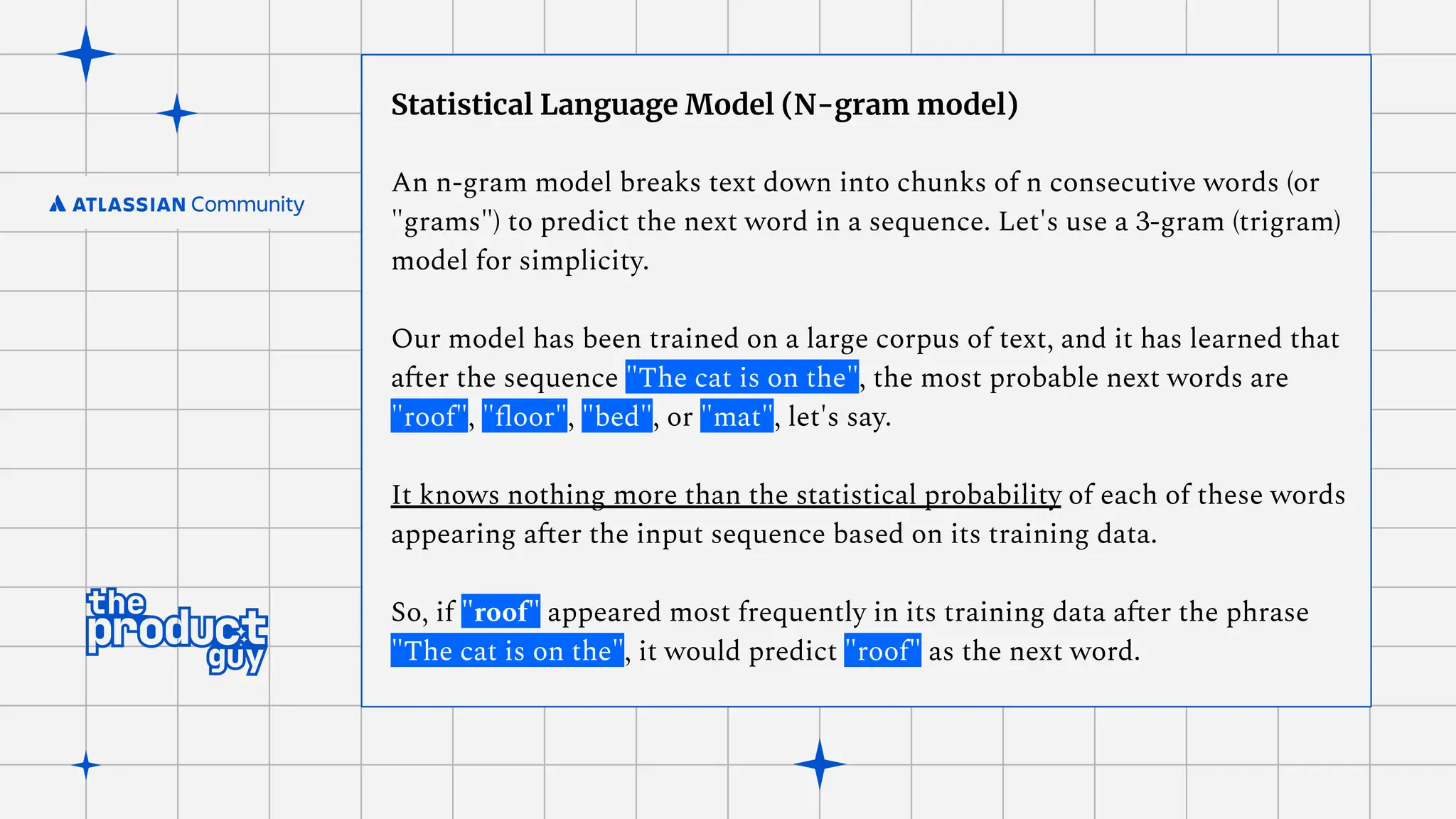
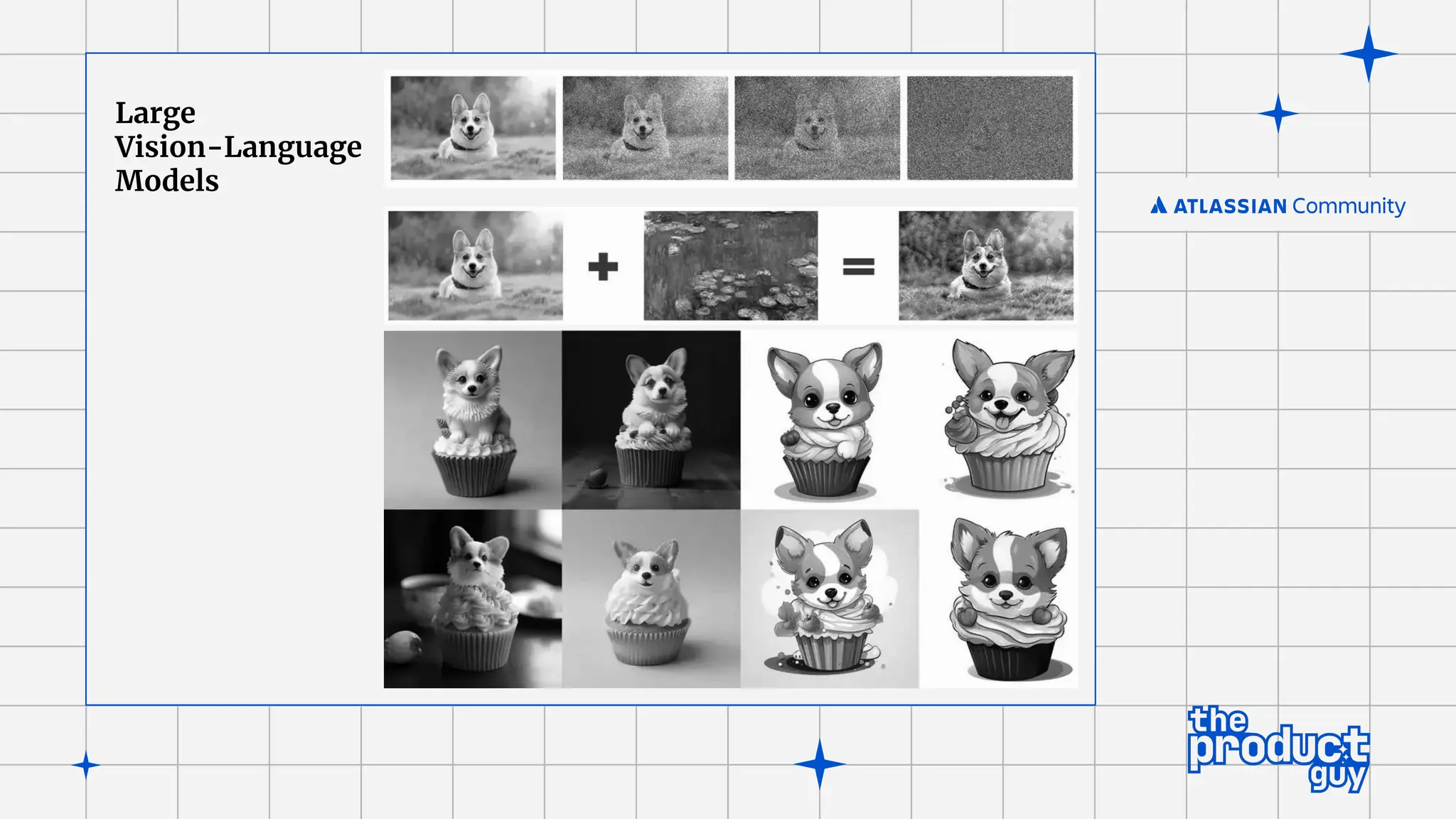
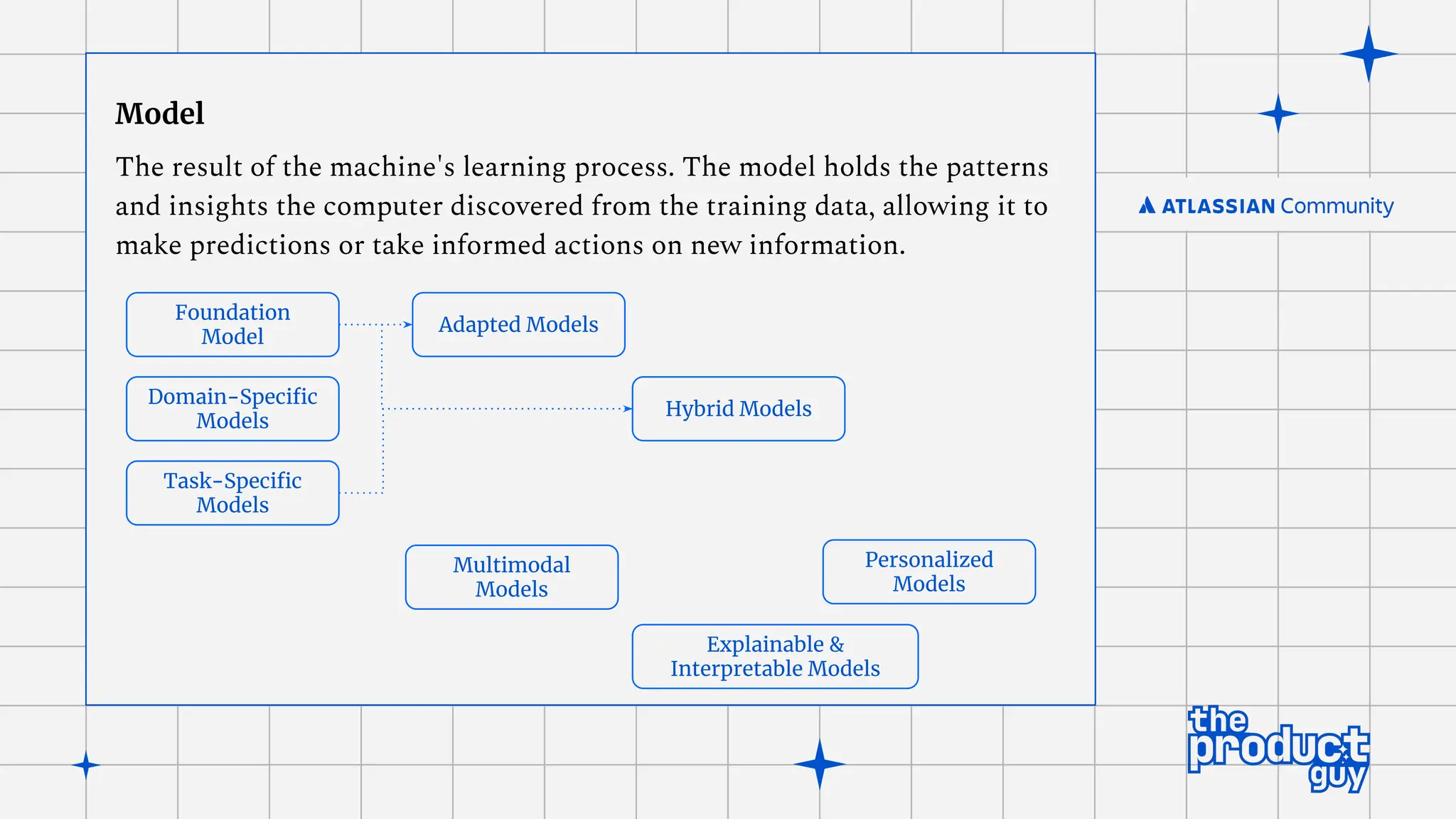
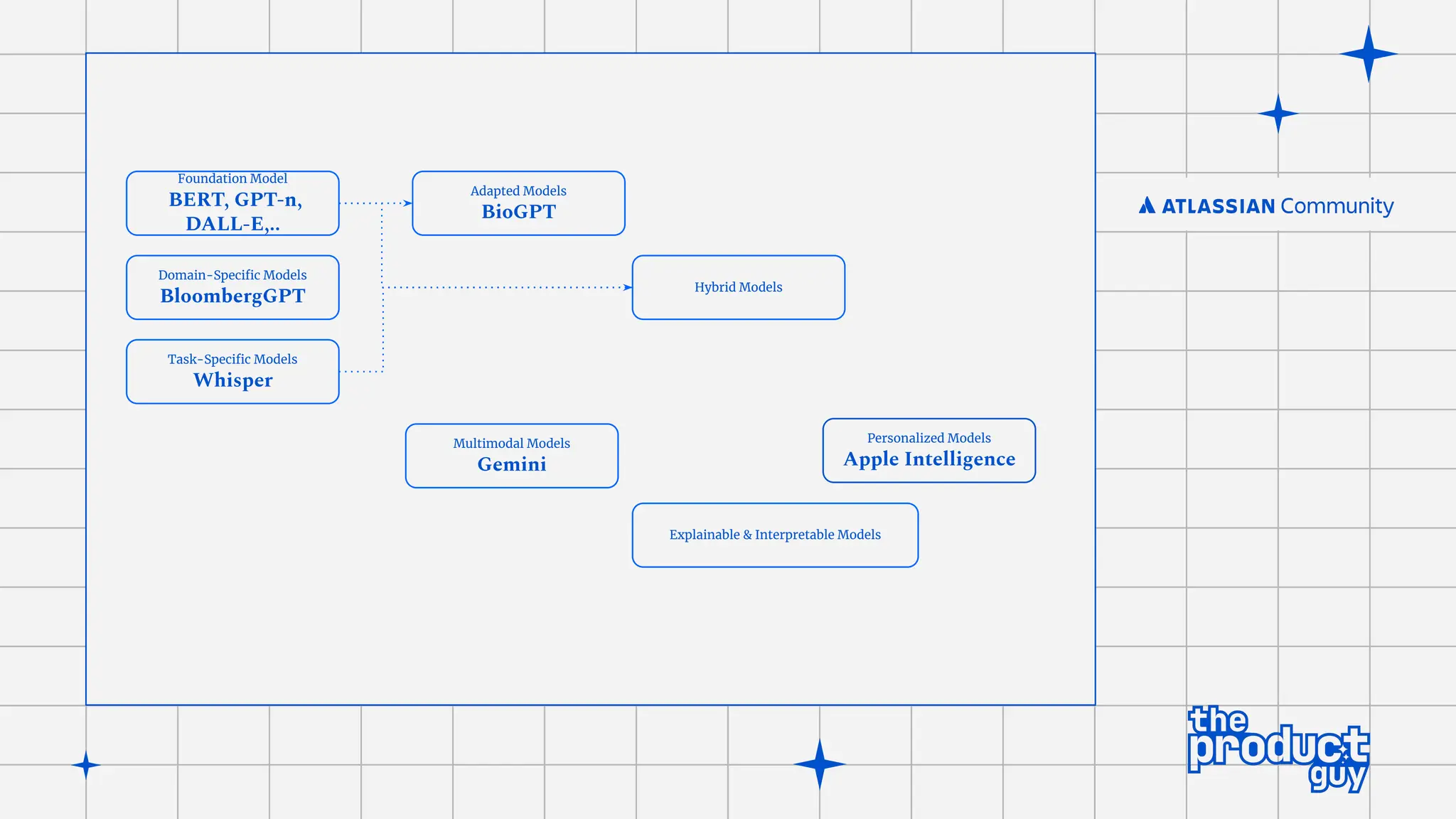
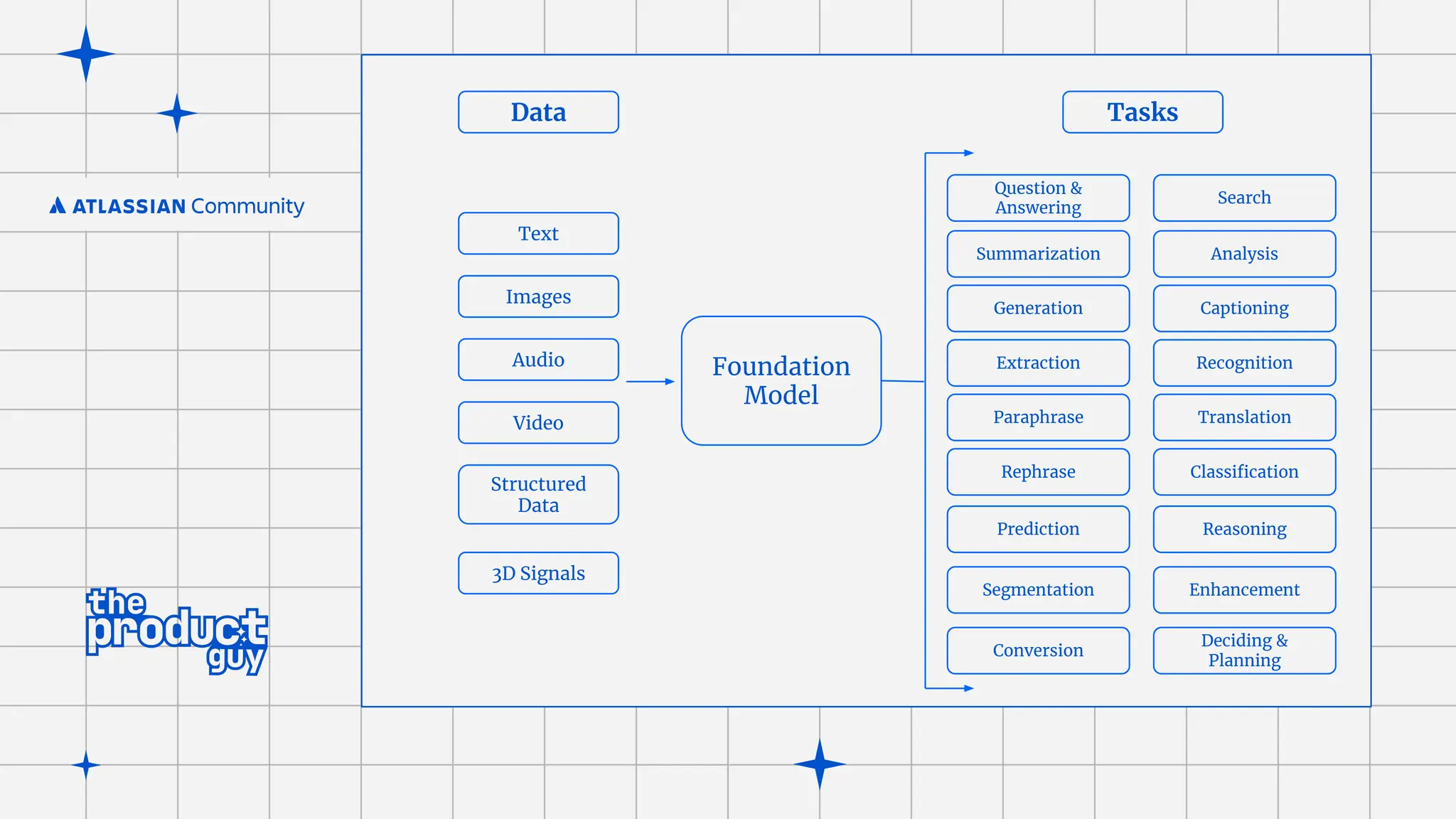
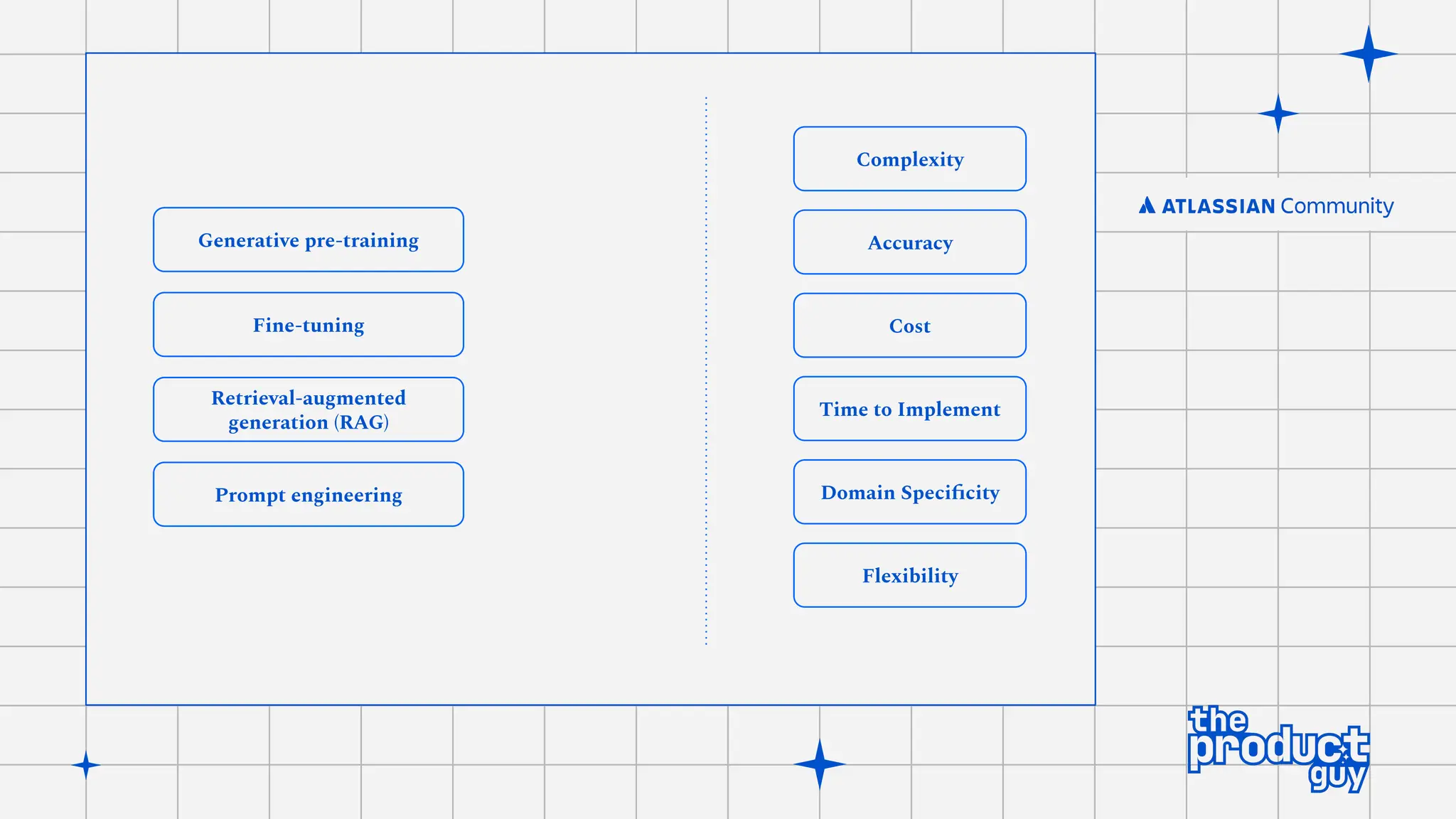
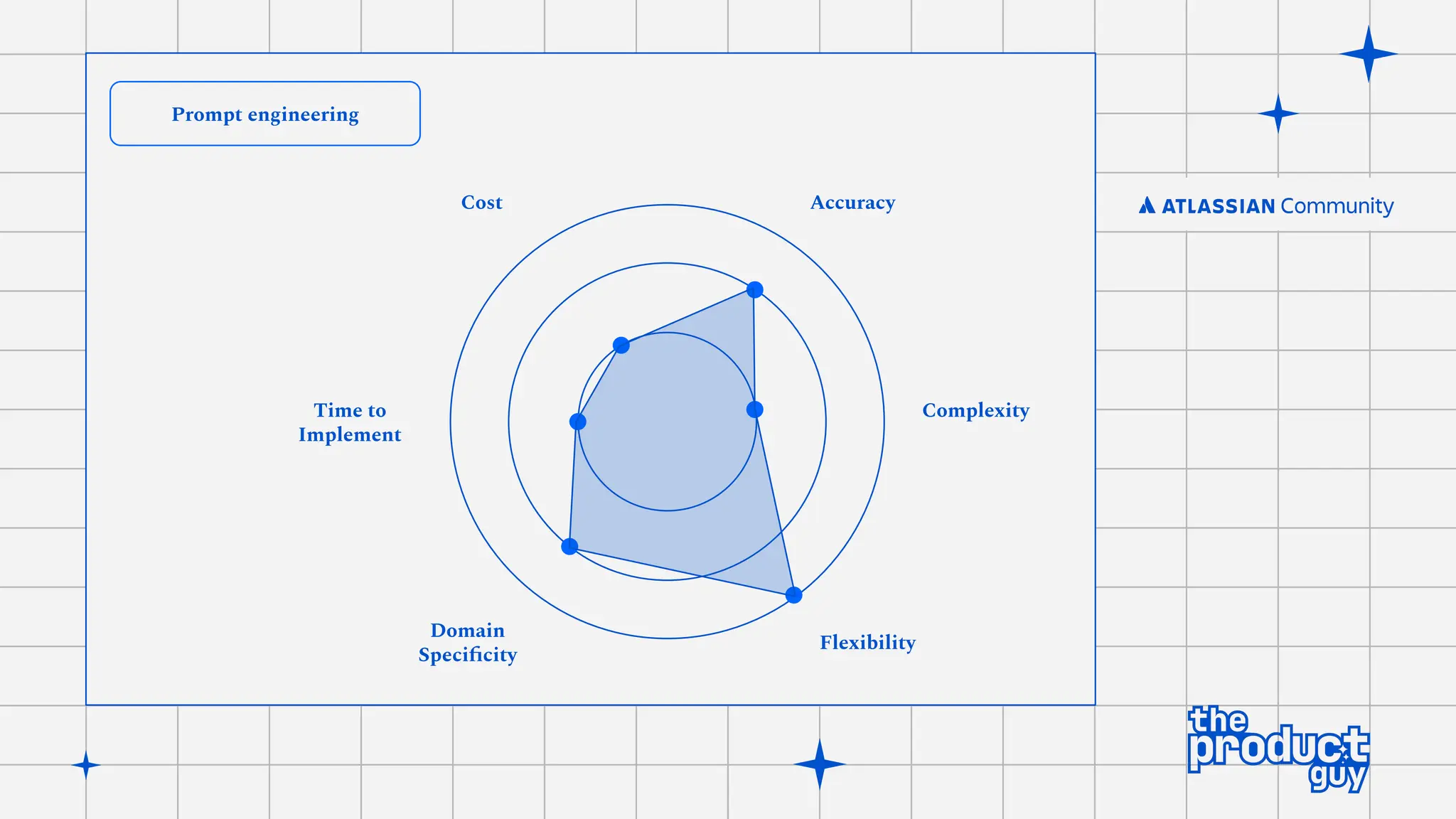
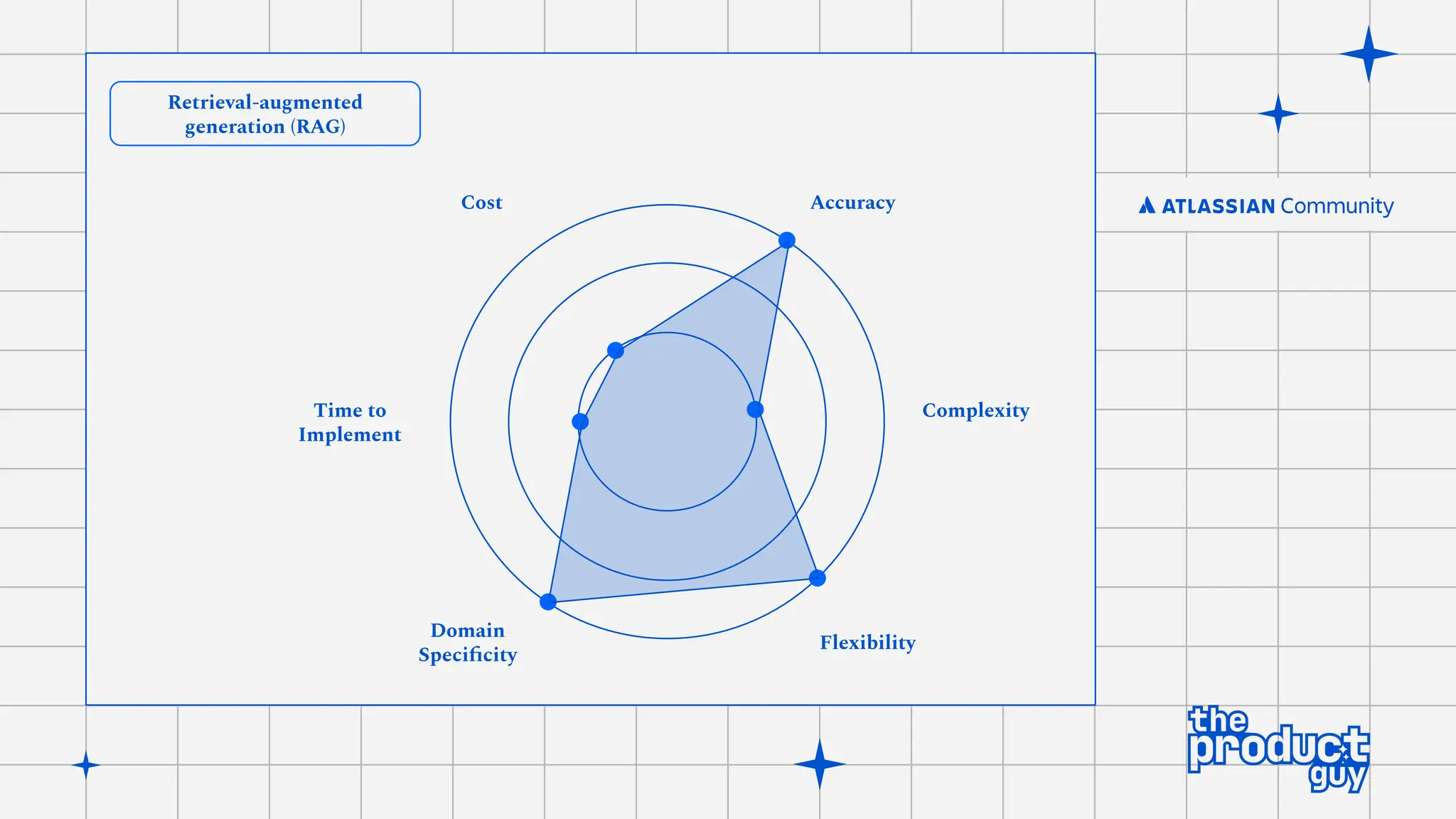
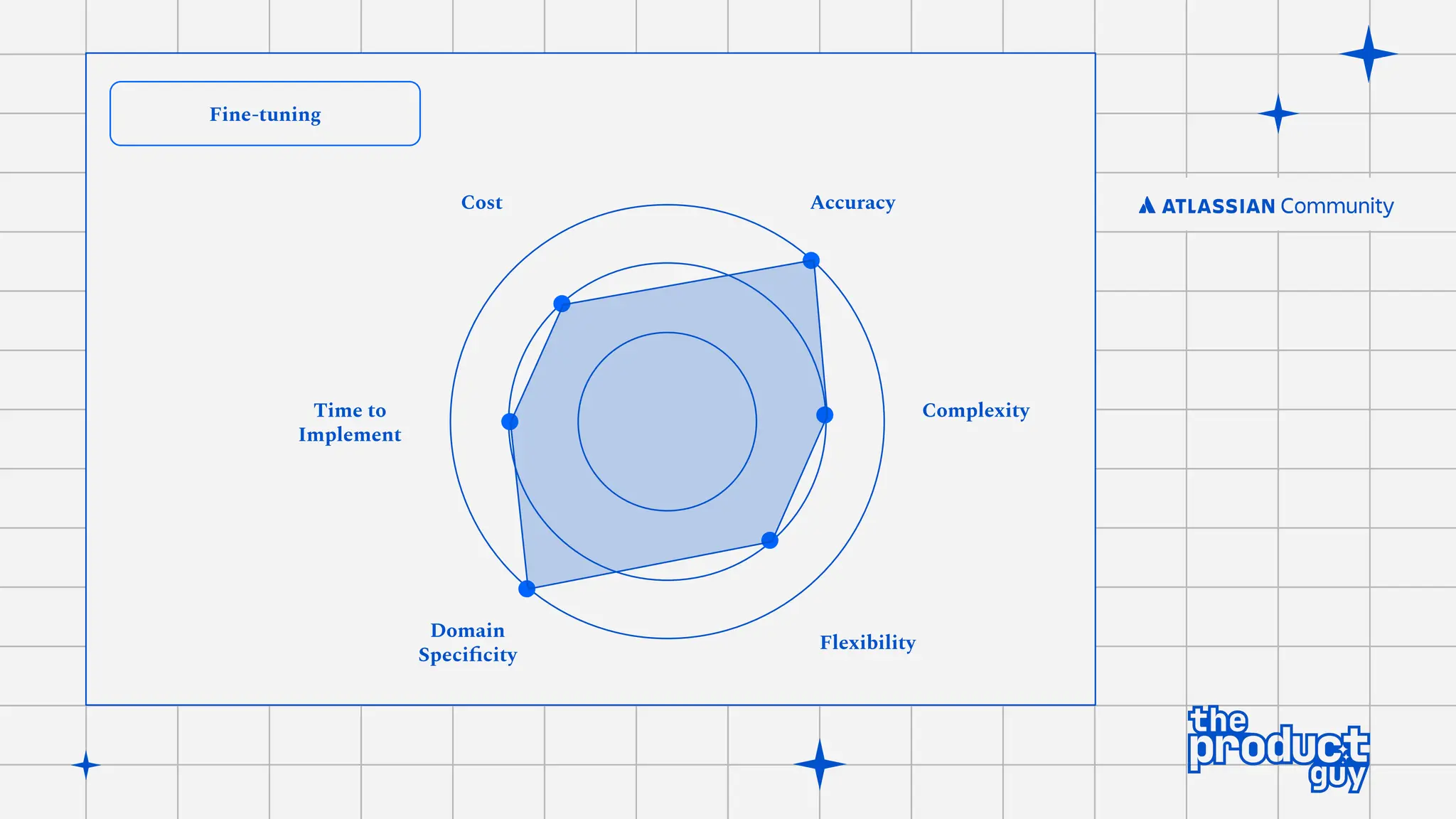
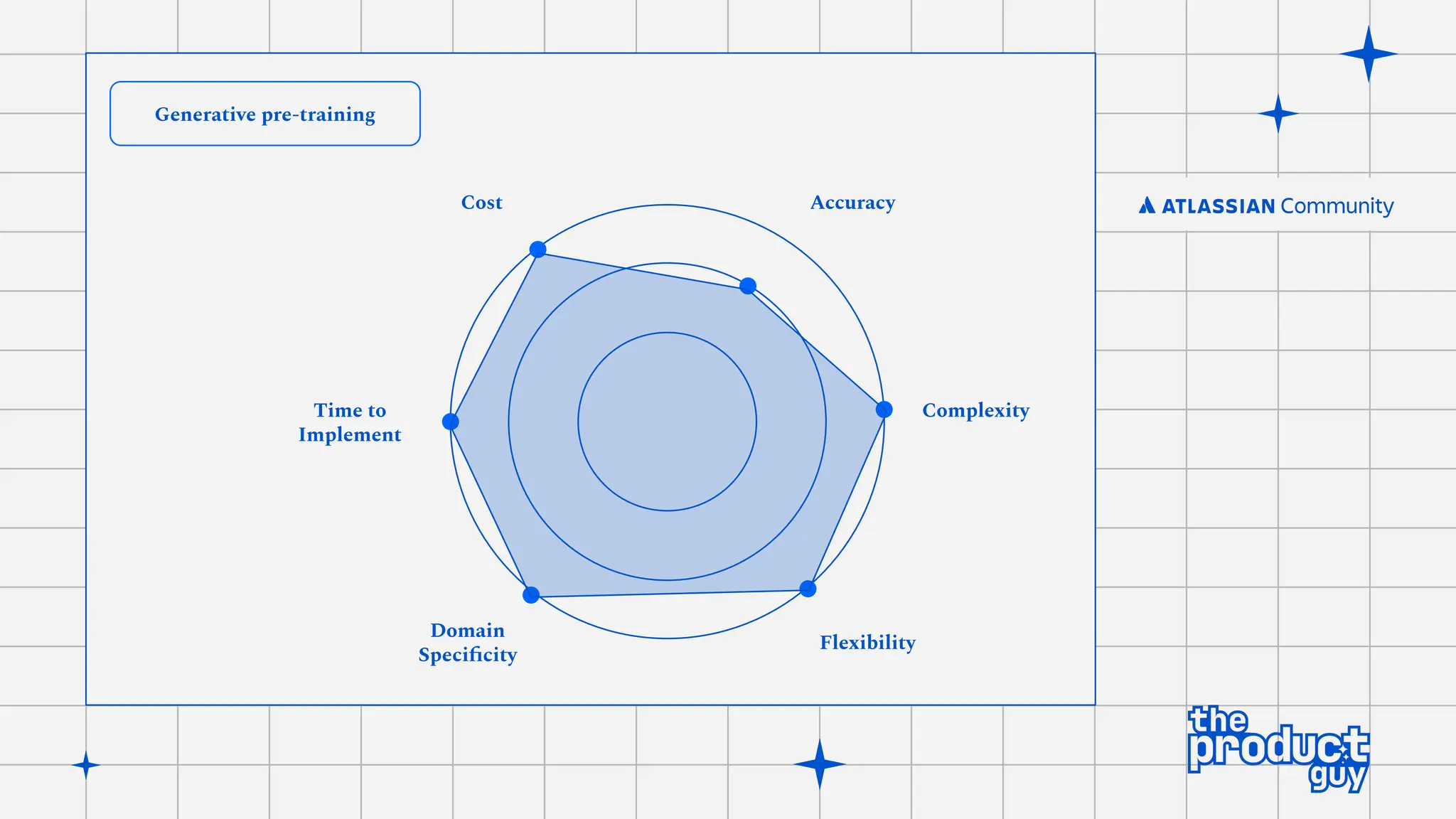
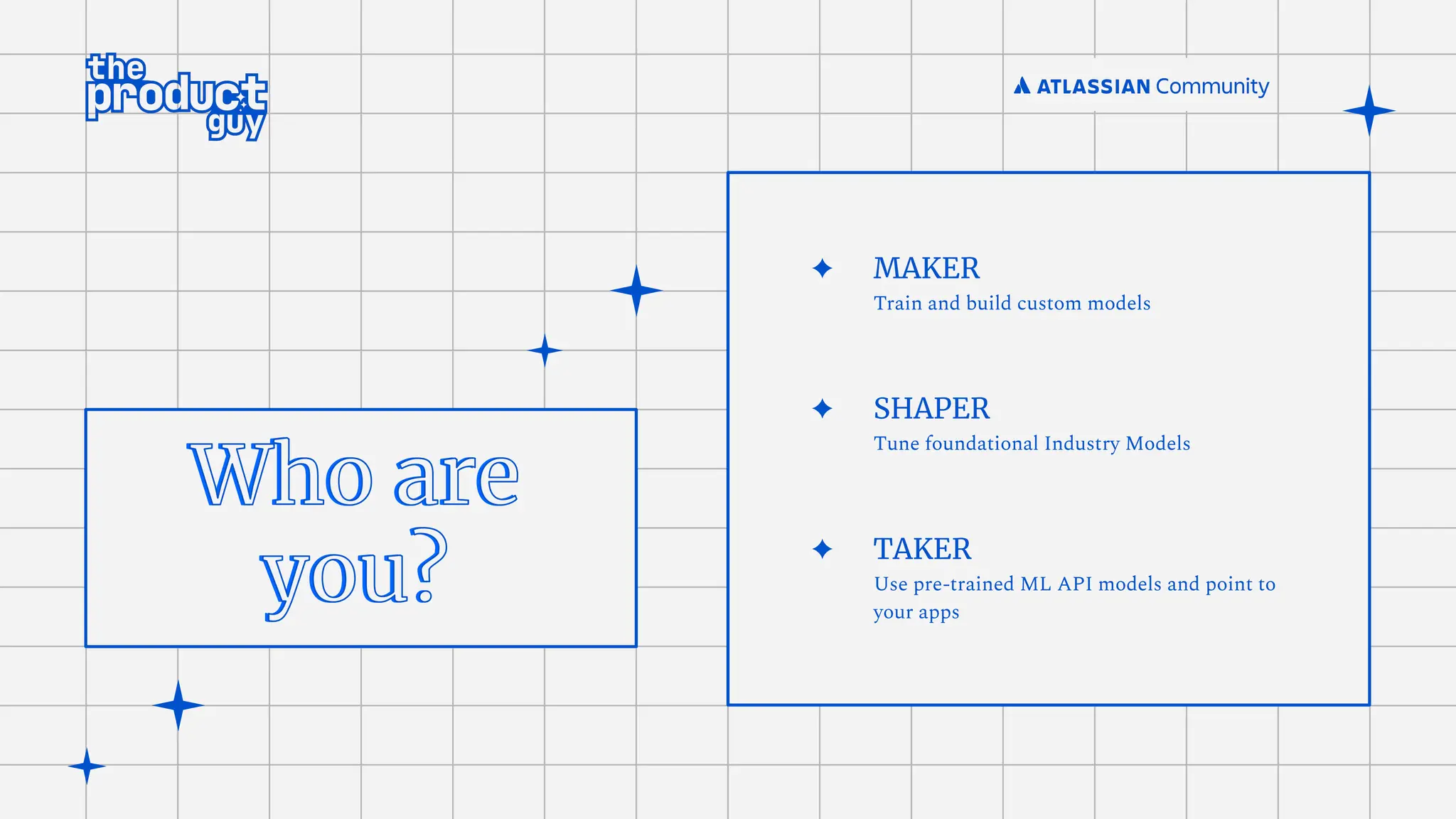
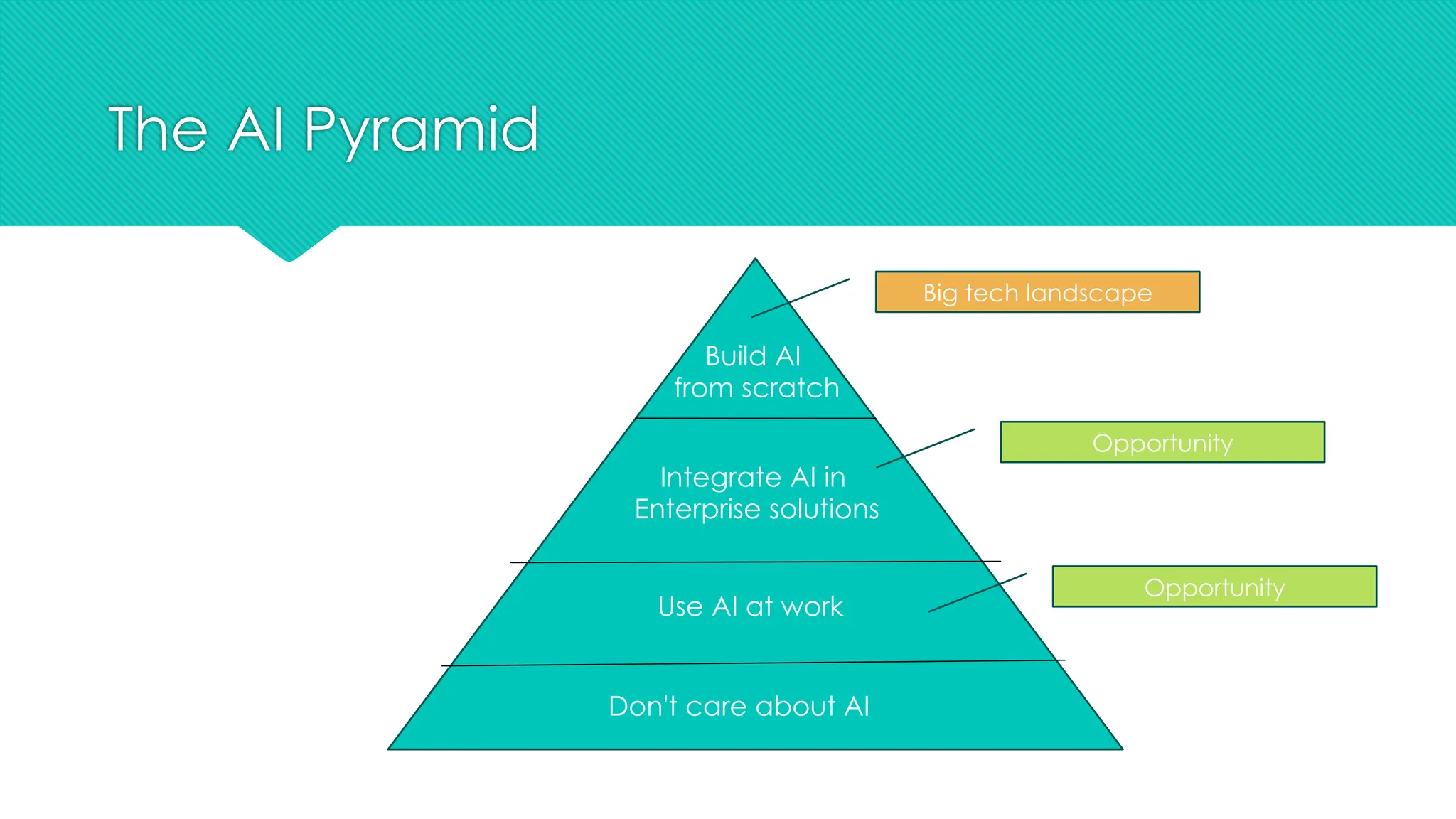
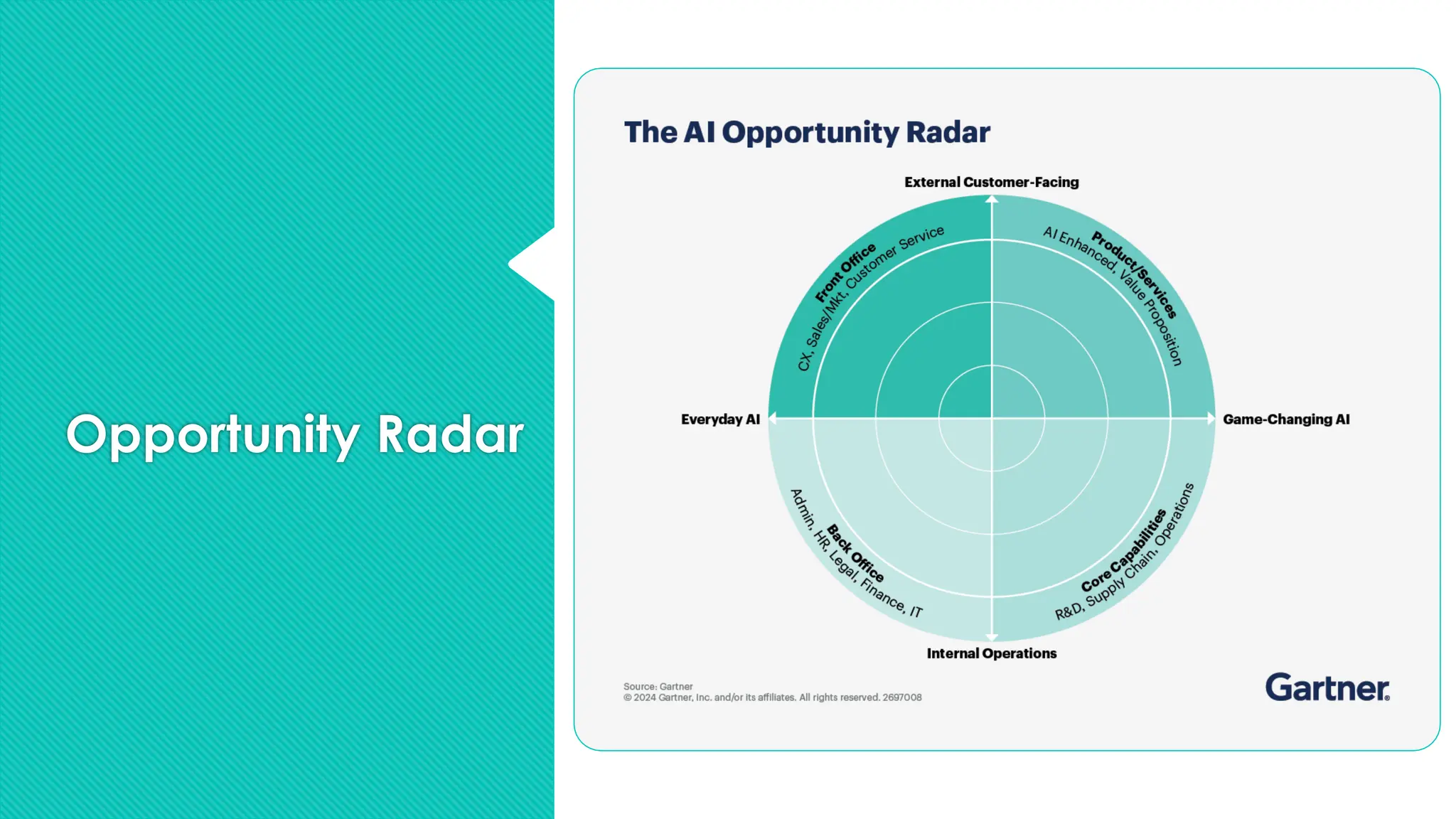
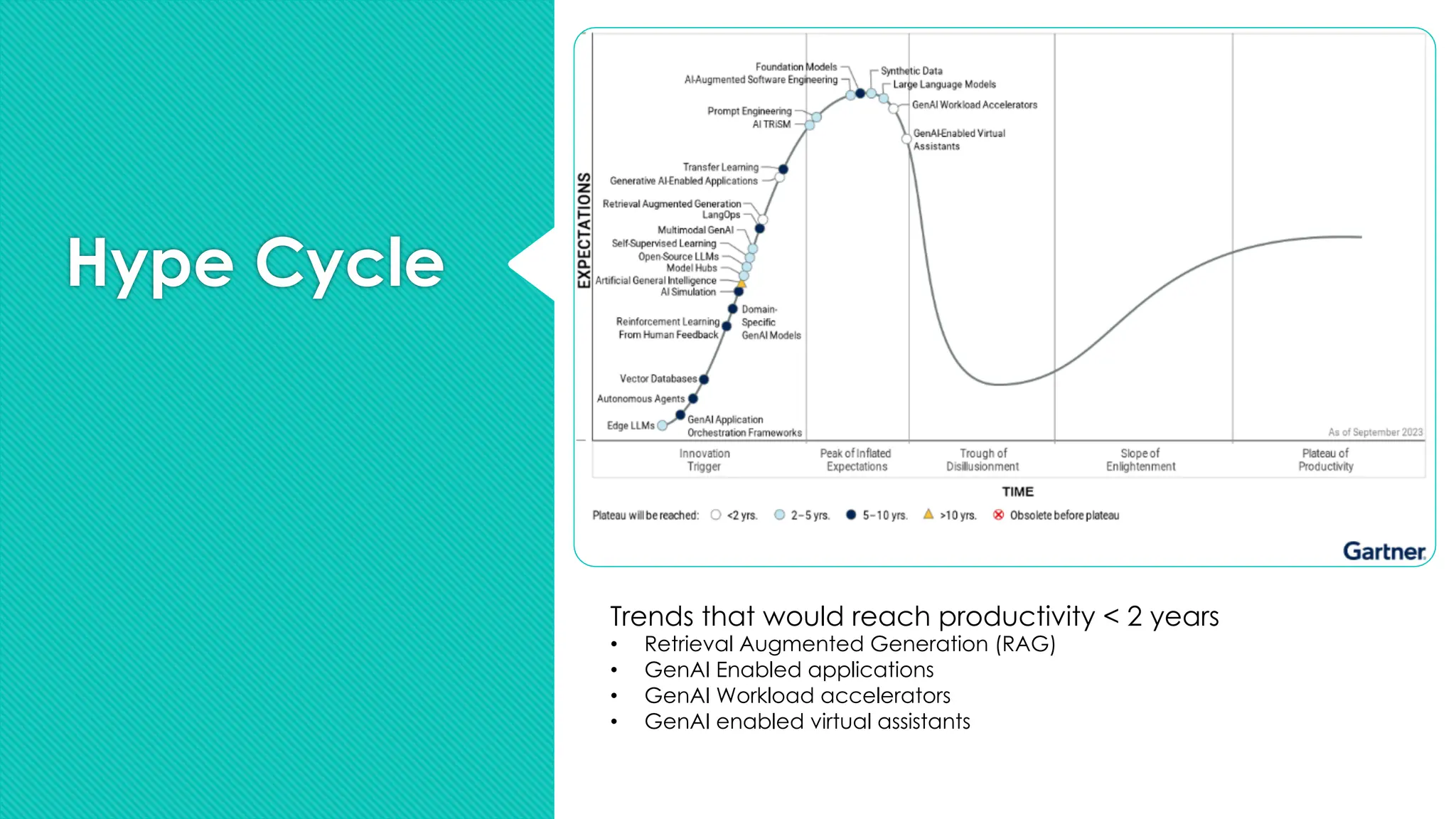
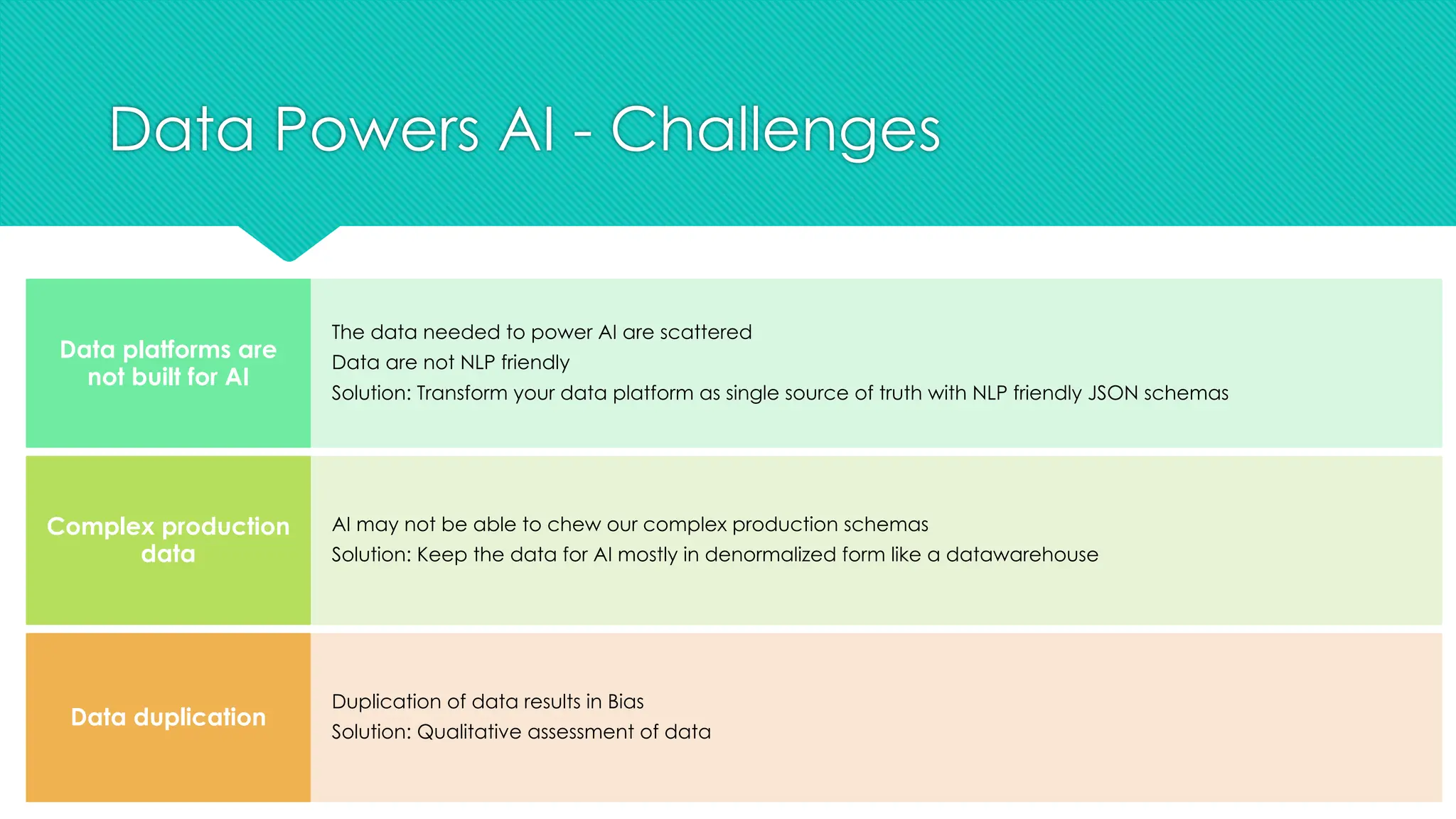
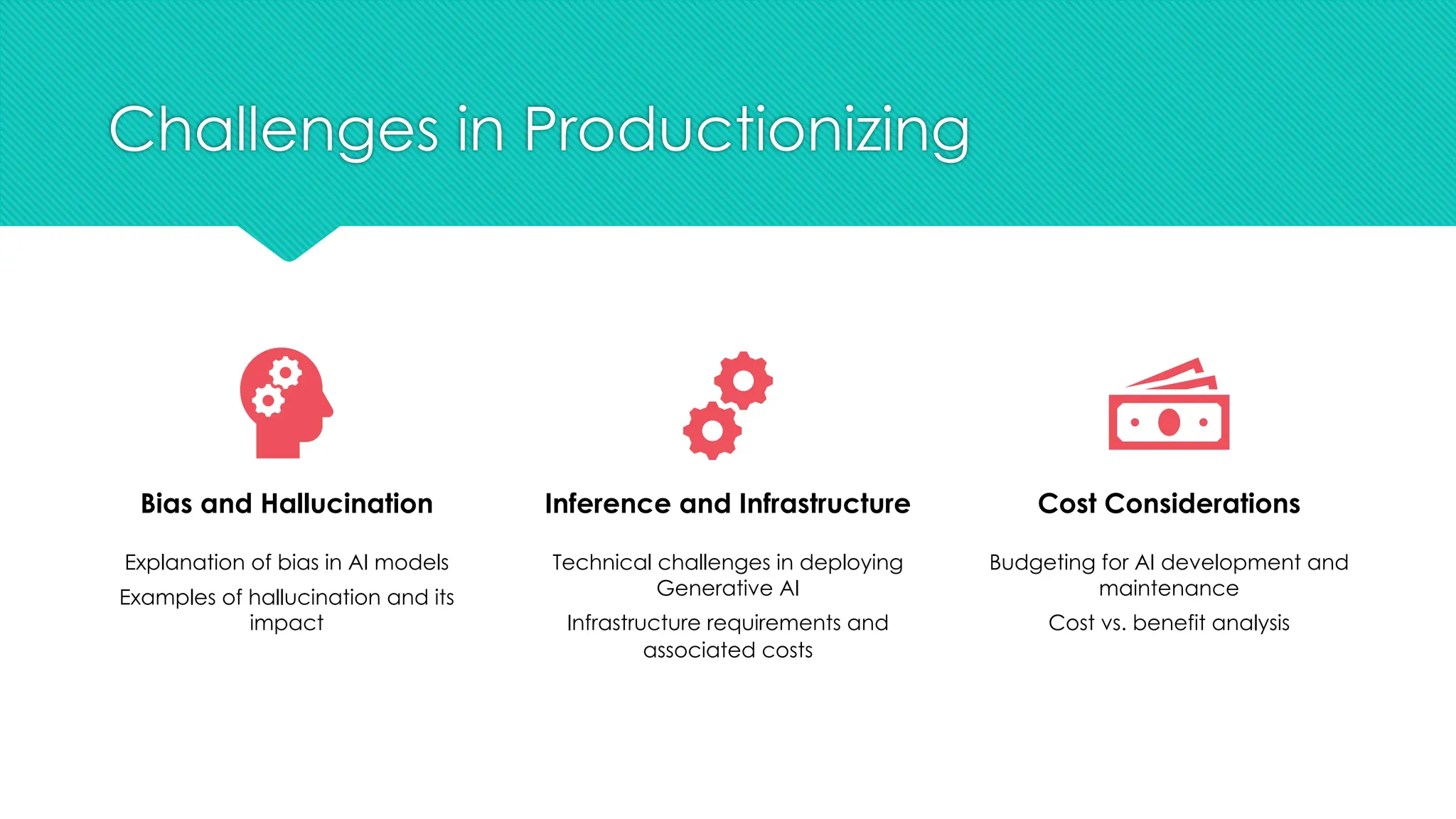
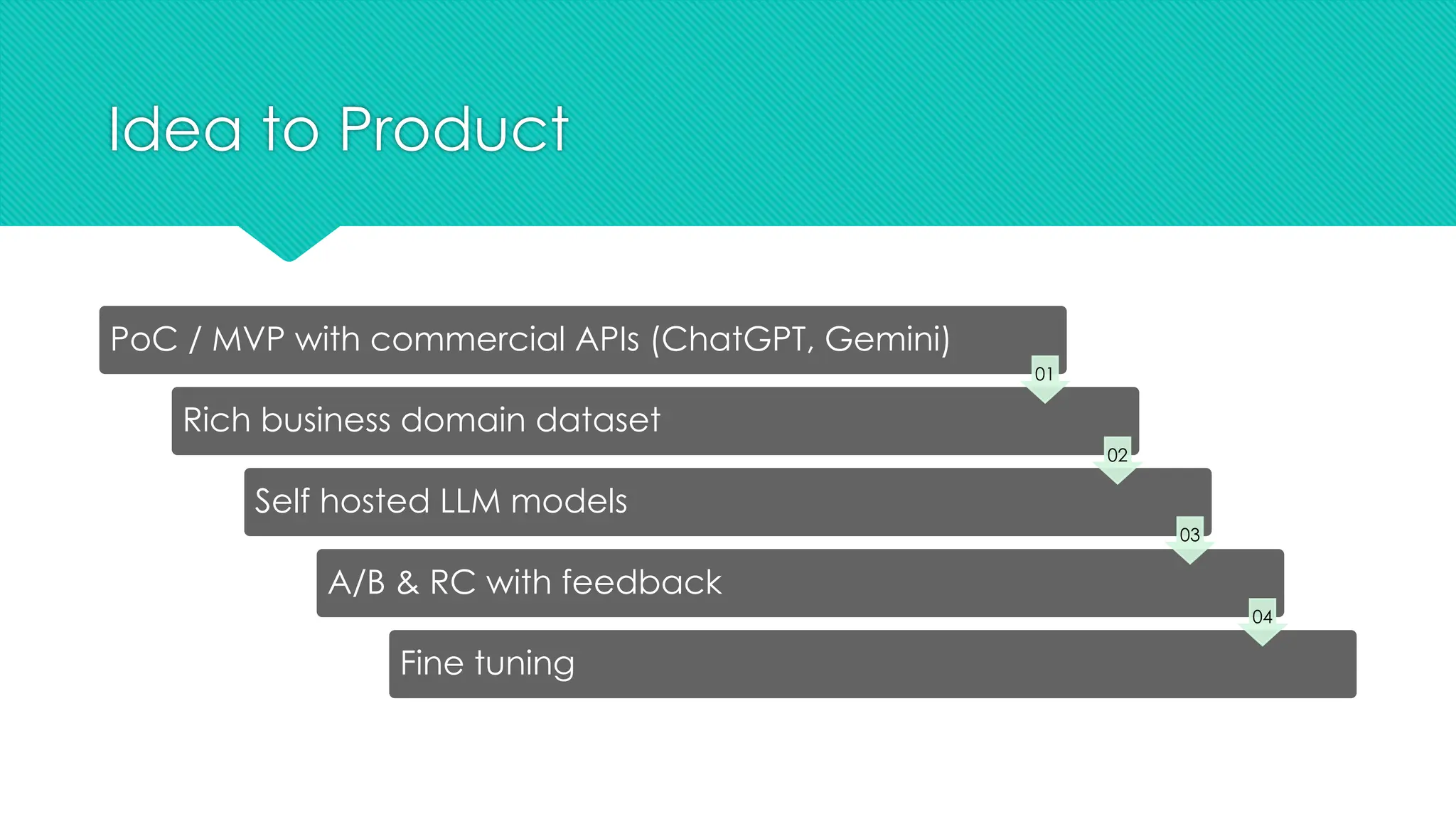
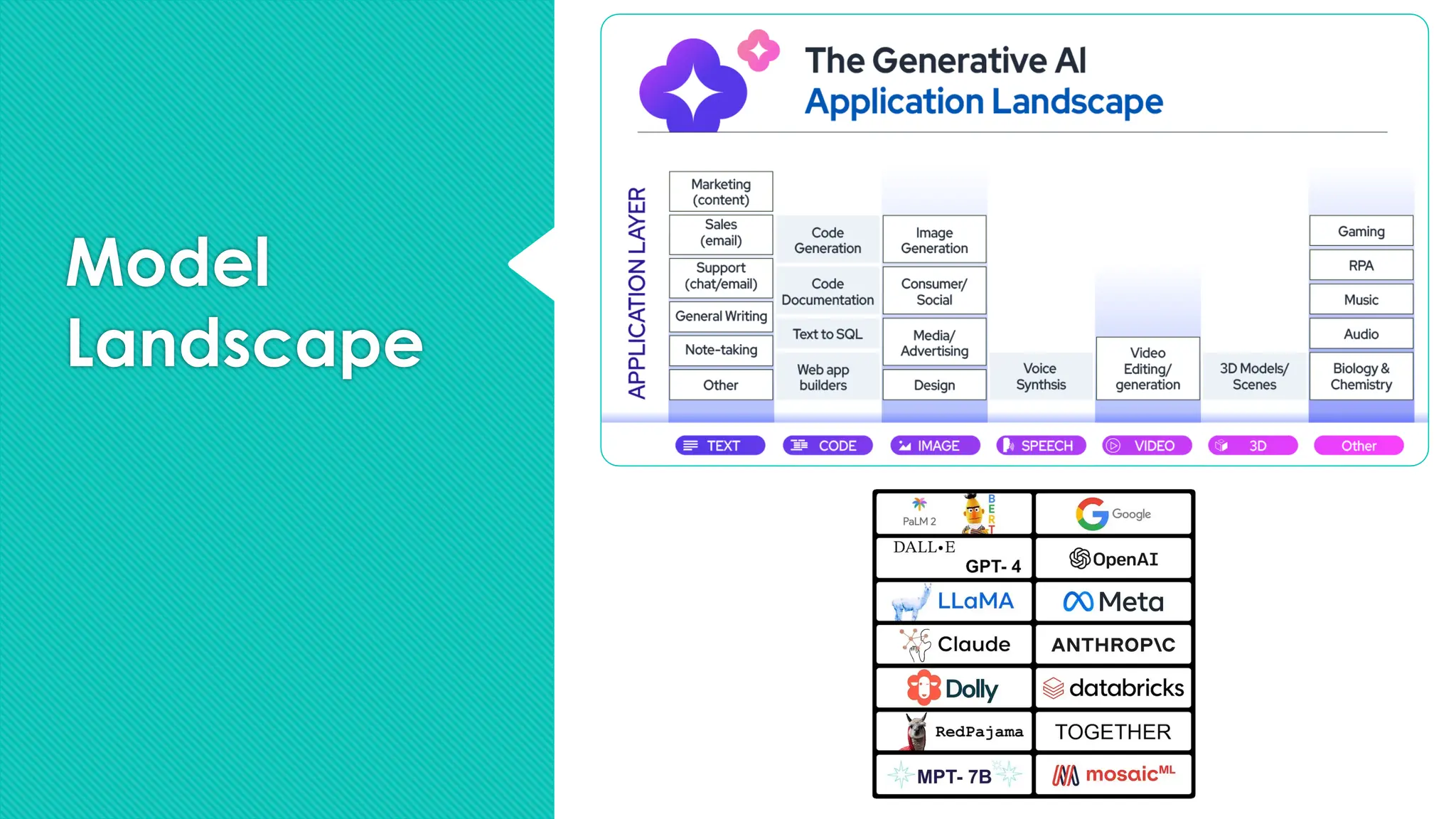
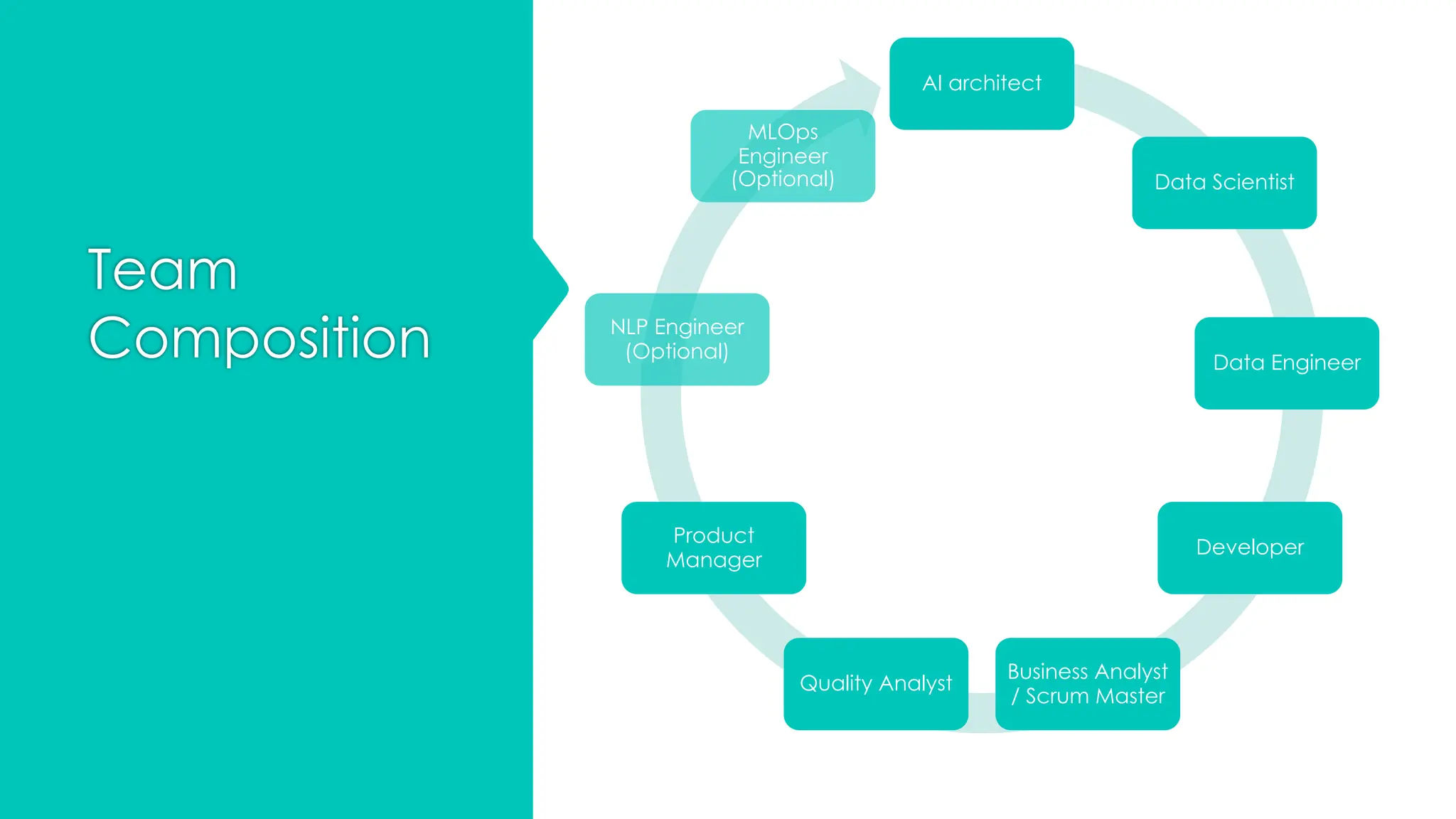
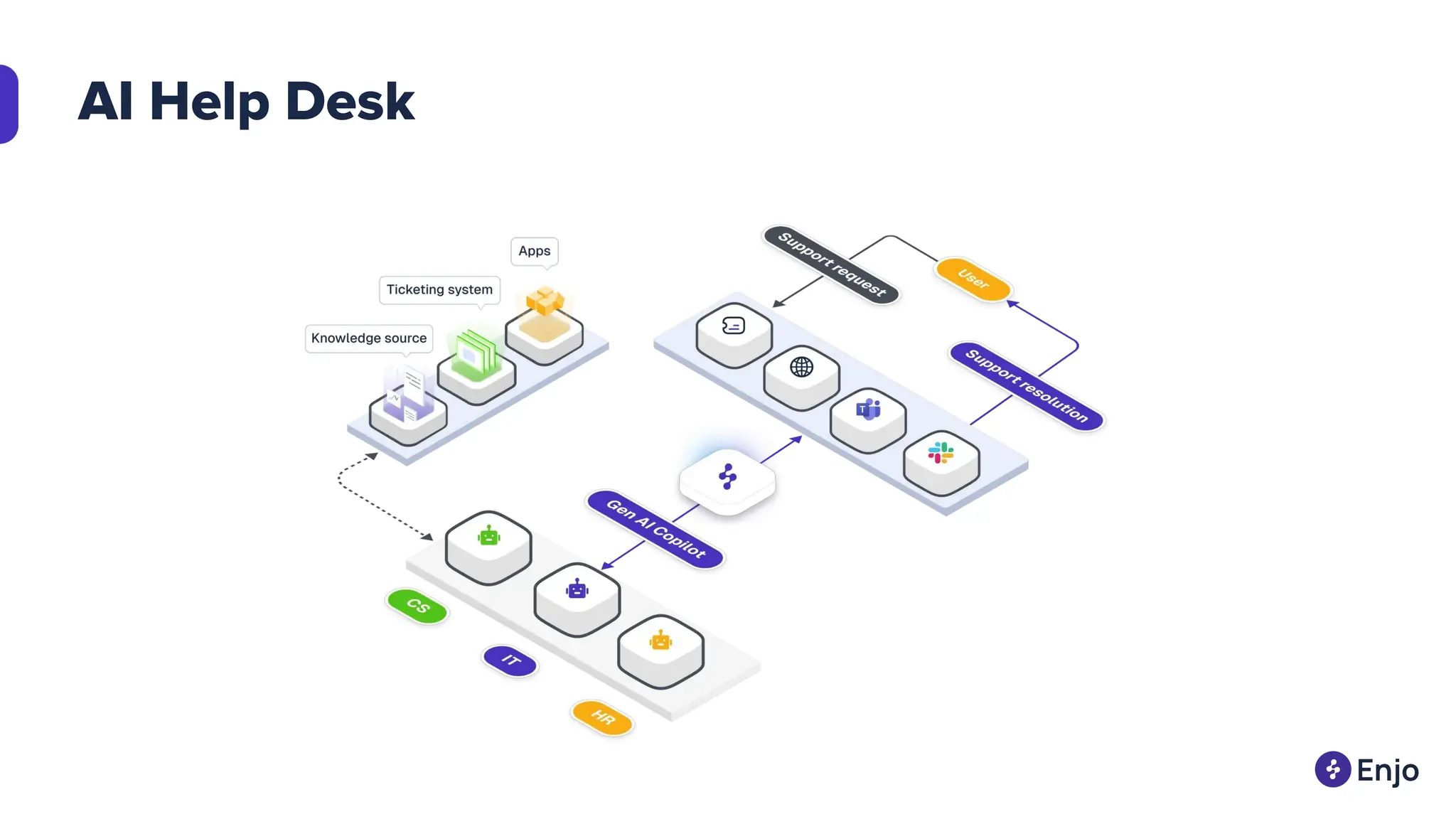
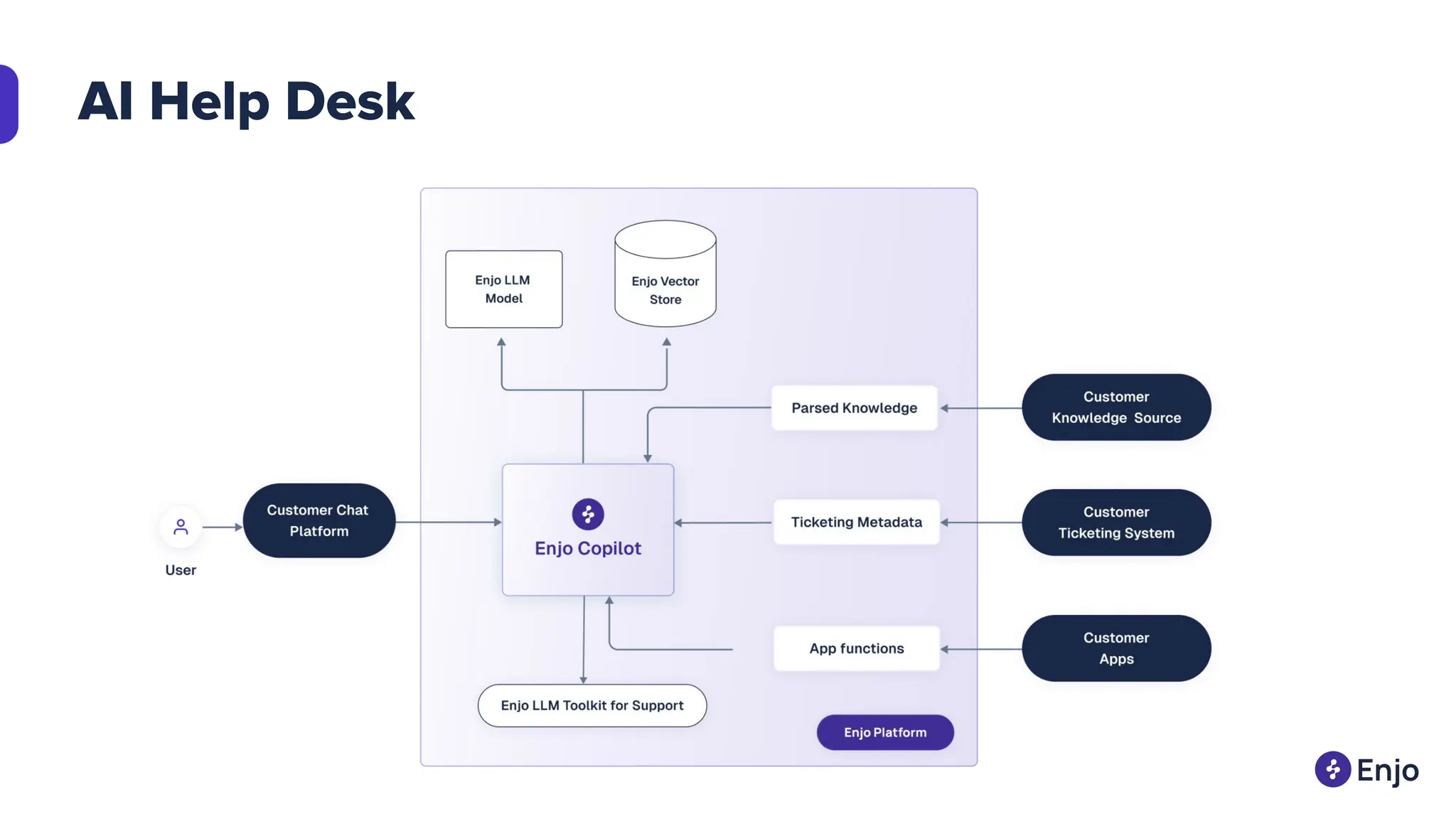
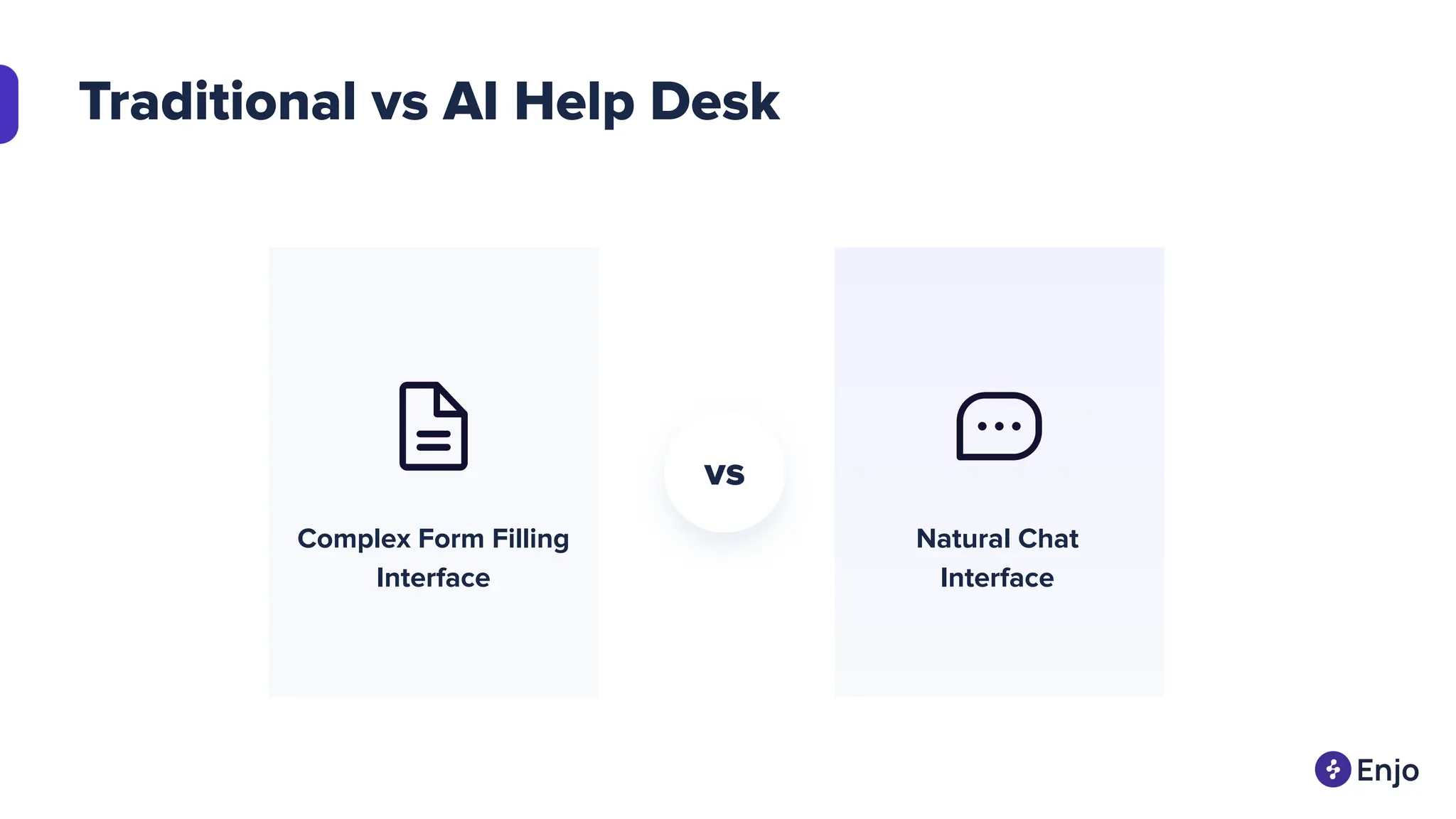
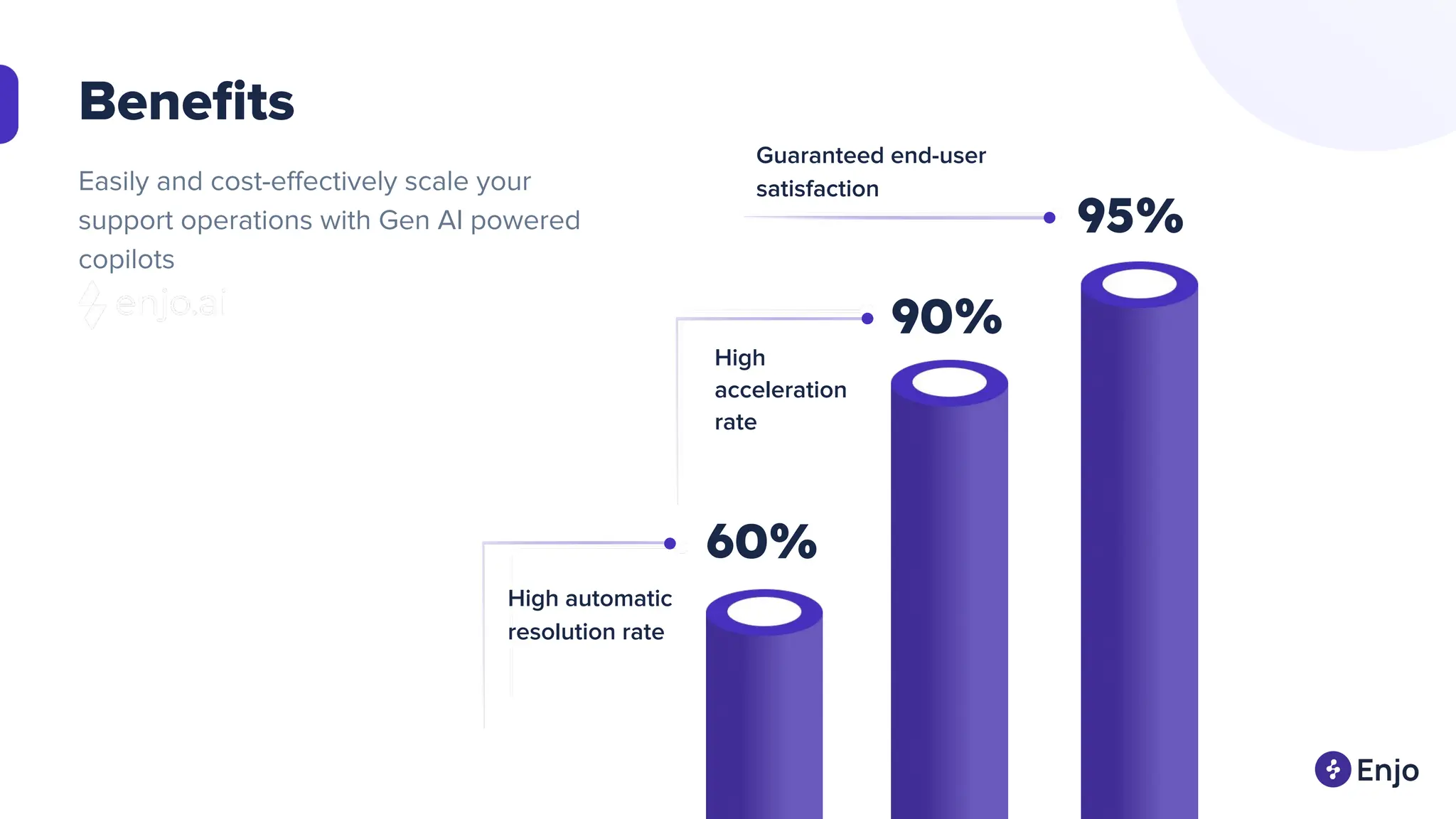
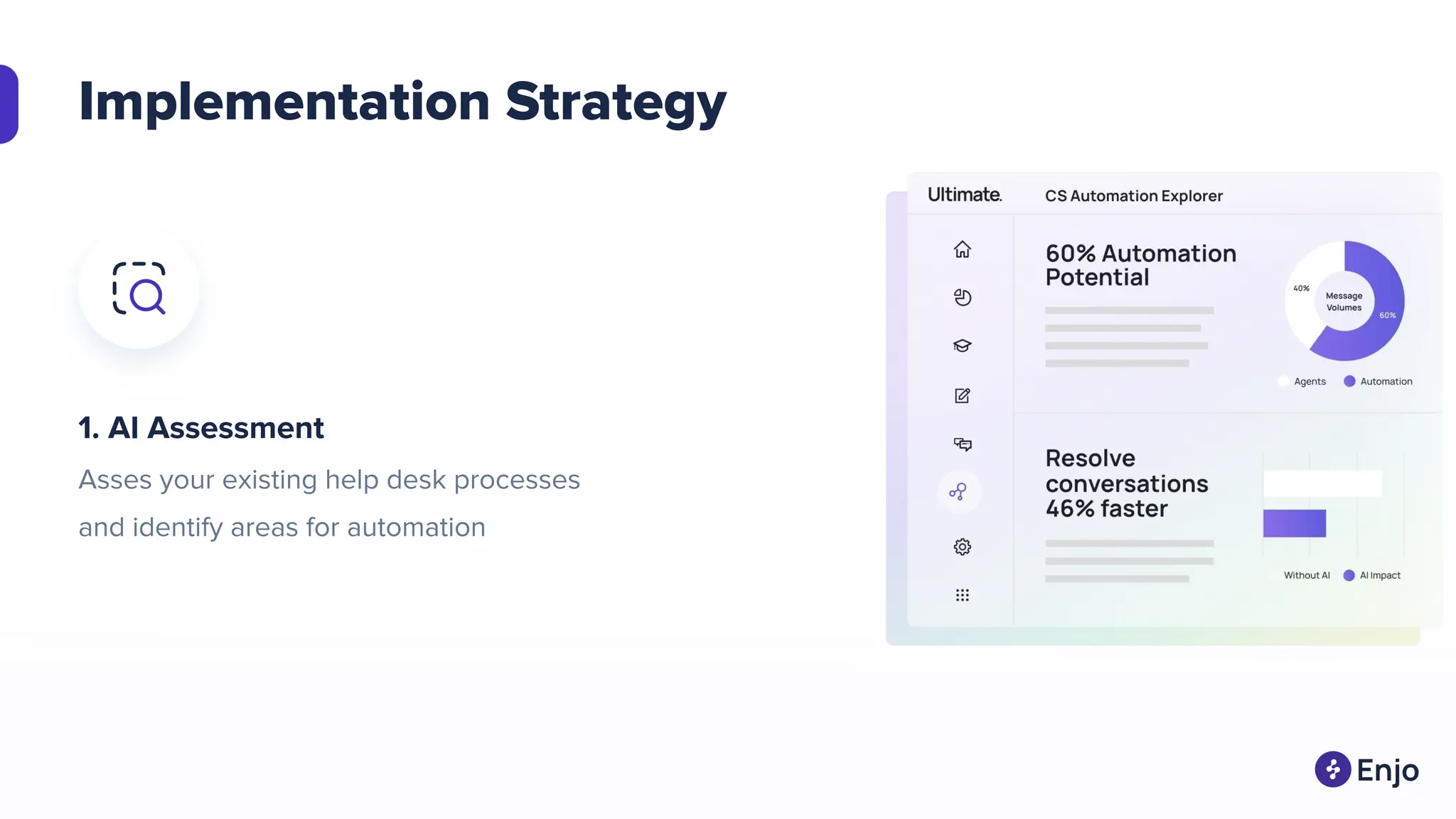
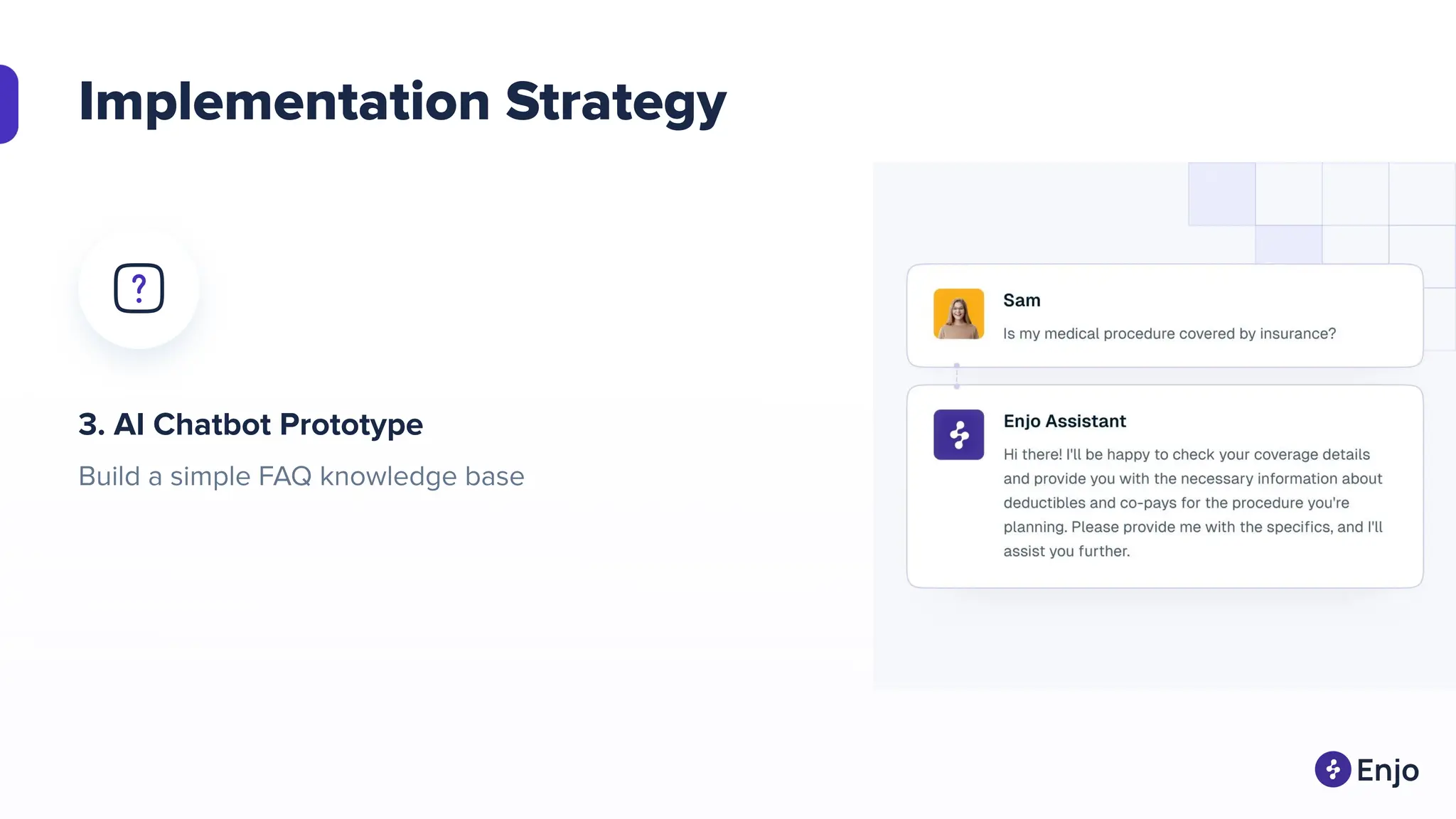
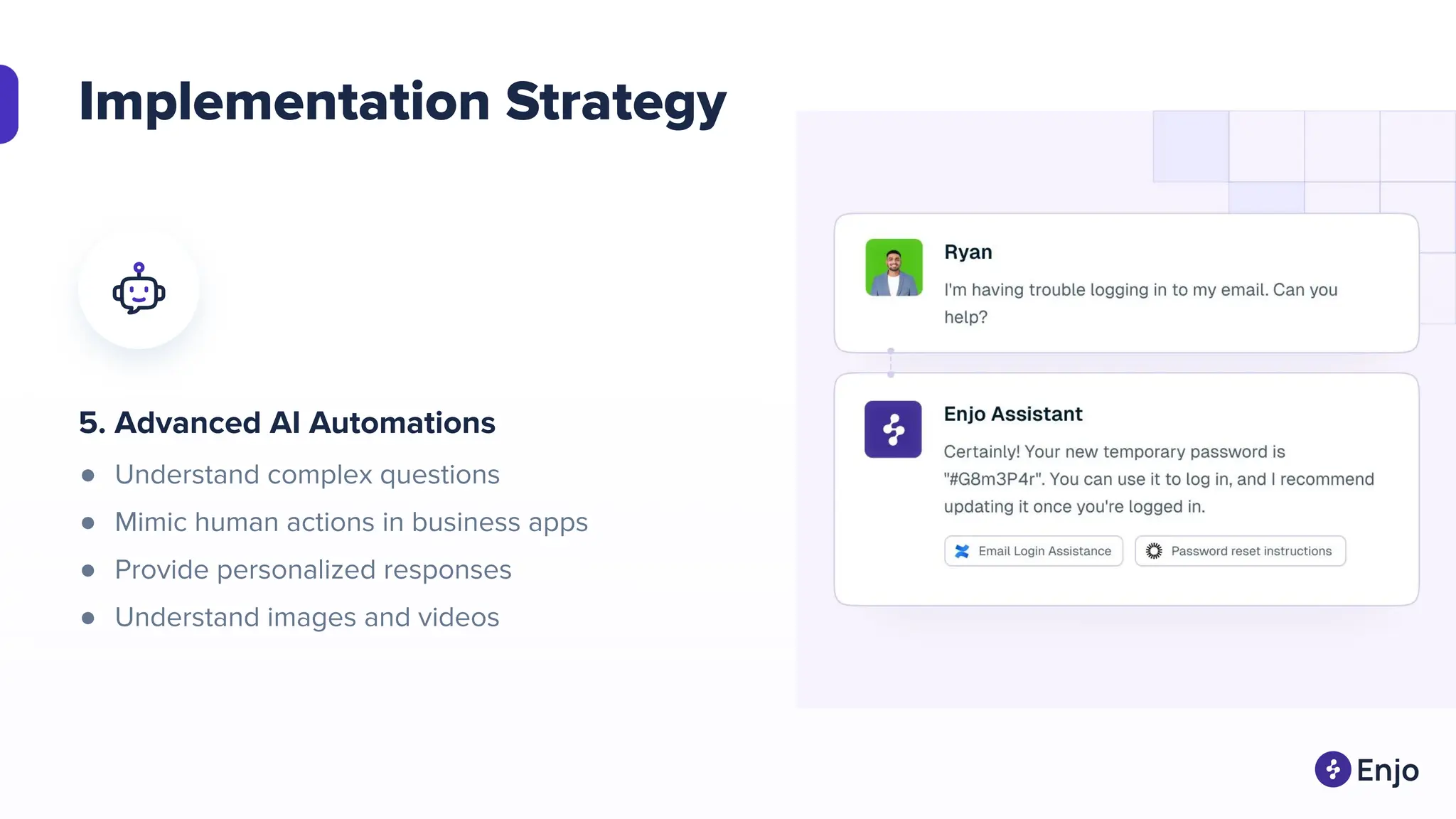
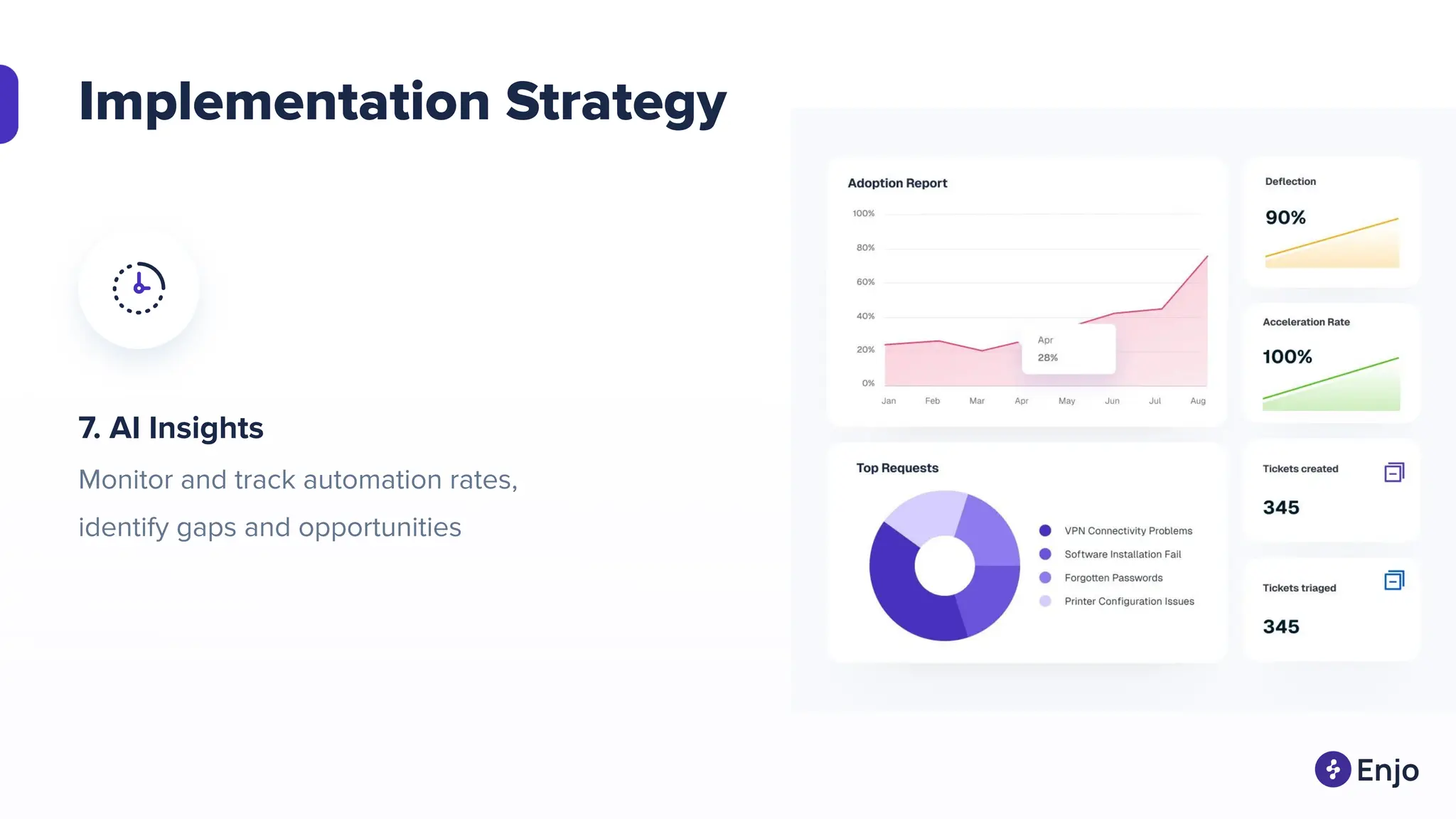
The document discusses the strategies for implementing AI in help desk systems, comparing traditional help desks with AI-powered options and highlighting the benefits such as cost reduction, enhanced customer satisfaction, and 24/7 availability. It covers various workplace applications, common help desk queries across IT, HR, and customer service, and outlines a comprehensive implementation strategy including AI assessment, knowledge engineering, and chatbot development. Additionally, it addresses generative AI's capabilities, challenges, and fallacies, emphasizing the importance of tailored data and human oversight in successful AI deployments.


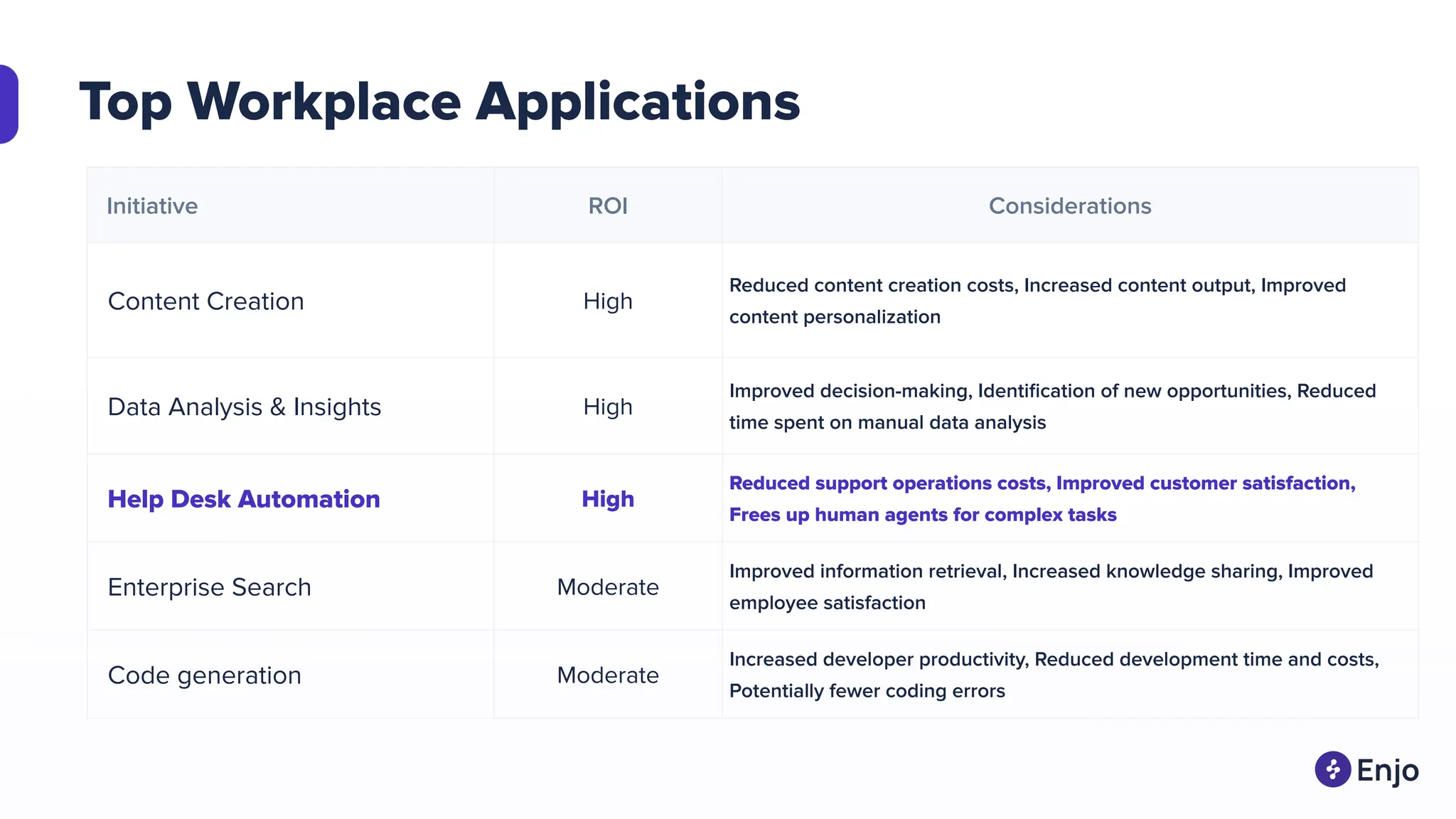


![Common Help Desks
Customer Service Help Desk
Provide support and assistance to external customers
Common queries:
- How do I change our account administrator?
- How do I cancel my subscription?
- We're experiencing [specific error]. How can we resolve this?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acecoimbatore-aiandfutureofhelpdesks-merged-240701093453-fc514f97/75/AC-Atlassian-Coimbatore-Session-Slides-22-06-2024-6-2048.jpg)











![Artificial
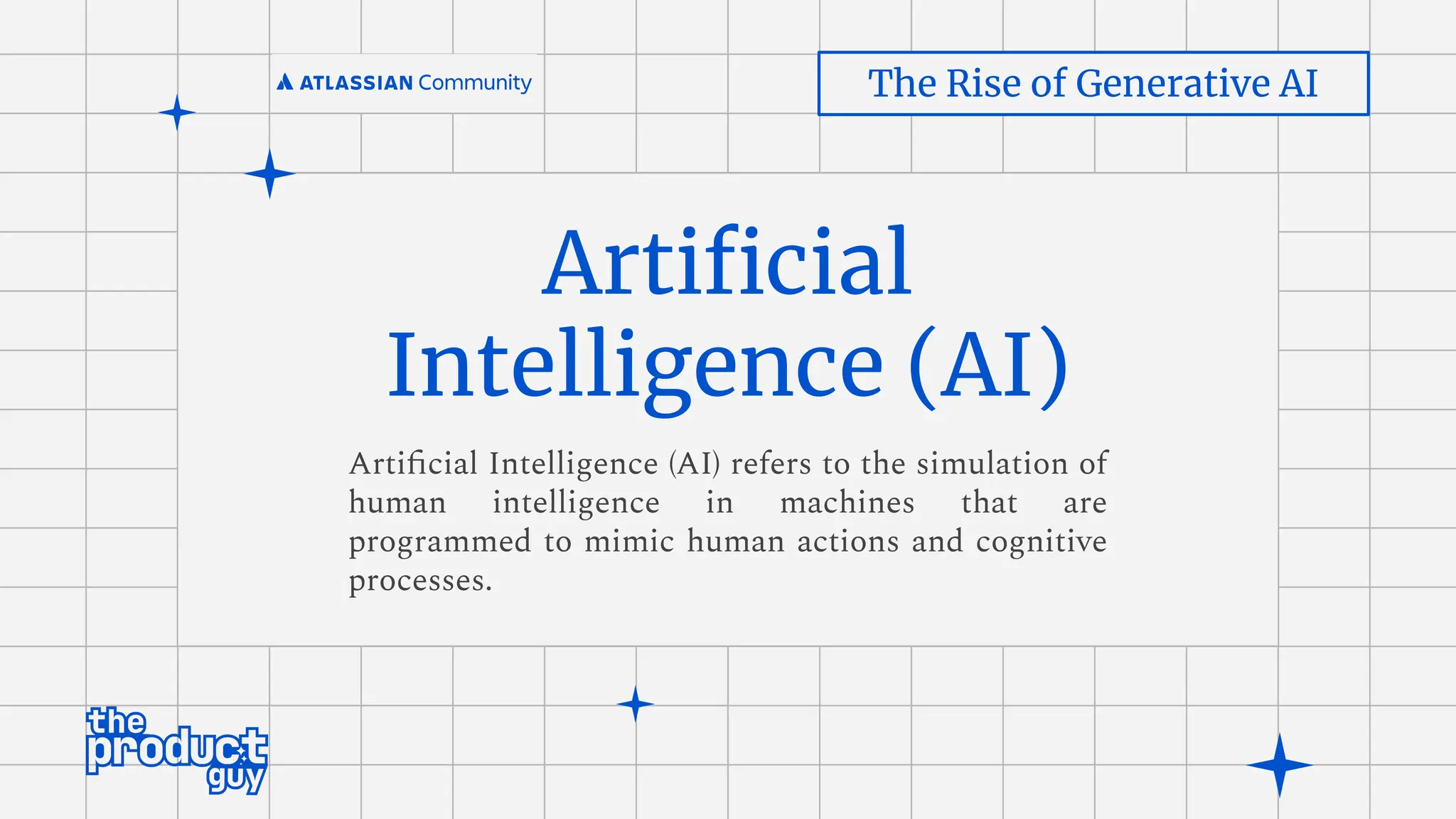
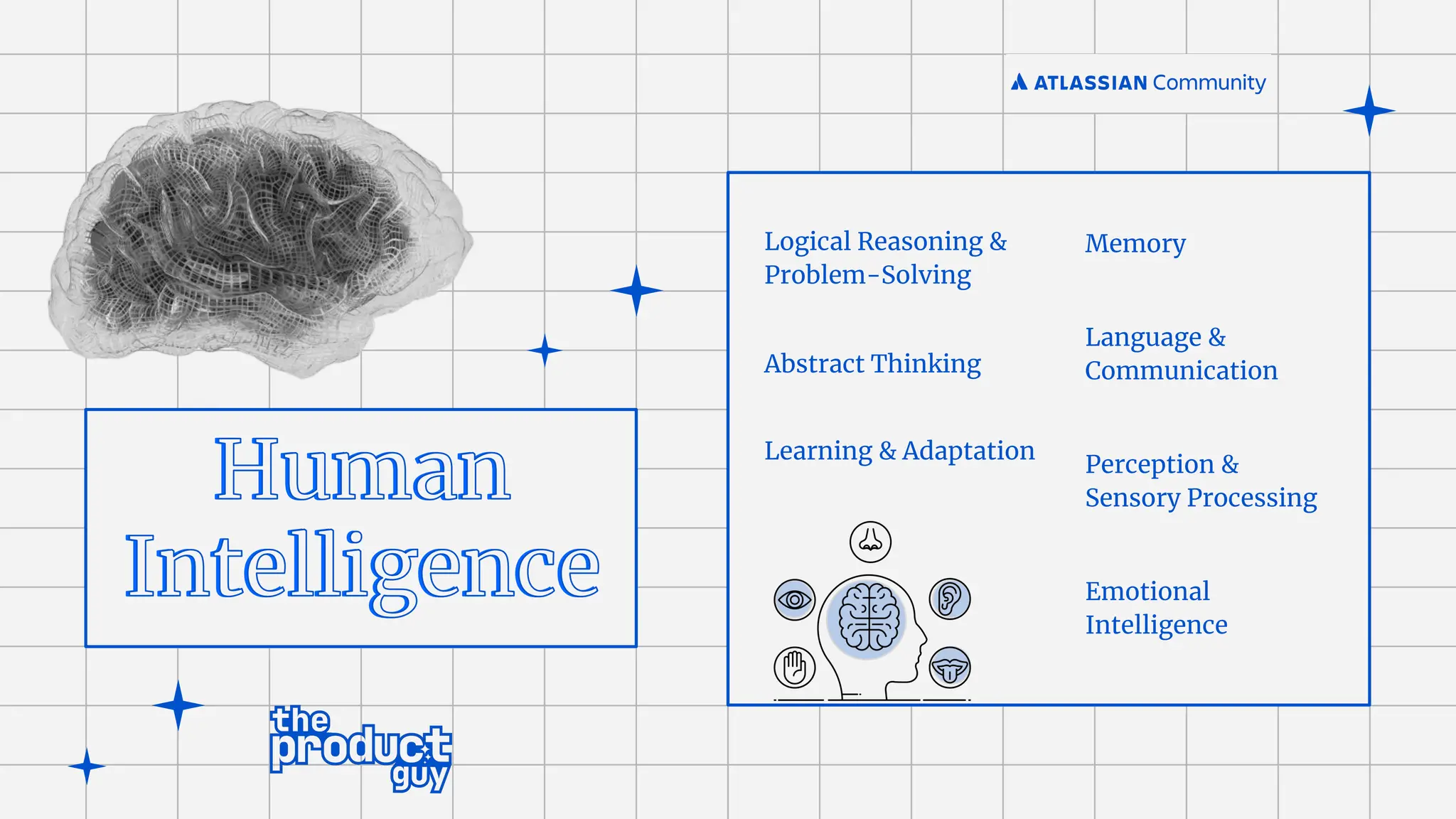
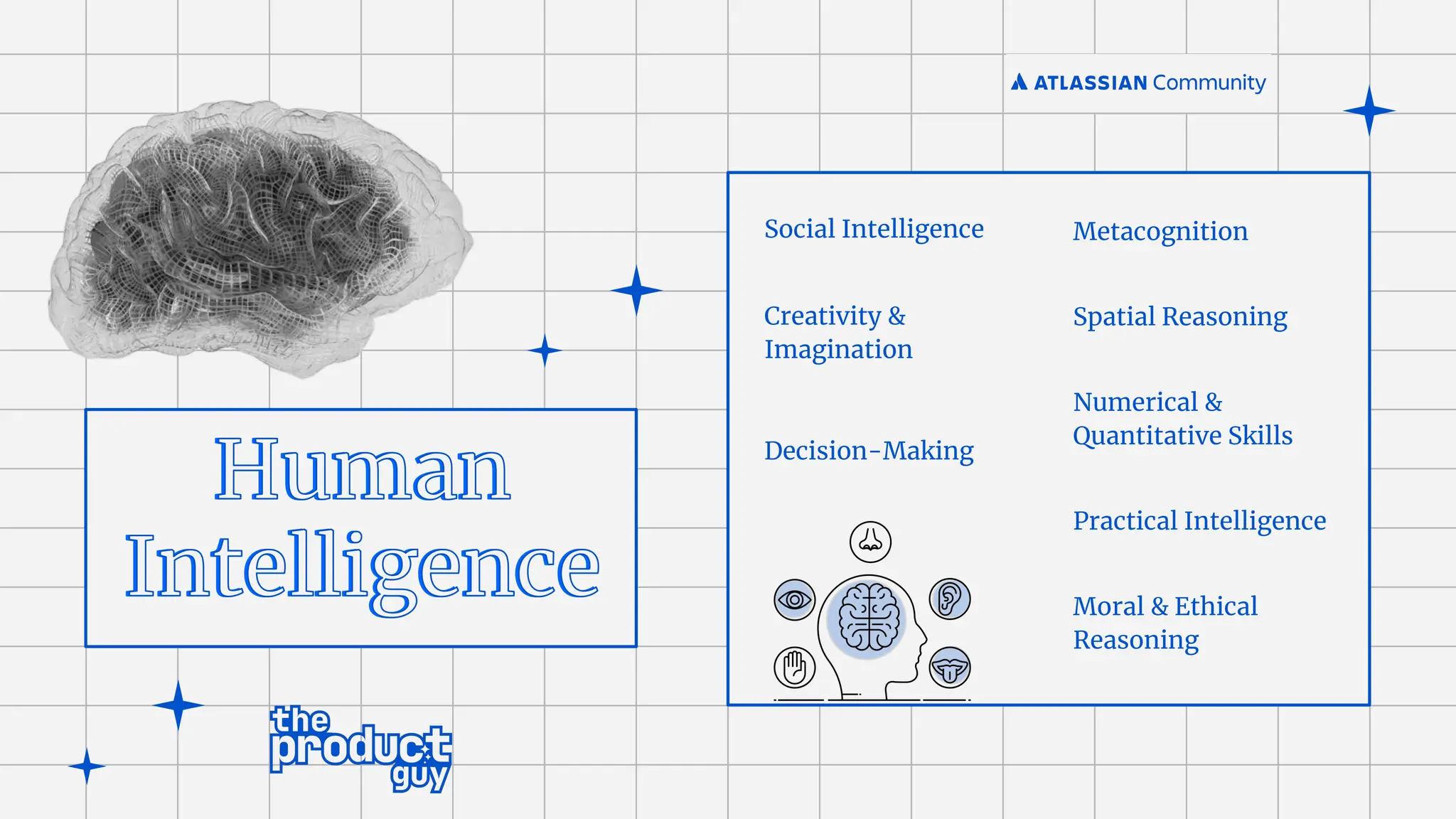
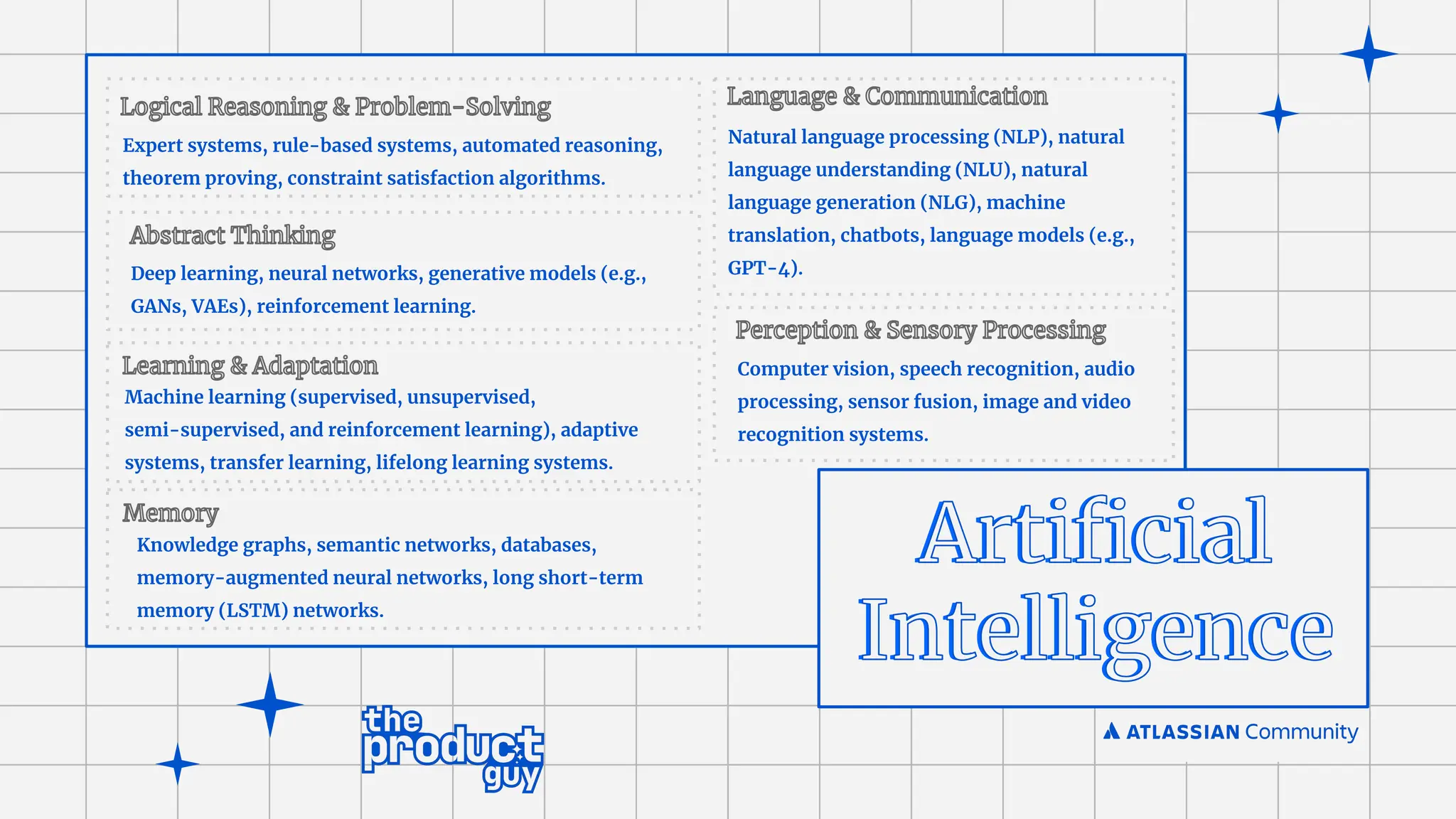
Intelligence[AI]
Machine
Learning [ML]
Natural Language
Processing [NLP]
Deep Learning
Vision Speech
Robotics
Planning
Expert
Systems
Neural Networks
Generative AI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acecoimbatore-aiandfutureofhelpdesks-merged-240701093453-fc514f97/75/AC-Atlassian-Coimbatore-Session-Slides-22-06-2024-34-2048.jpg)