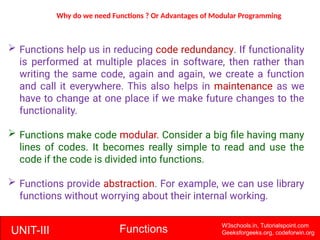
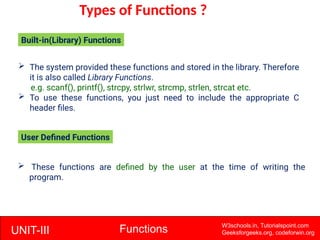
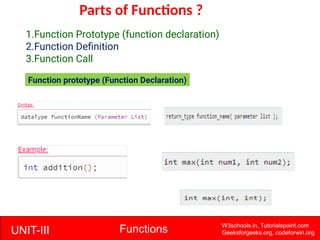
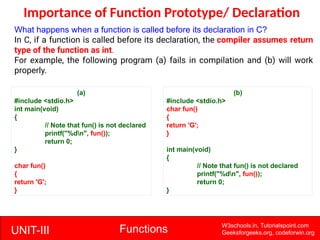
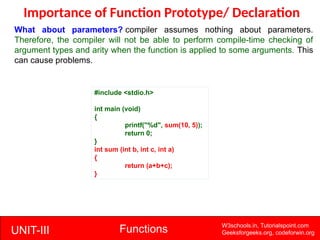
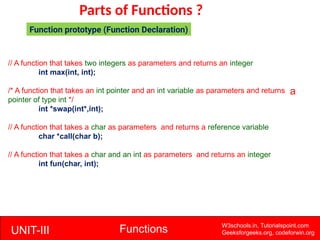
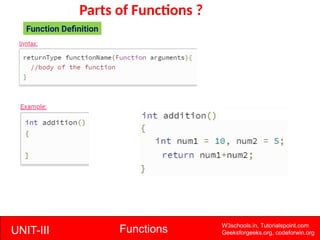
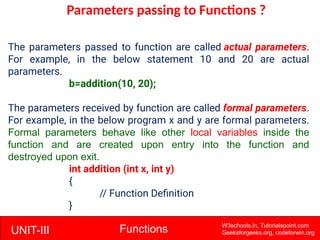
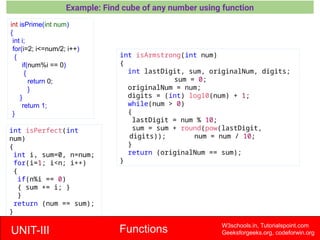
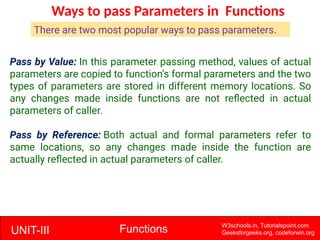
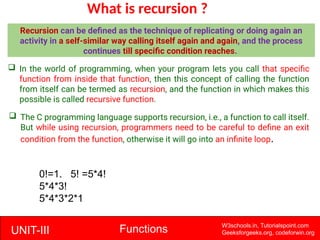
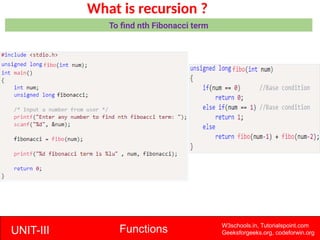
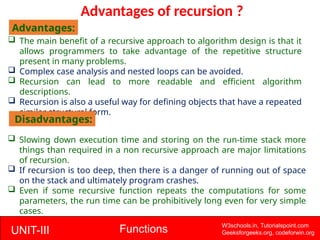
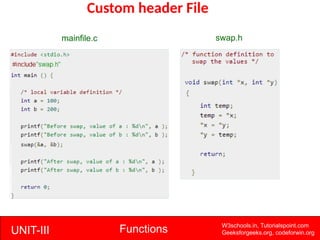
The document provides a comprehensive overview of functions in C programming, explaining their definition, types, advantages, and usage with examples. It covers aspects such as how to declare, define, and call functions, the importance of function prototypes, and the differences between value and reference parameter passing. Additionally, it addresses recursion, including its advantages and disadvantages, alongside practical exercises for further understanding.