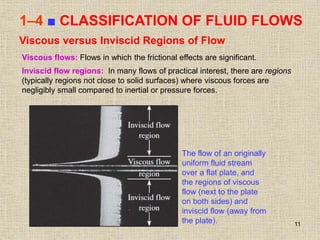
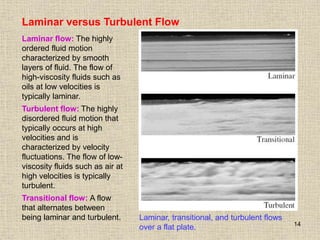
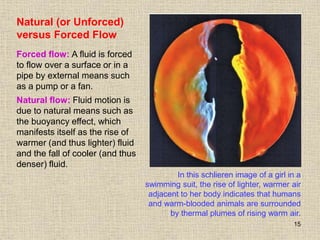
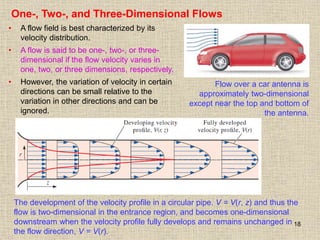
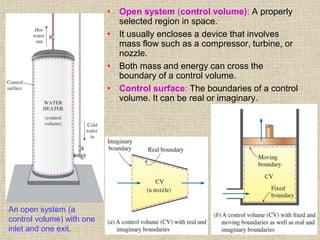
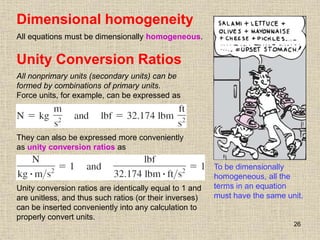
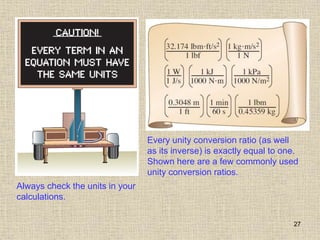
1. Unlike liquids, gases expand to fill their entire container and do not form a free surface. This is because gas molecules are widely spaced and interactions between them are very weak.
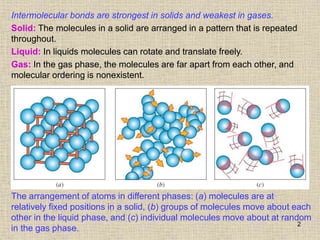
2. Gases, liquids, and solids differ in the arrangement and movement of their molecules. In gases, molecules move randomly and independently of one another. In liquids, molecules can move relative to one another but maintain a constant volume. In solids, molecules are arranged in a repeating pattern with little movement.
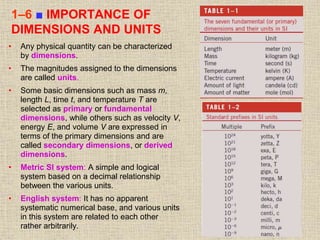
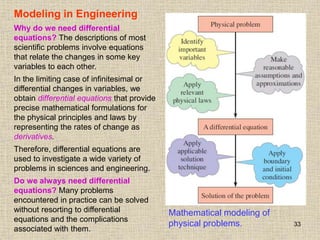
3. Fluid mechanics analyzes fluid behavior on both the microscopic scale of individual molecules and the macroscopic scale of observable properties. It has many applications including artificial heart design and wind turbine technology.