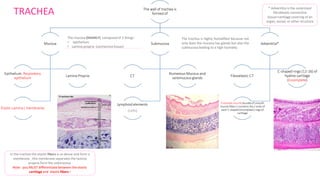
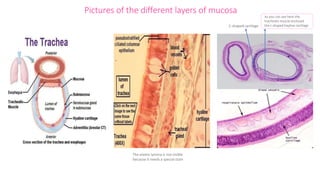
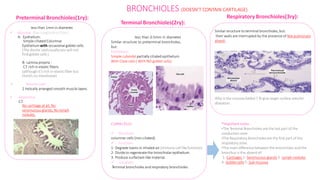
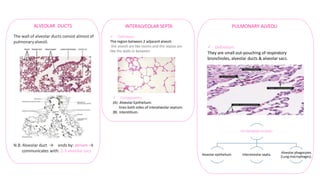
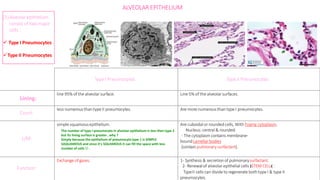
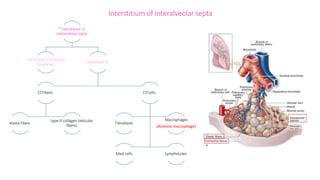
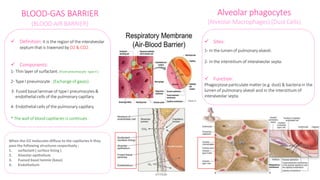
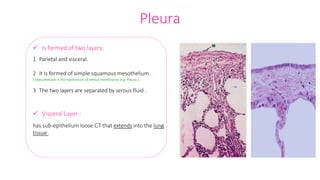
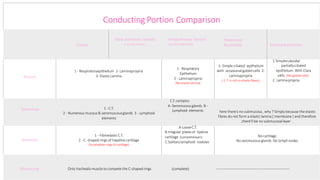
The document summarizes the histology of the lower respiratory tract and lungs. It describes the microscopic structures of the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, interalveolar septa, and pleura. Key points include that the trachea contains C-shaped cartilage rings completed by the trachealis muscle, while bronchi contain smooth muscle layers. Bronchioles lack cartilage and glands. Alveoli are lined by type I and type II pneumocytes and separated by interalveolar septa containing capillaries. Type II cells produce surfactant. The pleura is a serous membrane formed of mesothelium and fluid.