The document provides an overview of a presentation on the process for becoming a chartered engineer through the Institution of Chemical Engineers (IChemE). It discusses the requirements, application process, and includes a sample competency and commitment report format. The presentation also covers the role of mentors in supporting candidates through the application process and preparing for the professional review interview.



















![Experience
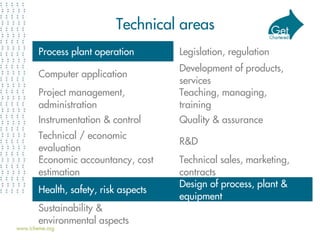
• Principles: aware of all, applying some
• Technical areas: 4 – 6 in depth
• Experience tells us it takes min 4 years post
grad experience before candidate should
apply [Focus on skills not time]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/IChemEPresentation-123435573482-phpapp03/85/I-Chem-E-Presentation-21-320.jpg)





























































































