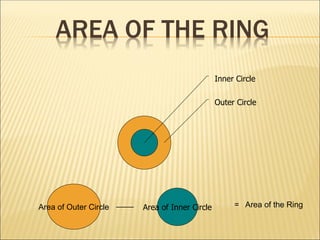
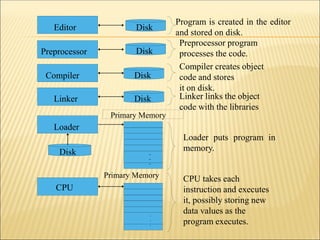
The document outlines the fundamentals of programming, emphasizing critical skills such as analysis, critical thinking, and attention to detail necessary for designing effective programs. It covers course objectives, including the need for programming languages, structured programming methodology, and proficiency in C language, along with various programming concepts like control structures and software categories. The document also discusses tools of the trade, including editors, compilers, and integrated development environments.