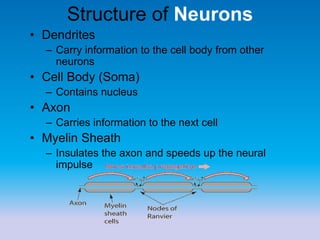
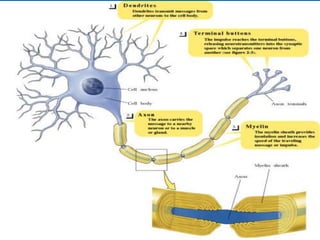
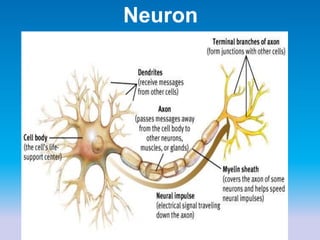
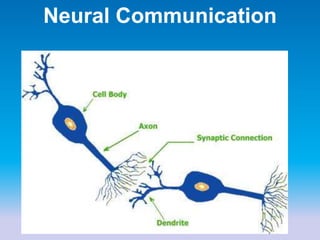
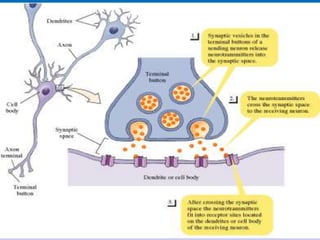
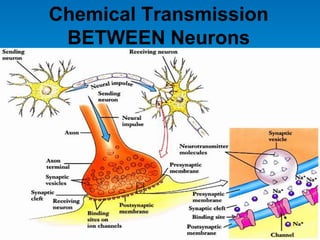
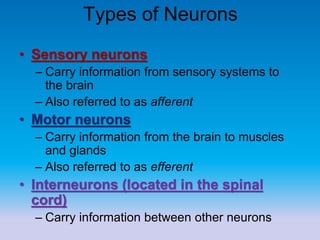
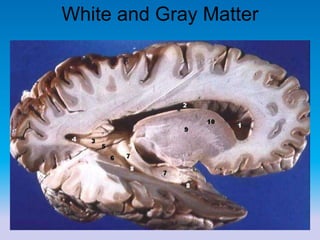
This document summarizes key concepts in biological psychology including the basic parts and functions of neurons. It describes the unique features of neurons including dendrites, cell body, axon, terminal buttons, synaptic vesicles, and receptor sites. The document also outlines how neurons communicate through chemical transmission at synapses using neurotransmitters released from synaptic vesicles that bind to receptor sites on receiving neurons.