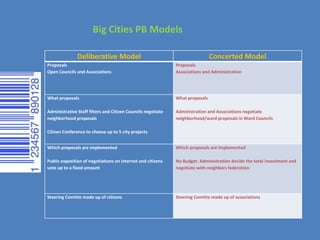
Participatory budgeting has expanded globally since 1989, including to large cities like New York, Hamburg, Paris, and Madrid. This presents new challenges of scale involving millions of people and large public budgets. Models in large cities include neighborhood and city/ward budgeting, focusing on either hard infrastructure or social programs. Cities like Paris use a deliberative model where citizen councils negotiate proposals, while Madrid uses a concerted model where associations and administrators negotiate proposals. Effective participation in large cities requires moving beyond small groups to also use the internet to engage more citizens in transparency and decision making. However, connecting participation to administrative realities is complex, and underlying these projects are important democratic questions about who is legitimized to make decisions and who represents the