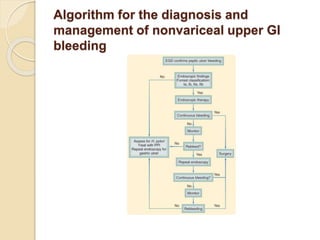
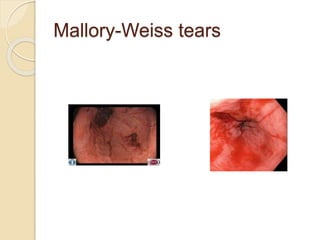
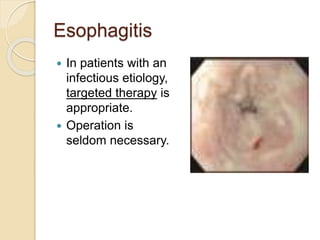
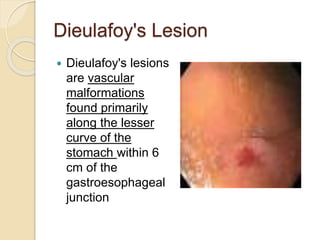
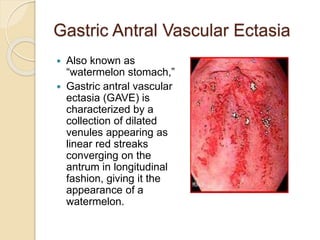
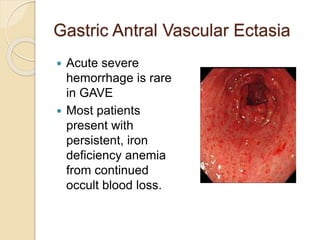
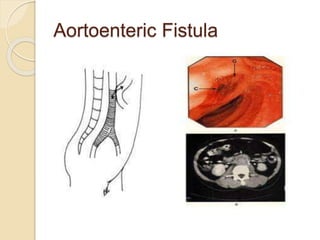
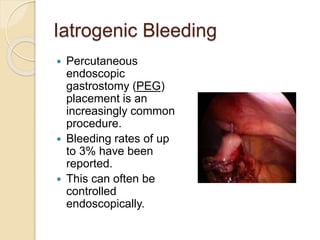
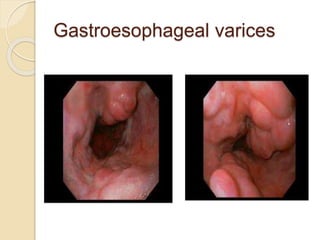
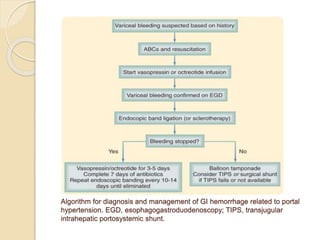
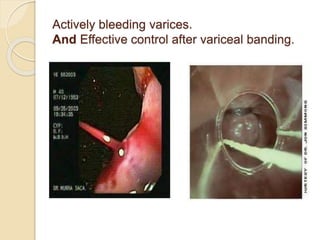
This document discusses upper gastrointestinal bleeding, including its definition, causes, and management. The causes are categorized as nonvariceal bleeding (80% of cases, most commonly from peptic ulcer disease) or bleeding related to portal hypertension (20% of cases, usually from gastroesophageal varices). Early endoscopy within 24 hours is recommended to identify the source of bleeding and guide treatment. Treatment depends on the specific cause but may include endoscopic therapies like epinephrine injection or thermal coagulation, as well as medications like PPIs. Surgery is considered if endoscopic treatment fails or for high risk lesions.