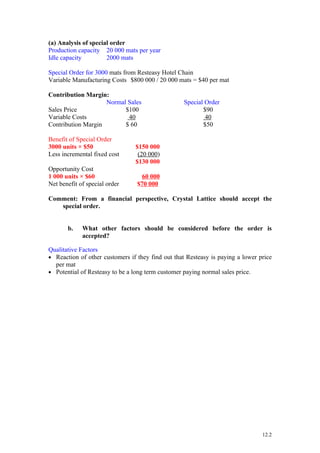
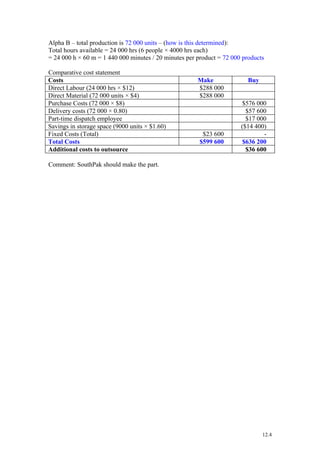
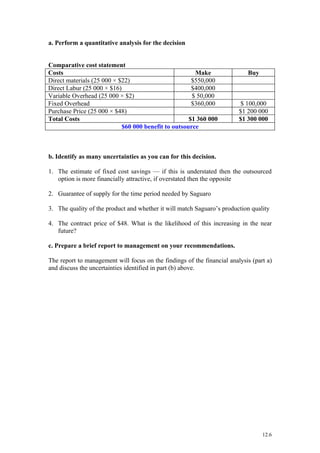
Crystal Lattice produces exercise mats and has spare annual capacity of 2,000 mats. Resteasy hotel chain placed a one-time order for 3,000 mats at $90 per mat instead of the normal $100 price. Accepting the order would earn a contribution margin of $50 per mat compared to $60 normally, for a net benefit of $70,000 after factoring in the $20,000 cost of an embossing machine needed for the order. Qualitative factors like reactions from other customers and Resteasy's potential as a long-term customer should also be considered before accepting the order.