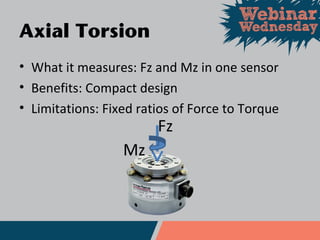
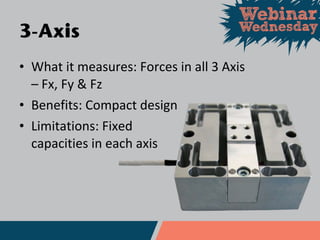
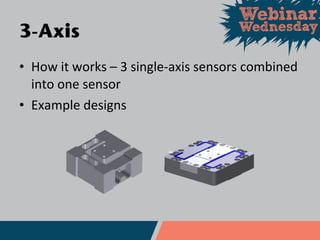
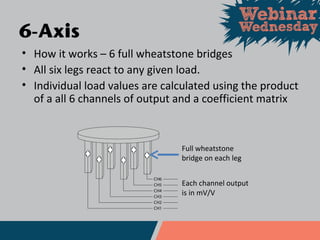
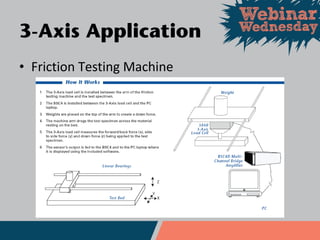
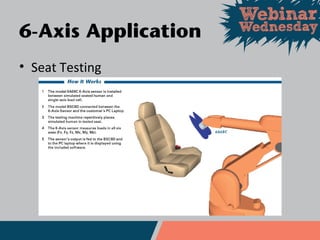
This document discusses different types of force and torque sensors, including single-axis, 2-axis, 3-axis, and 6-axis sensors. Single-axis sensors measure only one force or torque. 2-axis and 3-axis sensors provide more compact designs by measuring combinations of forces and torques. A 6-axis sensor uses a grid of strain gauges and a coefficient matrix to calculate forces and torques in all three dimensions simultaneously. Examples applications discussed include cutting force measurement, friction testing, and wind tunnel testing.