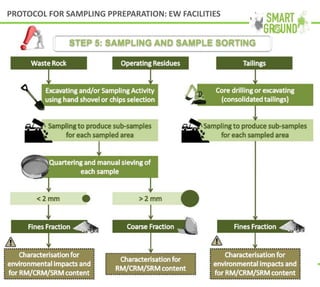
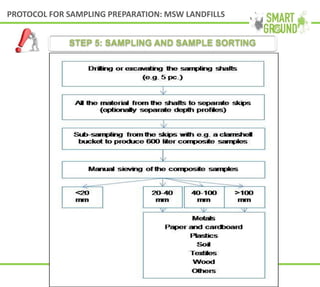
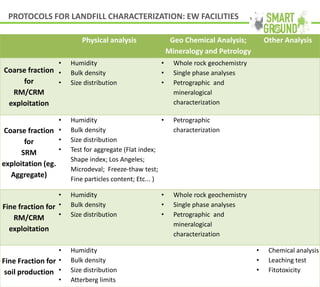
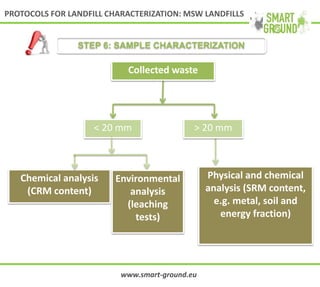
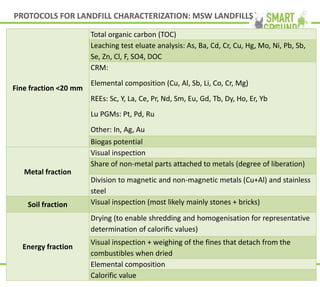
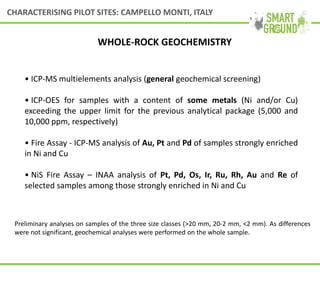
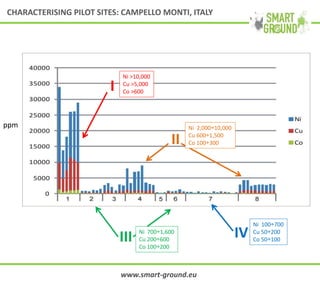
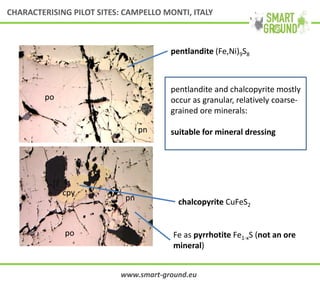
This document summarizes the SMART GROUND project which aims to enhance availability and accessibility of data on secondary raw materials in the EU. It outlines the project's approach to characterizing extractive waste facilities, municipal solid waste landfills, and other sites to identify secondary raw materials and critical raw materials. The characterization involves preliminary research, geophysical and drone surveys, sampling schemes, sample analysis, and pilot site characterization activities. The goal is to understand the waste deposits and identify materials that could be exploited for secondary raw materials or recycled.