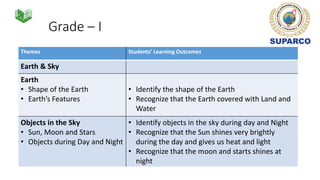
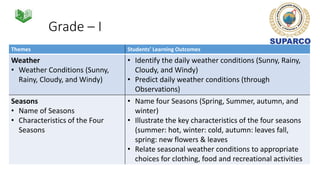
1. The document discusses space education provisions in the Pakistani K-12 curriculum. It outlines concepts related to earth, sky, weather, and seasons that are taught in grades 1-3.
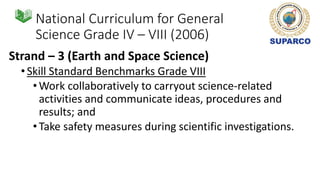
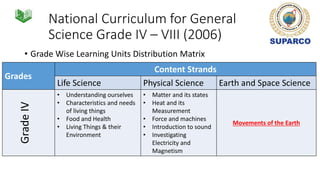
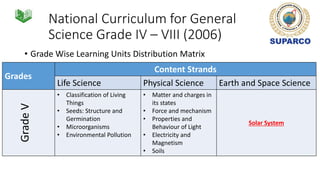
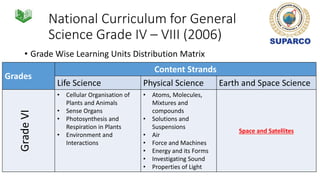
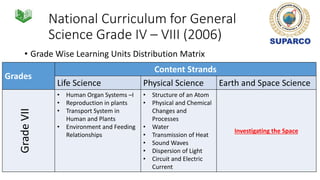
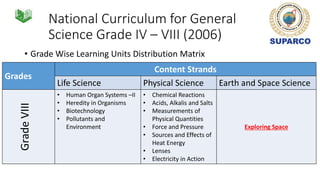
2. For grades 4-8, the national science curriculum includes an Earth and space science strand that covers topics like the solar system, moon phases, eclipses, and space exploration.
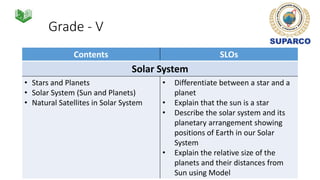
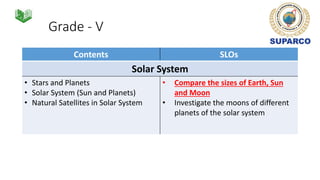
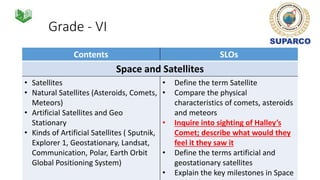
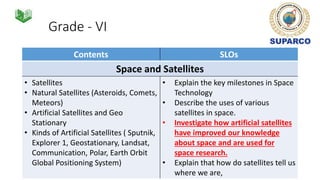
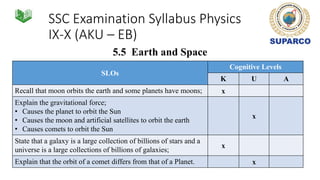
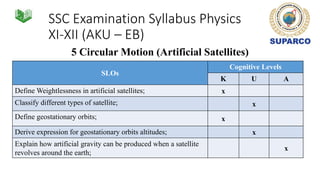
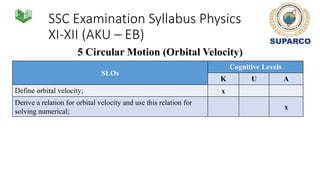
3. Specific concepts taught by grade are outlined, such as properties of the sun and stars in grade 5 and the solar system and gravity in grade 8. The curriculum also includes skills standards around questioning, observation, investigation and communication.