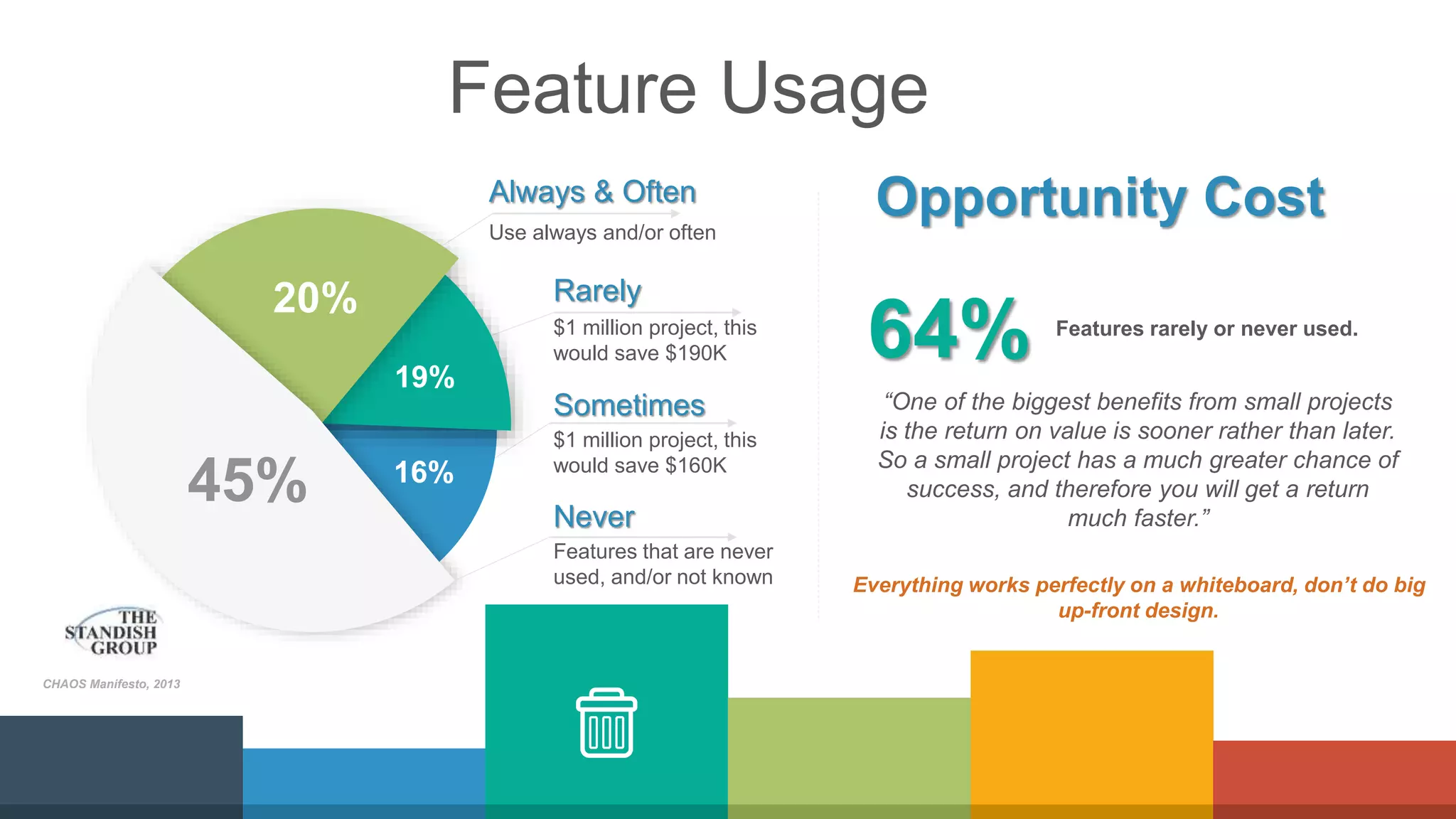
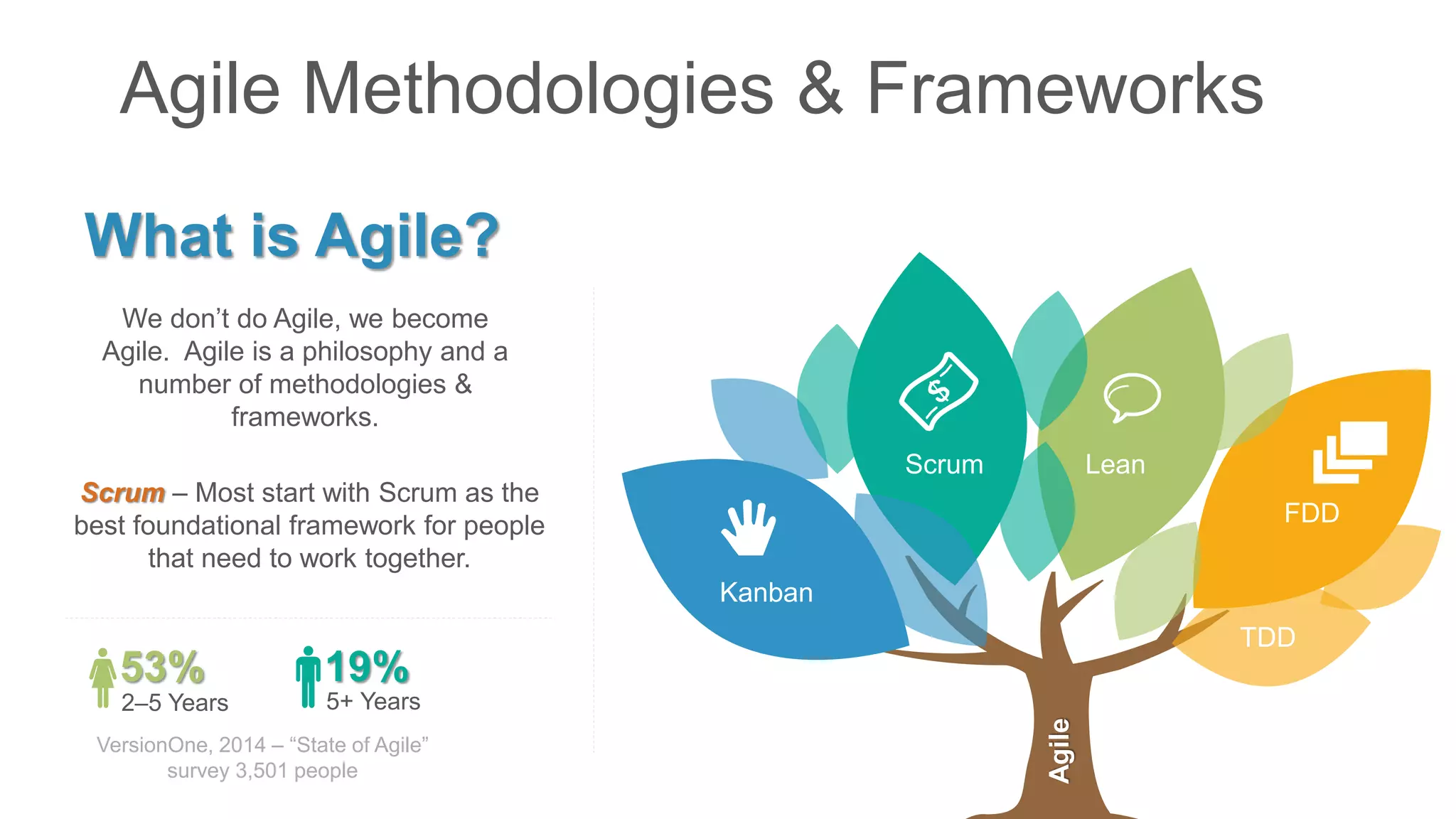
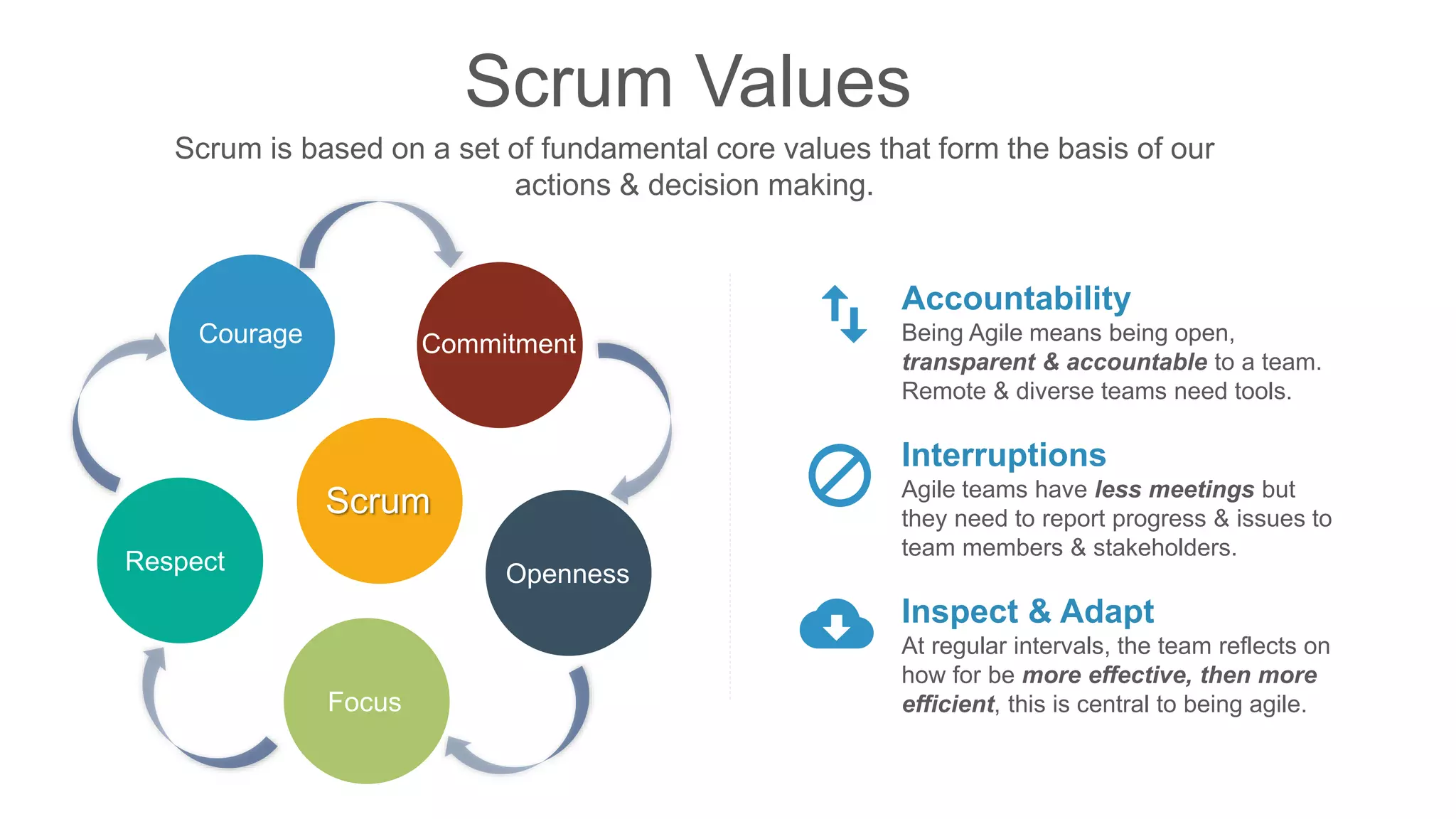
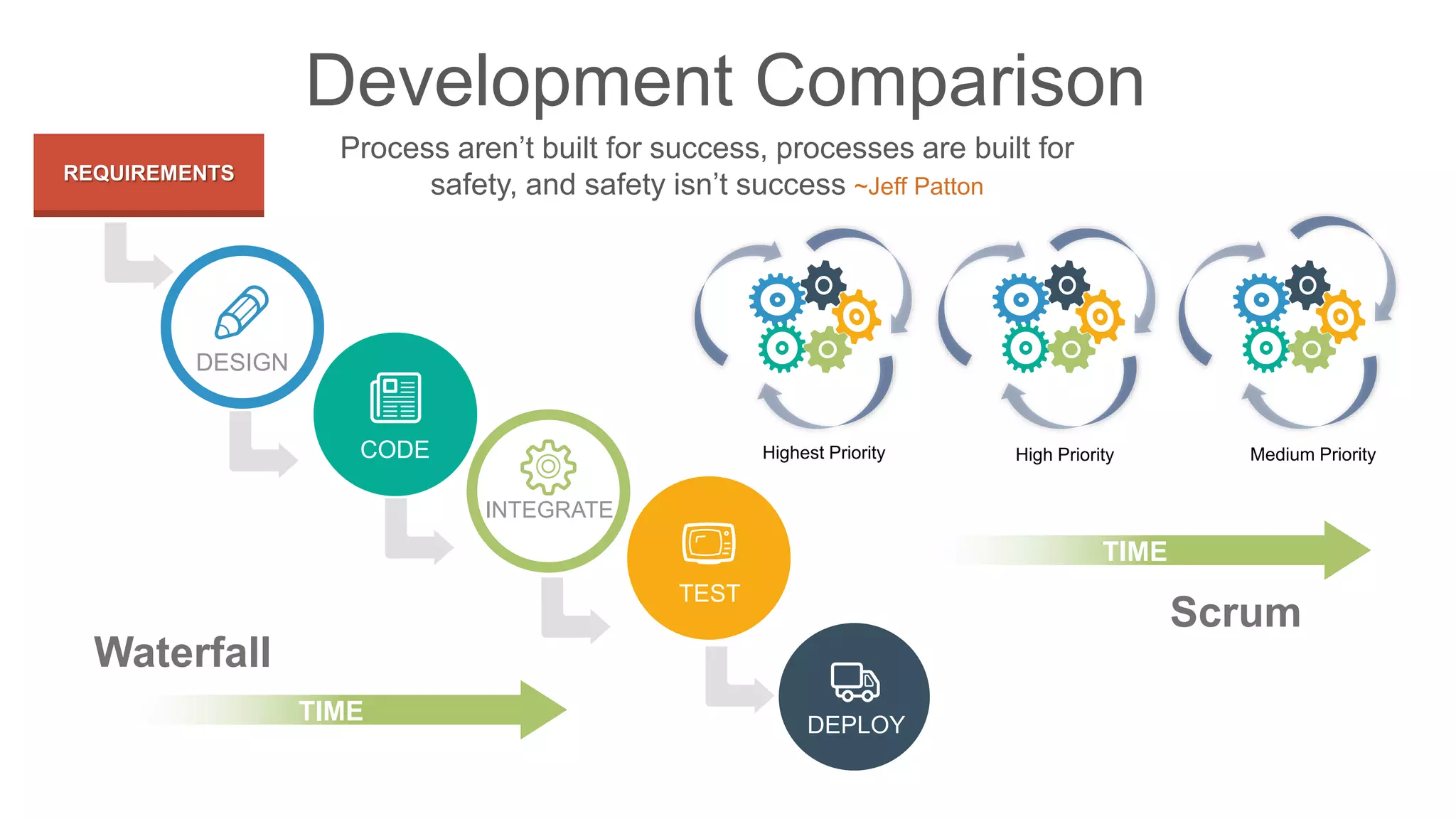
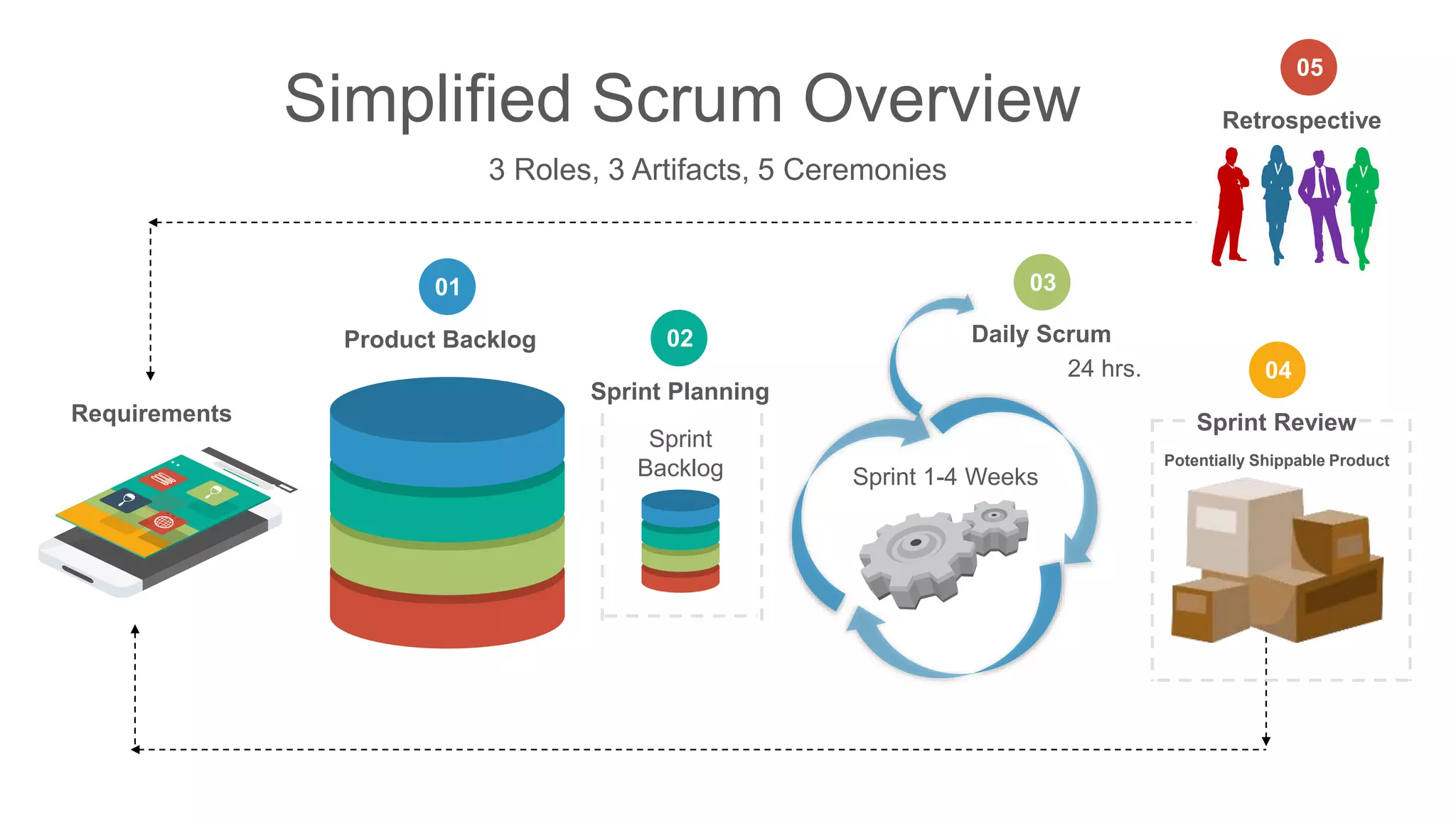
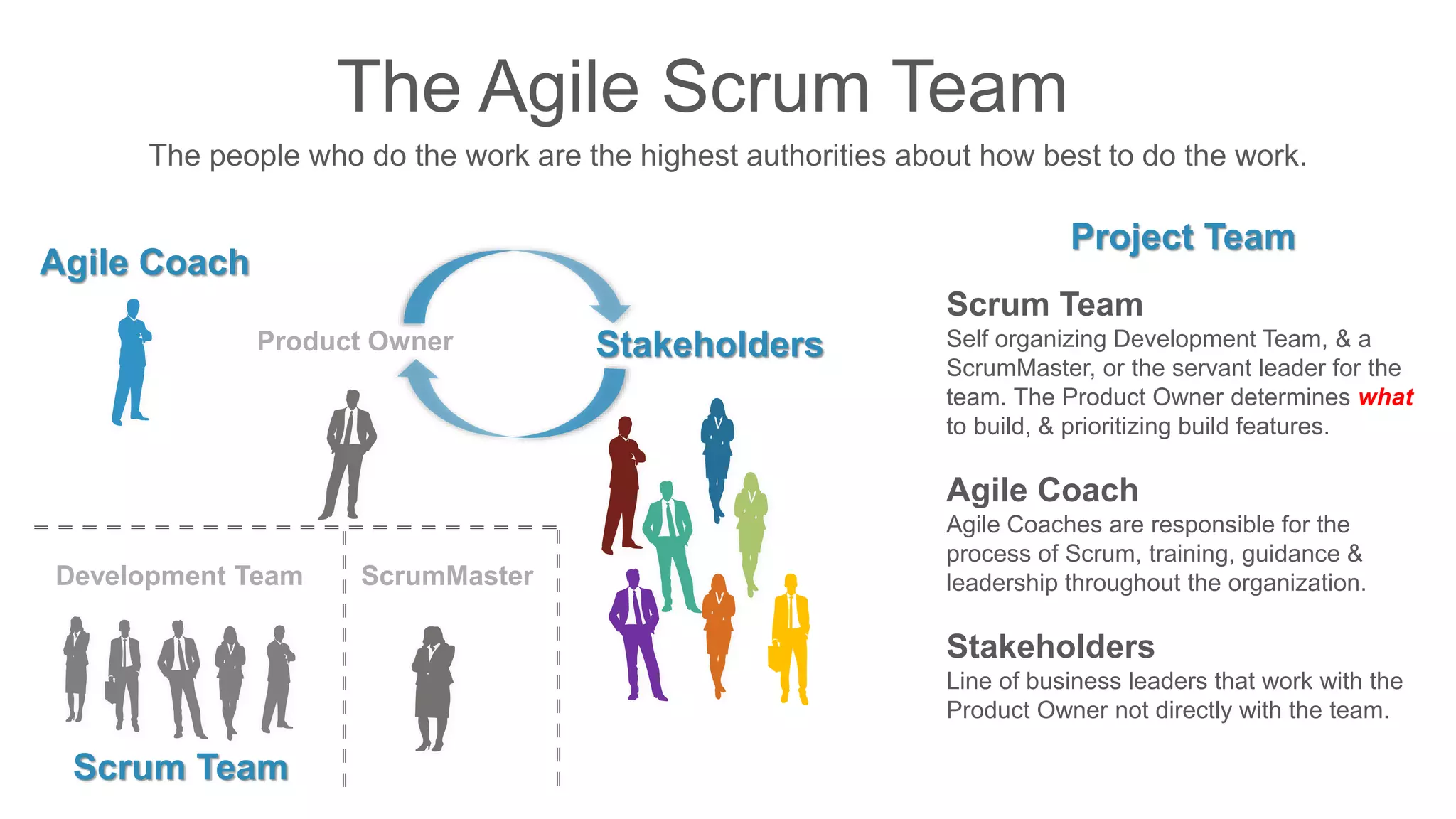
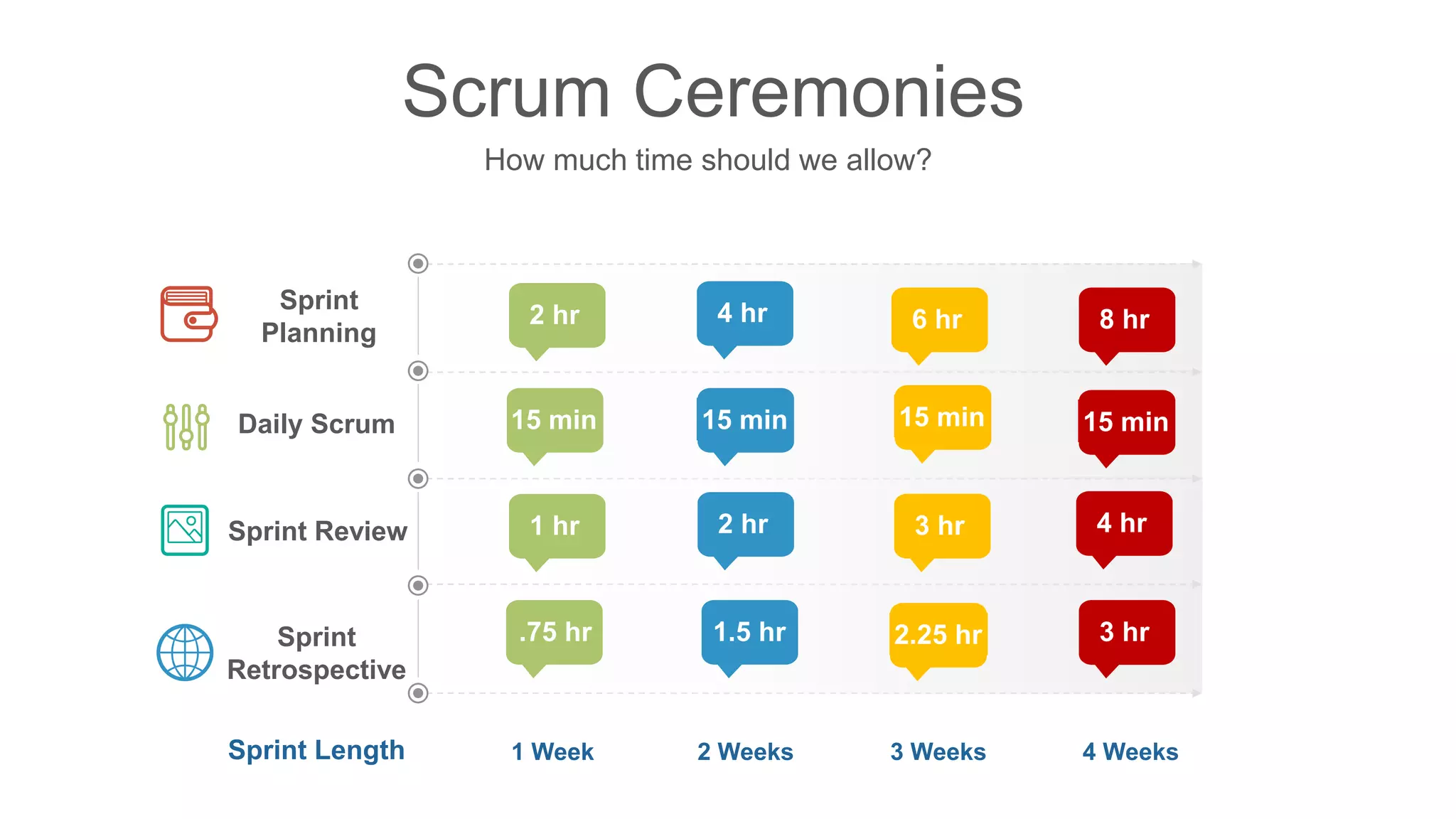
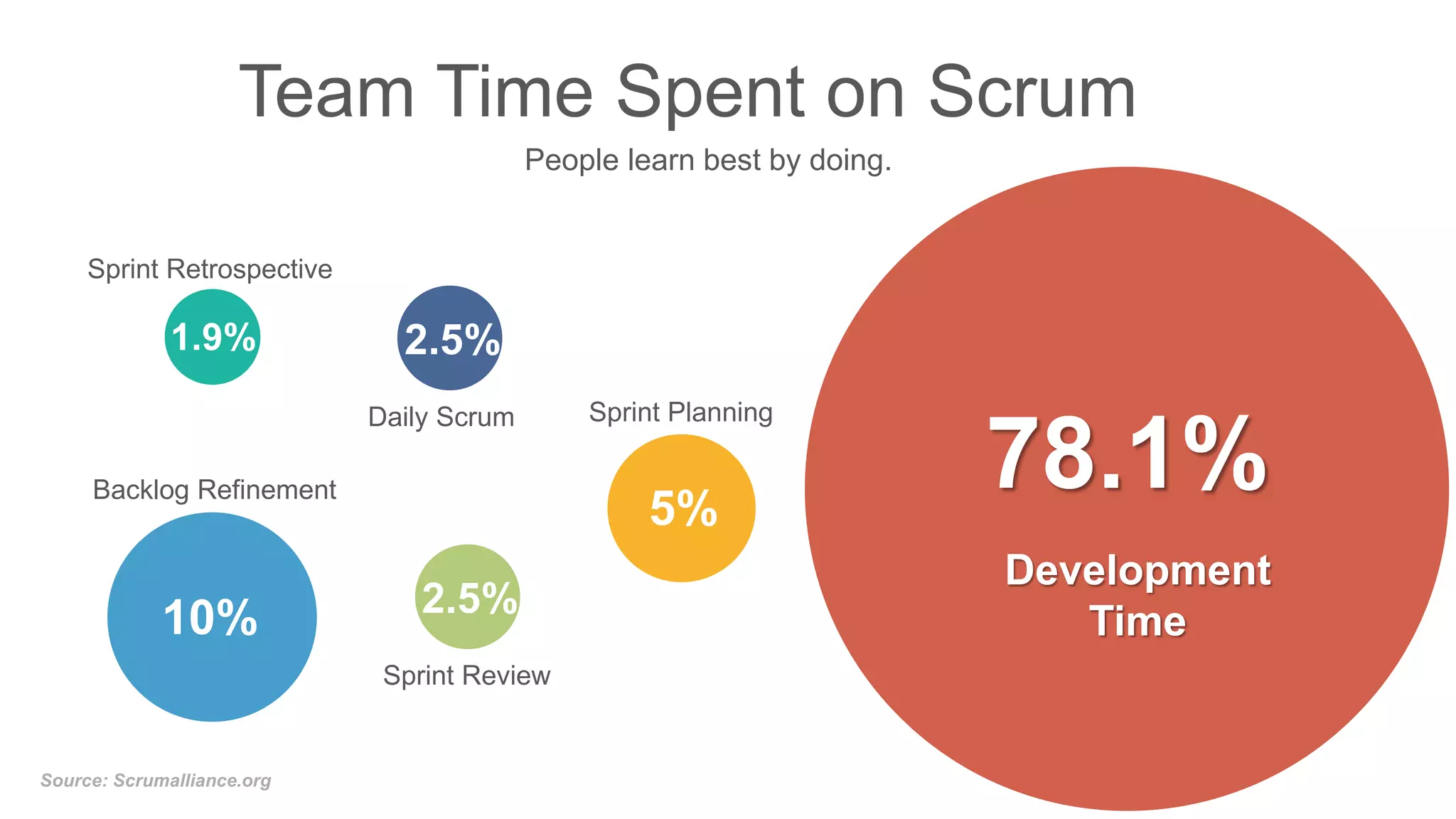
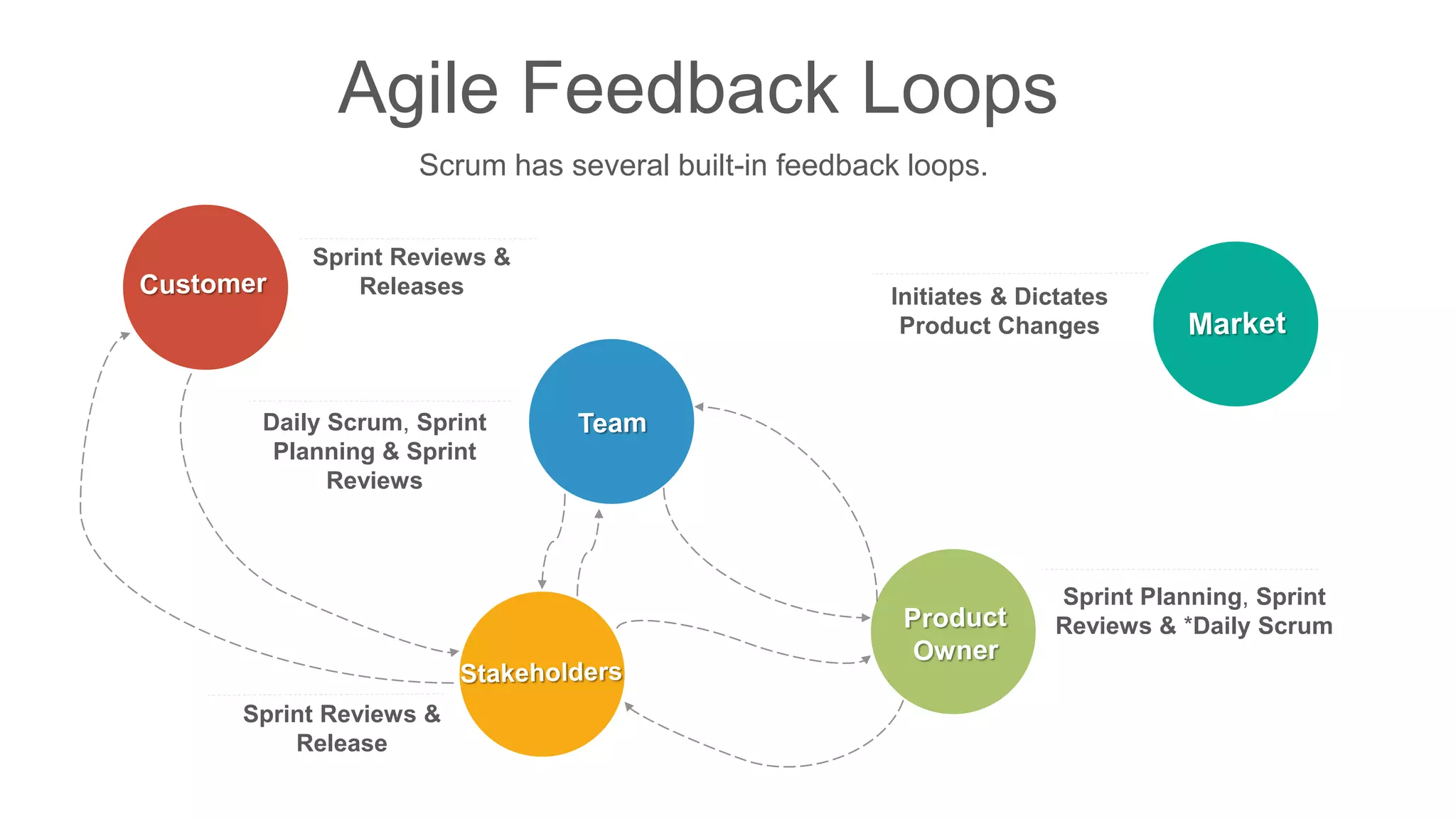
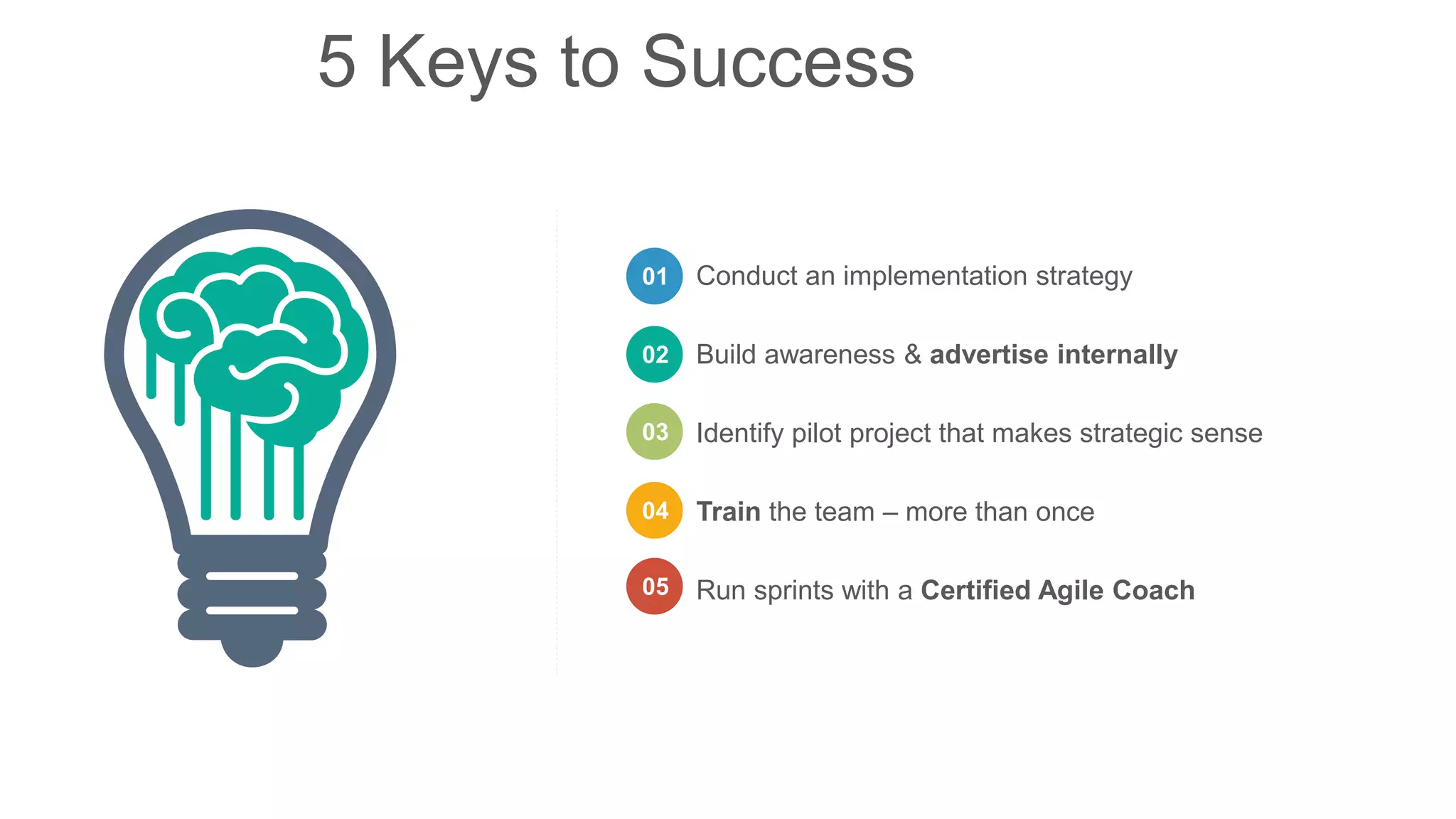
The document compares traditional waterfall and agile product development approaches. It summarizes research finding that agile projects succeed three times more often than waterfall projects. Key aspects of agile methodologies like Scrum are outlined, including roles, ceremonies, and values. Challenges of adopting agile approaches are also discussed.