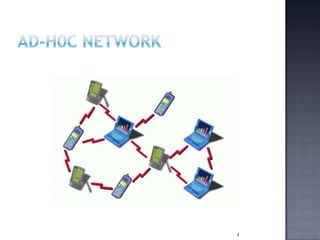
This document presents information on ad-hoc sensor networks. It discusses that ad-hoc sensor networks are decentralized wireless networks that do not rely on existing infrastructure, with each node participating in routing by forwarding data. The key advantages of ad-hoc sensor networks are that they have no infrastructure requirements and are scalable, mobile, decentralized, and robust. Popular applications of ad-hoc sensor networks include military operations, emergency response, home and personal networks, and environmental monitoring. The document concludes that ad-hoc sensor networks can help cover weaknesses in infrastructure by allowing nodes to self-configure into a network.