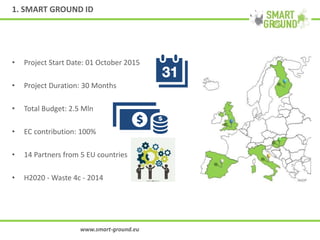
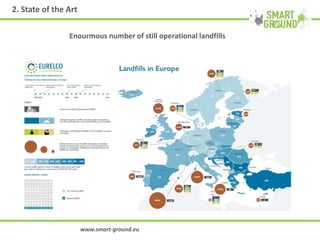
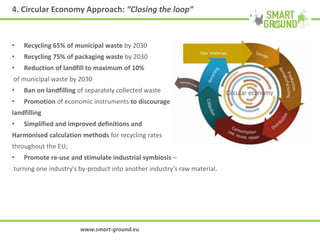
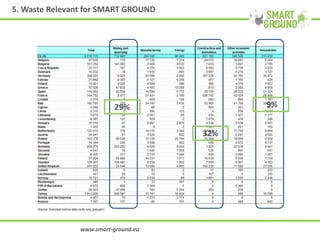
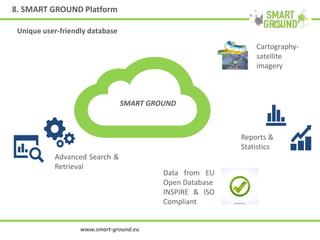
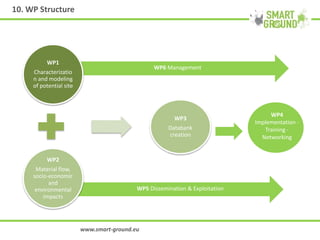
The networking session provided an overview of the SMART GROUND project, which aims to (1) collect and integrate quantitative and structural data on secondary raw materials (SRMs) from landfill sites across the EU, (2) identify the most promising markets for SRMs, and (3) evaluate the environmental, economic, and social impacts of extracting SRMs from landfills. The project involves characterizing pilot landfill sites, estimating their potential SRMs, building an online database, and creating a marketplace to connect SRM suppliers with potential customers like construction companies. The overall goal is to help advance the circular economy and EU waste management targets by exploiting landfills as a source of new resources.