Recommended
PPTX
PPTX
EMT/EMR INTRODUCTION TO EMS & RESEARCH POWERPOINT TRAINING MODULE
PDF
emt-1introductiontoemsv-2-170221033651.pdf
PPTX
Ch 1 EMS Systems, Research, & Public Health.pptx
PPT
Introduction to advanced prehospital care
PPT
Chapter_01 EMS Systems.ppt
PPT
Introduction to advanced prehospital care
PPTX
PPTX
PPT
Chapter 1 Power Point.pptttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttt
PPTX
Section 1.pptx emergency medical technician
PPT
PPT
Chapter 1 Powerpoint - Emergency Medical Responder
PPTX
Justin gardner final_presentation
PPTX
AEMT chapter 2 Emergency Medical Services
PPT
PPT
Ch01eec3 110623151514-phpapp01
PPTX
Delivering-Pre-Hospital-Patient-Care-Emergency-Medical-Services-NC2.pptx
PPT
PPT
Starting an EMT Program at Your High School
PPT
PPTX
PDF
PPT
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care
PDF
Emt and paramedic training
PPT
PPTX
PEC12 Chap 1 - EMS Systems_accessible.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Greengnorance Toolkit Module1 Climate Change
PDF
Pratishta Educational Society., Courses & Opportunities
More Related Content
PPTX
PPTX
EMT/EMR INTRODUCTION TO EMS & RESEARCH POWERPOINT TRAINING MODULE
PDF
emt-1introductiontoemsv-2-170221033651.pdf
PPTX
Ch 1 EMS Systems, Research, & Public Health.pptx
PPT
Introduction to advanced prehospital care
PPT
Chapter_01 EMS Systems.ppt
PPT
Introduction to advanced prehospital care
PPTX
Similar to AEMT Chapter 1 Introduction to Advanced EMT.pptx
PPTX
PPT
Chapter 1 Power Point.pptttttttttttttttttttttttttttttttt
PPTX
Section 1.pptx emergency medical technician
PPT
PPT
Chapter 1 Powerpoint - Emergency Medical Responder
PPTX
Justin gardner final_presentation
PPTX
AEMT chapter 2 Emergency Medical Services
PPT
PPT
Ch01eec3 110623151514-phpapp01
PPTX
Delivering-Pre-Hospital-Patient-Care-Emergency-Medical-Services-NC2.pptx
PPT
PPT
Starting an EMT Program at Your High School
PPT
PPTX
PDF
PPT
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care
PDF
Emt and paramedic training
PPT
PPTX
PEC12 Chap 1 - EMS Systems_accessible.pptx
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Greengnorance Toolkit Module1 Climate Change
PDF
Pratishta Educational Society., Courses & Opportunities
PPTX
Fluorimetric Analysis- Theory, Instrumentation and Application
PPTX
ELIMINATION NEEDS Fundamentals of Nursing .pptx
PPTX
Overview of How to set priority in Odoo 19 Todo
PPTX
How to Track & Manage My Time Section in Odoo 18 Time Off
PDF
Orlando by Virginia Woolf: The Granite and The Rainbow
PDF
Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Unit 1 (BP606T)
PPTX
Greengnorance Toolkit Module 5 Waste Management
PPTX
How to perform product search based on a custom field from the Website Shop p...
PDF
How "Raiders of the Lost Ark" and "Ordinary People" Employ Non-Verbal Acting
PPTX
PRE TERM LABOR ( PREMATURE LABOUR IN PREGNANCY)
PDF
Judgement Regarding Land Acquisition Act not Applicable to Encroachers.pdf
PPTX
Math 8 Quarter 4 Week 4-SECONDARY DATA.pptx
PPTX
Greengnorance Toolkit Module 3 Shopping and Food
PPTX
How to Add an Icon in Systray in Odoo 18
PPTX
Types of counselling Directive, Non Directive, Eclectic Counselling
PPTX
Plant fibres used as surgical dressings & Sutures – Surgical Catgut and Ligat...
PDF
Family and Marriage __ Sociology __ Jhasketan Kuanar __ NURSING VIBE ONLY .pdf
PPTX
Greengnorance Toolkit Module 6 Water Resources
AEMT Chapter 1 Introduction to Advanced EMT.pptx 1. Advanced EMT: A Clinical-Reasoning
Approach
Second Edition Update
Chapter 1
Introduction to Advanced
Emergency Medical
Technician Practice
Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
2. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
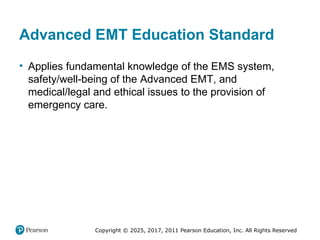
Advanced EMT Education Standard
• Applies fundamental knowledge of the EMS system,
safety/well-being of the Advanced EMT, and
medical/legal and ethical issues to the provision of
emergency care.
3. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Learning Objectives
1.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter.
1.2 Describe the competencies, roles, responsibilities, and
professional characteristics of the Advanced EMT.
1.3 Describe the scope of practice of the Advanced EMT.
1.4 Place the roles and responsibilities of the Advanced EMT
in the larger contexts of emergency medical services (EMS),
health care, and public health.
1.5 Discuss key issues in the contemporary practice of the
Advanced EMT, including professionalism, the focus on
patient safety, research, and evidence-based practice.
4. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Think About It
• How should Jane and Kevin proceed?
• What are their overall goals in managing this situation?
• What knowledge and skills do you think Jane and Kevin
will be calling on?
5. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Introduction
• AEMTs
– are a critical part of the emergency medical services
(EMS).
– provide comfort, emergency medical care, and
transportation.
– provide a link between patients and the health care
and public health systems.
6. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
EMS and EMS Providers
• Initially, training focused on patients in MVCs and/ or
cardiac arrest.
• Over time training has evolved to meet new demands in
EMS in a variety of situations.
7. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 1-1
Advanced EMTs work in a variety of settings.
8. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
The Contemporary EMS Profession (1 of 4)
• EMS knowledge defined in documents published by N
HTSA.
– National EMS Core Content
– National EMS Scope of Practice
– National EMS Education Standards
9. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
The Contemporary EMS Profession (2 of 4)
• EMT Oath and EMT Code of Ethics describe the
professional conduct expected of EMS personnel.
• EMS providers must be aware of activities and agendas
of major EMS state and national professional agencies
and organizations.
10. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
The Contemporary EMS Profession (3 of 4)
• EMS Agenda for the Future (1996)
– envisions EMS playing a much more important role in
health care
▪mobile integrated healthcare (MIH)
▪community paramedicine (CP)
▪ Planning for the Future: EMS Agenda 2050
– EMS provide important roles in assessment, health
education, and health services
– Using technology to improve response, diagnosis,
and care
11. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
The Contemporary EMS Profession (4 of 4)
Figure 1-4 EMS is developing and growing to include additional components of health
care and public health.
Source: EMS Agenda 2050 Technical Expert Panel. (2019, January). EMS Agenda 2050:
A People-Centered Vision for the Future of Emergency Medical Services (Report No. DO
T HS 812 664). Washington, DC: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
https://www.ems.gov/issues/planning-for-the-future-ems-agenda-2050/
12. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
EMS Provider Levels (1 of 5)
• Four nationally recognized levels of EMS providers
– Emergency medical responder (EMR)
– Emergency medical technician (EMT)
– Advanced emergency medical technician (AEMT)
– Paramedic
13. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
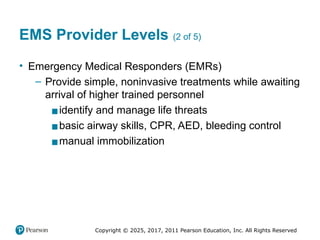
EMS Provider Levels (2 of 5)
• Emergency Medical Responders (EMRs)
– Provide simple, noninvasive treatments while awaiting
arrival of higher trained personnel
▪identify and manage life threats
▪basic airway skills, CPR, AED, bleeding control
▪manual immobilization
14. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
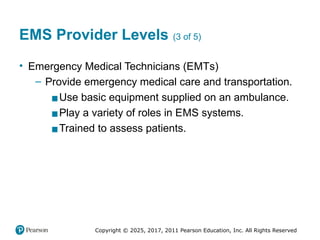
EMS Provider Levels (3 of 5)
• Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs)
– Provide emergency medical care and transportation.
▪Use basic equipment supplied on an ambulance.
▪Play a variety of roles in EMS systems.
▪Trained to assess patients.
15. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
EMS Provider Levels (4 of 5)
• Advanced EMT (AEMTs)
– Training includes all knowledge and skills of EMRs
and EMTs.
– Able to provide limited number of advanced life
support (ALS) interventions.
– Must practice within the Scope of Practice approved
by state and EMS service physician medical director.
16. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
EMS Provider Levels (5 of 5)
• Paramedics
– Allied health care professionals who provide complex
assessments and interventions for critical and
emergent patients.
– Complex understanding of anatomy, physiology,
pathophysiology, and treatment modalities.
17. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Roles and
Responsibilities (1 of 7)
• Advanced EMT’s authorization to practice is based on
– state legislation
– employer policies and procedures
– guidance by a physician medical director
18. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Roles and
Responsibilities (2 of 7)
• Emergency vehicle readiness and operations
– Emergency vehicle must be in good mechanical
repair and driven safely.
– Vehicle must have adequate amount of required
equipment and supplies.
19. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 1-5
Advanced EMT responsibilities include making sure equipment and the
emergency vehicle are prepared to respond to emergency calls.
20. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Roles and
Responsibilities (3 of 7)
• Safety responsibilities
– own safety, and safety of coworkers, patients, and
others
– medical errors account for between 44,000 and
98,000 deaths annually
▪Cost of medical errors can reach 29 billion
annually
▪EMS is not immune to medical errors
21. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 1-6
Teamwork is required to integrate the tasks of patient care and patient
transportation.
22. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Box 1-1: Select EMS Tasks with High Risk
for Errors and Patient Injury
• Transferring care from one provider to another at the scene or at the
hospital
• Communicating, either in writing or verbally
• Identifying and using medications
• Assessing and managing the airway
• Lifting and moving patients
• Responding and transporting by ambulance
• Assessing the need for and taking spinal precautions
Source: O’Connor, R. E., C. M. Slovis, R. C. Hunt, R. G. Pirallo, and M. R. Sayre. 2002.
“Eliminating Errors in Emergency Medical Services: Realities and Recommendations.”
Prehospital Emergency Medicine 6, no. 1: 107–13.
23. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Box 1-2: Ways to Minimize the Risk of
Mistakes and Patient Injury
• Maintain current knowledge and competence in skills.
• Make the environment as conducive as possible to quality care (maximize
space and light, minimize distractions).
• Have a clear understanding of protocols.
• Organize drugs to minimize mistakes.
• Reflect on actions and question assumptions.
• Obtain feedback on performance.
• Ask for help when needed (contact medical direction, consult with your
partner).
Source: O’Connor, R. E., C. M. Slovis, R. C. Hunt, R. G. Pirallo, and M. R. Sayre. 2002.
“Eliminating Errors in Emergency Medical Services: Realities and Recommendations.”
Prehospital Emergency Medicine 6, no. 1 (January–March): 107–13.
24. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Roles and
Responsibilities (4 of 7)
• Scene leadership, management, teamwork
– Be confident and in control
– Be empathetic
– Carry out the plan
25. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Roles and
Responsibilities (5 of 7)
• Patient assessment and management
– Ability to assess and manage patients who have a
variety of illnesses and injuries, from minor to critical.
– Be aware of the most current trends and practices in
EMS.
– Be willing to discard outdated knowledge and practice
to add new ones.
▪spinal motion restriction vs. spinal immobilization
practices
26. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Roles and
Responsibilities (6 of 7)
• Maintaining certification or licensure
– Individual professional obligation of each health care
provider
– Requirements include
▪documentation of mandatory continuing education
activities
▪ medical director verification of skills
▪ submission of CPR card
▪ payment of a fee
27. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 1-7
Advanced EMTs work closely with other health care and public safety
providers.
28. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Roles and
Responsibilities (7 of 7)
• Working with other public safety and health care
personnel
– Emergency medical services are cross-disciplinary;
both public safety and health care personnel.
– Strive to maintain cooperative relationships with other
professionals.
29. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Professional
Characteristics (1 of 2)
• Professional characteristics defined by
– Expectations of public
– Professional group itself
– Other related professional groups
– Most visible way patients and families can judge
professionalism is through interactions with them
30. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Advanced EMT Professional
Characteristics (2 of 2)
– Integrity
– Empathy
– Self-motivation
– Appearance and hygiene
– Self-confidence
– Communications
– Time management
– Teamwork
– Patient advocacy
– Careful delivery of service
31. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Figure 1-8
Why is it so
important that
EMS
personnel
wear
uniforms?
Appearance and demeanor are critical elements of professionalism.
32. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Chapter Summary
• AEMTs are an essential part of EMS and of the health
care and public health systems.
• AEMTs are health care professionals of whom the public
has high expectations.
33. Copyright © 2025, 2017, 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Copyright
This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their
courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of
any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will
destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work
and materials from it should never be made available to students
except by instructors using the accompanying text in their
classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these
restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and
the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials.
Editor's Notes #1 If this PowerPoint presentation contains mathematical equations, you may need to check that your computer has the following installed:
1) MathType Plugin
2) Math Player (free versions available)
3) NVDA Reader (free versions available) #11 Six guiding principles are as follows. Adaptive and innovative, Inherently safe and effective, Integrated and seamless, Reliable and prepared, Socially equitable, Sustainable and efficient, and Adaptive and innovative. Each principle is represented by corresponding icons.