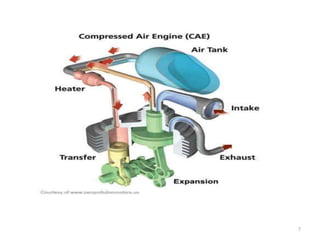
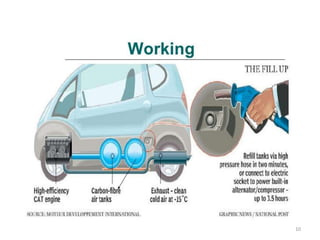
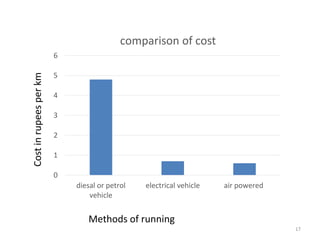
This document provides an overview and analysis of air-powered vehicles as a potential future of transportation. It discusses how air-powered cars work using compressed air to power an engine similar to internal combustion. The key components of an air-powered car are compressed air tanks to store energy, an air engine with intake and exhaust chambers, an air filter, and an electrical system. Refilling the compressed air tanks can be done at home or stations and takes only a few hours or minutes. Air-powered cars have advantages of lower costs, reduced emissions, and simpler maintenance compared to gasoline or electric vehicles. However, their range is limited to 200km currently and top speed is 110kph. Companies like Tata Motors are working on developing