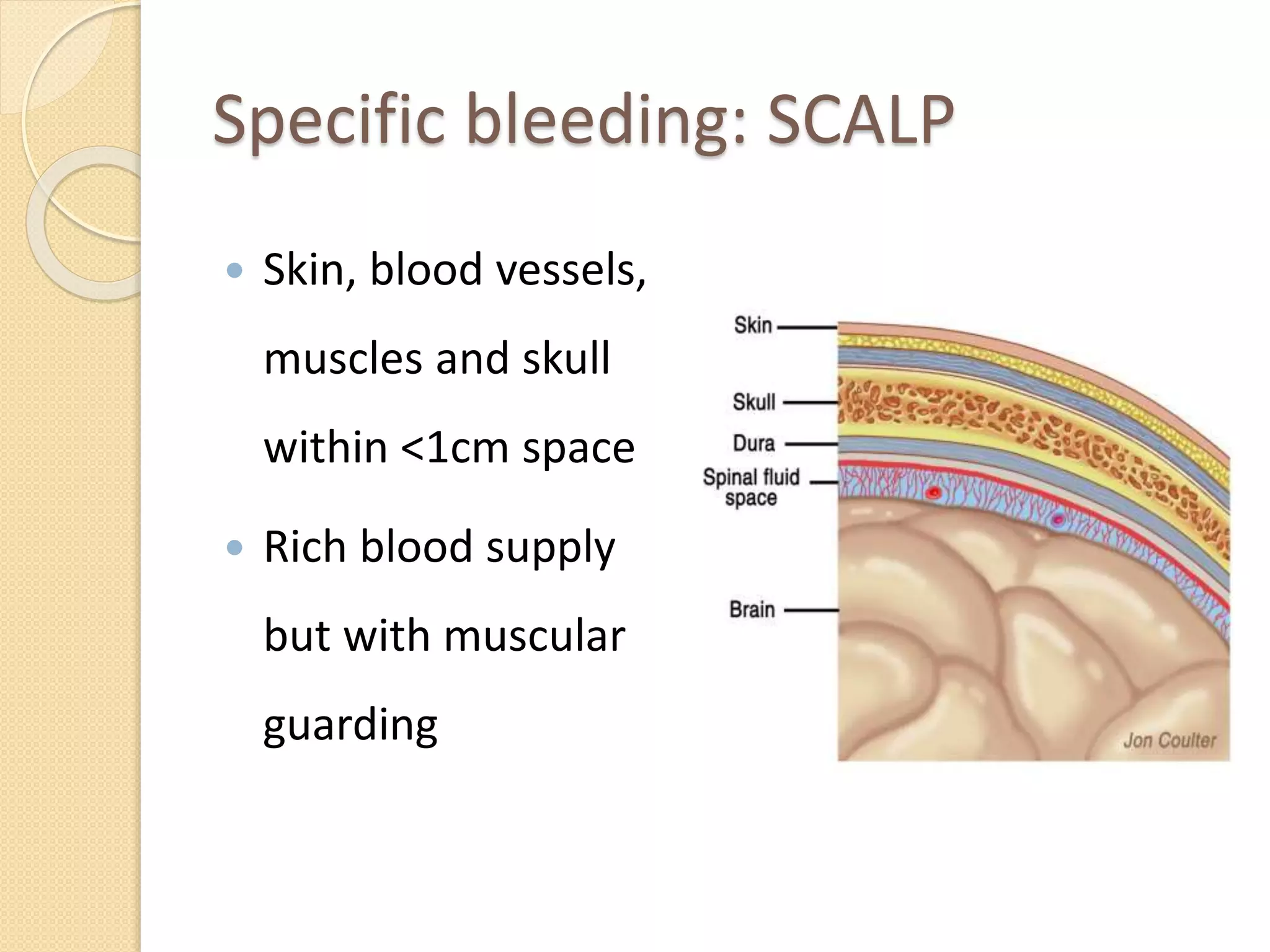
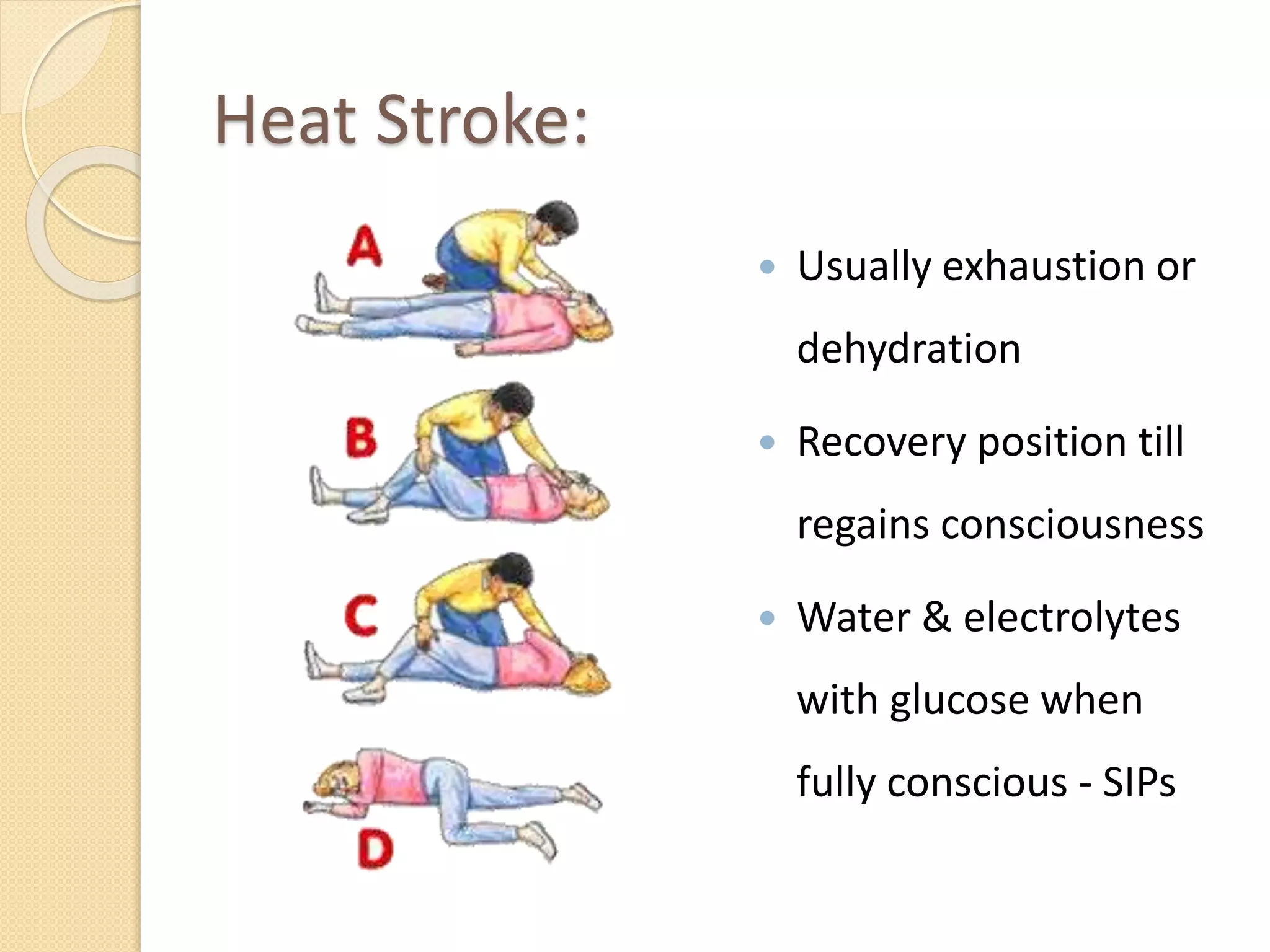
The document outlines essential first aid knowledge, emphasizing the importance of stabilizing an injured person until professional medical help arrives. It covers various topics such as bleeding control, handling convulsions, fractures, head injuries, burns, and electric shock, providing step-by-step instructions for each scenario. Additionally, it advises on what actions to avoid in a first aid situation to prevent further complications.