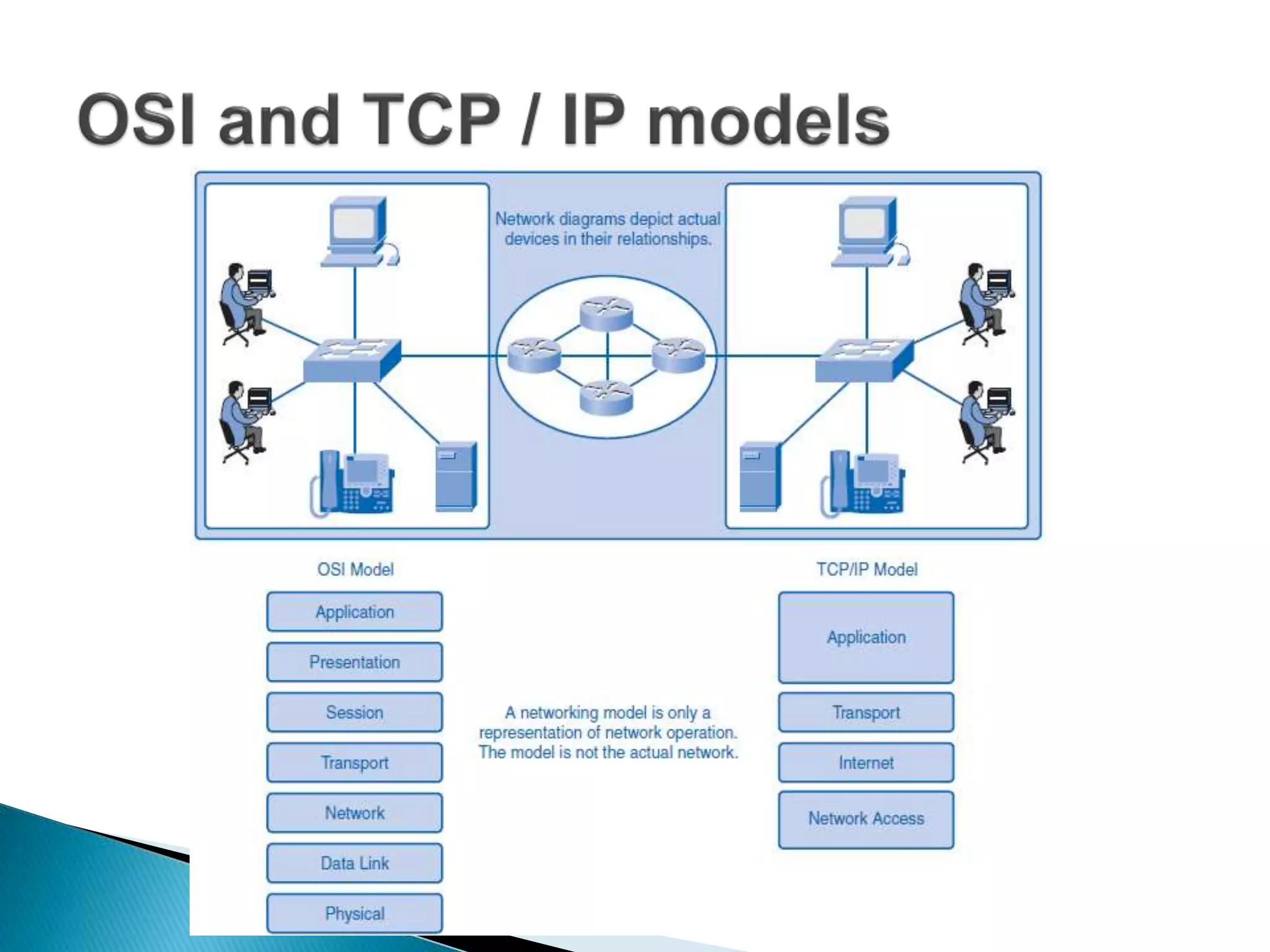
Protocols define rules for communication between network devices to ensure successful transmission of messages. They specify how to initiate and terminate connections, message formats, and how devices share path information. Related protocols are grouped into protocol suites, like TCP/IP. Networking professionals use protocol models that describe specific suites and reference models that provide a common framework, like the OSI model, to understand network communication processes.