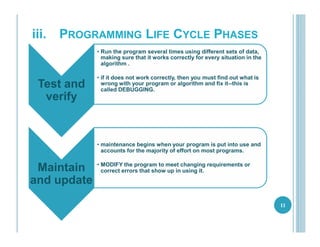
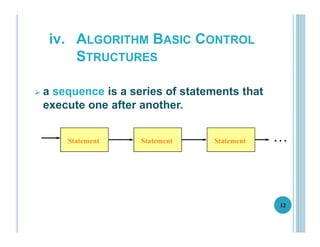
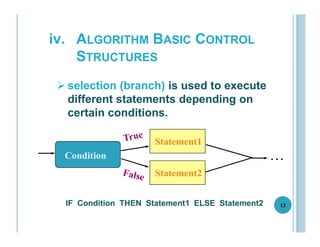
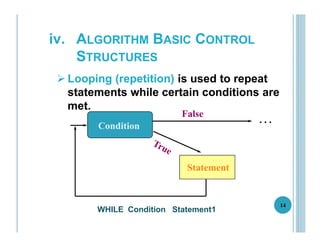
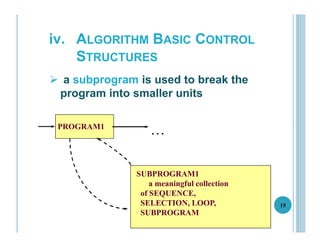
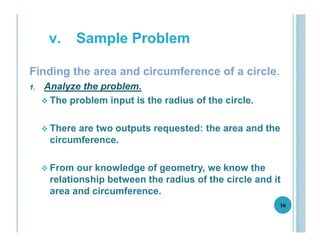
This document outlines the goals, topics, grading system, and textbook for the CC112 Structured Programming course. The course aims to introduce programming concepts and have students begin writing programs in C. Over the course, students will learn about program structure, data types, control flow statements, functions, arrays, and more. Assessment includes exams, assignments, and a final exam. The recommended textbook is C How To Program by Paul and Harvey Deitel. Lecture 1 provides an overview of computers, programming, and the programming lifecycle. It also gives examples of basic control structures and walks through solving a sample problem to find the area and circumference of a circle.