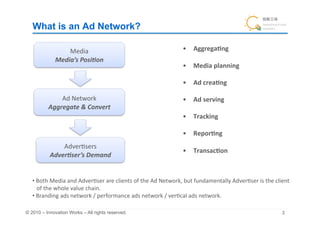
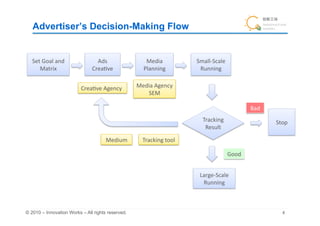
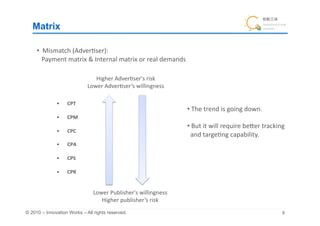
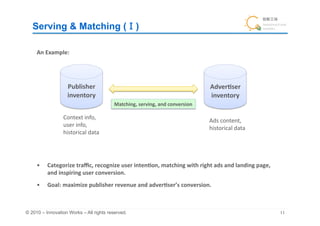
The document discusses the fundamentals of ad networks and their role in media aggregation, ad creation, and serving to advertisers and media clients. Key topics include the difference between branding and performance ads, strategies for profitability, pricing models, and the importance of tracking and reporting for advertisers. It also touches on challenges such as spam and methods for improving ad serving and matching through various targeting techniques.