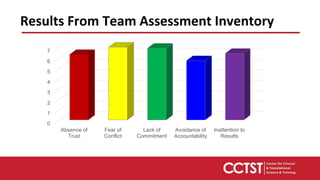
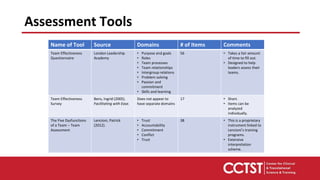
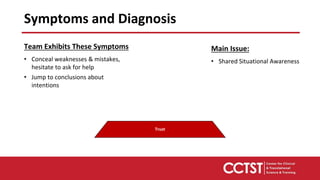
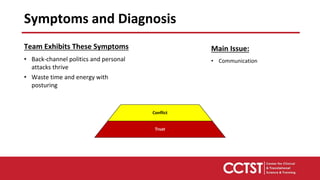
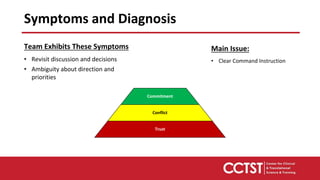
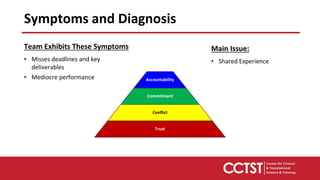
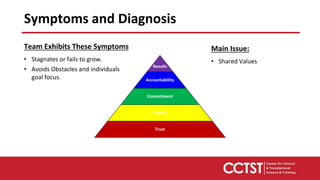
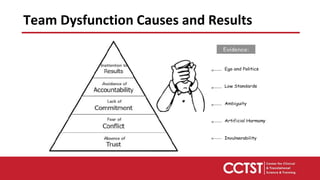
This document provides an overview of team dysfunctions and interventions. It discusses the five main dysfunctions: absence of trust, fear of conflict, lack of commitment, avoidance of accountability, and inattention to results. For each dysfunction, it describes common symptoms, compares dysfunctional versus functional teams, and provides an activity for teams to address the issue. The document emphasizes that effective teams embrace accountability, achieve commitment, master conflict, build trust, and focus on collective results. It encourages applying these skills to strengthen one's own teams.