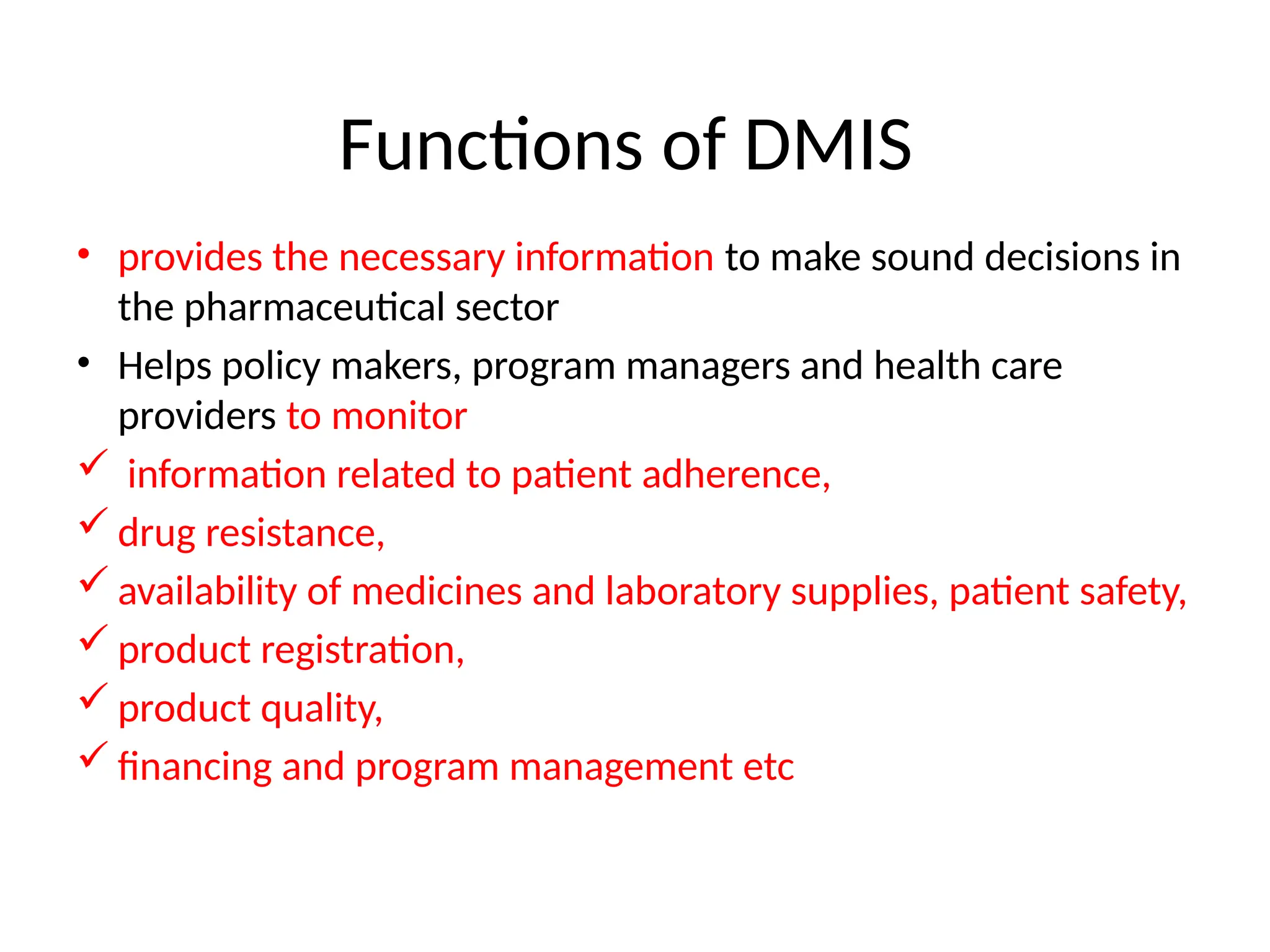
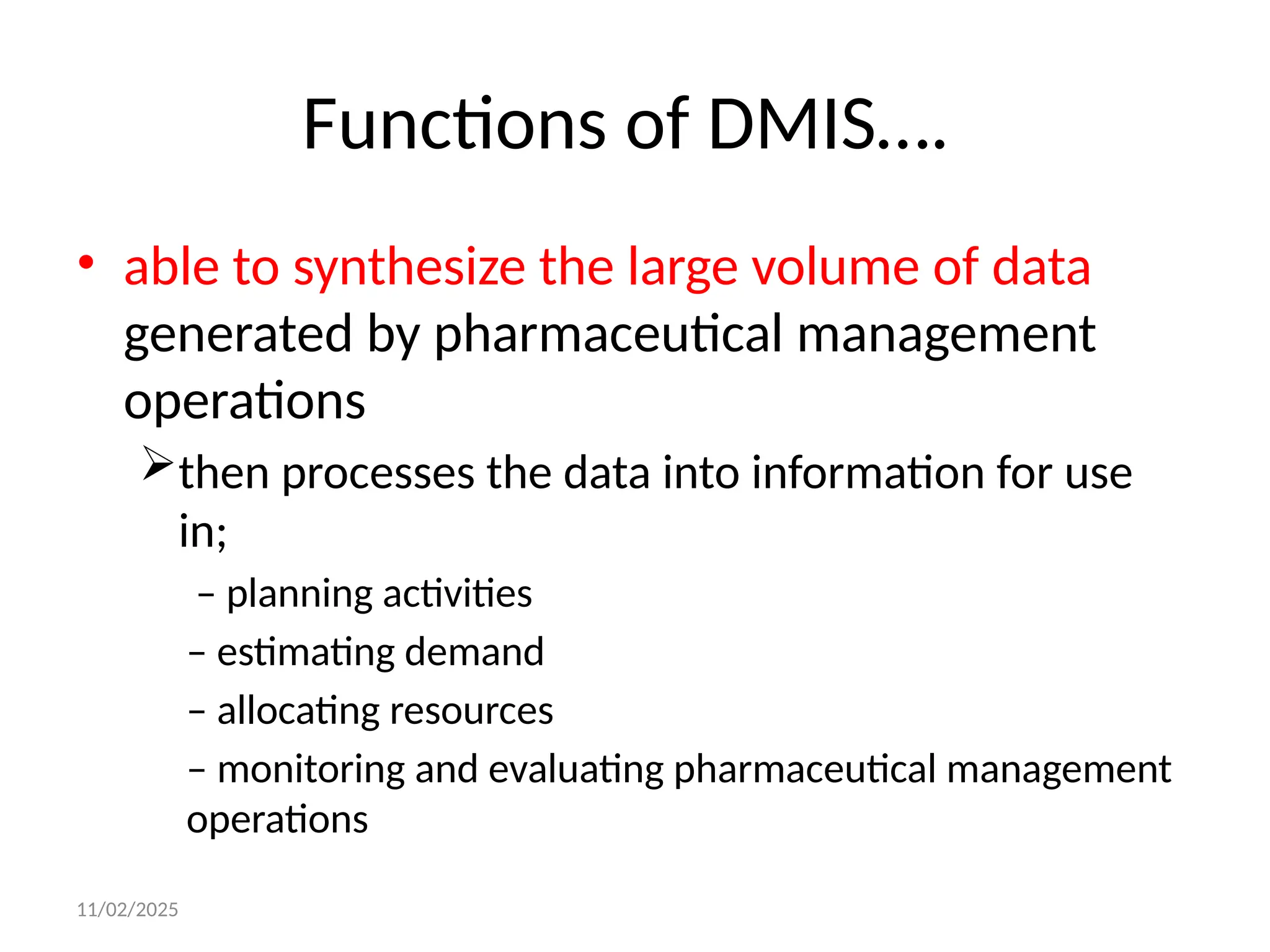
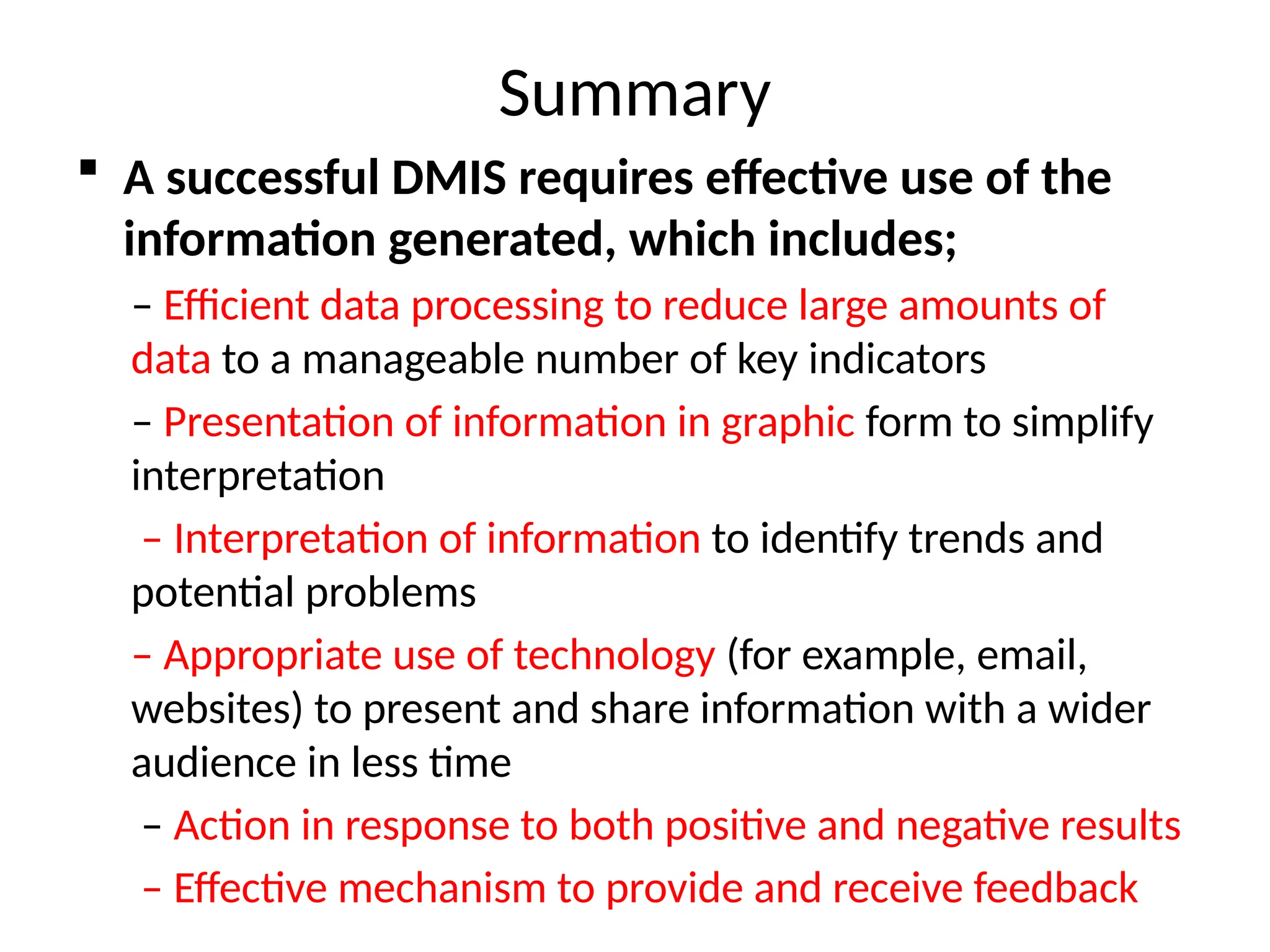
The document outlines the principles and practices of rational drug use, emphasizing the roles of healthcare providers in prescribing, dispensing, and monitoring drug therapies. It identifies factors contributing to irrational drug use and proposes strategies to promote rational prescribing and dispensing through education, management, and regulatory measures. Additionally, it highlights the importance of drug management information systems for improving drug accessibility, patient safety, and healthcare efficiency.