This document appears to be an excerpt from an English grammar textbook. It provides instruction on word classes, word order, the present simple tense, and includes practice exercises for students to complete. Key details include explanations of word class and word order, examples of statements using the present simple tense, and tasks for students to change verbs to their present simple form or complete sentences using the correct present simple verb forms.












![4 Present simple 2: negatives and questions
Do you like zoos?
n o n
c v
Do you (ike zoos?
Do you think zoos are a good idea?
Welcome t o A n i m a l W o r l d Park i n C a l i f o r n i a , USA.
The p a r k i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m o t h e r zoos. We h e l p a n i m a l s
i n d a n g e r . When i t i s p o s s i b l e , we r e t u r n young
a n i m a l s t o t h e i r homes.
We have more t h a n 30 g o r i l l a s
i n t h e p a r k . A m o t h e r g o r i l l a
d o e s n ' t have many b a b i e s . A baby-
g o r i l l a s t a y s w i t h i t s m o t h e r f o r
t h r e e y e a r s .
You o f t e n f i n d c o l o b u s monkeys i n
zoos. They a r e i n danger because
t h e y have b e a u t i f u l f u r . Young
c o l o b u s monkeys d o n ' t have b l a c k
and w h i t e f u r - t h e i r f u r i s
w h i t e .
atotot money.
m
Find t h e n a m e s o f t h e animals in t h e p h o t o s .
Xa>|uoui snqo]03 e pile B||uo8 E :J9MSUV
Present simple 2: negatives and
questions
1 To make negative f o r m s in t h e present simple, use don't
and doesn't + t h e infinitive f o r m w i t h o u t to o f t h e verb.
They don't have black and white fur.
A mother gorilla doesn't have many babies.
negative X
1/ You / W e /They do n o t (don't) believe
H e / S h e / I t does n o t (doesn't) believe
2 To make a question, use do or does in f r o n t o f the subject.
Do you like zoos ?
Does the park cost a lot of money?
3 Use do or does in t h e affirmative short answer and don't
or doesn't in t h e negative short answer.
Yes, I do.
No, he doesn't.
There is no -s on t h e main verb after does or doesn't.
She doesn't think... N O T She doesn't thinks...
Does she know? N O T Does she knows ?
question ? short answer / X
D o 1 / you / we / t h e y like...? Yes, (1) do.
No, (1) don't.
Does he / she / i t like...? Yes, (he) does.
No, (he) doesn't.
1 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-13-320.jpg)
![PracticeA Underline the correct o p t i o n .
1 I don't know /doesn't know the answer.
2 Most trees don't grow/doesn't grow very quickly.
3 Do/Does Sara understand this?
4 Do/Does you want t o talk about it?
5 The price don't include/doesn't include service.
6 I don't think/doesn't think he's very nice.
7 We don't see/doesn't see our grandparents very often.
8 They don't live/doesn't live very near.
B Complete the t e x t about black rhinos using t h e correct
present simple f o r m s o f t h e verbs in brackets.
W e 1
WW (have) a large number o f rhinos
living here. Black r h i n o s 2
(not live) in
groups. T h e y 3
(prefer) t o live alone.
Black rhinos are in danger because o f their horns. People
4
(use) the
horns as medicine.
A mother black rhino
5
(not have)
many babies. A baby
6
(stay) w i t h
its mother for three t o four
years. The mother rhino
7
(not stay) w i t h the father.
Rhinos 8
(not fight) w i t h other animals in
the park. In fact, they are friendly animals.
C Make present simple questions f r o m t h e words, t h e n
answer the questions in your n o t e b o o k using short
answers.
1 a mechanic / fix cars
Dees a mechanic {i£ cars?
2 y o u / w o r k at the weekend
Oojoa worfc. attkt, wukudL
3 a vet / look after animals
4 zoo keepers/work in shops
5 a young colobus monkey / have white fur
6 w e / g o t o school on Sundays
7 nurses / work in a hospital
8 y o u / d o sport in the evening
D Read part o f an i n t e r v i e w w i t h a gorilla keeper.
C o m p l e t e her answers, using t h e verbs in t h e box.
not eat not fight got up not go home
have not look after love
have
1 Yes, I tyt U.p at 6.30 every morning.
2 Yes, but they bananas all the time. They
like a lot o f other fruit, too.
3 The gorillas in the park are all friends. They
4 Yes, it does. The park more than 50 gorillas.
5 Yes, they do. We a baby gorilla in the park
at the moment.
6 Yes, but sometimes a mother
her baby. Then we help the baby.
7 Yes, I give the baby milk every four hours, day and
night. I in the evening. I sleep at the park.
8 I my j o b ! No day is the same!
mum
J W h a t did t h e i n t e r v i e w e r ask? M a k e present simple
questions using t h e w o r d s in brackets and w r i t e t h e m
in your n o t e b o o k .
1 PojSMfct ap earUjf* (early)
2 ? (bananas)
3 ? (fight)
4 ?(a lot o f gorillas)
5
6
7
8
?(have babies)
? (stay w i t h its mother]
? (drink milk)
'(like)
N o w t h i n k o f at least three more present simple questions
f o r t h e gorilla keeper and w r i t e t h e m in your notebook.
B: No, I don't,
c Do you want
c doesn't visit
Circle t h e correct o p t i o n .
1 A: t o go t o the zoo?
a You wants b W a n t you
2 We zoos very often,
a aren't visit b don't visit
3 M y sister zoos.
a doesn't like b doesn't likes c don't like
4 She says the animals a very happy life,
a not have b doesn't have c don't have
5 A: Do the rhinos fight w i t h other animals?
B:No,
a doesn't they b it doesn't c they don't
' . V S O T W S V V V W W W
DCJ Of E £ (l 0 :SJ9AASUE j;S3J_ A"AJ
Present s i m p l e 2 1 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-14-320.jpg)

















![1 2
Present perfect 1
They've already invented it!
They've a l r e a d y i n v e n t e d it, Dad!
The taxi's j u s t a r r i v e d !
Sorry I'm late. I
h a v e n ' t left y e t !
Find six w o r d s
rCC O from t h e c a r t o o n s
in t h i s w o r d snake:
Present perfect 1
1 Use t h e present perfect f o r a past event
which t h e speaker feels is connected
w i t h t h e present.
The taxi's arrived. (The taxi is here now.)
2 W e o f t e n use t h e present perfect t o t a l k
about a recent event. Use t h e adverb
just t o emphasise t h a t t h e event is
recent.
The taxi's just arrived.
3 W e can use t h e present perfect w i t h
already and yet. Already and yet mean
'before now'. W e use yet in questions
and negatives. Already comes a f t e r has
/have and before t h e main verb. Yet
comes at t h e end o f t h e sentence or
question.
They've already invented it.
I haven't left yet.
Have the boys arrived yet?
4 St/7/ w i t h t h e present perfect negative
stresses t h a t t h e situation is continuing
now.
/ st/7/ haven't left home.
5 M a k e t h e present perfect using t h e verb
have + past participle.
I've just seen her.
I haven't visited the museum yet.
'jsnf'ya] 'Apeaj|e 'paAUje 'pajuaAU! :SJ9MSUV
statement / negative X
1 / Y o u / W e / T h e y have fve) visited have n o t (haven't) visited
H e / S h e / I t has fs) visited has n o t (hasn't) visited
question ? short a n s w e r / /
Have 1 / you / we / they visited...? Yes, (1) have.
No,(l) haven't.
Has he / she / it visited...? Yes, (he) it has.
No, (he) hasn't.
A d d -ed t o f o r m t h e past participle
o f regular verbs, e.g. visited,
arrived, tried. (These are t h e same
as t h e past simple verb forms.)
See page 182 for spelling rules.
's = is and has
he's visited = he has visited
he's cold = he is cold
However, t h e r e are many irregular forms.
be been go + gone
break -> broken give -> given
come -* come steal -> stolen
do -> done
see •# seen
speak •* spoken
wake up •* woken up
Some irregular past participles are t h e same as t h e past
simple f o r m .
find •* found -* found read •* read -> read
have •* had -> had say •* said -> said
leave -* left -* left spend -> spent-* spent
lose -* lost -* lost tell -* told -> told
make -> made -> made win -> won -* won
3 2 • See page 181 for a list of irregular verbs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-33-320.jpg)
![Practice
A Match the pairs of sentences.
1 She can't do sports.^ ~x a
2 He's still not feeling well. 1 b
3 She's crying. V-c
4 I'm very happy. d
5 The car won't start. e
6 I have no money. f
7 You're looking worried. g
8 We can go now. h
9 I'm not ready t o go. i
She's lost her bag.
He's just had flu.
She's broken her arm.
I haven't had a shower yet.
I've spent it on CDs.
I haven't left yet.
The taxi has just arrived.
M y football team has just won.
W h a t has happened?
B Complete the sentences using the words in brackets in the
I correct form and position.
I I He can't find his keys. I think MSWKt them, (lose)
[ 2 Haven't you done your homework yet?
I it. (finish / already)
3 It's midnight and she home yet. (not / come)
4 lunch yet? (you / have?)
5 This is terrible. Someone my bike, (steal)
6 We a really cheap car! (just / buy)
7 Take your boots o f f before you come in. I
the carpets, (just / clean)
8 the doctor yet? (you / phone?)
9 They the film, (see /already)
C It's Sunday night and Dad is asking Joe whether he is ready for
f school in the morning. W r i t e Dad's questions and Joe's replies
in your notebook
1 pack school bag [/]
j3 do your science homework [/]
5 wash the dinosaur [X]
7 buy the dinosaur f o o d [X]
1 0: ffavejou packedjour school bayjet f J: /es, I have
2 tidy your cave [X]
4 have a bath [X]
6 make your sandwiches [/]
What four things hasn't Joe done yet? W r i t e sentences.
Example: He hasn't tidied his cavejet.
D W r i t e reasons for each of these situations. Use
the words in brackets and the correct form of
the verb.
1 I don't have my glasses.
I stilt haven't (ound them. (find / still)
2 He's still asleep.
(wake up /yet)
3 The book looks very new.
(I / read / still)
4 She isn't here any more.
(go/just)
5 I don't have my old phone any more.
(give it t o my dad)
6 She doesn't know.
(they / t e l l her /still)
7 I still haven't received the letter.
(postman / come / yet)
8 There's no more milk.
(I / finish/just)
MV TURN!
Imagine it's Sunday evening. In your notebook,
write three things you have done and three
things you haven't done.
Example: I've cleaned RUj bike,
• • * • i
Circle the correct option.
1 The taxi hasn't arrived a already b just c yet
2 He's his new watch. a breaked b broke c broken
3 He left home four hours ago and he t o say he's arrived, a still hasn't phoned b haven't phoned yet
c hasn't just phoned
4 yet? a Have you eaten your vegetables b You have eaten your vegetables c Have you your vegetables eaten '
5 A: Is Alex there? B: O h sorry. He's . a gone already home b just gone home c gone home yet I
Q S v B £ oz 3 1 : S J 3 M S U E N S A J _
Present p e r f e c t 1 3 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-34-320.jpg)

![ractice
Answer the questions with present perfect short answers.
1 Have vou ever tried raw fish?
frig, I tUMKt.
2 Have you ever used chopsticks?
3 Have you ever seen a banana tree?
4 Have you ever put sugar in a sandwich?
5 Have you ever made ice cream?
6 Have you ever eaten chips w i t h sugar?
7 Have you ever drunk coconut milk?
8 Have you ever cooked a meal f o r your family?
C Complete the sentences using the present perfect of
the verbs in the box.
break ever forget go ever have not meet
not play see not speak never spend write
1 I've broken my nose before.
2 He plays the guitar but he in a band before.
3 They Christmas away f r o m home.
4 W e our new neighbours.
5 M y friends aren't here now, they home.
6 M y sister an article for the local newspaper.
7 I t o my parents about my exam results.
8 your teacher
t o give you homework?
9 W e the new James Bond film.
10 She's the best friend I
Which of these things have you done or not done?
Complete the sentences using the present perfect o f
the verbs in brackets.
1 1 haven't won a competition, (win)
2 t o Cuba, (be)
3 a book in one day. (read)
]4 rugby, (play)
5 an elephant, (see)
6 a famous person, (meet)
7 a leg. (break)
in a restaurant, (work)
9 ten kilometres, (run)
Do you know people who have done these things?
Write true sentences about people you know.
Example: Mij brother has met a famous person,
, .
D Complete the sentences with gone or been.
1 M y grandparents have yone to Australia.
They'll arrive t o m o r r o w - the journey takes 22 hours.
2 They've visited the UK, but they haven't
t o Scotland.
3 M y family loves travelling. We've
t o 10 different countries together.
4 They've out and left the lights on.
5 A: Where have you ?
B: To post a letter.
MY TURN!
^ m ^ o u M i o ^ things you
have done in the past.
Example: I've been to Australia,
Now write three questions to ask a friend using Have
you (ever)...?
Example: ffavejou ever been to Australia?
W r i t e about your friend.
Example: Setty has never been to Australia,
Circle the correct option.
1 My sister sushi three or four times, but she doesn't like it. a tries b has tried c is tried
2 I've tried most things, but an insect. a I've ever eaten b I haven't never eaten c I've never eaten
3 A: on TV? B:Yes, he has. a Has Heston ever been b Has Heston been ever c Heston ever has been
4 It's our favourite restaurant. there many times. a We's been b We've gone c We've been
5 A: Have you ever been t o The Fat Duck? B: a Yes, we've b Yes, w e been c No, we haven't
—
D S 3 f E
£ 3 ? Q I : S J 3 M S U E J ; S 3 X X ^
Present p e r f e c t 2 3 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-36-320.jpg)

![A Complete each t i m e expression w i t h for or since.
Ml for a long time.
1 2 t w o weeks.
1 3 2003.
I 4 last year.
1 5 three years.
1 6 only a day!
• 7 Christmas.
8 I was 12.
| Now answer the question.
I How long have you lived in your house?
I I've lived in my house
B Complete the sentences w i t h t h e present perfect o f t h e
verbs in brackets. Use short f o r m s w h e r e possible.
1 They W always wanted t o visit New York, (always
want)
2 We my cousins since the beginning
of last year. They are always very busy, (not see)
3 It a really good summer. I don't
want it to end. (be)
4 They in the same house all
their lives, (live)
5 My sister and I share a bedroom. We
our own rooms, (never have)
6 How long you
your mountain bike? (have)
7 He his home
town, (always love)
8 How long she ill? (be)
9 He in the
same bank for years, (work)
10 I he was the
best, (always think)
C Ask questions a b o u t t h e celebrities using How long...?
and t h e present perfect.
1 Michael Douglas and Catherine Zeta-Jones are married.
....(few (Gnj have thej been married?
2 Madonna drives a M i n i Cooper car.
3 Sienna Miller lives in Marylebone.
4 Paul McCartney plays the piano.
5 Ringo Starr is a vegetarian.
6 Jennifer Connelly speaks Italian.
MY TURN!
f ^ a k e s e r ^ and a t i m e phrase
which is t r u e f o r you. W r i t e t h e m in your notebook.
1 I / be / hungry
I've been hungry since 16 clock this morniny.
2 I / not see / my cousin
3 I / be / a t t h i s school
4 I / know / my / best friend
5 I / not d o / t h e washing-up
6 M y family / live/here
Circle the correct o p t i o n .
1 t o meet Madonna.
a I always have wanted b I've always wanted c I've wanted always
2 We've lived in Marylebone
a forages b ages ago c since ages
3 They've had their flat in Marylebone since they married.
a get b got c have got
4 A: How long ? B: For about six years.
a are they famous b have they been famous c they've been famous
5 She London since she was a child.
a isn't visit b didn't visit c hasn't visited
3
S QT? <K e
Z Q I : S J 9 M S U E J } S 3 ] _ A Y /
Present p e r f e c t 3 37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-38-320.jpg)
![1 5
Present perfect or past simple?
The company has invented the Mac and the iPod.
S t e v e Jobs w a s b o r n in 1 9 5 5 a n d w a s a m u l t i -
m i l l i o n a i r e b e f o r e t h e a g e o f 3 0 . He is d y s l e x i c
a n d o n e o f his t e a c h e r s a t school r e m e m b e r s his
' d i f f e r e n t w a y o f l o o k i n g a t t h i n g s ' .
I n t h e 1 9 7 0 s , c o m p u t e r s w e r e large m a c h i n e s a n d
o n l y l a r g e c o m p a n i e s u s e d t h e m . I n 1 9 7 6 , S t e v e
l o b s a n d S t e v e W o z n i a k c h a n g e d all t h a t . T h e y
s t a r t e d t h e c o m p a n y A p p l e I n c a n d p r o d u c e d t h e
w o r l d ' s f i r s t p e r s o n a l c o m p u t e r , A p p l e I. Since
t h e n , A p p l e I n c h a s also p r o d u c e d M a c i n t o s h
c o m p u t e r s a n d t h e iPod.
S t e v e Jobs also h e l p e d t o s t a r t Pixar A n i m a t i o n
S t u d i o s . S o m e o f t h e b e s t - l o v e d a n i m a t e d f i l m s
h a v e c o m e f r o m Pixar, i n c l u d i n g Toy Story, Finding
Nemo a n d Ratatouille. Pixar h a s w o n m a n y
O s c a r s ™ o v e r t h e last 2 5 y e a r s .
1
V C o m p l e t e t h e s e n t e n c e w i t h t h r e e possible answers: Steve Jobs is f a m o u s f o r
sojpnjs uojiewmv Jexy 'pcy; am'sjsjndwoD Ljscnupeyv '| 9]ddv'3U| 9|ddy :s.iaMSiie aiqjsscy
Present perfect or past simple?
1 Use t h e present perfect t o t a l k a b o u t recent events o r
a past event w h i c h t h e speaker feels is connected w i t h
t h e present.
Certain t i m e expressions are c o m m o n w i t h this use
o f t h e present perfect. These include already, yet,
just, ever, never, before.
I haven't eaten yet. (= I'm hungry now.)
Has he left? (= He isn't here now.)
Use t h e past simple t o t a l k a b o u t a finished action.
Certain t i m e expressions may be used w i t h t h e past
simple. These include yesterday, last week, ago, then,
when, in + year.
In the 1970s, computers were large machines.
When did Apple invent the iPod?
3 Use t h e present perfect t o t a l k about an event or
s i t u a t i o n w h i c h began in t h e past and continues now.
W e o f t e n use t i m e expressions w i t h since and for w i t h
this use o f t h e present perfect, e.g. for a week, since
yesterday, for a long time, since 2004, and ask questions
w i t h How long?
How long have you worked at Pixar?
I've worked here for ten years.
4 The choice o f t h e past simple or present perfect can
sometimes depend on t h e p o i n t o f v i e w o f t h e speaker,
or on t h e c o n t e x t .
/ didn't see George this morning. (The speaker is talking
at the end o f the day and this morning is finished.)
/ haven't seen George this morning. (The speaker is
talking in the morning - this morning is still going on.)
3 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-39-320.jpg)


![[Practice
A Charlie is now a millionaire but he used t o be poor. In your
notebook, w r i t e sentences about Charlie's life w i t h used to
and didn't use to.
1
Now 10 years ago
1 He gets up at 11.00. 7 £ 0
2 He doesn't work. supermarket
3 He has a very big house. X big house
4 He plays golf. X g o l f
5 He wears expensive clothes. cheap clothes
6 He is unhappy. happy
1 tie used tojet up at 7.00
B Underline the correct o p t i o n . Sometimes b o t h options are
possible.
1 I had/used to have a shower last night.
12 Kurt was I used to be a very good friend.
I 3 It snowed/used to snow a lot in winter.
4 I met/used to meet Janice yesterday.
5 Children didn't watch/use to watch so much TV.
: 6 It wasn't/never used to be very expensive.
i 7 My sister went/used to go to Mexico in 2007.
8 My sister went/used to go t o Mexico every summer.
C Read these sentences about life 2,000 years ago. (Four are
I true, four are false.) I f t h e sentence is t r u e , r e w r i t e it w i t h
I used to. If the sentence is false, r e w r i t e it w i t h didn't use to.
I I Latin was an international language.
Uttn used to be an international lanjuaje.
2 People used to think that the w o r l d was round.
People iiih't use to think, that the world was round,
3 There were bears in England.
4 People ate a lot o f meat.
5 Builders made houses out o f w o o d .
6 Most people lived in towns.
7 Travelling by sea was dangerous.
8 Children learned English.
D C o m p l e t e this advertisement w i t h used to or the
past simple o f t h e verbs in t h e box.
not answer be chan;;e criticise do
get lose not isten sit not worry
M j o u j e t out of bed this morning ond feel terrible?
much filter ond beolfhier once?
jr answer is 'yes', you need powetf l a k e s !
Eva Clark (England):'!3
about my health but
I never4
exercise and my health got
worse and worse. Then I tried Powerflakes! Now I feel like a new woman.'
Andrei Wojdylo (Poland): 'My friends5
me all the time because I was so lazy and unfit but 1 6
to them. I 7
in front of theTV all night and eat chocolates. If the phone rang,
I 8
it! Last
year everything9
because I
1 0
my job and I needed to change
my life. Now, I have Powerflakes and life is perfect!'
In your notebook, w r i t e sentences about changes in
your life w i t h used to, didn't use to or never used to.
Example: I used to dojudo but now I do karate,
. . . . . .
— — — — Hi — — —
] Circle the correct o p t i o n .
| 1 She wants t o be a vet now, but she want t o be a doctor
1 2 He eat healthy food, but now he only eats vegetables.
I 3 go t o the doctor very often when you were young?
I 4 My dad used t o smoke, but he when I was born
I 5 My parents give us medicine when we were sick.
a use t o b used c used t o
a didn't used b didn't use t o
a Did you use t o b You used t o
a used t o stop b stopped c used t o stopped
never didn't use t o b didn't never use to c never used to
c doesn't used t o
c Did you used
L -
°S qVE
£ m ]
T :sJ9Msue i;s9i /(YV
Used to 41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-42-320.jpg)


![Practice
|A Write the short f o r m o f each f u l l f o r m . I f no short f o r m
is possible, put X.
1 I will try yoga. (It
2 Shall we sit down? %
3 We will feel better.
4 Will she like it?
5 That will not be easy.
| 6 Shall I play it again?
7 I will not listen again.
18 Will the course be expensive?
9 I will stop the CD.
10 The instructor will not repeat it.
11 I hope it will be fun
B Read the text and make predictions about Victoria's
new life. Complete t h e sentences w i t h will, '11 or won't.
! Victoria is f r o m Russia. She m o v e d t o V a n c o u v e r
Mast week w i t h h e r p a r e n t s . V i c t o r i a is 13 a n d
she is a g o o d s t u d e n t , b u t s h e d o e s n ' t s p e a k
much English. W h a t d o y o u t h i n k V i c t o r i a ' s n e w
Life in C a n a d a w i l l b e l i k e ?
1 She It learn English very quickly.
2 Victoria like Canadian f o o d .
3 Her friends in Russia write t o her.
4 She forget Russian.
5 The climate be a problem.
6 Her parents worry about her.
7 She feel homesick.
18 Victoria get lost in Vancouver.
9 Her grandmother visit her.
llO Her life be very different.
C Use the phrases in the box and will/'ll t o make decisions.
buy some tomorrow do it t o m o r r o w got my coat
give her some milk have a swim talk t o him
i l I'm cold.
litj e t ituj coat.
2 The baby is hungry.
3 I don't have any eggs.
4 I'm tired.
5 The sea is lovely.
6 There's Tom.
Underline t h e correct o p t i o n .
Paul: W h a t do you think,l
shall/will Sunday be all right
for the picnic?
Sunday z
will/won't be fine for me. But, wait...
Sunday is my dad's birthday.
3
Shall/WillNe have the picnic t o m o r r o w then?
4
Shall/ Will we have enough time t o buy the food?
We s
will /won't need much, just some snacks. M y
mum 6
shall/will probably make something nice.
7
Shalt/ Wilt I call everyone or 8
shall/will you do it?
I 9
7//won't do it, it's no problem.
Great. It l0
shall/will be a lovely picnic.
I just hope i t 1 1
7 / / won't rain.
Sue:
Paul:
Sue:
Paul:
Sue:
Paul:
Sue:
Paul:
I In your n o t e b o o k , w r i t e predictions about t h e f u t u r e
w i t h iv/7/ and won't. Begin each sentence w i t h / [don't]
think, I hope or I'm (not) sure.
1 everyone / speak Chinese
I'm not sure everjone witt speak Chinese.
2 we / live / on Mars
I hope we won't tive on Mars.
3
4
5
6
7
8
robots / do / all the housework
children / drive / t o school
everyone / have / a computer
people / live / until they are 120
I / rich
the w o r l d / be / very different
omul• * •»s
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • * * •
i
i
I 3
I Circle t h e correct o p t i o n .
I 1 I hope my sister this yoga CD.
I a w i l l likes b will liking c will like
I'm sure t i m e t o do yoga,
a she won't has b she won't have
c she won't be have
A: t o our new CD now? B: Yes!
a We shall listen b Shall we listened
c Shall we listen
A: W i l l I be good at yoga?
B: Yes,
a you will b you won't c you do
I think this yoga CD. It's t o o difficult,
a I'll stopped b I'll stop c I stop
I 5
i • • • • • • • < • • • • • • I q s *<v 3£ m 3 i : i J S 3 i A w
Will, shall, won't 45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-46-320.jpg)






![20 Modal verbs: can, could, be able to
How can dogs help us?
r ^ H o w c a n d o g s h e l p u s ? j
D o g s c a n h e a r a n d see m u c h b e t t e r
t h a n h u m a n s . T h e y c a n a l s o s m e l l
m a n y t h i n g s t h a t h u m a n s c a n ' t .
D u r i n g W o r l d W a r I, m a n y soldiers
w e n t b l i n d . Dogs w e r e a b l e t o
l o o k after t h e b l i n d soldiers.
I n W o r l d W a r I I ,
dogs w e r e a b l e
t o s m e l l o r hear
s u r v i v o r s that
p e o p l e c o u l d
n o t f i n d .
Sony's A i b o .
W i l l a r o b o t
ever b e a b l e t o
replace a dog?
W h y are dogs v e r y g o o d a t finding people?
suewnq UEL|; jauaq ipnw ]|aws pue sas 'jeaq UBD Aaqx :J3MSU/
Modal verbs: can, could, be able to
1 Use can t o t a l k about ability.
Dogs can hear and see much better than humans.
2 Can does n o t change. It is t h e same w i t h all subjects.
/ can swim. He can swim. They can swim.
3 Can is f o l l o w e d by a second verb. The second verb is t h e
infinitive w i t h o u t to.
Dogs can hear much better than humans.
N O T They can to hear...
4 The negative o f can is cannot. The short f o r m is
can't. The short f o r m is m o r e c o m m o n , especially in
conversation.
Emily can't swim very well.
statement / negative X
1 / Y o u / H e / S h e /
I t / W e / T h e y can swim.
cannot (can't)
swim.
5 M a k e questions and short answers as f o l l o w s :
question ? short answer / X
1 / you / he / Yes, (he) can.
Can s h e / i t / swim? No, (he) can't.
w e / t h e y
H o w can do;*s help us?
Use could (not) or was / were (not) able to for t h e past.
In World Warn, dogs were able to smell or hear
survivors that people could not find.
Use will be able to for t h e f u t u r e . The negative f o r m o f
t h e f u t u r e is will not be able to o r won't be able to.
A robot will / won't be able to replace a dog.
Will a robot ever be able to replace a dog?
See Unit 21 for can (request).
See Unit 22 for can't (forbid).
5 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-53-320.jpg)

![21 Modals for requests: can, could, may
Could we go on a safari?
e p ]
Write to^lOTand tell him your dreams. For one
lucky winner, your dream will come true!
Dear Jim,
Could we go on a safari in South Africa? We'd really
like to see some real lions. Can our friends come too?
Best wishes, Claudia and Elena (13 years old)
Dear Jim,
May I have a baby sister, please? I have two brothers
but I really want a sister to play with.
Best wishes, Rita (10 years old)
P.S. Please could she have brown hair and brown eyes
like me?
Dear Jim,
Can you send me a model Ferrari? I emailed you last
month but you didn't send it. Could you answer 'yes
or 'no'? (I hope 'yes'.)
Best wishes, Charles (11 years old)
Dear Jim,
Could I work in the circus? I'm still at school but all
my teachers say I am a clown. May I send you a video
clip of myself?
Best wishes, John (123
's years old)
Match each person
t o their request:
1 Claudia
2 Charles
3 John
4 Rita
a a sister
b a holiday
c a car
d ajob
E
17 P£ D
2 I T :J3AASUV
Modals for requests: can, could, may
1 Use can, could and may t o ask f o r s o m e t h i n g politely; can and
could are more c o m m o n t h a n may.
Can you send me a model Ferrari?
Could I have a cake?
May I have a baby sister?
2 Use can and could, but n o t may, t o ask people t o do things.
Could she phone me when she's free?
Can you come here?
W e can use can, could and may w i t h the first
person t o ask for permission. Could is more
polite than can. May is formal. W e usually give
permission w i t h can, or w e can just say Of course
or Sure.
A: Can I leave the room? B: Yes, you can.
A: Could we have some more? B: No, you can't!
A: May I start? B: Of course.
Please + imperative is not very polite.
Please + can / could / may + t h e
infinitive w i t h o u t to is polite.
D o n ' t say Please do it!, say Please can
you do it?
5 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-55-320.jpg)



















![31 So and neither
Neither do I.
chat M.t&£.aO)t boards. contact us litotes
T H E 1 2 3 C H A T R O O M f o r t e e ^ s o ^ L y
SEND US Y O U R C O M M E N T S .
Tell us things you don't need in your life.
[ e m m a ]
[ n i c k o ]
[suzi a n d a b i ]
[ t o d d ]
[ n i c k o ]
[ t o d d ]
[ e m m a ]
[suzi a n d a b i ]
[ e m m a ]
[ t o d d ]
Easy. My b r o t h e r . M a t h s . W i n t e r . M i l k c h o c o l a t e
N e i t h e r d o I. Dark c h o c o l a t e is t h e b e s t .
H e l l o , E m m a ! Y o u ' r e r i g h t . W i n t e r is so b o r i n g .
H i , e v e r y o n e . I t h i n k w i n t e r is OK.
M e t o o . I l o v e snow. A n d t h e r e ' s f o o t b a l l
I'm a M a n c h e s t e r U n i t e d f a n .
So a m I. ©
I h a t e f o o t b a l l . ©
So d o w e . A n d c a b b a g e .
Does a n y o n e l i k e cabbage?
No.
Yuk!
I d o n ' t l i k e i t
So and neither
1 Use so + auxiliary verb + subject t o mean ' t o o ' or 'also'.
A: I'm a Manchester United fan.
B: So am /.'(= I'm a Manchester United fan, too.)
A: I think winter is OK.
B: So do I. (= I think winter is OK, too.)
A: I hate football.
B: So do we. (= We hate football, too.)
2 The negative is neither + auxiliary verb + subject.
A: I don't like it.
B: Neither do I. (= I don't like it either.)
3 Use t h e same auxiliary verb after so or neither as t h e
auxiliary verb in t h e original statement.
A: I am a football fan.
B: So am I.
I've never been to Spain. Neither has my brother.
4 If t h e r e is no auxiliary verb in t h e original statement,
use a f o r m o f do.
A: Nicko likes white chocolate.
B: So does Todd.
A: I hate football.
B: So do we.
5 A f t e r so and neither t h e auxiliary verb comes before the |
subject.
So am I. N O T So I am.
Neither does she. N O T Neither she docs.
6 Instead o f So am I or So do I w e can say Me too. Instead
o f Neither am I or Neither do I w e can say Me neither.
You can pronounce neitherwlth an / a i / or an / i : /
sound. The first is more c o m m o n in Britain, t h e
second in t h e USA.
76](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-77-320.jpg)



![A M a t c h t h e questions about Rosa t o t h e correct answers.
1 Is Rosa beautiful? H
2 W h e n is her birthday? •
3 Has she been t o India? •
4 W h a t does she like? LJ
5 What's she like? •
6 W h y does she speak English well? •
7 W h o likes her? •
8 W h o does she like? •
9 Where does she live? •
10 How is she? •
a She's very nice,
b In February.
c W e all like her. She's very popular,
d Yes, she has.
e Because her dad is f r o m Scotland,
f She likes Brad Pitt. She thinks he's cool,
g She likes horses and dancing,
h Yes, she is.
i Not very well. She feels sick today,
j In the city centre.
B Make questions by p u t t i n g t h e words in t h e correct order.
1 o f / W h a t / like / do I kind / music / you?
What (ana cfmusic a6.JJ.tt tike, ?
2 book / W h o / favourite / w r o t e / your?
?
3 your / are / H o w / parents / old?
?
4 you / d o / c o m p u t e r / W h o s e / use?
6 visited / H o w / have / many / you / countries?
7 eyes / a r e / W h a t / y o u r / c o l o u r ?
5 a r e / f r i e n d s / y o u r / W h a t / like?
8 games / you / H o w / do / often / computer / play?
9 school / H o w / it / t o / take / does / get / long / to?
N o w answer t h e questions f o r yourself.
C C o m p l e t e t h e dialogues, using question tags, short
answers and so or neither.
1 A You're 15, aren't ^<5U. ?
B No, I'lHWt I'm 14.
A Really? 5oami !
2 A You write poems, 3
B No, I write songs.
A D o you? J
3 A You didn't go t o Phil's party, i
B Yes, But I didn't go t o Helen's party.
A Didn't you? !
4 A You can't speak Chinese, i
B Yes, But I can't speak Korean.
A Can't you? !]
5 A You've lived here for eight years, fl
B No, I've lived here for 11 years.
A Have you? 1
6 A You don't like mushrooms, I
B Yes, . B u t I don't like fish.
A Don't you? 1
7 A Your sister is going on holiday t o Peru, ?j
B No, She's going to Chile.
A Is she? my sister!
8 A Your brother has broken his arm, ?
B No, He's broken his leg.
A Has he? my brother!
80](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-81-320.jpg)

![33 Have and have got
Have you got a favourite crocodile?
The Samutprakan Crocodile Farm (Thailand) h a s g o t over
60,000 crocodiles. The farm h a s a zoo, it's g o t a research
centre a n d the shops, of course, h a v e lots of crocodile
souvenirs. M r Utai h a d t h e i d e a of opening the m u s e u m in
1950. He h a d s o m e free t i m e yesterday to answer questions
Question: Does the farm h a v e any unusual crocodiles?
M r Utai: W e ' v e g o t the biggest crocodile in the w o r l d .
Come and see it h a v e b r e a k f a s t t o m o r r o w m o r n i n g !
Question: H a v e y o u g o t any plans for the future?
M r Utai: I'm going to h a v e a crocodile T V show. Crocodiles
h a v e n ' t g o t a good i m a g e . H o l l y w o o d films only s h o w
crocodiles t r y i n g to eat people! We need to h a v e more
information about crocodiles.
Have and have got
1 W e can say have or have got. Have is m o r e c o m m o n .
W e can use have got in conversation, especially in
British English.
The farm has a zoo.
It has got over 60,000 crocodiles.
Does the farm have any unusual crocodiles ?
2 In t h e past and f u t u r e , w e can only use have.
I'm going to have a crocodile TV show.
In 1950 the zoo didn't have many crocodiles.
Did the shop have any crocodile T-shirts yesterday?
3 W e can use have + noun f o r many everyday activities.
Have w i t h activities can be in t h e continuous f o r m .
He didn't have much free time yesterday.
The crocodile is having breakfast.
You can have:
an accident / a break / a rest / a sleep / a cold
tea I coffee; breakfast / lunch / dinner; a sandwich
a chat I a discussion / a talk
fun I a good time / a nice day / a holiday
a shower / a bath / a swim / a run / a walk
4 W e do not use have got in t h e f u t u r e or past. W e use
have instead.
/ had a dog but it died. N O T / had got a dog...
5 M a k e questions and negatives w i t h have using t h e
auxiliary verb do.
Do you have a pen? She doesn't have it.
82
U n d e r l i n e t h e correct
O o p t i o n : M r U t a i eats/
likes/sells crocodiles.
sa>)i] :J9MSUV
statement / negative X
1 / You / W e / have do not (don't) have
They
H e / S h e / I t has does not (doesn't) have
question ? short a n s w e r / X
D o 1 / you / we / they have...?
Yes, (1) do.
No, (1) don't.
Does he / she / it have...? Yes, (he) does.
No, (he) doesn't.
M a k e negative f o r m s of have got w i t h not. M a k e |
questions w i t h Have / Has + subject + got...? j
statement / negative X
1 / You / W e / have (Ve) got have not (haven't) got
They
He / She / It has fs) got has not (hasn't) got
question ? short answer / X
Have 1 / you / we / they got...?
Yes, (1) have. j
No, (1) haven't. I
Has he / s h e / it got...? Yes, (he) has. ?
No, (he) hasn't. j](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-83-320.jpg)



![Prepositional verbs
Think about it!
L o o k a t a menu in a
restaurant in the United
States and you'll find French
fries. But don't a s k f o r
French fries w h e n you go to
France. The French call them
pommes frites which means
'fried potatoes'.
Do you w o r r y a b o u t too
much salt in your diet?
Then listen to t h i s - y o u
need a little salt. Your
body d e p e n d s o n salt for
healthy blood pressure.
T h i n k a b o u t it! Salmon b e l o n g s t o a
group offish which have Omega-3.
Omega-3 helps you think!
W h y is salt g o o d f o r y o u ?
ajnssajd poo]q Aqi|e3L| Jty ij spaau Apoq mo :j3Msuy
Prepositional verbs
1 Prepositional verbs have t w o words. The t w o words are:
verb + preposition.
Think about it!
Don't ask for French fries.
I'm listening to some music.
O t h e r verbs include:
(dis)agree with depend on learn about suffer from
believe in
belong to
come across
consist of
get off
get on
go with
laugh at
look after
look at
look for
pay for
talk about
wait for
worry about
86
Sometimes t h e meaning o f t h e verb + preposition is
very different f r o m t h e meaning o f t h e verb on its own.
/ didn't get many birthday presents.
Get off the bus at the next stop.
Some verbs can be f o l l o w e d by a different preposition
t o give a different meaning.
Look at the menu.
I'm looking for my glasses - have you seen them?
We looked after my neighbour's dog last weekend.
Questions w h i c h begin w i t h a Wh- w o r d and use
prepositional verbs o f t e n finish w i t h t h e preposition.
What are you looking at?
See Units 26 and 27 for more information on forming
questions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-87-320.jpg)





![-38 Verb + -ing or verb + to-infinitive;
like and would like
Learn to speak any language in two weeks!
Do you like travelling? Do you enjoy meeting people? Do you want to communicate with
people easily? Would you like to speak other languages? If your answer is 'yes' to any of
these questions then we have the product for you - SUP6I* Lifl£0!
Learn to speak any language in two weeks
with our new Super Lingo! system. Yes, two
weeks! And thanks to your big vocabulary,
you won't need to carry a dictionary around
with you.
If you decide to try Super Lingo! then
telephone 095 973 2593 or send an email to
i.smith@superlingo.net. We promise to give
your money back if you're not happy.
W e h o p e t o h e a r f r o m y o u s o o n !
O U n d e r l i n e t h e c o r r e c t o p t i o n : Super Lingo! is a dictionary / a study programme / a language school.
rb + -ing or verb + to-infinitive;
e and would like
Some verbs, e.g. enjoy, take another verb w i t h -ing.
I enjoy learning English.
I finished talking.
2 Some verbs, e.g. want, take another verb w i t h to-
infinitive.
/ want to learn English.
I decided to try the course.
3 Some can take either -ing or to-infinitive.
/ like helping people.
OR / like to help people.
O n l y -ing
avoid
enjoy
finish
mind
suggest
O n l y to-infinitive
decide plan
hope promise
intend refuse
learn wait
need want
offer
-ing or to-infinitive
begin
continue
hate
like
love
prefer
start
Very much is an adverb, so it cannot go between
t h e verb and t h e object.
/ like playing tennis very much.
N O T / like very much playing tennis.
• See Unit 56 for more information on the word order of adverbs.
W h e n you learn a new verb, learn w h a t comes
after it.
decide /di'said/
• verb 1 © [I OR T] to choose something, especially after thinking
carefully about several possibilities: They have to decide by next
Friday. O / don't mind which one we have-you decide.
O [+ to INFINITIVE] In the end, we decided to go to the theatre.
Would like (short f o r m : 'd like) is one way o f saying want
or might want. The negative is would not (short form:
wouldn't). Use Would you like + to-infinitive for a polite
invitation.
/ would like to learn Greek one day.
You wouldn't like to be in a strange town without any mo/|
Would you like to come to the cinema with me?
92](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-93-320.jpg)







![r
42 Articles 1
Do you know the answer?
What happened?
R o m e o and J u l i e t a r e in a room. T h e y a r e
in t h e middle o f t h e r o o m , on t h e floor.
T h e y a r e d e a d . N e x t t o t h e m t h e r e is
s o m e g l a s s . T h e g l a s s is b r o k e n . In t h e
r o o m you can also s e e an open w i n d o w . It
isn't a h o t d a y b u t t h e w i n d o w is still o p e n .
H o w did R o m e o a n d J u l i e t d i e ?
O Is t h e r e an a n s w e r t o t h e puzzle?
•AEME UBJ IBD a q i wocu a q i ui auiED puE asiou aqi pjesii
UEW v ]Moq a m a>|Ojq JED ai|j. MopujM a q j LjSnojqi u| BWED JED XjSunij
V IMoq qsq ua>(Ojq B W 0 4 SJ SSE|S 3 i | i qsy ajE laqnf puE oawoy :J3MSUV
Articles 1
1 Articles (a, an or the) go before nouns. Sometimes,
t h e r e is no article before a noun.
/ saw a cat outside.
I gave some fish to the cat.
I like cats.
2 Names o f people and places usually have no article.
Romeo and Juliet lived in Verona.
3 W e don't use articles w h e n w e are t a l k i n g about things
in general w i t h plural or uncountable nouns (e.g. houses,
information).
I like puzzles.
Cats drink milk.
4 W e use a or an w i t h singular countable nouns w h e n w e
are t a l k i n g about only one person or one t h i n g .
Juliet had a brother.
Do you want an apple?
5 Use a or an t o t a l k about w h i c h j o b somebody has.
My mum is an engineer.
Shakespeare was a writer.
6 Use a before a consonant sound (/b/, /t/, /s/, etc.) and an
before a v o w e l sound (/e/, / o / , / u / , etc.).
There is a room.
You can see an open window.
102
h is a consonant, so use a w i t h words which begin
w i t h h in sound and spelling.
It isn't a hot day.
A hungry cat.
You say an hour and an honour because hour /'aus/
and honour /'ona/ start w i t h v o w e l sounds.
Use the before singular and plural countable nouns and
uncountable nouns.
The window is open.
What's the news?
Use the w h e n t h e speaker and listener both know what
is being t a l k e d about.
The glass is broken. (= the glass was mentioned in the
previous sentence)
/ saw the cat. (= the cat we both know)
The bank is closed. (= our bank)
N o t e t h e difference:
/ have an idea. (= but I haven't told
you what it is yet, so you don't know)
/ like the idea. (= we both know which
idea we're talking about)
See Unit 40
for article
use with
countable a
uncountable
nouns.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-103-320.jpg)


![Practice
| Complete the sentences w i t h a, an or the.
1 Do you play tke guitar?
2 It's second house on the left.
3 Esperanto is language.
4 longest river is in Brazil.
5 When I was young I had dog.
6 Wear dress you bought last week.
7 I love sea.
8 That is interesting idea.
Match the pairs.
1 1 can see — ^ a money.
2 Everyone n e e d s — b the money.
3 Turn on a the light.
4 Plants die w i t h o u t b light.
5 The bread a is easy t o make.
6 Bread b is in the kitchen
7 1 want t o study a music.
8 Listen to b the music.
9 Football a is in the car.
10 The football b is a sport.
Make sentences by p u t t i n g t h e words in t h e correct
order. Add a, an or the i f necessary.
1 i n / I / mountains / live
I im in tke mountains.
2 w h e r e / t o m o r r o w / i s / party / ?
3 night / was / it / exciting
4 most / is / beautiful / who / ?
5 animal / is / horse
6 hot / nice / is / m i l k / o n / cold / day
7 c a r / f u l l / i s / p a r k / a g a i n .
8 m u s i c / n e e d / p e o p l e .
D Cross o u t t h e pictures in this story and w r i t e t h e correct
words w i t h a, an, the or - (= no article).
tke^uitar «*]
Billy wanted t o play r
~V*ji^ — because he loved 2
J 4 .
But there was a problem. He had no money t o buy one.
He lived near a big forest and every day he walked in
3
and dreamed about a guitar. One day Billy sat
u n d e r 4
a n d listened to .They sang
beautifully. B | was shining. Billy was thinking.
'Guitars are made o f ' . I can make 8
}JJ~' "!' He
walked back t o 9
^0^, went home and g o t 1 0
,-ff^^ and
some string. He went back to !
. Billy made his
guitar. The birds sang and Billy played. He was happy now.
^ m ^ o u n T o t ^ ^ w i t h a, an,
the or - (= no article) and t h e noun.
1 W h a t is a carrot? r) vegetable.
2 W h a t musical instrument would you like t o play?
3 W h e r e can you swim in salt water?
4 W h a t do you put in coffee?
5 W h a t was the Titanic?
6 W h a t object can you see in the sky at night?
7 W h a t plastic thing can you use in a shop?
8 M o n e y cannot buy...?
Circle the correct o p t i o n .
1 I'm sorry. I've broken your Stratocaster. I was playing music on the beach and it fell in sea.
2 most expensive Stratocaster costs about $12,000. a A b An c The
3 I usually play , but sometimes I play it for money.
a guitar for the fun b the guitar for a fun c the guitar for fun
4 My friend has just bought old guitar. It's 4 0 years old and it sounds fantastic. a an b the c
5 Who invented electric guitar? a an b the c -
— — — — — 1
I
a a b the c - |
qS e-fc. D£ JZ q i :SJ9MSUE iJsaj. ^W
A r t i c l e s 2 105](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-106-320.jpg)


![44 This, that, these, those
This is me.
tftllo - I'kvt A.v^usVou.vu> av^d I live i-kv
£}haiA,a.
These children are studying at school
we leam, Kas.ev^a^a^[zaM, ov^e of
the languages of Cyhav^a, avuX also
e^ujllsh at school.
This is kvte fit home. Whet^ I grow up,
I wai/vtto be a photographer. I'd lltee to
take photos of the people av^d children
Lwv w.y country. TViat's ncy dream.
I live lev the kvorth of
cjmav^a where It's very
dry. But yvot all of the
country Is dry. This
photo Is of the port of
Accra, av^d those are
fishing boats.
True
This, that, these, those
1 Use this or that w i t h a singular noun.
th/'s photo, that girl
2 Use these or those w i t h a plural noun.
these friends, those hills
3 W e usually use this or these f o r people and things
which are near.
This photo is of the port of Accra.
Are these your children?
4 W e usually use that or those for people and things
which are not near:
Who's that girl over there?
Those are fishing boats.
5 Use this for things which are happening n o w or w i l l
soon happen.
This TV programme is really interesting. (= the TV
programme I am watching now)
You'll laugh when you hear this story. (= the story I am
about to tell you)
O n t h e phone, w e usually use this is t o say w h o
is speaking.
Hello. This is Fatima.
o r False? A n u s i b u n o speaks English as her first language.
•]Ooips b L|S!]8ug sujea| ai|s '!ue>|ueueuase>| steads aqs as|ej
6 Use that for things which happened in t h e past or have
j u s t finished.
That was a great holiday.
What was that noise?
7 Use that t o say more about something t h a t someone
has j u s t said.
/ want to be a photographer. That's my dream.
A: She wants to be a photographer.
B: Really? I didn't know that.
8 W e can also use this, that, these and those on their own.
This is me. (= This person in the photo is me.)
These are my friends. (= These people in the photo are
my friends.)
Who's that?(= Who's that person in the photo?)
The short f o r m o f that is = that's. This is, these
are and those are do not have short forms.
108](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-109-320.jpg)

![45
Some, any, no, none
There are no trains or buses.
Do you have any plans for
your vacation? None?
Good, then ...
V i s i t K n o y d a r t !
Knoydart is a beautiful place in Scotland. It's
perfect for a holiday. You won't find any pollution
in Knoydart and there are no cars. There are some
boats to Knoydart but none of them carry cars. Don't
worry, there are some roads but you'll have plenty
of exercise because there are no trains or buses!
Knoydart has a post office, a school and some small
hotels. The hotels are very nice but none of them are
very big and some are only open in summer. Do you
have any questions? The website at the bottom of the
page has some useful information.
U n d e r l i n e t h e c o r r e c t o p t i o n : K n o y d a r t is a g o o d place for
p e o p l e w h o like: quiet holidays/driving/big luxury hotels.
Some, any, no, none
1 Use some and any t o t a l k
about a l i m i t e d q u a n t i t y
o f something. Use not...
any, no and none w h e n
there is nothing t h e r e .
You can see some birds.
The beach doesn't have any cafes.
There are no tourists.
Are there any people swimming? No, none.
Use some and any w i t h countable plural nouns and
uncountable nouns.
Some people like quiet holidays, (people = plural noun)
Do you have any news?(news = uncountable)
/ need some information, (information = uncountable)
See Unit 40 for countable and uncountable nouns.
W e o f t e n use some in statements.
Knoydart has some roads.
W e usually use any in negative sentences. W e also use
any in questions instead o f some.
There isn't any pollution.
Do you want any milk with your coffee ? 10
sAep!]oi| iamb :J3MSUV
W e can use some in questions when we expect the answeij
'yes', especially for offers, requests and suggestions.
Do you have some good ideas? I'm sure you do!
Would you like some help? (offer)
Can I have some sugar?(request)
Shall I take some photos?(suggestion)
W e can use any in statements t o mean 'it doesn't matter|
w h i c h one'.
Use any colour.
W e can use some and any w i t h o u t a f o l l o w i n g noun whej
it is clear w h a t some and any are referring t o .
There are hotels but some are only open in summer.
We have time for some questions. Do you have any?
Use no w i t h countable plural nouns and uncountable
nouns. No is o f t e n more emphatic than not any.
There are no trains.
None = not any.
/ wanted some water but there was none.
W e can use o f after some, any and none, before the or a |
pronoun.
/ read some of the website.
Do any of you speak English?
... none of them are very big.
110](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-111-320.jpg)


![Practice
A Match t h e sentence beginnings t o t h e correct endings. D W r i t e sentences which mean t h e opposite.
1 Anything that can go wrong,
2 Worrying
3 Try something
4 Nothing
5 If you have hope,
6 Nobody's
7 Everyone needs
B Underline t h e correct o p t i o n .
a someone t o talk to.
b lasts forever,
c perfect,
^ d will go wrong,
e won't help anyone,
f new today,
g you have everything
1 Let's go somewhere /everywhere special.
2 She doesn't have anything/nothing nice t o wear.
3 I think there's something/anything strange about him.
4 I have nothing/anything new t o read.
5 Look in the fridge i f you're hungry. You can have
anything/something you want.
6 This music is boring - I want t o listen t o something/
everything different.
7 I've met someone/anyone special.
8 Everybody/Everything loves a good story.
C Complete t h e sentences w i t h an appropriate p r o n o u n .
Sometimes t h e r e is m o r e t h a n one right answer.
1 A: Have you seen the dog?
B: No, I've looked everywhere
2 I've got in my eye.
3 You must come t o the party - is
going t o be there.
4 There's at the door.
5 Has seen my watch?
6 My cousin is very shy - she never says
I
7 I need t o buy f o r dinner.
8 Can come t o the party or do you
need a ticket?
9 She lives in France.
1 She doesn't have anywhere t o live.
Sde das somewhere to live,
2 I could see no one.
3 I told the police officer everything.
4 The woman t o l d me something interesting.
5 Everyone is happy.
6 Nobody knows.
7 There was nothing unusual about her.
8 He hasn't been anywhere.
1 K)o One knows the answer.
2 There's in the garden.
3 says it's true.
4 I can't see him
5 D o and will happen.
6 loves a happy ending.
7 is always right.
pUffl. _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Circle the correct o p t i o n . |
1 Please tell me about your family. a something b anywhere c everyone
2 A: What do you want f o r your birthday? B: I don't mind. I'll be happy w i t h something small.
a Everything b Anything c Something
3 I didn't know at the party, so I went home again. a nobody b anybody c no one
4 mistakes. a Everyone makes b Anybody make c Everybody make
5 A: I can't find my keys B: Where have you looked? A: Everywhere. a somewhere b anything c anywhere I
]
S E
t? <K m E
T :sJ3Msue u s a i X w
Something, everywhere, nobody, anyone 113](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-114-320.jpg)
![r
47 Much, many, a lot of, a little, a few
A lot of fun!
- o.-
D o t o u r i s t s at Port Stephens
• usually see d o l p h i n s ?
•u!i)d]op e aas },uop
not, ajai^M sduj Aueiu JOU aje ajam sax IJBMSU v
The Eco-Blog
Read what our eco-tourists say about travelling in Australia.
A lot of fun! by Kelly, 24t h
October
I ve been on dolphin-watching trips before and often you only get a little time with the dolphins
... but this was different. Port Stephens on the coast of New South Wales is the perfect place to
watch dolphins. I saw lots of dolphins jumping over the waves ... fantastic!
There are not many trips where you don't see a dolphin. But if you are unlucky and only see a
dolphin for a few moments, the captain will give you a free ticket for another trip.
And the best thing is - it doesn't cost much. What are you waiting for? Buy your ticket today!
Much, many, a lot of, a little, a few
many, a lot of,
lots o f
some not many, a f e w
m > ^ J 8 p
much, a lot of, some not much, a little
lots o f
Use much w i t h singular uncountable nouns and many
w i t h plural countable nouns.
We do not have much time.
There are not many trips.
Use a lot of or lots o f w i t h b o t h singular uncountable
nouns and plural countable nouns.
It was a lot of I lots of fun.
I saw a lot of I lots of dolphins.
W e use a lot of or lots of in statements and negative
sentences and in questions.
There is a lot of marine life in the Port Stephens bay area.
Not a lot of tourists know this place.
Are there a lot of different types of dolphin?
4 W e usually use much and many in negative sentences
and questions.
We do not have much time.
Are there many dolphins in the Port Stephens bay area?
5 W e don't usually use much in statements - w e prefer a
lot of or lots of
It was a lot of fun! N O T It was much fun!
6 W e sometimes use many in f o r m a l statements.
Scientists have discovered that many female dolphins
live in groups of six or eight animals.
7 A lot of or lots of are more c o m m o n in informal
statements.
/ saw lots of dolphins jumping over the waves.
8 Use a little w i t h singular uncountable nouns and a few
w i t h plural nouns.
You only get a little time with the dolphins.
You only see a dolphin for a few moments.
You can leave o u t t h e noun after much, many, a
little, a few, a lot of and lots of.
It doesn't cost much. (= It doesn't cost much money.)
How much time do we have? Only a little. (= Only a
little time.)
It doesn't cost a lot. (= It doesn't cost a lot o f money.)
How much money do we have?Lots!
114](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-115-320.jpg)
![Practice
A Complete the sentences w i t h much or many.
1 There aren't Mty days before the exam.
2 Not snow has fallen in the Alps this
winter.
3 people are surprised when they first
seethe dolphins.
4 Do the boys have homework tonight?
5 Did children come t o the party?
6 There won't be hotel rooms at this
time of year.
7 Do you eat meat?
8 Did you get presents for your
birthday?
9 Maria didn't give me good advice.
I 10 There are different plants, animals and
insects in the rainforest.
B Complete each o f these sentences in t w o different
ways, using phrases f r o m t h e box and appropriate
forms of the verb.
C C o m p l e t e t h e blog using a lot of, lots of, much, many, a
little or a few.
love
knowledge
arguments
a little bad marks
a few salt in your f o o d
sweets
rain
days off
1 f) tittle rain is
f] few <%» off are }a good thing.
j n o t bad for you.
j b e t t e r t h a n none.
|nothing t o worry about.
Kuranda Train and Skyrail, Australia
by Ido, 4 t h
July
This is a great day trip. Take the
train through the mountains
and come back by Skyrail.
The train trip was beautiful - we
went p a s t 1
a tot of waterfalls and through
2
tunnels! We wanted to see the traditional
markets at Kuranda, but there weren't
good shops - just shops selling tourist souvenirs - so you
won't need'' money.
hours in town should be enough for
most people. You can visit the Butterfly Sanctuary - if you
want to - but there are 6
butterflies
flying around you for free!
You don't need 7
time to get to the
Skyrail. Skyrail is a cable car that travels only
metres above the top of the
rainforest. Unfortunately we only had 9
time. I wanted to stay all day!
MY TURK!
^ ^ n s v v e ^ t h ^ ^ using a lot, not
much, some, only a little, not many or only a few.
1 H o w much time do you spend on your homework
every evenmgr AM
2 H o w much time do you spend watching TV every
week?
3 H o w many plants do you know the names of?
4 H o w many different butterflies do you know?
5 H o w much money do you have in your pocket?
6 H o w many hours' sleep did you have last night?
7 H o w much snow was there last winter?
8 H o w many times have you been on a plane?
1
Circle the correct o p t i o n .
1 We travelled around Australia w i t h friends. There were about six o f us. a a little b a few c much
2 We didn't have time in Port Stephens - only a f e w days. a many b a lot c much
3 W e h a d a free time at the end o f our trip, so we did some shopping. a few b lot c little
4 A: Did you see other animals? B: Yes, lots. a many b much c a lot
5 A: How much did it cost t o fly t o Australia? B: It was very expensive. a Much b A lot o f c A l o t
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — _ _ J
D£ Bf7 3£ 1Z q i :SJBMSUE jjsaj_Xw
Much, many, a lot of, a little, a few 115](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-116-320.jpg)


![M y name is Joe. I live in Philadelphia
in t h e U n i t e d S t a t e s . I work in m y
f a t h e r ' s
M y g r e a t - g r a n d f a t h e r , Emilio, came
here f r o m Italy in 1 9 0 2 . Emilio's b r o t h e r
arrived two y e a r s later. A t f i r s t , my great-
g r a n d m o t h e r , Rosa, did n o t w a n t t o leave
her p a r e n t s ' h o m e in Italy. B u t she loved
g e t t i n g m y g r e a t - g r a n d f a t h e r ' s l e t t e r s ,
a n d finally she decided t o come. She came
in 1 9 0 5 w i t h their young children. The
f a m i l y w a s happy to be together again.
The family had little money. Emilio's first
j o b s were selling f r u i t a n d building roads.
They worked very hard to save money, and
in 1 9 1 5 t h e y bought their first little home.
They were happy t h a t t h e i r children's
f u t u r e w a s more certain.
49
Possessive's
My great-grandfather's letters
I f
Possessive's
1 A d d ' s t o a singular noun t o mean 'belongs to'.
my father's bakery
Emilio's brother
2 A f t e r a plural noun which ends in -s, j u s t a d d ' .
her parents' home
3 Add's t o irregular plural nouns (which do not end
in -s).
their children's future
4 W e can use's w i t h o u t a f o l l o w i n g noun, f o r
example w h e n w e answer questions w i t h Whose?
A: Whose bakery is it ? B: It's my father's.
• See Units 26 and 50 for Whose?
•X]EJ| LUO4 3WED SJU3JEdpUEj8-}B3J§
s|q )nq 'sajEis paijun aq; woy S| aof :ja/wsuv
W e o f t e n use's w i t h o u t a noun t o talk about
shops, businesses or someone's house
My aunt stayed at Rosa's. (= Rosa's house)
We had a great pizza at Mario's. (= Mario's restaurant)
5 W h e n t h e r e are t w o nouns, w e usually add's t o the
second noun.
It's my mother and father's bakery. (The bakery belongs
t o both my mother and father.)
s can mean:
1 possessive: Emilio's letters
2 is: he's poor
3 has: he's worked (he has worked)
6 W h e n a name ends in's w e still add's.
Lois's house.
118](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-119-320.jpg)












![Practice
A Complete the quiz questions using comparative f o r m s o f
the adjectives in brackets. T h e n underline t h e answers.
1 Which are higher : the Carpathians or the
Rocky Mountains? (high)
2 Which month is : February or March? (long)
1 3 Which is :
driving or flying? (dangerous)
4 Which is : 'I want the bread.' or
'Can you give me the bread?'(polite)
5 Which is : gold or silver? (rare)
6 Which is : one mile or one kilometre? (far)
7 Which city is :
Tokyo or Seoul? (expensive)
8 Which town is : Moscow or Madrid? (old)
9 Who was when he died: Mozart
or Shakespeare? (young)
10 Which is : a kilogram o f water or a
kilogram o f ice? (heavy)
Now check your answers a t t h e bottom o f t h e page.
B Use the information f r o m Exercise A t o complete t h e s e
sentences using less than or not as... as.
1 February is net as toruj as March
I 2 Flying
I 3 Silver
4 One kilometre
I 5 Seoul
I 6 Moscow
C Complete t h e sentences about t h e t w o hotels, using t h e
information in t h e table and t h e adjectives in t h e box.
Seaview Pushkin
1 Atmosphere © © © © ©
2 Management ©@© ©@©
3 Price per day 100 euros 70 euros
4 Size 6 7 rooms 6 7 rooms
5 Distance from the
beach
4 0 0 m 15 minute walk
6 Service ©© ©@©
7 Food © @ © © © © ©
8 Check-out time 11.00 12.00
bad big expensive far good
good interesting late n k e
1 The atmosphere at Pushkin is wcer
2 The management at Seaview is as^OCa" as
the management at Pushkin.
3 Seaview is 3 0 euros
4 Pushkin is Seaview.
5 Pushkin is from the beach.
6 T h e service at Pushkin is than at Seaview.
7 The food at Seaview is than at Pushkin.
8 T h e check-out time at Pushkin is
/ comparing t h e 1
If n r n hit and
In y o u r notebook, w r i t e sentences
animals. U s e much, far, a lot, a little or a bit and
comparative adjectives.
E x a m p l e : The^iraf(e is mu-ch tatter than the zebra,
Circle t h e correct option.
1 The beach in Sochi was the beach in my town,
a nicer than b nicer then c more nice than
2 T h e mountains in Sochi are a little than the
mountains in my country.
a bigger b biger c more big
3 This hotel used t o be very bad, but now it's
a very better b much better c much more good
4 D o you think the winter Olympics are as the
summer Olympics?
a more interesting b as interesting
c as much interesting
5 I'm much than I was a f e w years ago.
a less healthier b not as healthy c less healthy
3
S qt" q£ E
? E
I : S J 3 M S U B j i s a i A y v
j3wi?s aqi 9JE mog 01 JJezoyv 6 PMPE
W 8 3||wauo9
p]0§ 5 ^peajq am aA|3 noX uB3 ^ SujAupf Lpjew Z
isja/wsue v asp-iaxg
C o m p a r a t i v e s 131](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-132-320.jpg)



![5 7
Comparative and superlative adverbs
Which will fall faster?
Which w i l l fall f a s t e r : a ball
' of paper or a ball of wood?
Many people think that light objects always fall
m o r e s l o w l y . But - remember Galileo - if t h e balls
are t h e same size they w i l l hit t h e ground a t t h e
same t i m e .
iQ In a storm w e see t h e lightning before
w e hear t h e t h u n d e r . Why?
Because light travels
m o r e q u i c k l y than sound.
Which runs most q u i c k l y : an ostrich,
an e m u or a 100-metre runner?
An ostrich runs most q u i c k l y a t
around 56 km an hour. An e m u runs a t
about 48 km an hour and a 100-metre
runner at about 32 km an hour.
Which jumps f u r t h e s t : a kangaroo,
a frog or a flea?
A kangaroo jumps f u r t h e s t - aboutfl
metres. But t h e flea jumps best. It J
jumps 200 times its own body length]
Kangaroo
Runner
V U n d e r l i n e t h e correct o p t i o n . A k a n g a r o o can j u m p 9 metres / 32 metres / 200 metres.
Comparative and superlative adverbs
1 A d d more or less t o m a k e t h e comparative f o r m o f most
adverbs.
Light travels more quickly than sound.
Light objects do not fall less quickly.
2 A d d most or least t o m a k e t h e superlative f o r m o f most
adverbs.
Which runs most quickly?
Which runs least quickly?
3 M a n y short adverbs, such as early, fast, hard, high, late, long
and soon have comparative f o r m s w i t h -er and superlative
forms w i t h -est.
early -> earlier -» earliest, fast -> faster -> fastest
early -> less early -» least early, fast •+ less fast least fast
4 Some c o m m o n adverbs have irregular comparative
and superlative f o r m s .
well-> better-* best
badly -> worse -> worst
far •+ farther / further -> farthest / furthest
5 U s e as + adverb + as w h e n t w o or more people or
things are equal.
/ work as hard as you.
• See Units 54 and 55 for comparative and superlative
forms of adjectives.
• See Unit 56 for more information on forming adverbs.
136](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-137-320.jpg)








![61 Prepositions of place
I've left my keys at home.
Hi Chris! I'm at work, but I've left my keys at home. Could you
bring them?
O f course. Where are they?
I think they're in my room. They're probably in front of you - on
the table. I usually put them next to the photos.
No, they're not there.
Can you see the flowers in the corner?
Yes...
Maybe they're behind them ... or under some books?
Just a minute... there's somebody at the door... Hello, Jess?
The postman found your keys. You left them in the door!
u i a m spuLj ueuj^sod s^a>( jaij jso| seq ssaf :sj3Msuy
Prepositions of place
1 W e use prepositions o f place in front o f a noun or a pronoun to say where
something or someone is.
on the table, under some books, in front of you, next to that, at home
2 Some prepositions of place are in, at and on.
JjJ^^ m t
^ie
b°x
at the door on the table
Use in to say something is inside a
larger space.
in the box, in the city, in my study
Use at with a place or a point.
at the station, at work, at the door
3 Note the following uses of the prepositions at, in and on:
The shop is at 42 Culver Road,
(at = point)
The shop is in Culver Road, (in
= inside a larger space)
at
in
on
+ place: A: Where's Jo ? B: He's at the doctor's.
the top/the bottom (of): Look at the exercise at the top of the page.
the end (of): The post office is at the end of the street.
+ city / country: They live in Paris.
a taxi/the car: Let's go to the station in a taxi/in the car.
the north/the south/the east/the west: They live in the west of the country.
the corner: Let's sit in the corner.
the centre: There are a lot of shops in the centre of the town.
the top / bottom shelf: The present's on the top shelf of the cupboard.
the bus/plane/train: The passengers are on the train.
the ground/ first/second/top floor: His apartment is on the first floor.
the left/the right: It's the second door on the left.
TV: There's a good programme on TV tonight.
4 W e don't use the after the
preposition in some expressions.
at home, at school, at college,
in bed
5 Some more prepositions of
place are: under, above, below,
opposite, in front of, behind, next
to, between, outside, near, by
and inside.
under the books
above the clouds
below the clouds
opposite the house
in front of him
behind him
next to the photos
between the houses,
in I inside the house]
146
"-near / by tne house
outside the house-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-147-320.jpg)



![$3 Prepositions of movement
Get off the boat and swim to the island.
'ake .he road b e . w e T „ T „ ° " ' ° f t h e
^ ™ >
oyer t h e - J r C X T W a
" < ' " ,
" * ™ d
-
Vou w i „ come . 0 a b £ ^ G T ' W
° S m a 1
' h
° U S
« -
and got r i r 0 1 1 g l l l h e » tree. Open t h e d o o r
* n e . There is theI r e a s u r e T a k e i M L
° ° k
" n d e
" big
^ . 8 e , o „ , b e b o a , a n ; g o T
t n : : ^ * *
Underline the correct option: O n the island you will n o t see a forest / mountains / houses / pirates.
Prepositions of movement
1 /nto, through, etc. are prepositions o f movement.
They show where somebody or something is going.
Walk into the forest
Go through the door.
More prepositions o f movement:
across Walk across the bridge.
along She's driving along the road.
between The mouse ran between two chairs.
by You will pass by some shops.
down Jill fell down the hill.
from Has Max come back from London ?
in Jump in the water!
off Get off the horse carefully.
on Spider-Man climbed on the wall.
onto We got onto the ship.
out of 1 walked out of the disco.
over They ran over a big hill.
past You will go past Jim's house.
round (= around] The plane flew round the town twice.
towards The dog came towards me.
to Throw the ball to Simon.
under Go under the apple trees.
up Walk up Oxford Street for 10 minutes.
2 Some of these prepositions can also show position, not
movement.
Walk under the bridge.
She's under the bridge.
• See Unit 61 for prepositions of place.
Don't use to after arrive. Use arrive before at (places)
or in (very big places, e.g. cities, countries).
When you arrive at the hotel,... N O T . . . to the hotel...
I arrived in Paris. N O T . . . to Paris.
Use to after verbs o f movement like go, walk, come, fly
and travel.
Don't go to the island.
Don't use to after visit.
I visited my brother. N O T / visited to my brother.
Don't use to before home.
Run home! N O T Run to home!
Don't use go + to + an -ing word.
Use by to show how you travel.
Go by train.
It is faster by plane.
Use get on / onto and off with trains, buses, planes,
bikes, boats and animals.
Get on your bike.
Get off the boat.
Use get in / into and out ofwith cars (and small boats
and small planes).
/ got into my Mercedes.
Get out of my taxi!
150](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-151-320.jpg)





![65 Zero and first conditionals
If you study chemistry, you'll never stop learning.
Thinking About Your Future - Why Study Chemistry?
Chemistry is a good
subject to study if you
are thinking about
your future. You'll
be able to choose
from a lot of different
jobs if you have
a qualification in
chemistry. Maybe you
want to find some new
medicine, or solutions
to pollution . . .
If you study chemistry, you will understand how
many everyday things work. For example, if you cut
an onion, it makes you cry. But did you know this is
a chemical reaction? There is sulphur in onions which
turns to sulphuric acid in your eyes. If you cut the
onion under water, the sulphur reacts with the water
and not your eyes.
If you study chemistry, you'll never stop learning.
Find one reason w h y it is a good idea to study chemistry.
•Smuiea] dois . 1 8 A 8 U ll.nox >|JOM sSujqj XepAjaAa Xuew
Moq p u E } S j a p u n | ] | M ro sqofiua.ia.mp_jo } 0 | e ja§ oj ajqe aq ]no M S M S U V
Zero and first conditionals
1 Use the zero conditional to talk about things that are generally true.
If you cut an onion, it makes you cry.
2 In zero conditional sentences, use if + present tense... present tense.
If you cut the onion under water, the sulphur reacts with the water.
3 Use the first conditional to talk about something that we think is
possible in the future, and its result.
If I see Jack tomorrow, I'll talk to him about the problem.
4 The basic pattern for first conditional sentences is: if + present tense
... will + infinitive without to.
If you study chemistry, you'll never stop learning.
Both parts of a first conditional sentence talk about the future,
even though a present tense is used after if. W e do not usually
use iv/7/ after if.
If you study chemistry next year, you will learn how lots of things
work. N O T If you will study chemistry next year,...
5 Use might or could in the main part of the
sentence to indicate that something is
possible and not certain.
If you have a qualification in chemistry,
you might get a good job.
You could work with antibiotics if you are
interested in this.
• See Units 20,21 and 24 for more information
on could and might.
6 W h e n if comes at the beginning of the
sentence, we need a comma in the middle.
If you cut an onion, it makes you cry.
Chemistry is a good subject to study if you
are thinking about your future.
7 W e can use unless to mean if... not.
I run every morning if it isn't cold.
O R / run every morning unless it's cold.
That plant will die if you don't water it.
O R That plant wilt die unless you water it.
156](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-157-320.jpg)





![$7 Reported speech
She said she would never have a party again.
Sophie Brown's 18th birthday party was really bad. A radio station told listeners that
there was going to be a party the next day, so many teenagers thought the party
was open to everyone. The teenagers caused 30,000 euros of damage to the Browns'
expensive house. One teenager said he didn't know Sophie but he liked parties.
Sophie said that she felt terrible and that she would never have another party
again. Her father told reporters that he was thinking of getting the radio station
to pay for the damage. Sophie's mother said she couldn't understand why the
teenagers wanted to damage their lovely house. We tried to talk to Sophie again today
but her father says she is not talking to reporters any more.
Reported speech
1 We can talk about what people said or thought by using reported speech.
Sophie said that she wanted a party.
2 If the verb of saying or thinking is in the present, there is no change of
tense for the words reported.
Her father says that she is ill.
3 When the verb of saying or thinking is in the past,
the verb in the reported speech usually moves
into the past.
Sophie told her mum she was sorry.
direct speech reported speech
present simple ]• past simple
'It seems strange.' He thought that it seemed strange.
present continuous ]• past continuous
'1 am staying for a few days.' She said that she was staying for a few days.
can 1• could
'We can swim very well.' They said that they could swim very well.
will i• would
'It will be great!' She thought that it would be great.
Used to and would do not change in reported speech.
/ used to be Sophie's friend. -*
She said she used to be Sophie's friend.
How old was Sophie? •
9X jaMSuy
The verb in the reported speech does
not need to change if the information
is still true or relevant now.
Sophie told me that she is 18.
That often links the verb of saying or
thinking to the reported speech. That
can be left out, especially in speaking
and informal language.
She said that she wanted a big party. /
She said she wanted a big party.
Pronouns and time and place
expressions may change in reported
speech.
we -* they
now -* then
next week -* the week after
this morning -* that morning
tomorrow -* the next day
here -* there
John: 7 love parties.'-*
John said he loved parties.
'There will be a party tomorrow.'-*
A radio station told listeners that
there would be a party the next day.
See Unit 68 for more information on say
and tell.
162](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-163-320.jpg)
![P r a c t i c e
A Change these sentences from reported speech into direct speech.
1 Jim said he was tired.
Jim: I nvtired.'
2 Cathy said she wanted to go to Sophie's party.
Cathy:
3 Jim said he didn't know Sophie.
Jim:
4 Cathy told Jim that Sophie was having a party the next day.
Cathy:
5 Cathy also said that everyone was invited to the party.
Cathy:
6 Jim said that he was surprised that everyone was going.
Jim:
7 Cathy said that it would be great if they went together.
Cathy:
8 Jim told Cathy that he would think about it.
Jim:
B Report what the people are saying or thinking. Begin each
sentence with He / She / They said / thought.
i f^> ^T^i 7 7. f l have a lot of
1 'Its my ball!] 2 ^ 3 J w o r k t o d o
I need
"<gj> ^ f?fM
<
I'm not answering
your question!
1 f(e said it was (vis bait.
2
3
4
5
6
C Complete each sentence b so that it means the
same as sentence a in reported speech. Use no
more than three words.
1 a John: 'I come from a small town in New
Zealand.'
b John said that de came
from a small town in New Zealand.
2 a Felicity:'I need it this morning.'
b Felicity said she morning.
3 a John: 'We have a lot to do.'
b John told her a lot to do.
4 a Alice:'! am busy now.'
b Alice said that she
5 a Olive: 'Gary, I'll go next week.'
b Olive told Gary that she would
after.
6 a Mike:'I'll phone tomorrow.'
b Mike said he would phone
MV T U R N !
It was the morning after Sophie's party. Mr and
Mrs Brown came home and found the house in
a mess. What did they think and say? Write six
sentences in reported speech in your notebook.
Example: Mr Srswrv thought de was fiaviruj
a bad dream..
• • • • • * • • • • • •
" ""-•-fiMMfr"'"
• •••••••••••
Circle the correct option.
1 'I like big parties': Sophie says she big parties. a likes b would like c liked
2 'Sophie will be 18 tomorrow': The radio station said that Sophie 18 the next day. a was b would be
3 'You can't have a party next year': Mr Brown told Sophie that she have a party the next year.
a won't b can't c couldn't
4 'Sophie's helping to clean our house': Mrs Brown said that Sophie to clean their house.
a is helping b helped c was helping
5 'I'll come to your party tomorrow': Sophie's friend said she'd go to her party
a tomorrow b this day c the next day
c will be
og a^- D£ qz EX : S J S M S U E
i l S 3
l ^ W
Reported speech 163](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-164-320.jpg)







![Practice
A Match the pairs.
1 I sat down
2 I ran five km,-
3 I want to go out
4 It's Monday
5 Did you finish the test
6 Did you fail the test
7 Sarah looks older
8 I know Sarah
9 We can go for a meal
10 I don't have much time
a so I was tired,
b because I was tired.
a and it's raining again,
b but it's raining again.
a and did you pass?
b or did you pass?
a but she is in the same
class as me.
b because she is in the
same class as me.
a but we can have a coffee,
b or we can have a coffee.
B Complete the sentences using and, so, but, or, because.
1 It's very late, S O g o to bed.
2 Please come visit us in the summer.
3 Do you want to stay here do you need to
get home?
4 It's a big house my bedroom is small.
5 We're ready, let's go.
6 John finished university got a job.
7 Lucy was happy she got a present.
8 We can watch it at the cinema buy the
DVD You choose.
C Join each pair of sentences using linking words and write
them in your notebook.
1 Sally went to bed. She felt tired.
Salty went to bid because she felt tired.
Felix is friendly. His sister is really nice.
My dictionary is very small. The word isn't in it.
The party was OK. I felt a bit bored.
Have you been to Italy before? Is this your first time here?
I opened the bag. I saw the money.
Trevor can't sleep. He drank a lot of coffee.
We heard a strange noise. I phoned the police.
D Join some of the sentences in this story using
linking words.
so^joa
This is an interesting storyPVeu will like it. Shen-Nung
was an Emperor. He lived in China. One day he went
into the garden. He sat under a tree. It was a beautiful
day. It was too hot. It was too dry. Shen-Nung was
thirsty. He asked for a drink. Shen-Nung could drink
something cold. He could have a cup of hot water. The
Emperor chose hot water. It was his usual afternoon
drink. He waited. The servant brought the hot water.
Shen-Nung closed his eyes. He felt tired. He felt
sleepy. Some leaves fell from the tree. They went into
his cup of water. Shen-Nung woke up. He took his
cup. He drank the tea. He didn't notice the leaves. The
new drink was unusual. The new drink was very tasty.
He made another cup of hot water with leaves. Shen-
Nung is now famous. He invented tea.
Copy these sentences into your notebook and
complete them using and, or, so, but and because.
At the weekends I JO sdoppiruj or see nuj friends
This morning I got up
I like the place where I live
4 is difficult for me
5 When I leave school I might or
1
2
3
6 made me angry
7 I want or
my birthday.
English is important for me
Pollution is a problem
for
8
9
10 Two things I need for happiness are
1ES1!
I Circle the correct option.
| 1 Some people say you can easily see the Great Wall from the moon, it's not true. but
2 You can't see the Wall from the moon it's only 9 metres wide. a and b so
3 Some people use the Wall's stones for building, parts of the Wall are broken.
4 I want to goto China to visit Beijing visit the Great Wall. a because b and
5 Nobody wanted to destroy the Wall build a road. a or b but c so
a or b
c because
a and b but
c so
c so
c so
_ _ _ _ _ _ J
B
S W 3
£ J
Z q i : S J S M S U E j } S 3 ] _ Aw
• » • • • I • • • • • I
Linking words: and, but, or, so, because 171](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-172-320.jpg)



![Practice
A Underline the correct word.
1 There are two nice cakes. Both /Neither are delicious.
2 Either/Both Russia and Korea are next to China.
3 A: Do you want an apple or a banana?
B: Both/Neither. I'm not hungry.
4 We saw both/both of them at the station.
5 I'm not busy on Monday and Tuesday. Either/Neither day is
good to meet.
6 We didn't pass the exam, so either of/neither of us is happy.
7 I have a sister. We both/neither like football.
8 My computer is slow. It's either/neither broken or it's very old.
B In your notebook, compare Lyra and Roger using Both/Neither
of them... and Both/Neither Lyra and/nor Roger....
Lyra Roger
1 Where do you come from? Oxford Oxford
2 Do you like Oxford? No No
3 Can you use a compass? No No
4 Do you feel afraid? Yes Yes
5 Have you been to the North? No No
6 Would you like a map? Yes Yes
7 Do you know where the children
are?
No No
1 SofcK. of them come from Oxford. / Soth Lyra and ftyer come from Oxford.
C These symbols are used in computer logic. Make sentences using
both... and, either... or and neither... nor.
= both... and = either... or J ] } " = n e
' t n e r
- n o r
1 A computer is J^)-on/off.
f) computer is either on or off.
2 Programming is J3" a science / an art.
3 Computer logic is difficult / boring.
4 The symbols are clear / useful.
5 The software is ~^)" free/very cheap.
6 You need lJ3" a monitor / keyboard.
Complete the dialogue using both (of), neither
(of) or either (of).
Andrew: Hi, Clare. Have you see seen those two
DVDs I bought? I can't find:
either of
them.
They are2
on the coffee table.
You should take them back to the shop.
3
them will play.
Really? I watched4
on
Tuesday and they were OK.
Well, they don't work now. Take them
back to the shop. You can5
exchange them or get your money back.
I didn't like6
, anyway.
Andrew: I thought7
films were good.
8
you like those kinds of films
or you don't.
Clare:
Andrew:
Clare:
/In your notebook, write sentences about you and
your best friend using both (of) and neither (of).
(Think about your favourite things; what you do
every day; your family and friends; what you can /
can't do and have / don't have.)
Example: (Oe were both born in, 2000,
i ••••
i
1
Circle the correct option.
1 I love The Golden Compass. I
enjoyed the film and the
book. a neither b both of c both
2 Lyra travels between her world and ours, but
she doesn't feel comfortable in
a neither of b either c either of
3 Neither Lyra's mother her father
understands her.
a or b nor c neither
4 Both Lyra and Roger leave Oxford, but will
ever come home again?
a either them b they either
c either of them
5 A: Who wrote the book? Was itJK Rowling
or Lemony Snicket? B: It was
Philip Pullman.
I a Nor b Neither c Either
qS 3fr q£ m 3T:sJ9Msuejjs3iAy/
• • • •
Both, either, neither 175](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-176-320.jpg)
![Word order
Outside the port today
E v e n i n g T i m e s , 2 5 J u l y
N e w s i n B r i e f
Police are looking for the driver of a car which hit
a tree by the side of the M79 motorway. The car
was found earlier today.
Last night Fogmouth port was closed because
of strong winds.There were long lines of trucks
outside the port today. I have been here for
ten hours,' one driver told us angrily.
The Fire Service was called to afirein
Rexbrook town centre yesterday Thefirestarted
in some rubbish in Kelly Road at about 9.10 p m
Word order
1 Common expressions of time:
in the winter
in the afternoon
on Sunday
on Mondays
at the moment
at 9 o'clock
at lunchtime
for ten years
today
tomorrow morning
next week
last month
yesterday
daily
every year
early
again
now
then
recently
these days
at this time
Answer the questions.
1 When was the car found?
• 2 When was Fogmouth port closed?
3 Where did the fire start?
UMOj >|oojqxay u peoy A]|a>| u qsiqqru
aujos uj £ j q § ! U jse| z Aepo} jsjijea : S J 3 M S U V
If there is more than one of these at the end of a
sentence, the order is usually: manner, place, time.
There were long queues of trucks outside
Fogmouth port today, (place + time)
She brushed her teeth carefully at bedtime.
(manner + time)
He ran quickly to school in the morning.
(manner + place + time)
• See Unit 56 for more adverbs of manner.
2 Common expressions of place:
here
there
upstairs
in Italy
in Milan
in Ford Street
in the town centre
at the bank
at the end of the street
near the church
outside the fire station
An adverb does not usually come between a
verb and the object.
They closed the port yesterday.
NOT They closed yesterday the port.
• See Unit 1 for more information on word order.
We usually put expressions of time and place and adverbs of
manner at the end of a sentence. Sometimes we put them at
the beginning.
The Fire Service was called to a fire in Rexbrook town centre.
The police came immediately.
Last night Fogmouth port was closed because of strong winds.
176](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-177-320.jpg)



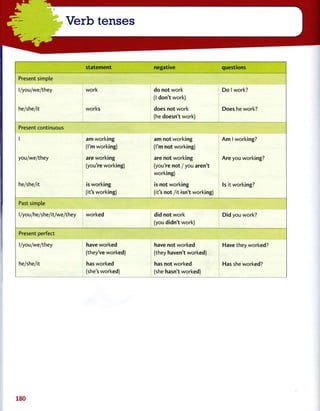
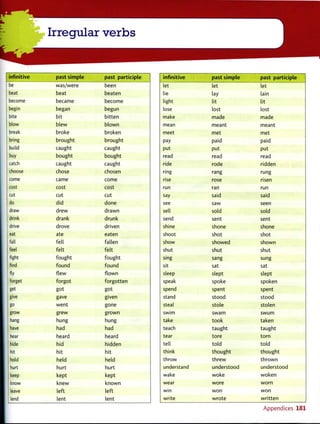
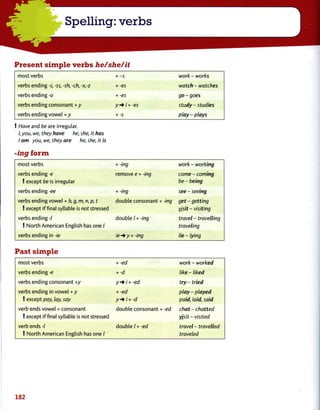
![Adjectives and adverbs
Comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs
most words + -er/-est fast-faster -
fastest
words ending -e + -r/-st nice - nicer -
nicest
words ending consonant + y y-¥i + -er/-est early - earlier -
earliest
words ending vowel + consonant double consonant +
-er/-est
big - bigger -
biggest
Adverbs ending in -ly
most adjectives + -ly bad - badly
adjectives ending -le e+y simple - simply
adjectives ending consonant + y y-*i + -ly busy - busily
Nouns
Regular noun plurals (countablenouns only)
most nouns + -s car- cars
noun ends -s, -ss, -sh, -ch, -x, -z + -es [adds a syllable] watch - watches
noun ends vowel + -o + -s radio - radios
noun ends consonant + o + -es tomato - tomatoes
noun ends consonant + y y-*i + -es diary - diaries
noun ends vowel + y + -s day-days
noun ends -f/fe
! except roof - roofs
f/fe -» ves knife - knives
Irregular noun plurals
man men
woman women
child children
person people
tooth teeth
foot feet
Appendices 183](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-184-320.jpg)











![B Possible answers
2 It's 11.30. 3 It's red, blue and white.
4 There's a man on a bicycle.
5 There aren't many. 6 It's Maria.
7 There are foxes and wolves.
8 It was on Monday.
9 There was a fi Im about dragons.
10 It was sunny.
C 2 brother's... he's 3 Samantha's ... parents'
4 It's ... isn't 5 friend's... doesn't
6 I'll 7 brother's... doesn't 8 children's
9 Maria's... horses' 10 Terry's
D 2 in Barry and Gary's / their
3 are my dad's 4 lend you mine
5 Their house is 6 listens to her
7 you give me
E 2 many 3 Everybody 4 Many 5 A
6 Nobody 7 much 8 Lots 9 of
10 lot of 11 little 12 any 13 much
14 many 15 anything
F 2 that 3 somewhere 4 some 5 That
6 any 7 any 8 lots of 9 any 10 a few
11 any 12 some 13 a few 14 the
15 some 16 a lot of 17 A few of 18 much
19 anywhere 20 nowhere 21 -
52 Adjectives
A ancient city
careless man /worker
cold weather / city / day
empty glass / city
great city / day / time / weather / worker
terrible day / time / weather / worker
ugly face / man / city
useful information / glass
young face / worker
B 2 a credit card 3 a CD player
4 a toothbrush 5 a bedroom
6 a train station 7 a postman
8 a taxi driver
C Possible answers
2 It is (It's) not far from here, (the cinema)
3 It was a very busy place, (the airport)
4 She doesn't look very well, (my friend)
5 These flowers smell lovely, (roses)
6 She does not (doesn't) seem very friendly, (my
neighbour)
7 It is not (It's not / It isn't) a good idea, (smoking)
8 He is (He's) my favourite actor. (Johnny Depp)
9 They do not (don't) taste nice, (olives)
10 He is fs) always asleep! (my brother)
D
Possible answers
2 The homework was
3 My lunch was quite
4 Atyrannosaurus rex was
5 I feel a bit
6 I am quite
7 My bedroom is a little
8 I am
9 I am very
10 The house is very
My Turn!
Possible answers
2 I felt nervous, but also excited.
3 Every visitor must go to the Charles Bridge. It's
a famous bridge across the Vltava river. It is very
busy in the day but at night it is quiet.
4 From an aeroplane the city looks very big. All the
houses have red roofs.
5 The people are very friendly.
6 The city seems safe at night.
7 I miss the culture. In Prague there are a lot of
interesting galleries and festivals.
53 Order of adjectives
opinion size quality age
amazing [big] dirty modern
famous enormous happy new
handsome short quiet
colour origin material
brown Asian cheese
golden Roman glass
white Swiss
B 2 heavy silver Olympic
3 tired Kenyan marathon
4 amazing new 100-metre
5 tall slim basketball
6 long 70-metre discus
C 2 football 3 brown 4 real 5 tall
6 hard 7 golf 8 family
My Turn!
Possible answers
2 my expensive new brown shoes
3 an enormous white plastic watch
4 a dirty old glass window
5 a famous young Asian footballer
6 an amazing big cheese sandwich
54 Comparatives
A 2 longer 3 more dangerous
4 politer / more polite 5 rarer
6 farther / further 7 more expensive
8 older 9 younger 10 heavier
B 2 Flying is less dangerous than / not as
dangerous as driving.
3 Silver is less rare than / not as rare as gold.
4 One kilometre is less far than / not as far as
one mile.
5 Seoul is less expensive than / not as expensive
as Tokyo.
6 Moscow is less old than / not as old as Madrid.
C 3 more expensive 4 as big as
5 further / farther 6 better
7 worse 8 later / better
My Turn!
Possible answers
2 The giraffe is a bit taller than the elephant.
3 The elephant is far heavier than the monkey.
4 The lion is a bit shorter than the zebra.
5 The snake is a lot more dangerous than the
monkey.
6 The zebra is a little slower than the lion.
55 Superlatives
A 2 most dangerous * safest
3 best* worst 4 most hard-working ? laziest
5 most interesting * most boring
6 oldest * newest 7 saddest * happiest
8 strongest * weakest 9 wettest * driest
B 4 The rabbit... the longest
5 The dog ... the biggest
6 The strawberry jam is the cheapest.
7 The raspberry jam is the most expensive.
8 Tom ... the most unusual
C Possible answers
2 The dog is the nicest.
3 The sheep is the most useful.
4 The mouse is the least useful.
5 The elephant is the least interesting.
6 The horse is the most interesting.
7 The horse is the fastest.
8 The elephant is the most dangerous.
9 The sheep is the least dangerous.
D 2 Mount Everest is the highest mountain.
3 The Vatican City is the smallest country.
4 The blue whale is the largest animal.
5 Antarctica is the coldest continent.
6 Hydrogen is the most common gas.
7 Sirius is the brightest star.
8 Baikal is the deepest lake.
My Turn!
Possible answers
2 This is the fastest car!
3 This is the lightest mobile!
4 This is the friendliest dog!
5 This is the most comfortable flat!
6 Our coffee is the best!
56 Adverbs of manner
A 2 badly 3 quickly 4 noisily 5 easily
6 slowly 7 carefully
B 2 far 3 happily 4 fast 5 well 6 carefully
7 early 8 immediately 9 suddenly 10 late
C Possible answers
2 Leonardo da Vinci could paint very well.
3 Rocky Marciano could hit hard.
4 Carl Lewis could run very quickly.
5 The Beatles could sing very well.
6 Pele could play football beautifully.
7 Garry Kasparov could play chess brilliantly.
My Turn!
Possible answers
2 She is fs) smiling happily.
3 They are fre) talking angrily.
4 He is fs) walking slowly.
5 He is fs) eating unhealthily / badly.
6 She is fs) leaving the house quietly.
57 Comparative and superlative adverbs
A 2 [early]-earlier-earliest
3 easily - [more easily] - most easily
4 [far] - farther / further - farthest / furthest
5 well - [better] - best
6 happily - more happily - [most happily]
7 slowly - [more slowly] - most slowly
8 [safely] - more safely - most safely
B 2 sooner 3 highest 4 more safely
5 worse 6 more seriously 7 accurately
8 most carefully
C 2 farther / further; False 3 more quickly; True
4 faster; True 5 higher; False
6 better; True 7 more easily; False
8 more deeply; True
D
Possible answers
2 My sister draws best.
3 My mum works hardest.
4 Stefan writes most clearly.
5 Marco lives farthest / furthest from here.
6 My dad sings worst.
7 My brother sleeps longest.
8 My cousin eats his lunch most quickly.
My Turn!
Possible answers
2 Tim has eaten his meal fastest.
3 Kim is eating most tidily and most slowly.
4 Kim is eating least quickly.
5 Kim has climbed higher.
6 Tim has climbed less high.
7 Kim is smiling more happily.
8 Tim is smiling less happily.
Answer key 195](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activegrammar1-170831201335/85/Active-grammar-1-196-320.jpg)




