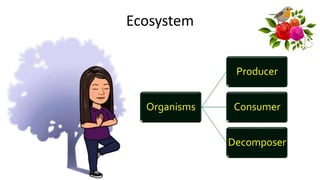
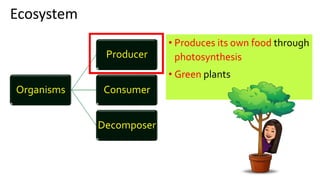
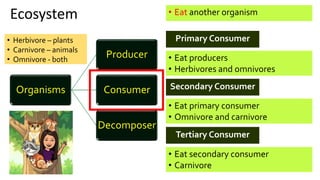
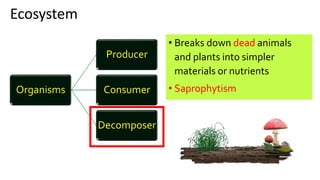
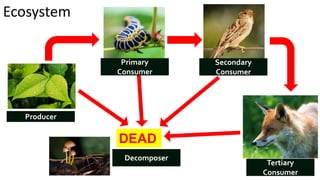
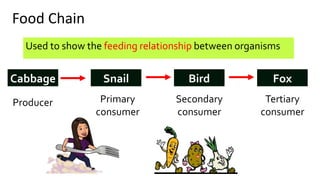
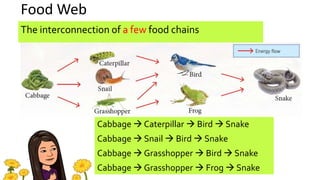
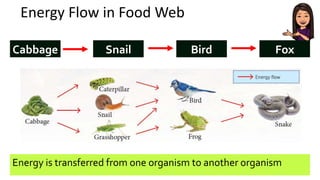
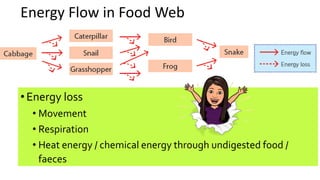
The document discusses energy flow in ecosystems. It states that the sun is the primary source of energy, which plants convert to chemical energy through photosynthesis. Producers are then eaten by primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers in a food chain. Decomposers break down dead organisms, recycling nutrients and matter. Food webs illustrate the interconnected food chains in an ecosystem and how energy is transferred between organisms as it makes its way through the system, with some energy lost at each transfer.