1) The document discusses fuel filtration for modern diesel fuels, covering changes in fuel composition, diesel engine fuel system basics, and fuel filter design, media, and efficiency.
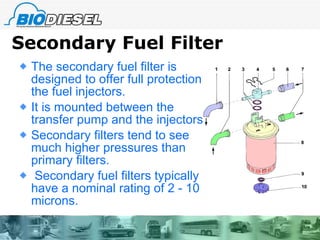
2) It describes various fuel filter components and how they work, including primary filters, secondary filters, and water separators.
3) The document provides information on maintaining fuel quality and filter performance, and potential contaminants that may be observed in diesel fuel filters.