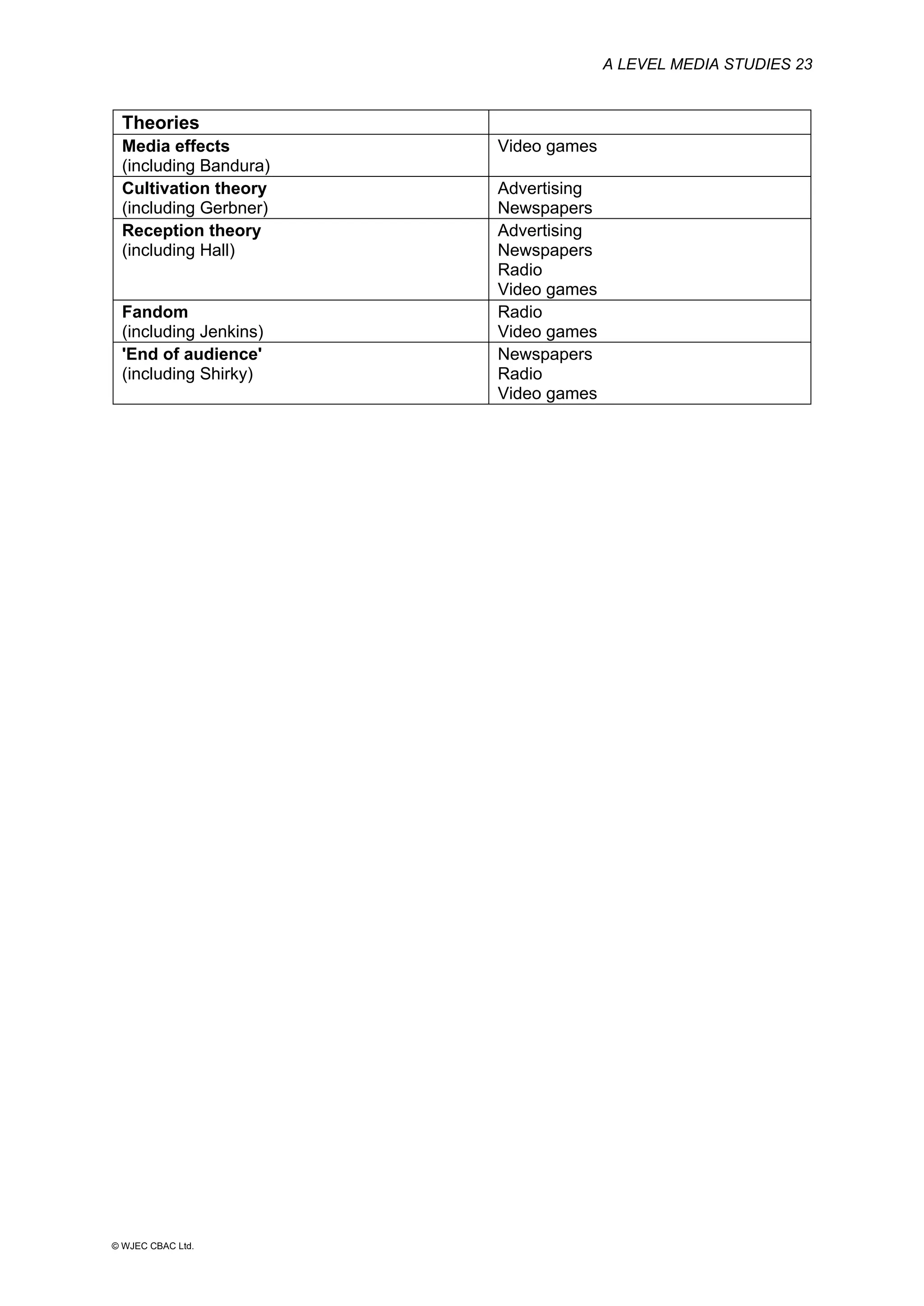
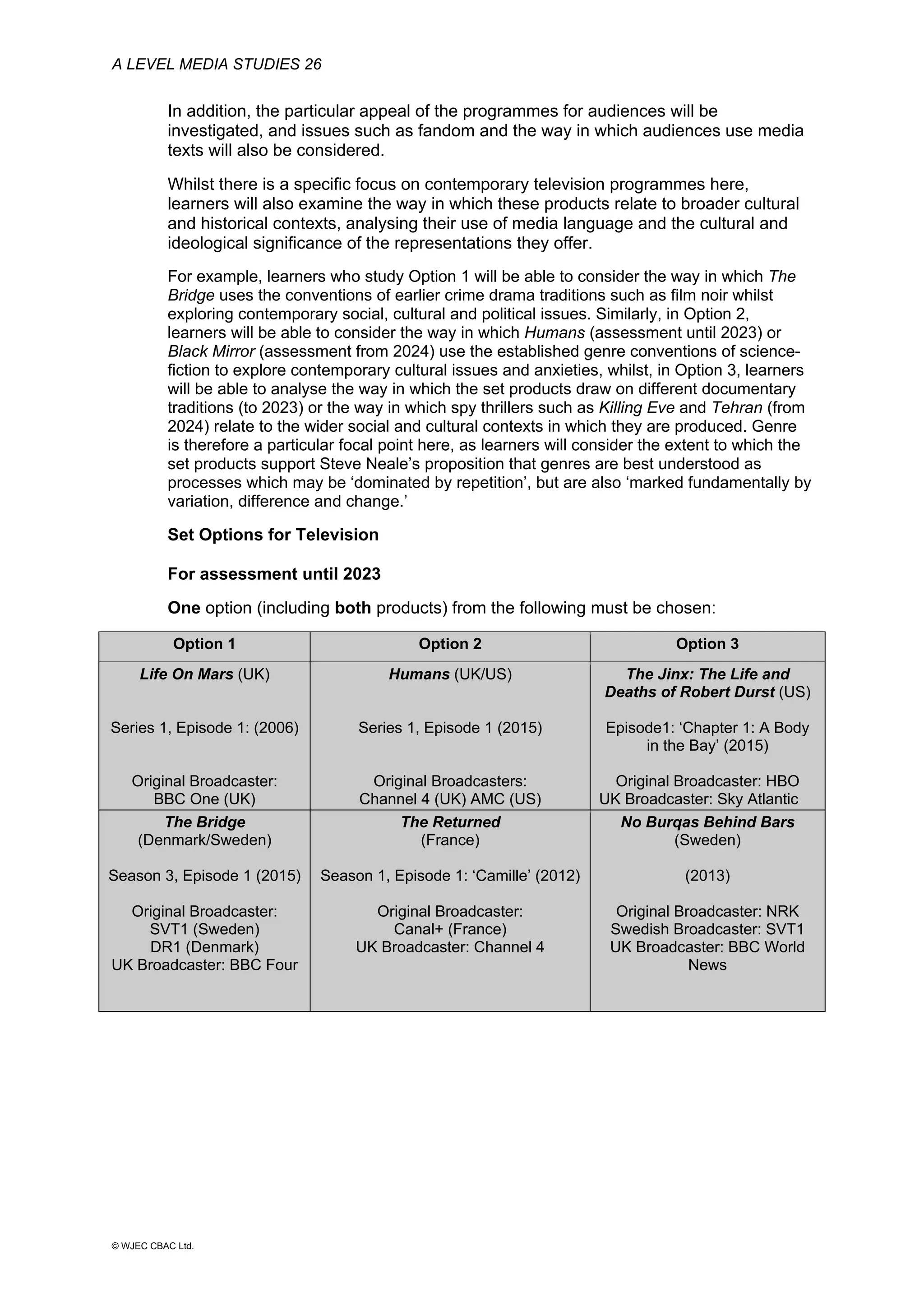
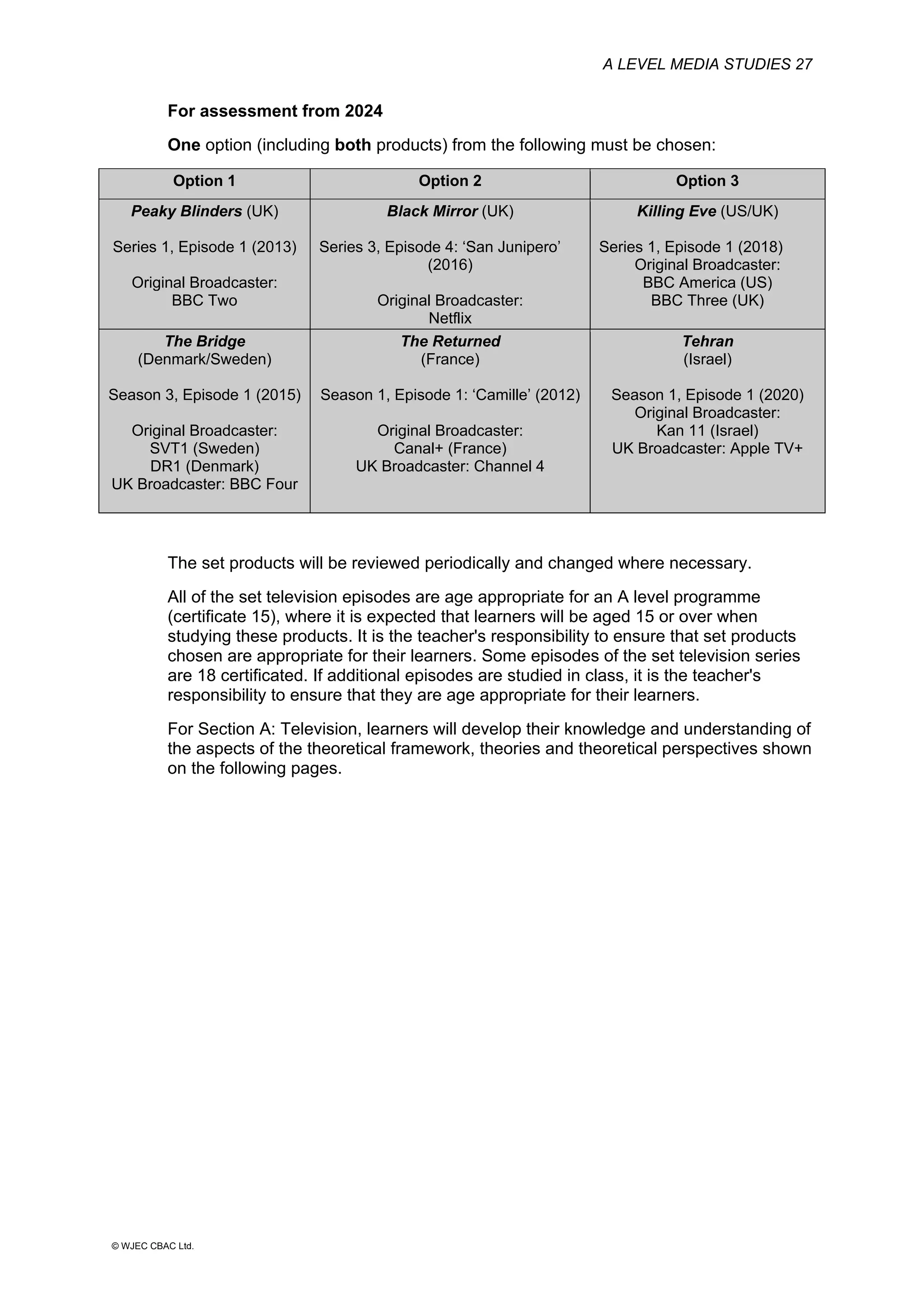
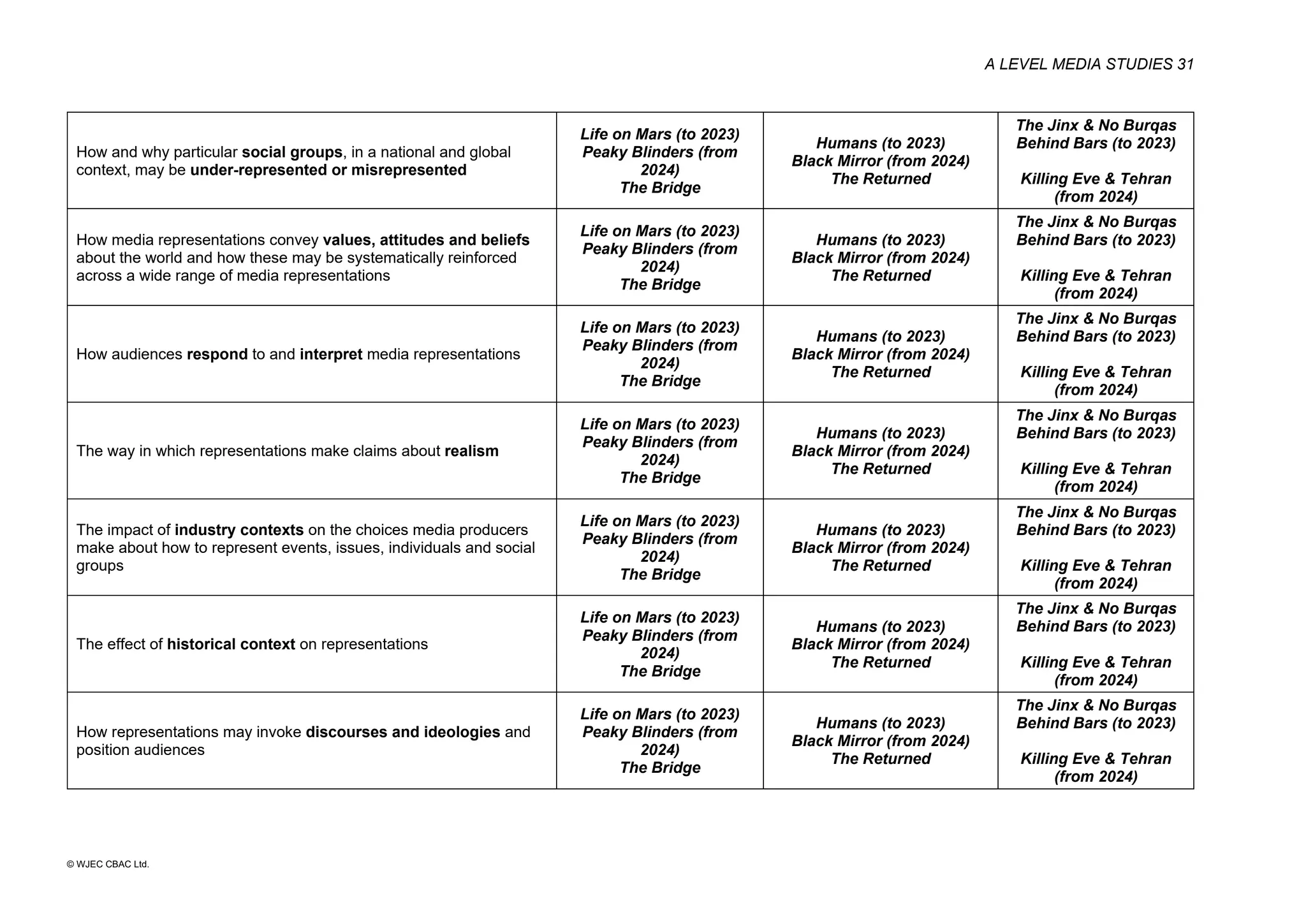
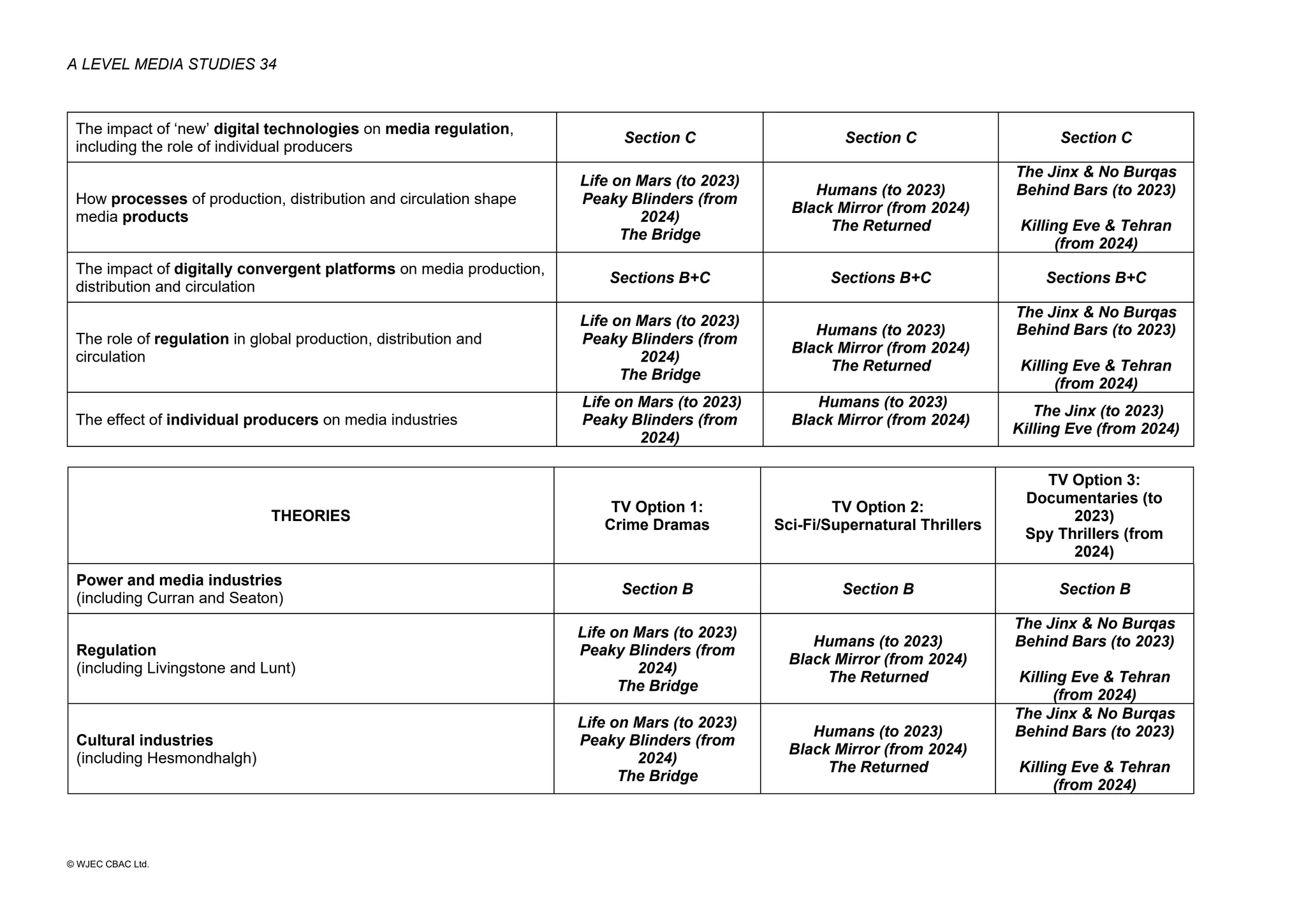
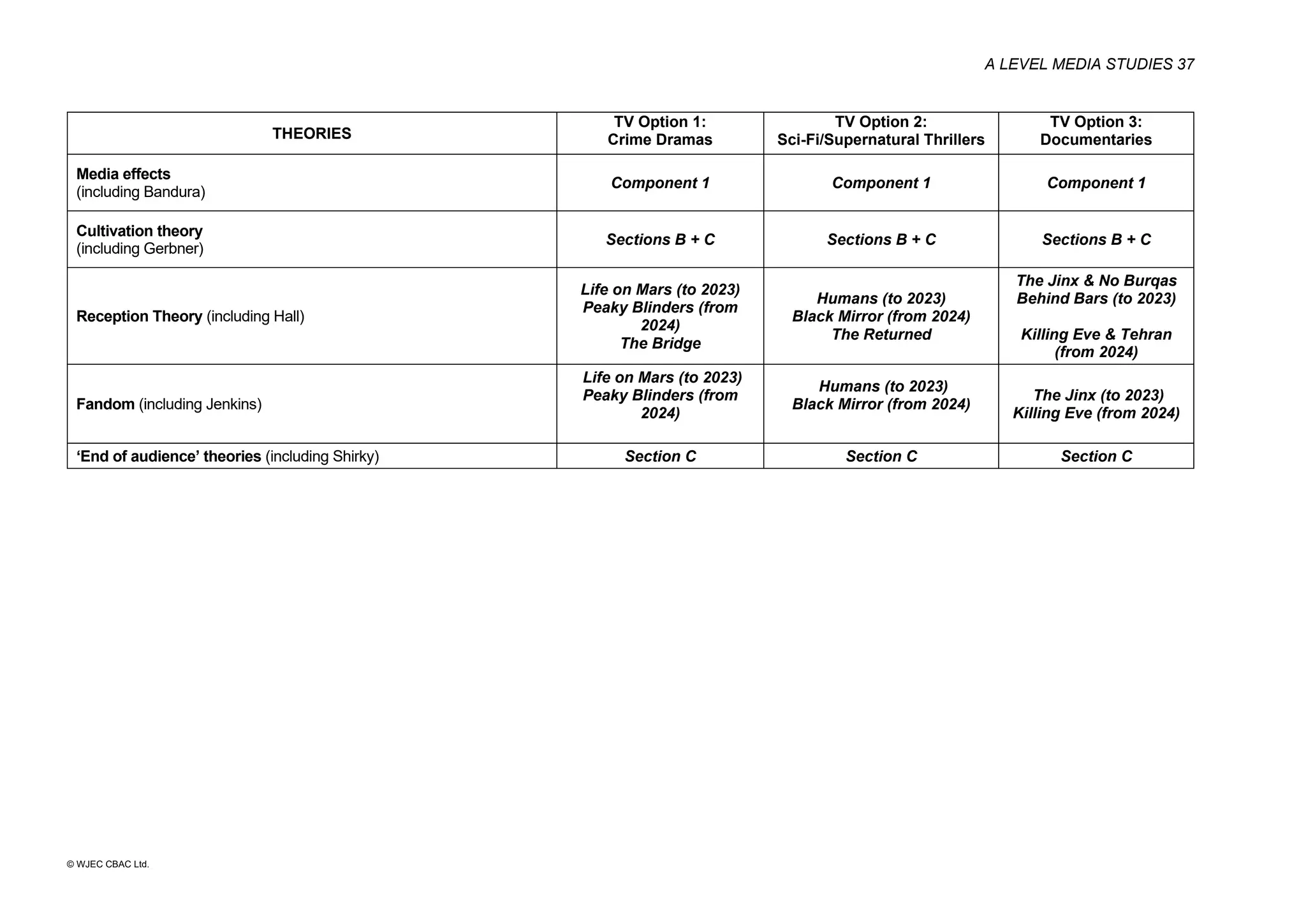
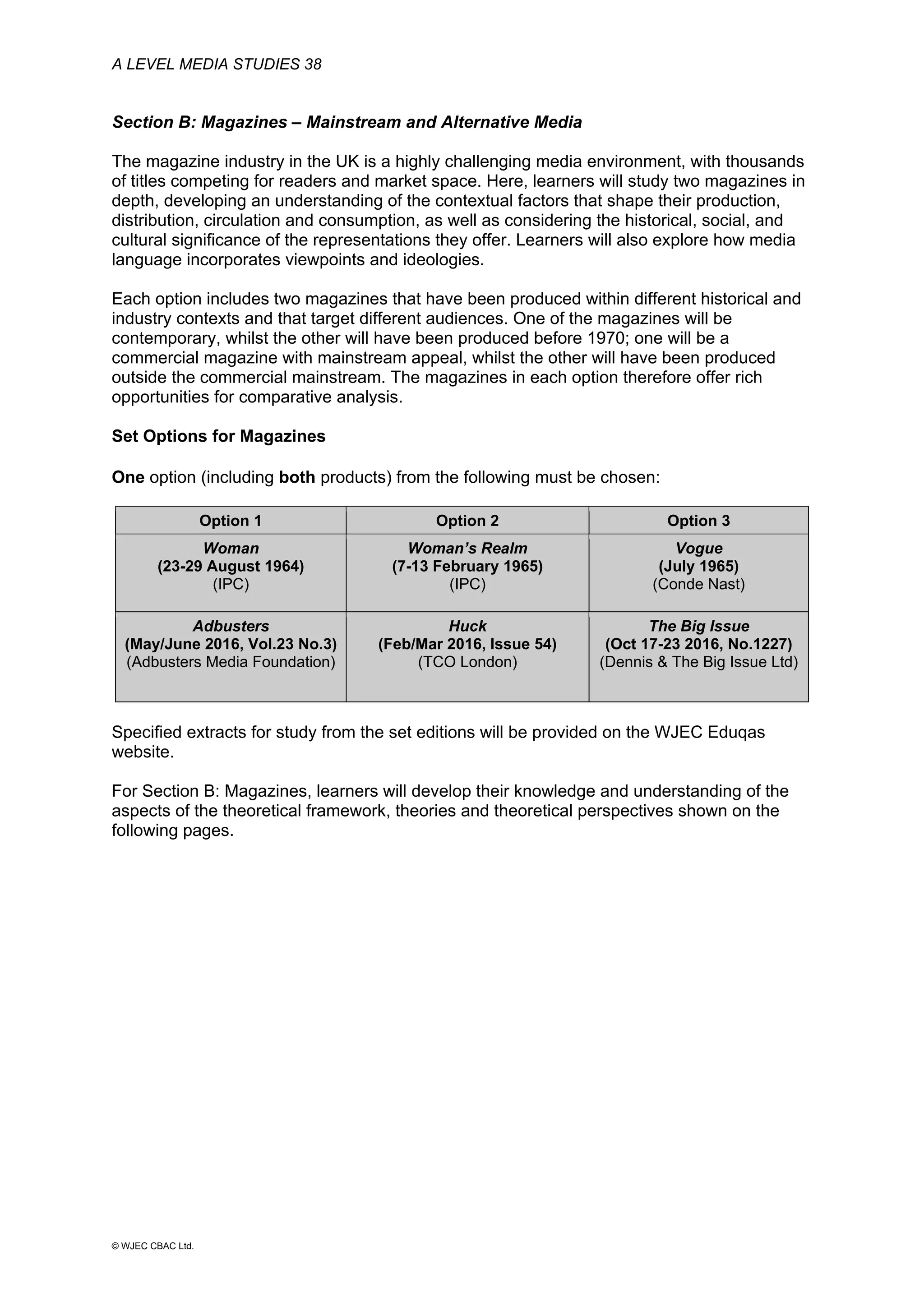
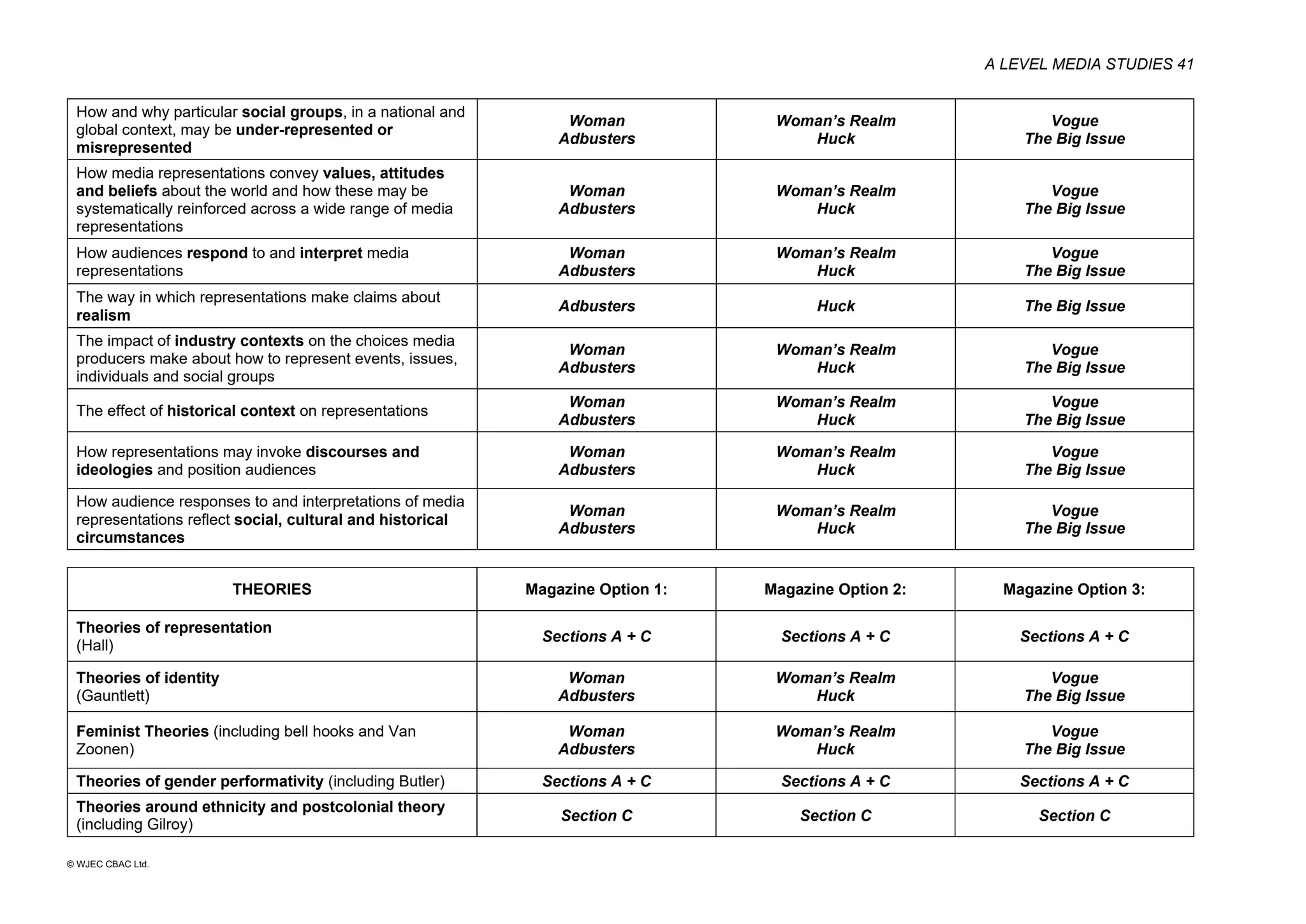
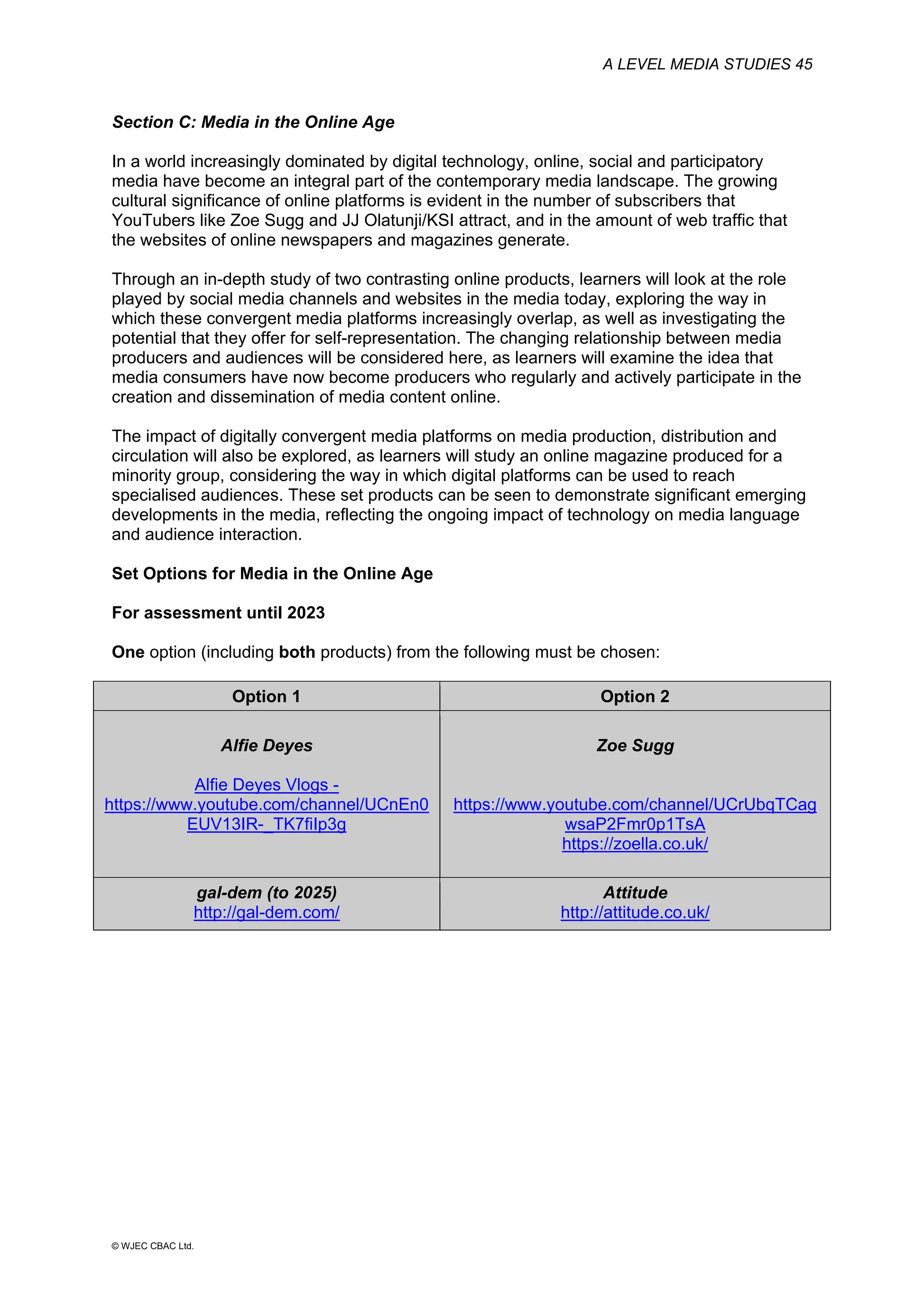
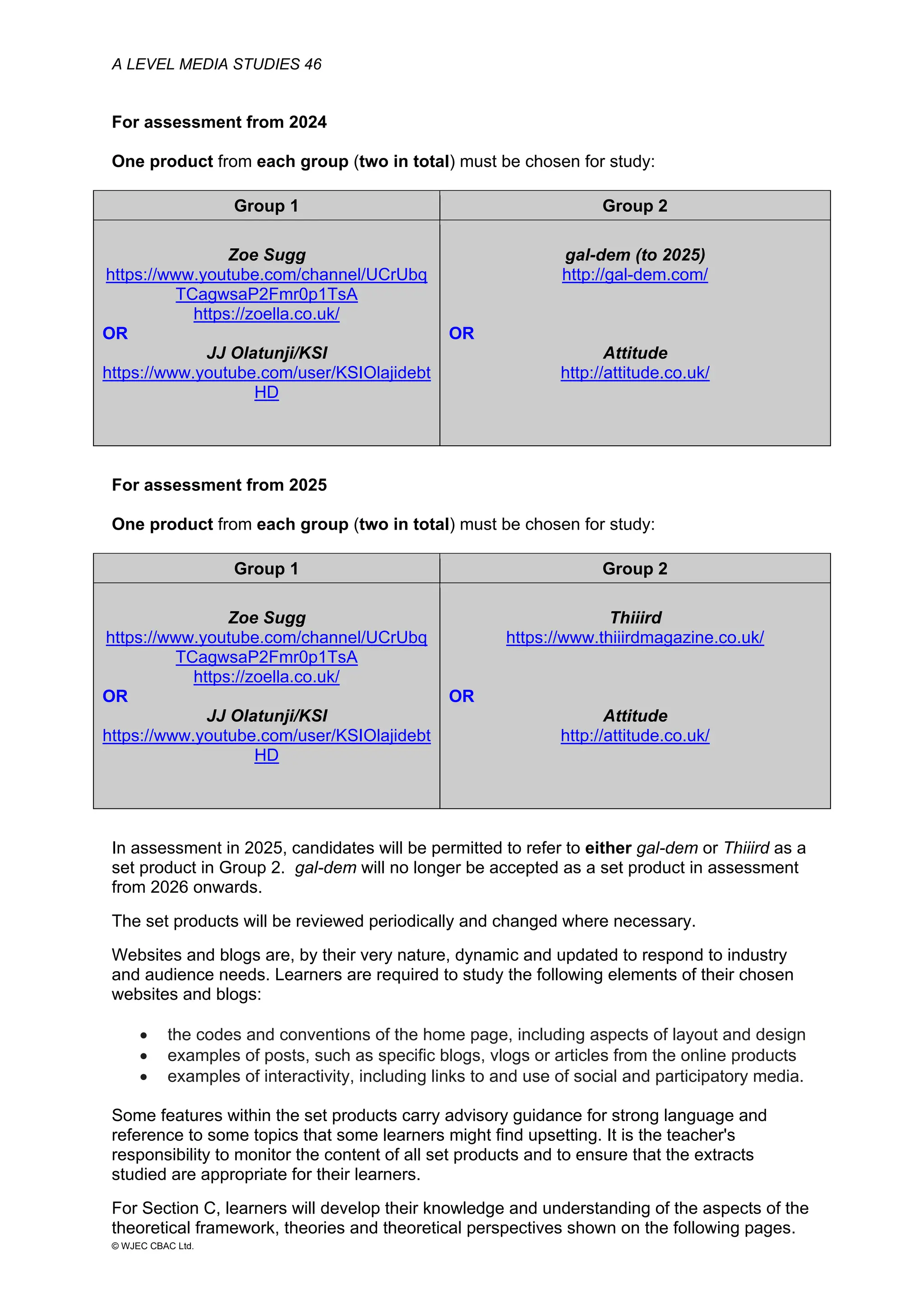
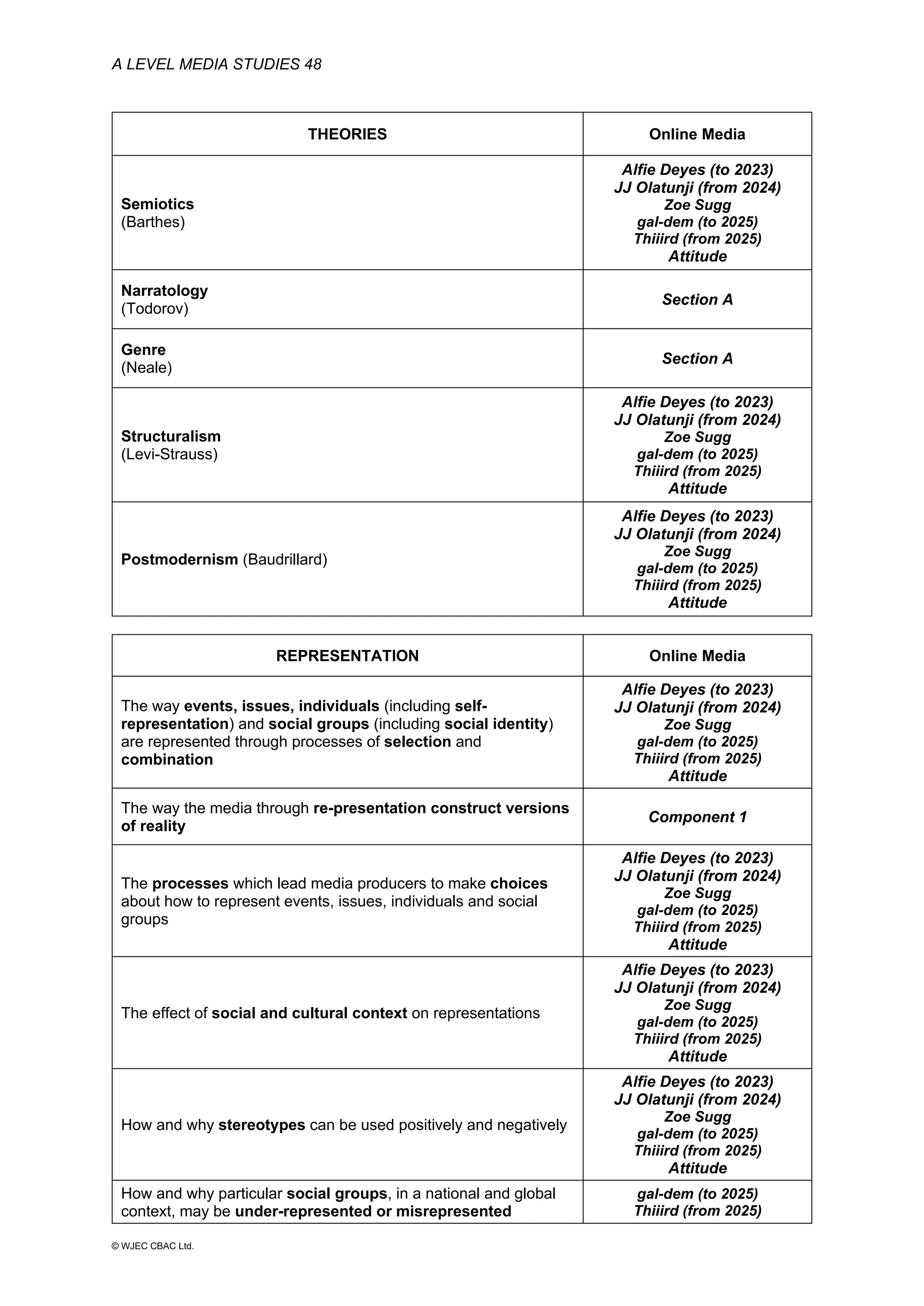
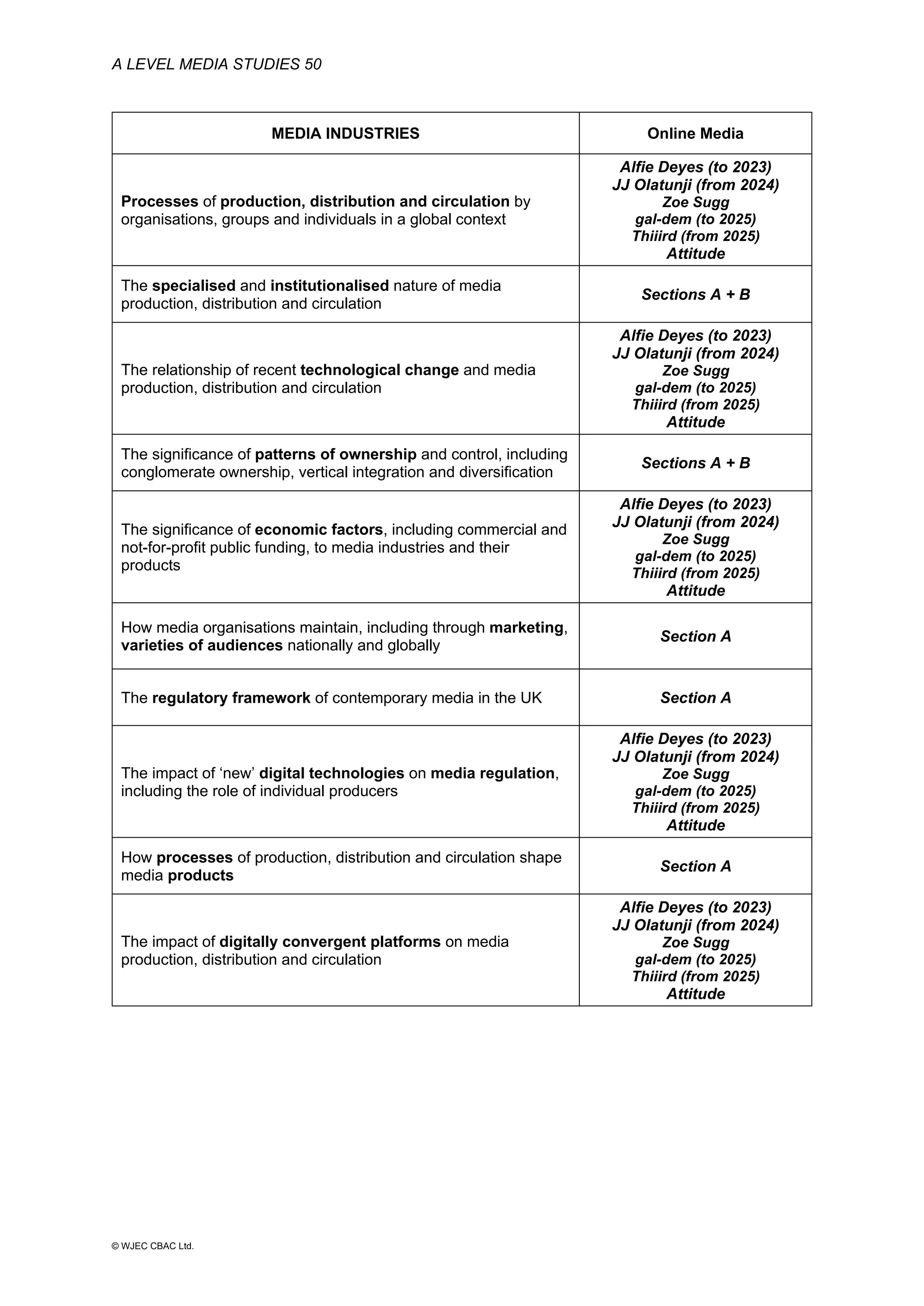
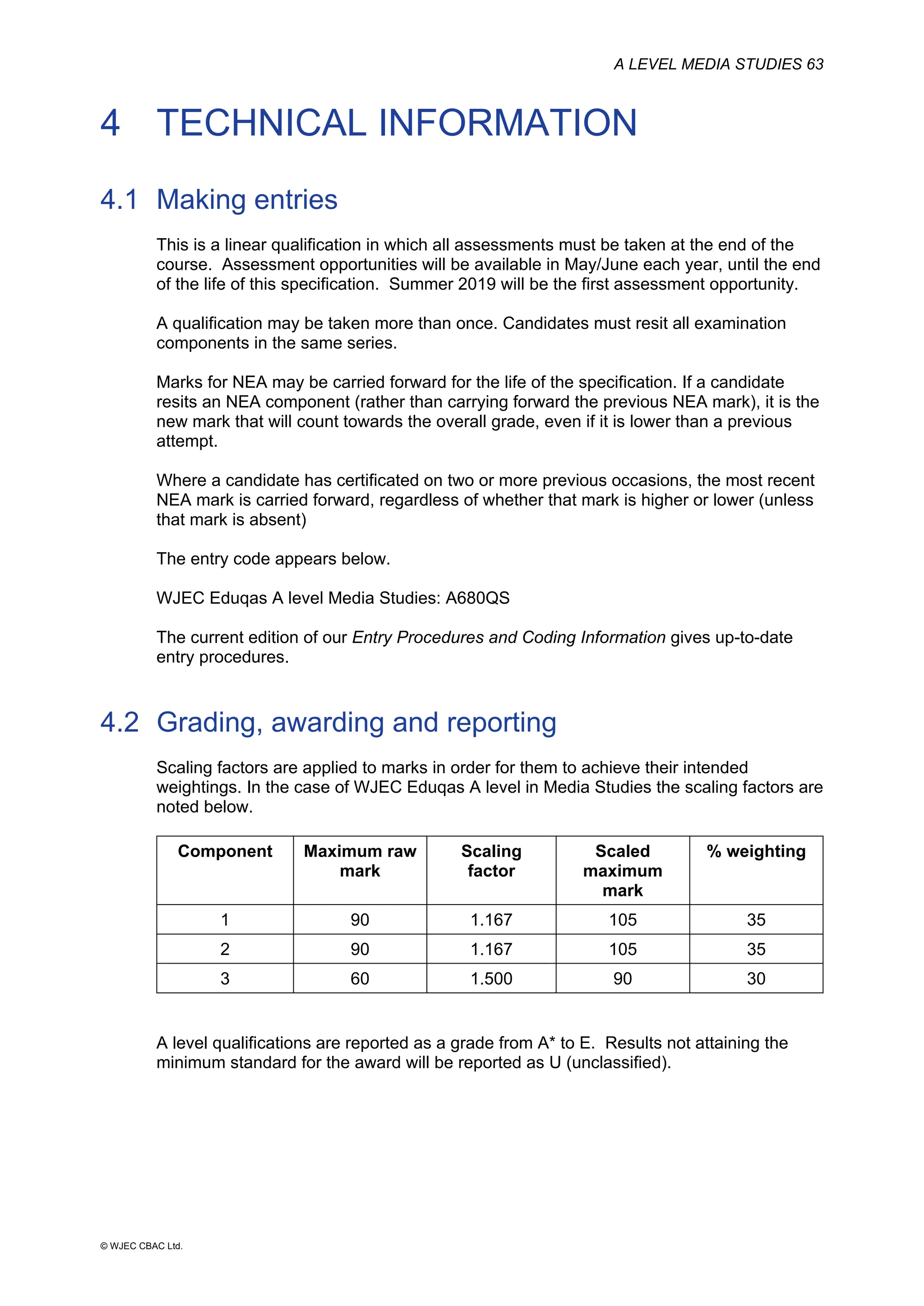
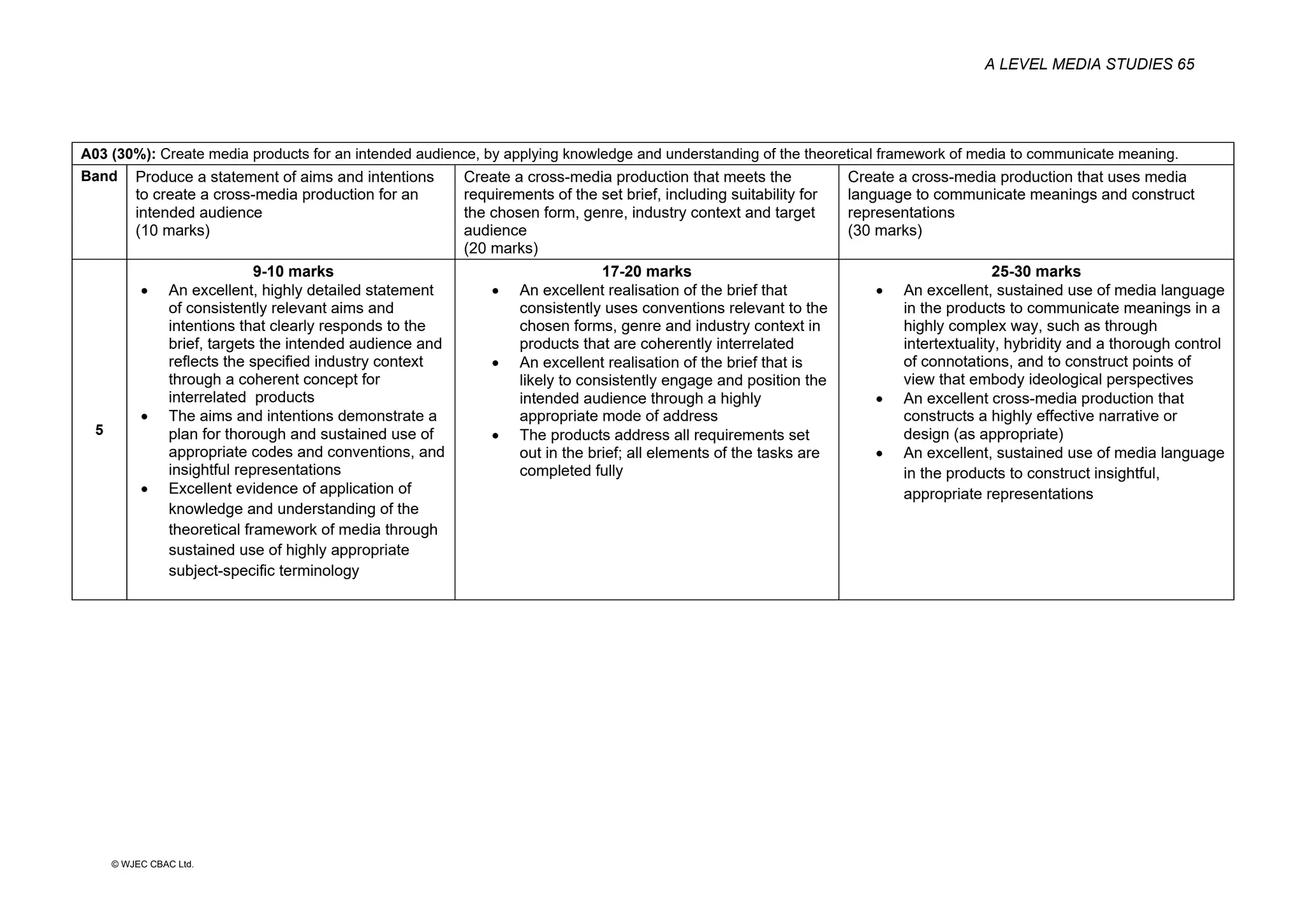
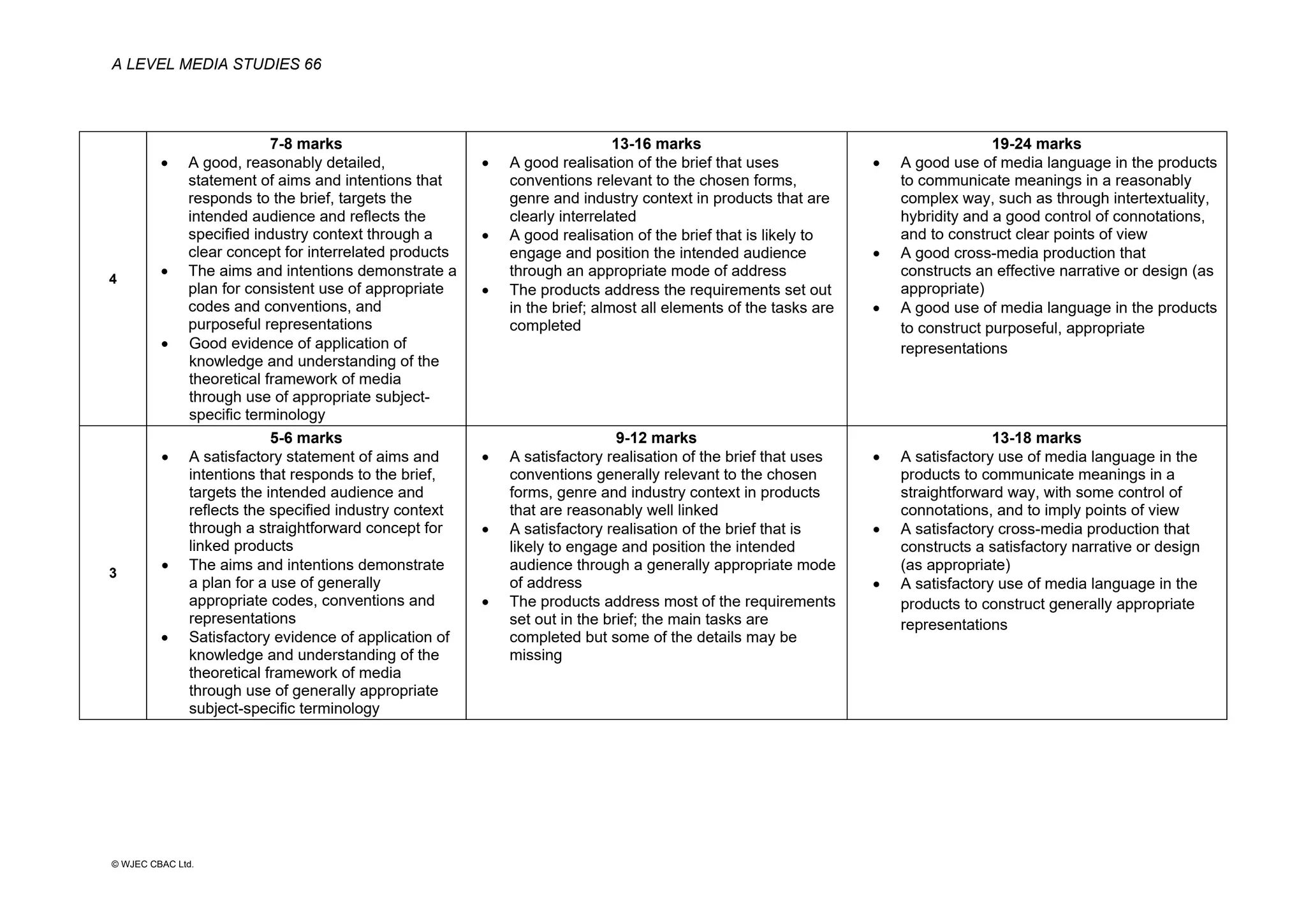
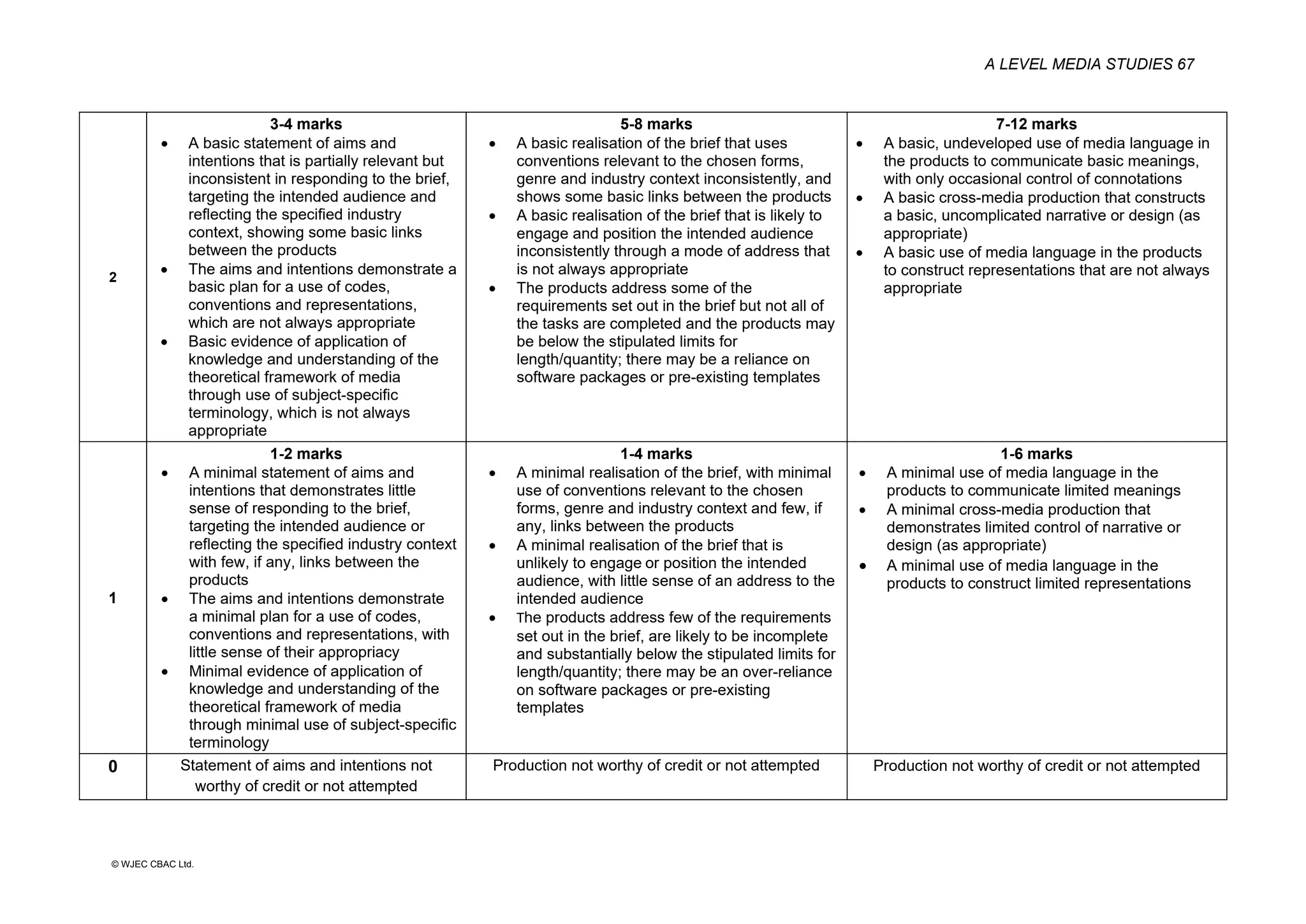
This document provides an overview of the WJEC Eduqas GCE A Level in Media Studies specification. It outlines the aims, content, and assessment of the qualification. The specification focuses on developing learners' understanding of media language, representation, industries, audiences, and contexts through the study of various media forms. Assessment consists of two externally examined components and one non-exam assessment component involving a cross-media production.