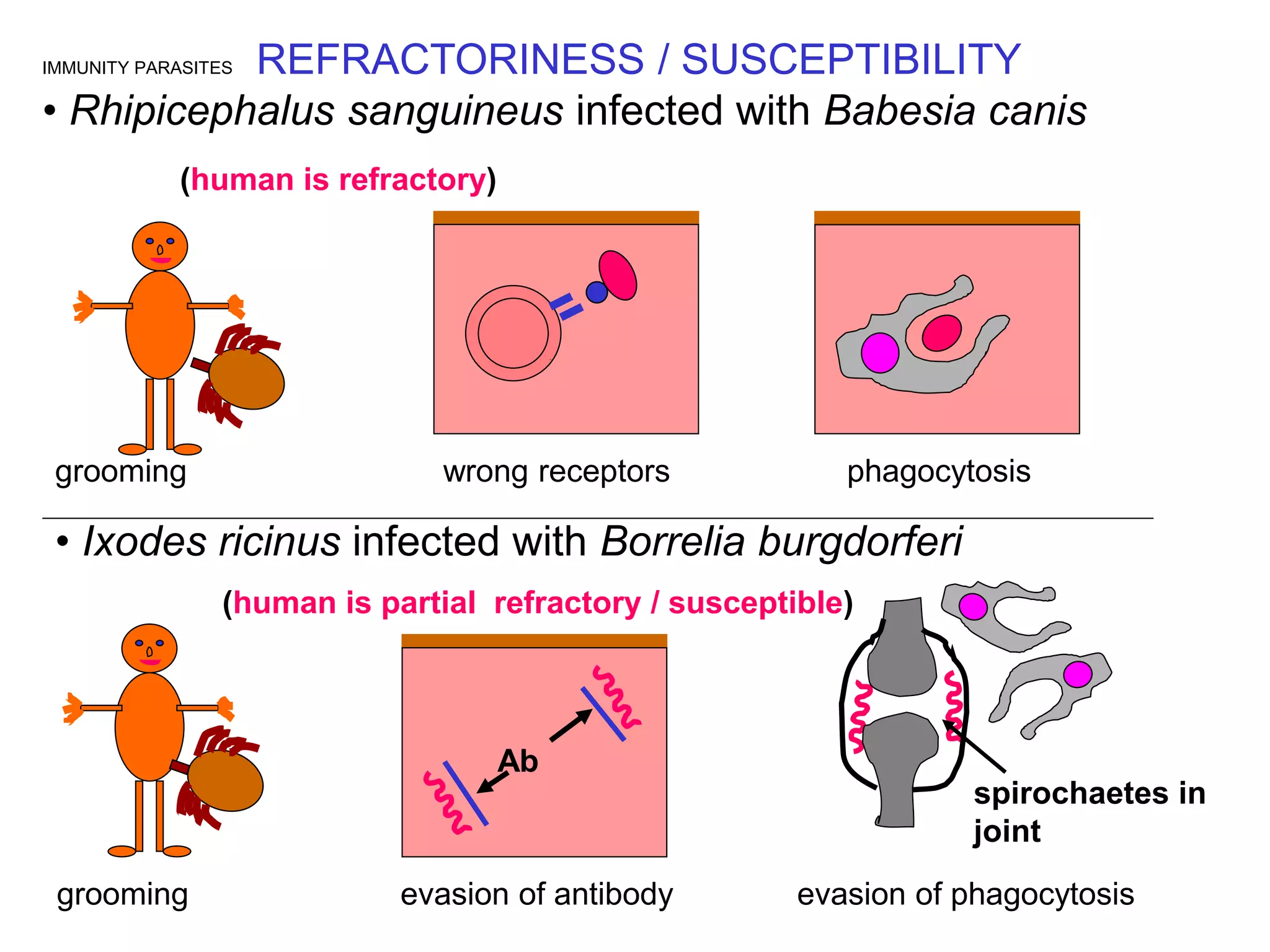
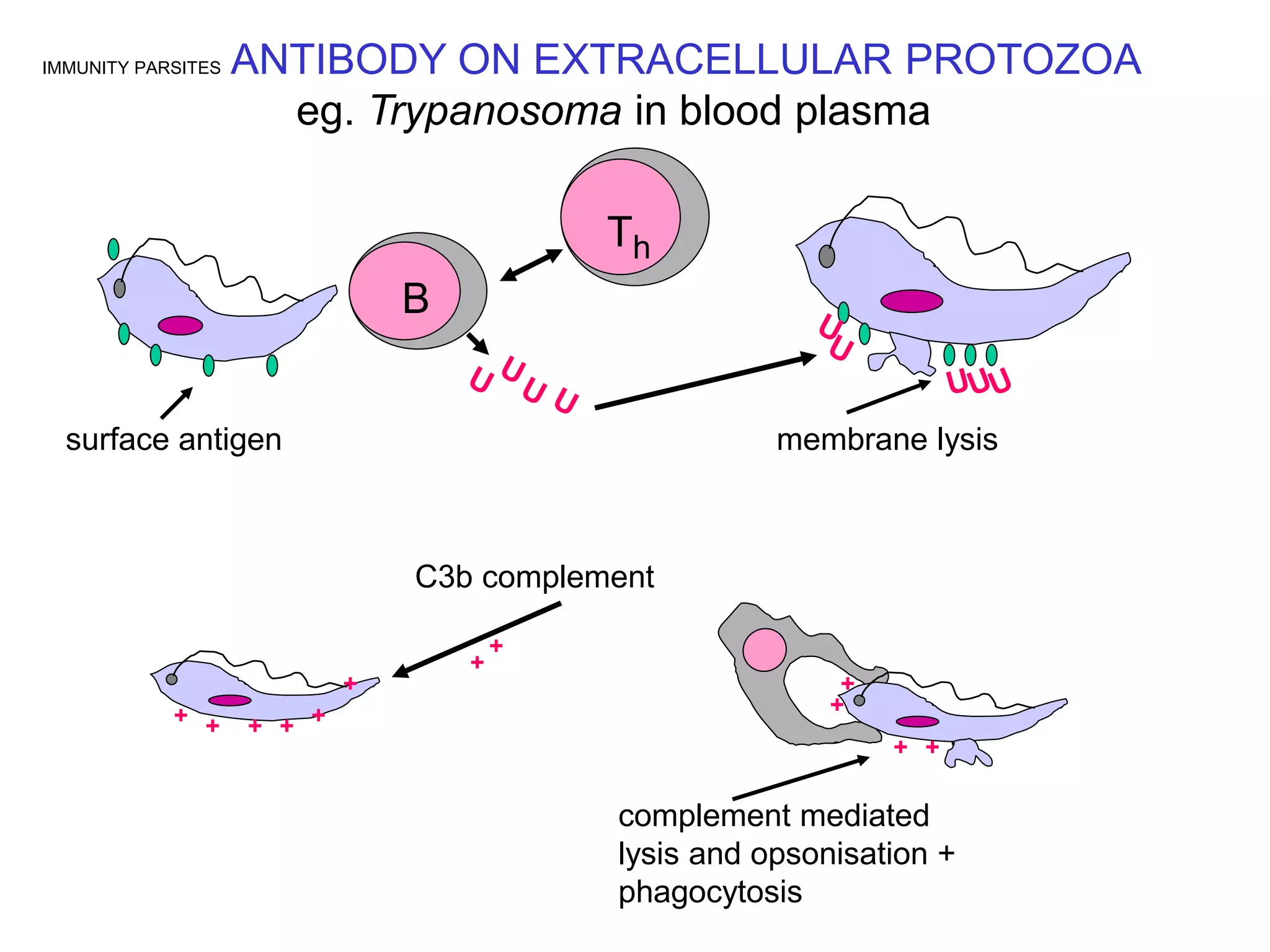
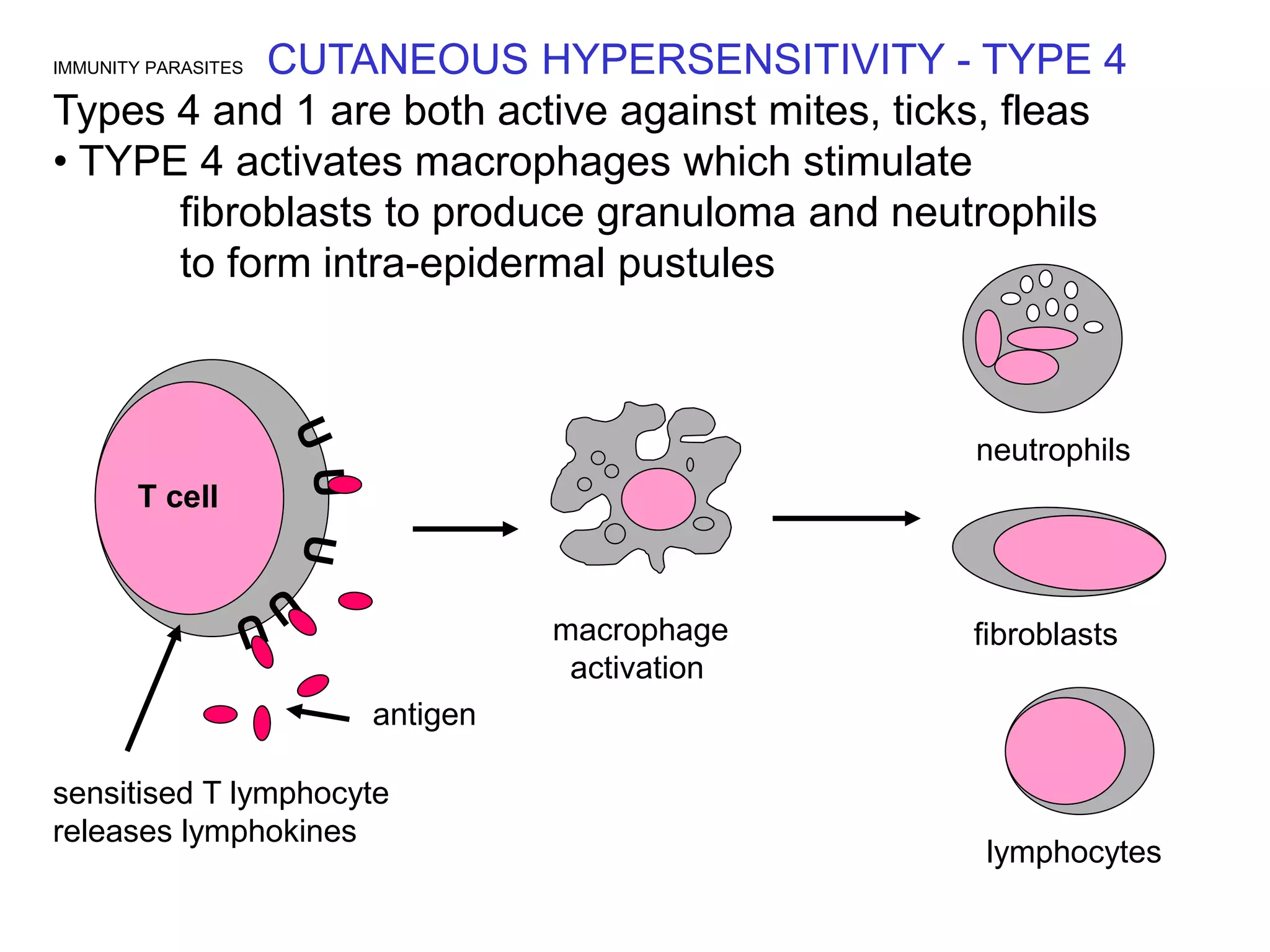
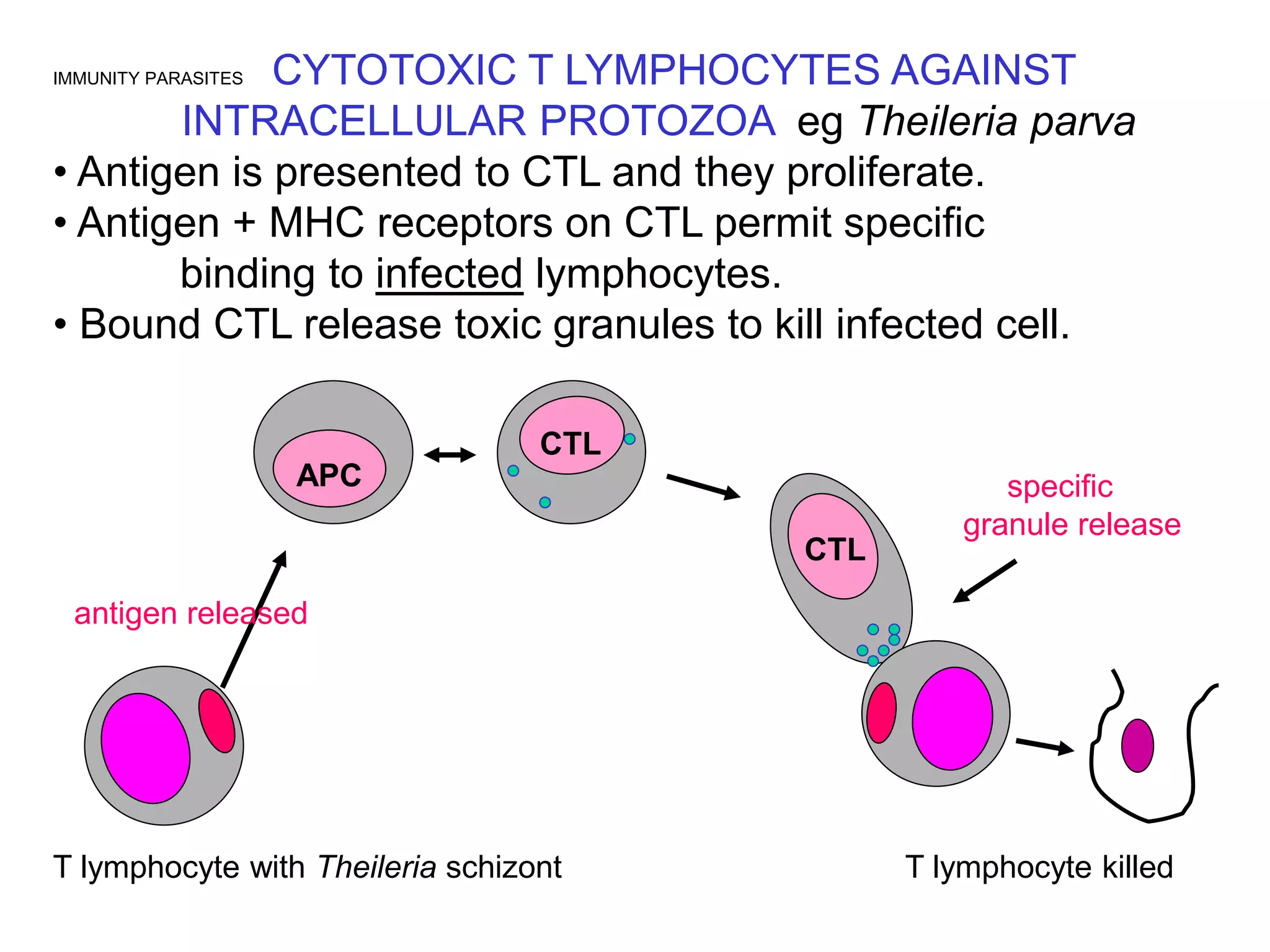
This document discusses multiple immune responses against parasites. It describes avoidance behaviors, grooming, antibody production, eosinophils, granuloma formation, and pustule development as initial responses against ticks. It also discusses refractory and susceptible responses to different parasites depending on the host, as well as antibody-mediated immunity against extracellular protozoa. Further immune responses discussed include immune expulsion of gut nematodes mediated by secretory antigens, antibodies, and mast cell degranulation. The document also examines cutaneous hypersensitivity responses types 1 and 4 against mites, ticks and fleas, eosinophil responses against tissue-based helminths, macrophage activation against intracellular protozoa, cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses against The