Embed presentation
Download to read offline

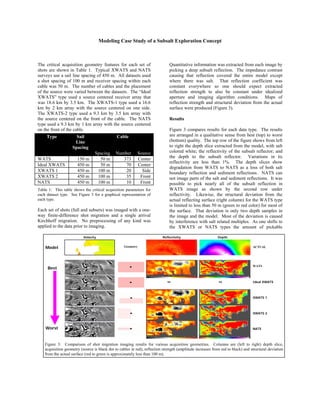
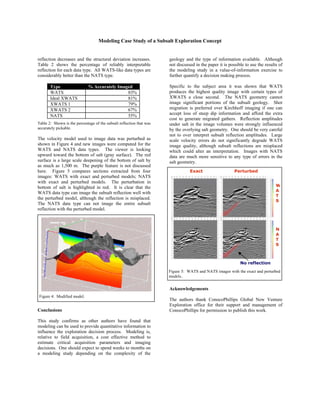
A modeling study compared seismic images from various marine streamer acquisition geometries, including wide azimuth towed streamer (WATS) and narrow azimuth towed streamer (NATS), to understand subsalt imaging challenges. WATS and certain wide azimuth cross-line towed streamer (XWATS) geometries provided the best subsalt imaging, resolving most structures of interest. However, subsalt illumination remained imperfect even for WATS, and velocity inaccuracies most impacted WATS imaging quality. Quantitative analysis of reflection strength and structure positioning helped evaluate each geometry.


