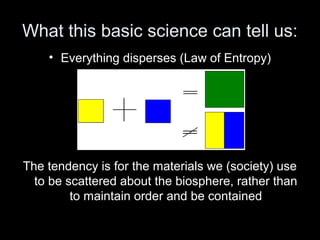
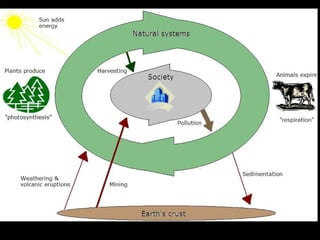
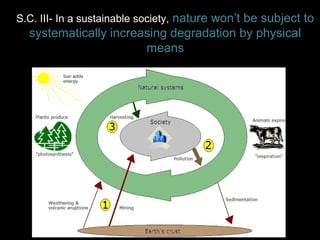
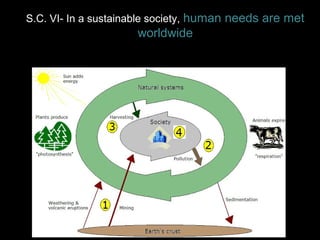
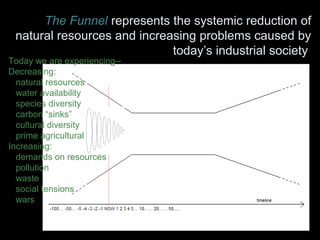
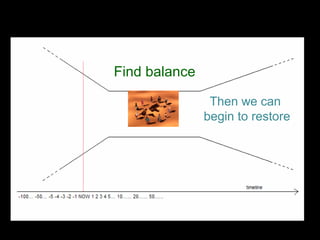
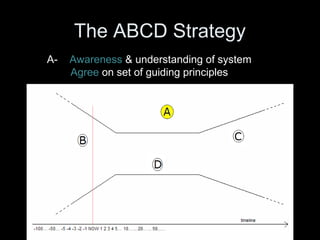
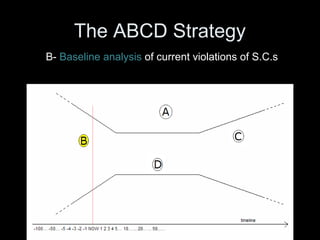
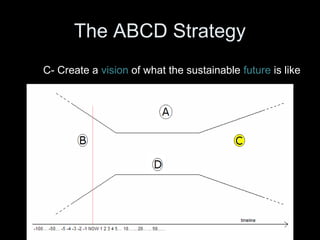
The Natural Step is an international non-profit organization founded in 1989 in Sweden to promote global sustainability based on the laws of thermodynamics. It has 11 member countries and offers a master's program in strategic sustainability leadership. The organization outlines four system conditions for sustainability: 1) nature is not subject to increasing concentrations of extracted substances, 2) nature is not subject to increasing concentrations of human-produced substances, 3) nature is not subject to physical degradation, and 4) human needs are met worldwide. The Natural Step uses an ABCD strategy of raising awareness, analyzing current practices, creating a vision for sustainability, and devising steps to achieve that vision through "backcasting from principles."