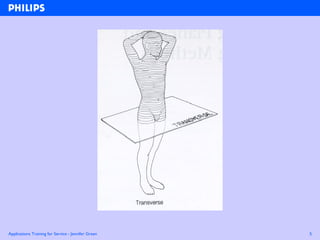
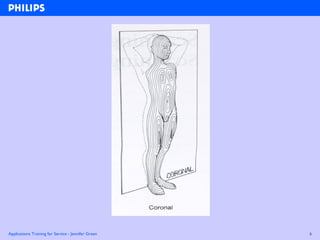
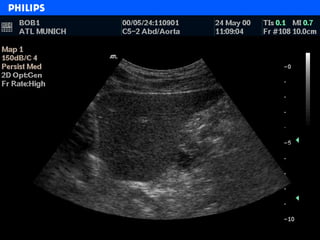
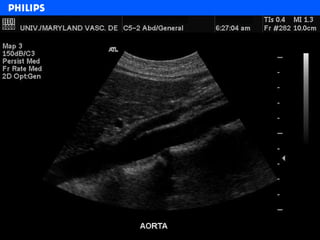
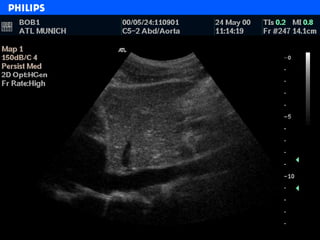
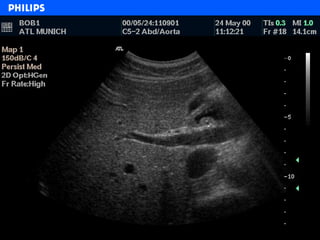
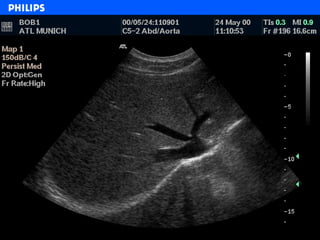
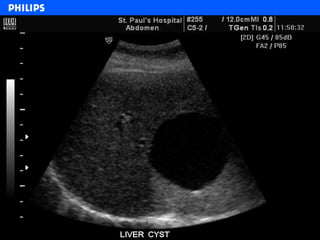
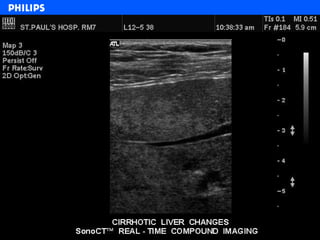
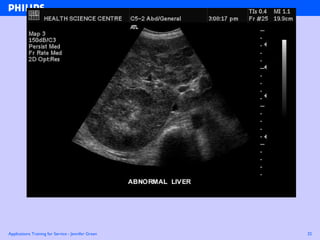
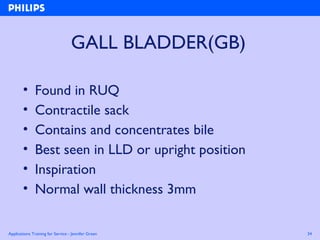
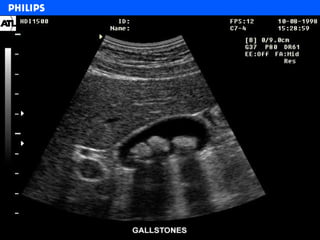
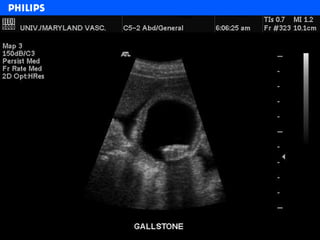
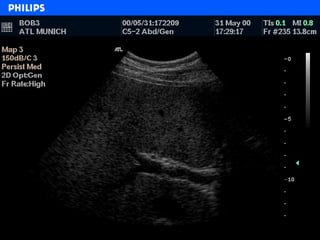
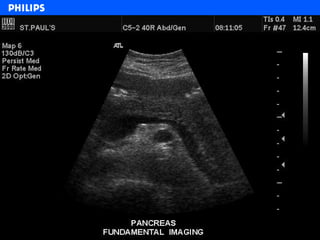
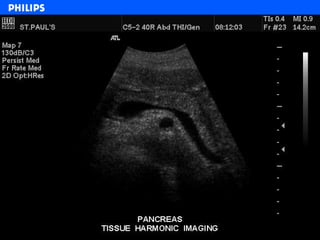
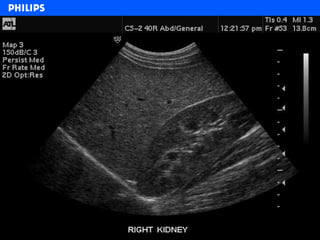
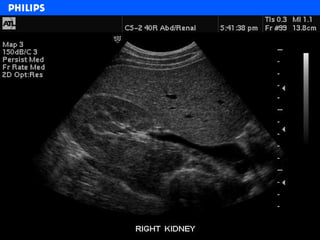
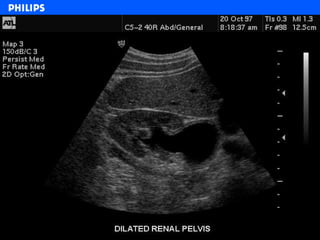
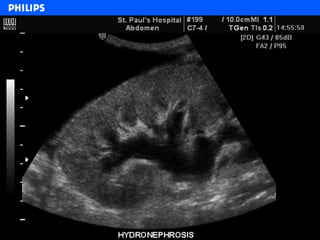
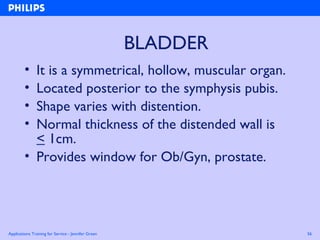
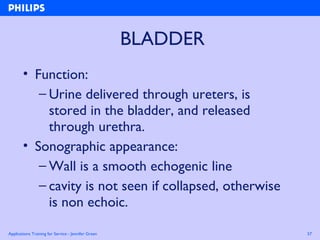
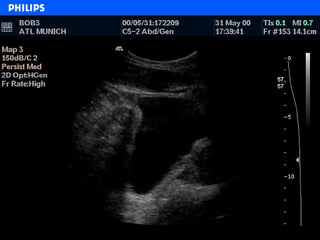
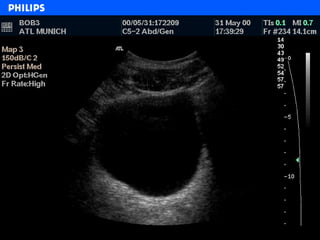
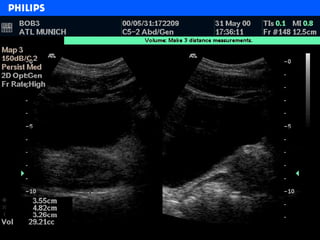
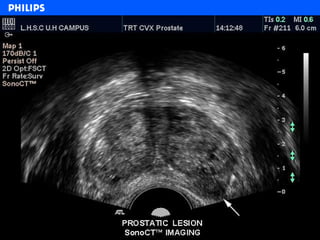
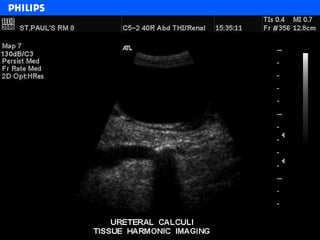
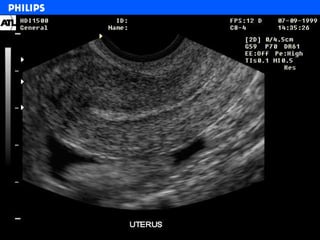
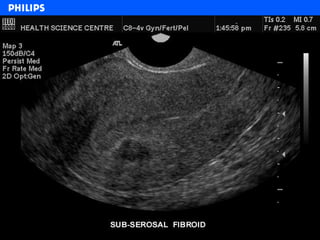
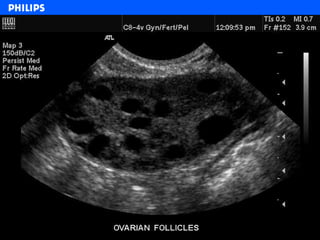
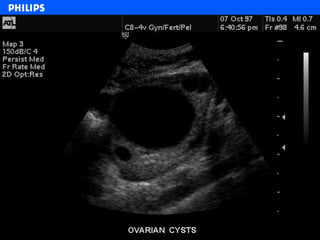
The document discusses abdominal ultrasound anatomy and scanning techniques. It provides an overview of abdominal ultrasound anatomy, including the liver, gallbladder, common bile duct, pancreas, kidneys, bladder, prostate, uterus and ovaries. It describes optimal scanning positions and planes for visualizing these organs, and terminology used in abdominal ultrasound scans.