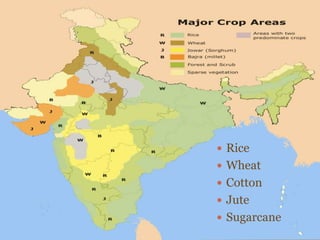
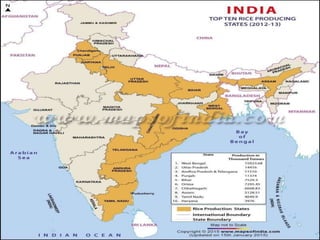
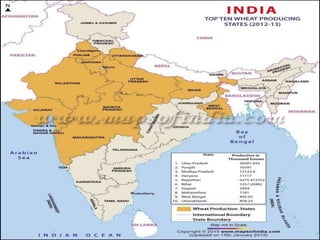
This document summarizes key cultivated crops in India. It discusses how agriculture is the backbone of India's economy and how crops are divided into Rabi, Kharif, and Zaid categories based on seasons. The major food crops described are wheat, maize, rice and millets, while cash crops include sugarcane, tobacco, cotton, jute and oilseeds. Key details are provided on India's top five crops - rice, wheat, cotton, jute, and sugarcane - including their climatic requirements, largest producing states, and yield details.