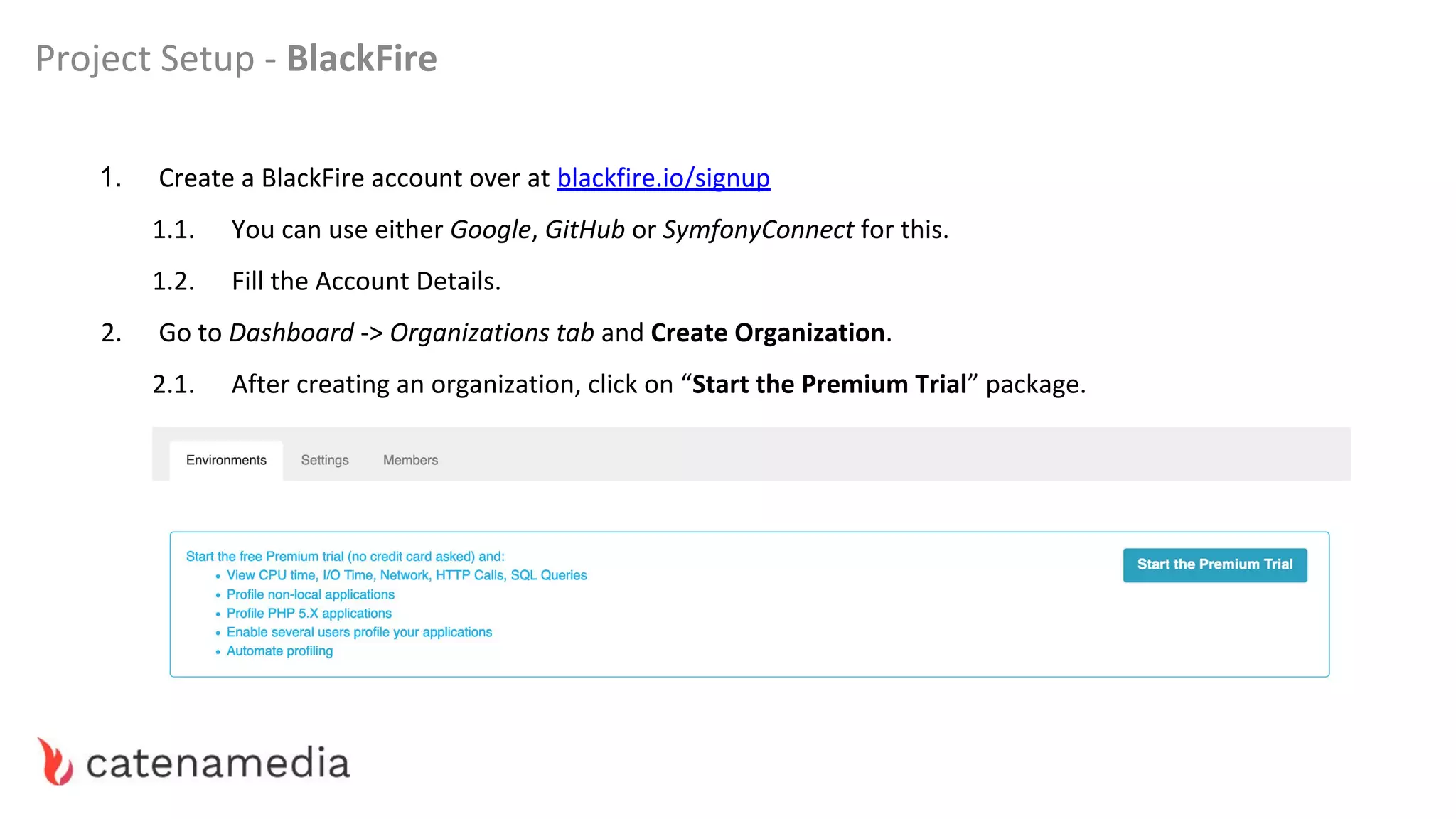
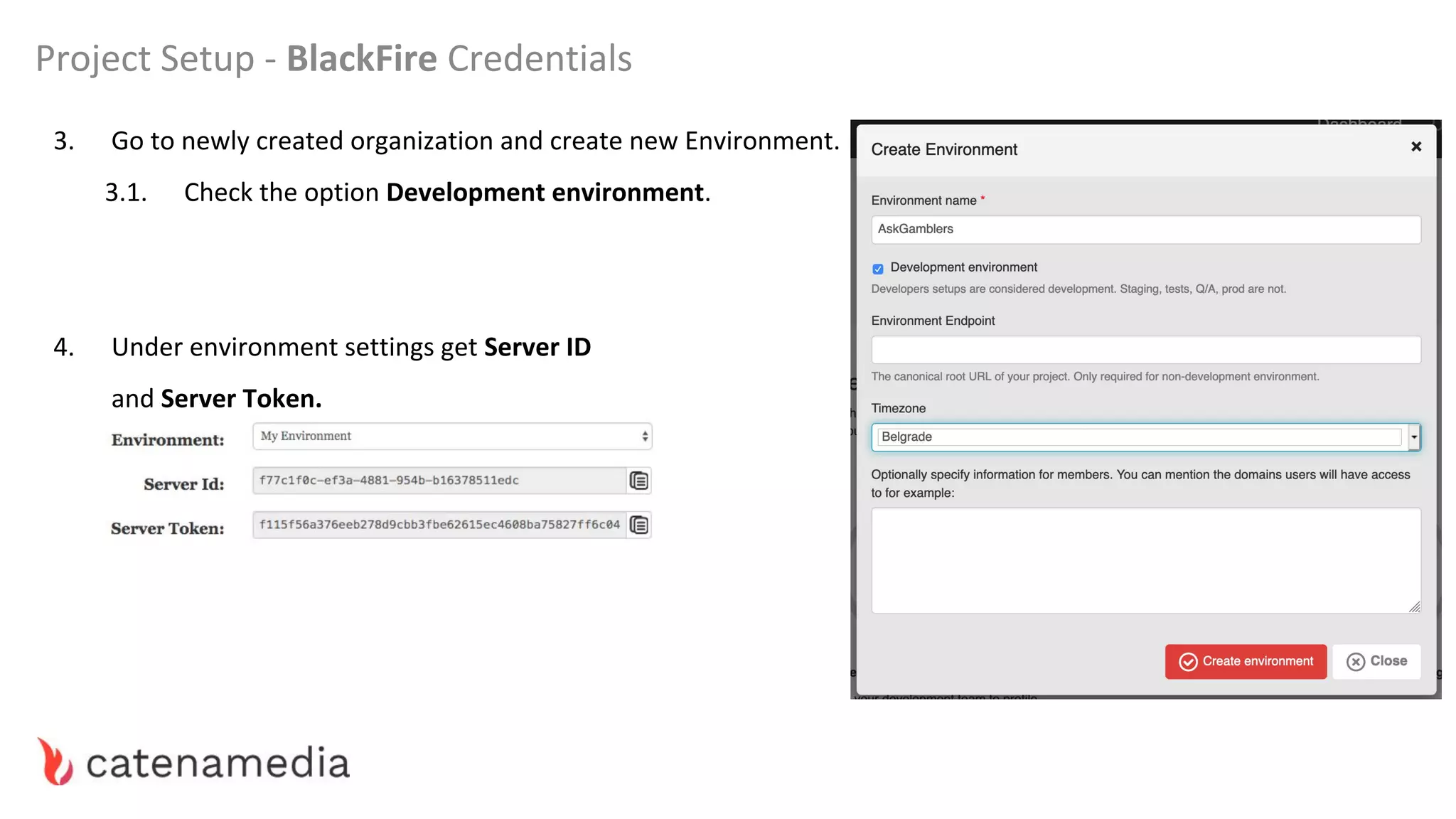
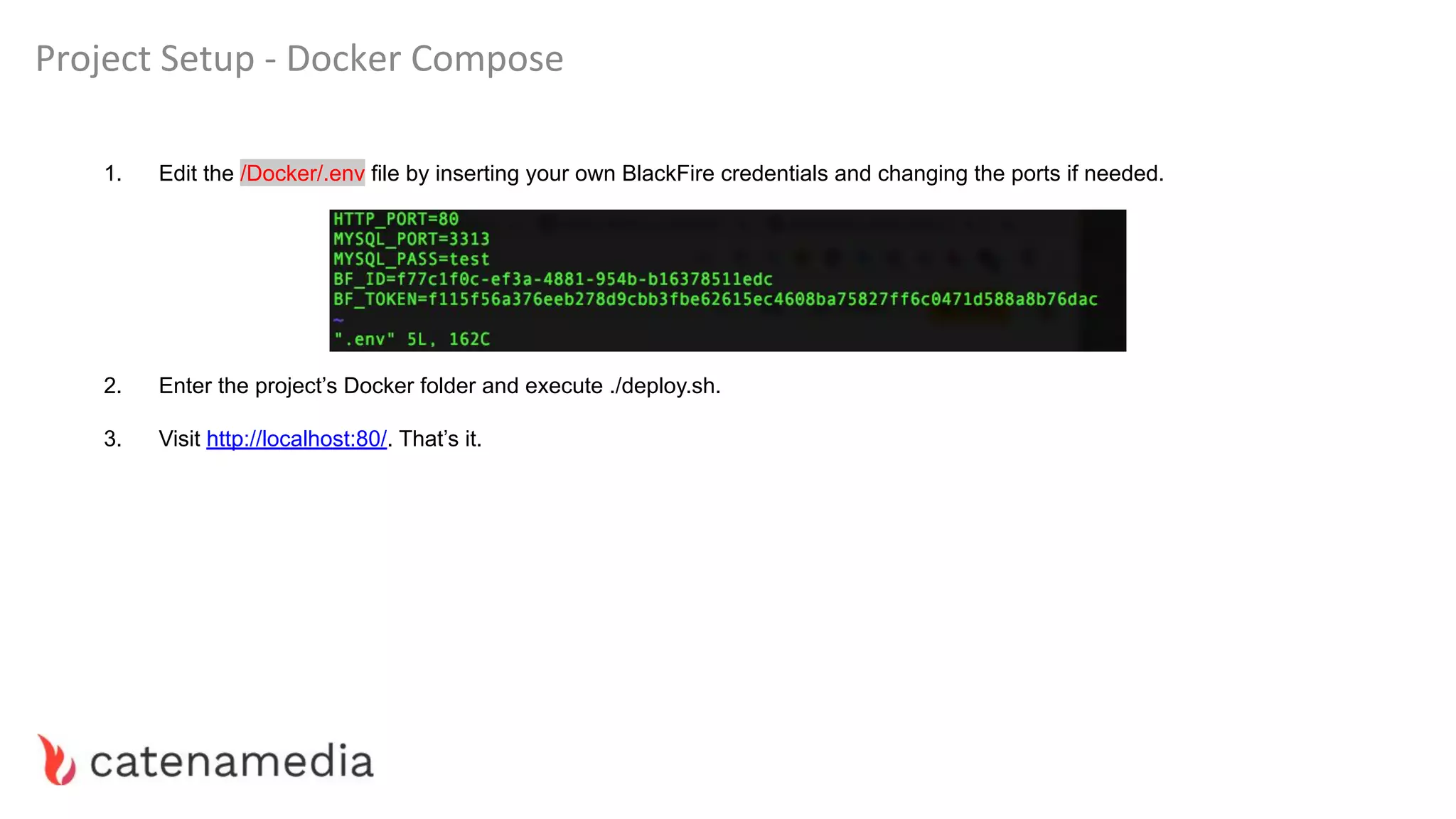
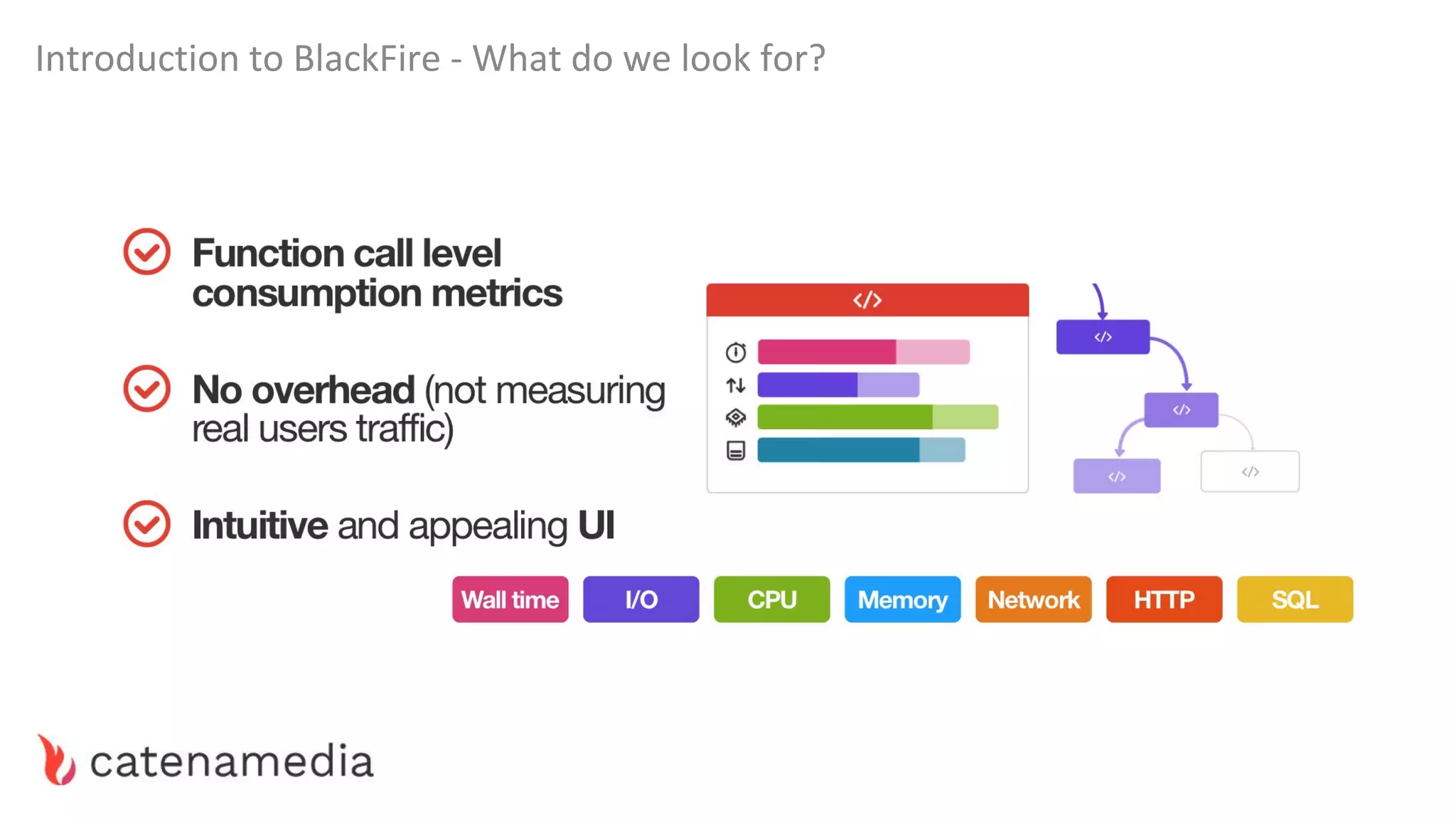
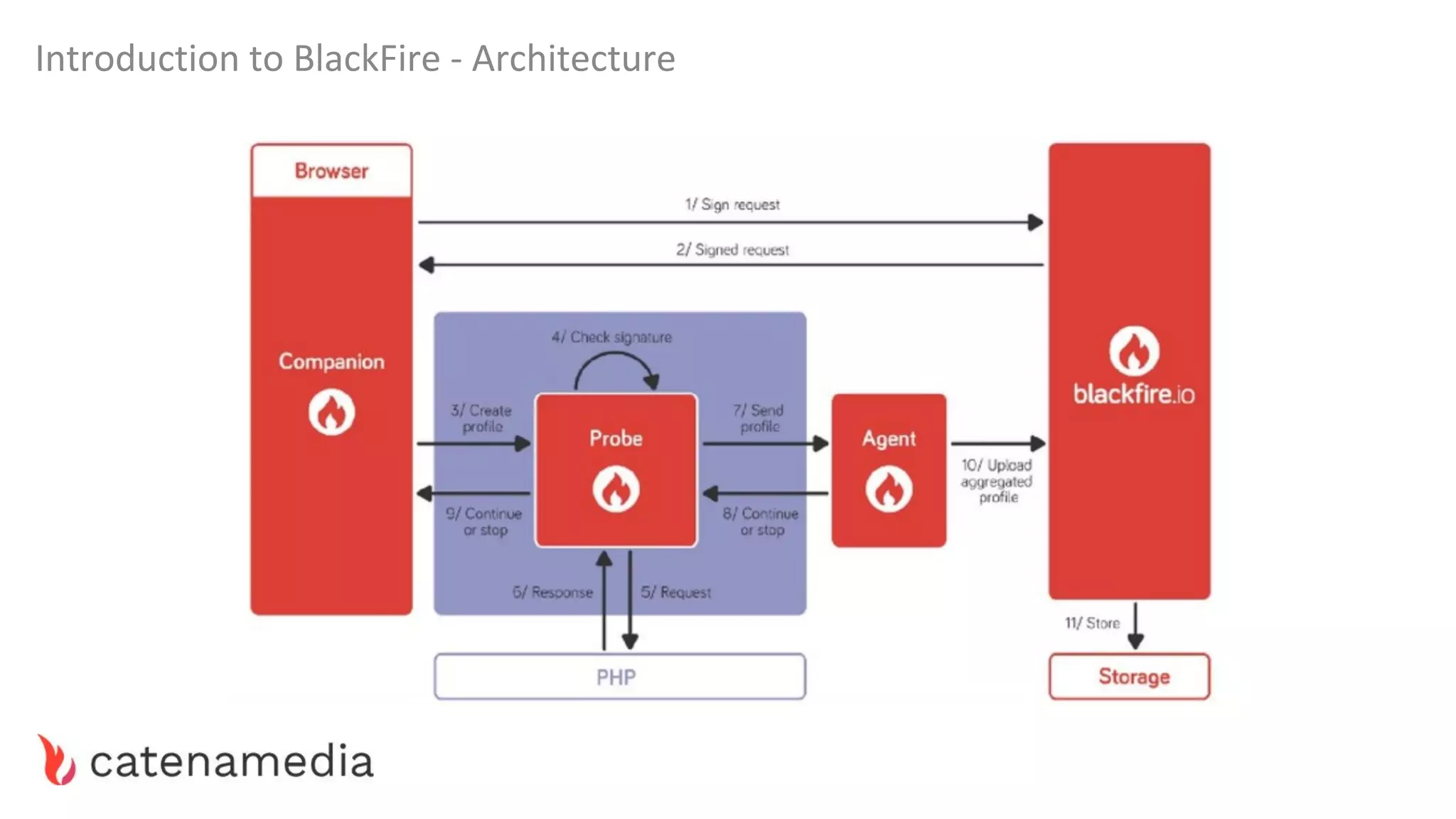
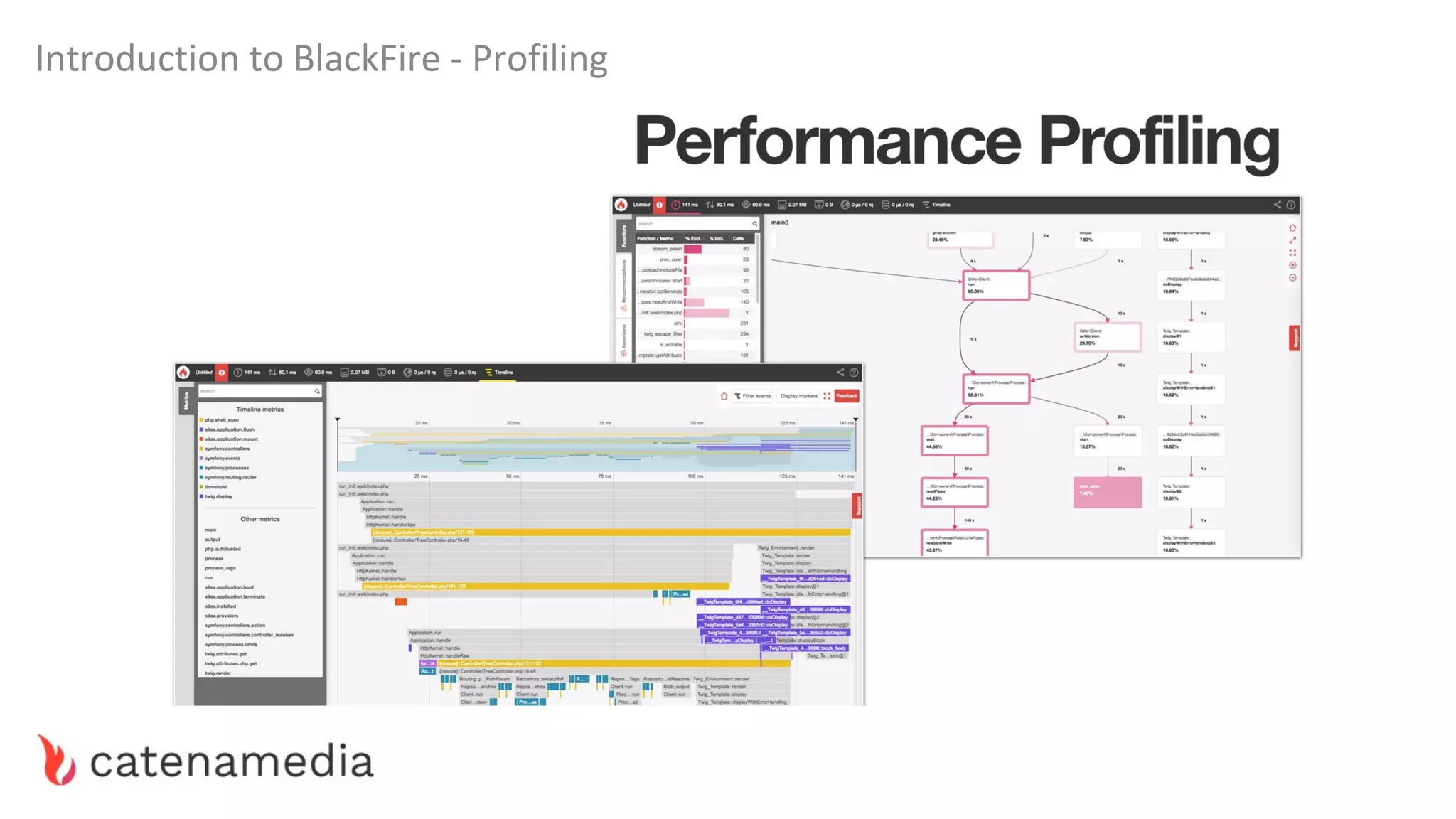
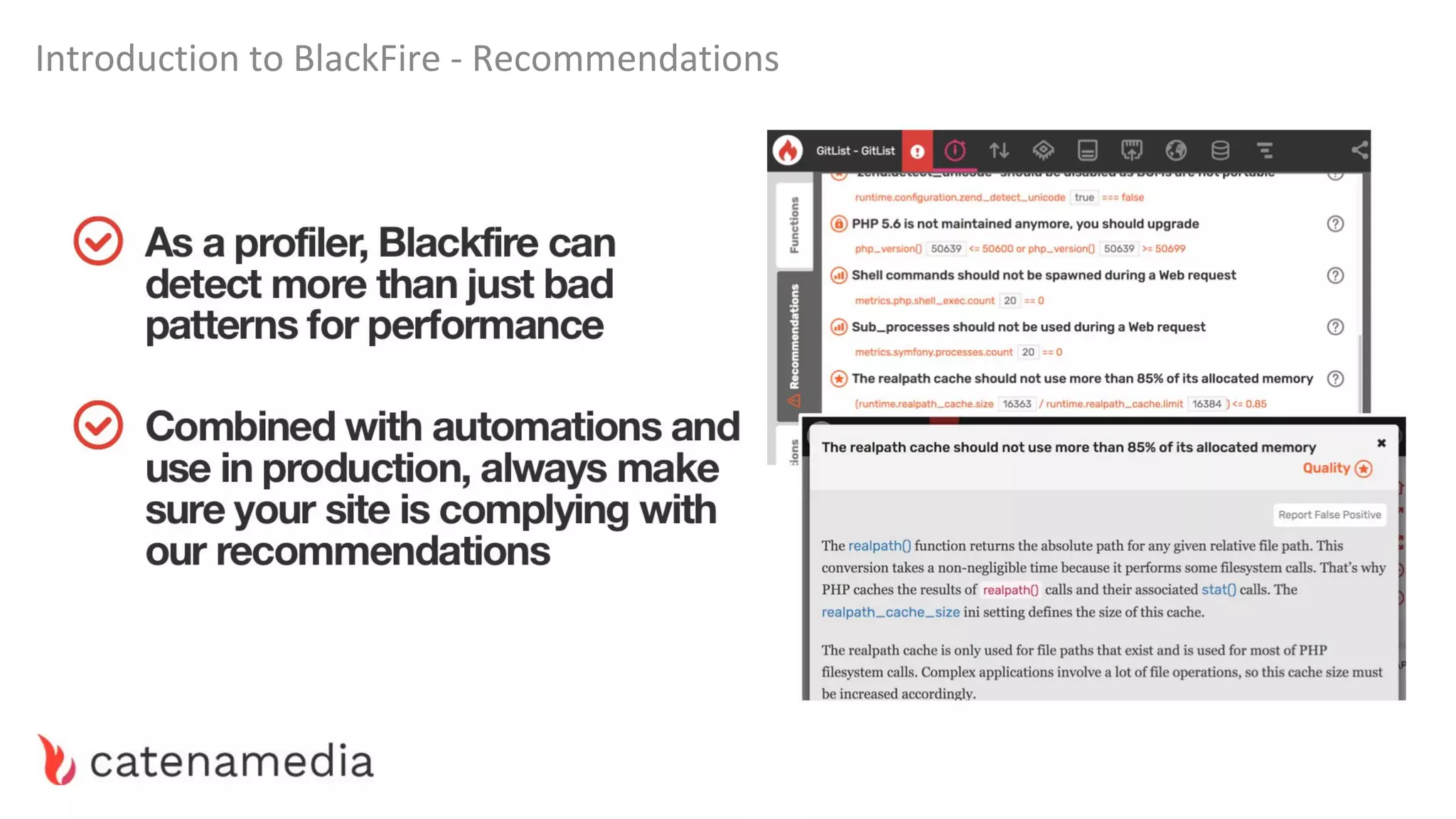
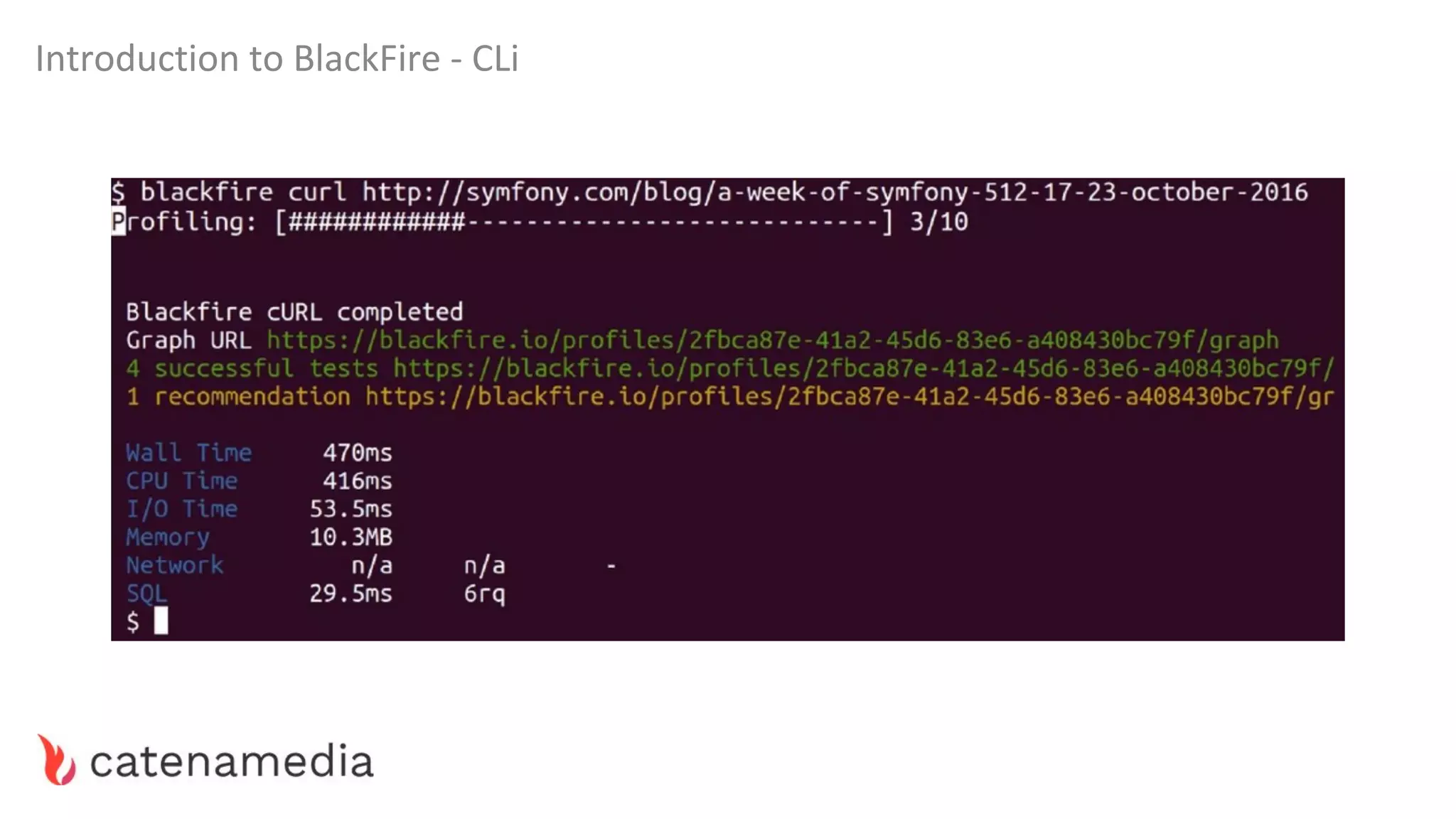
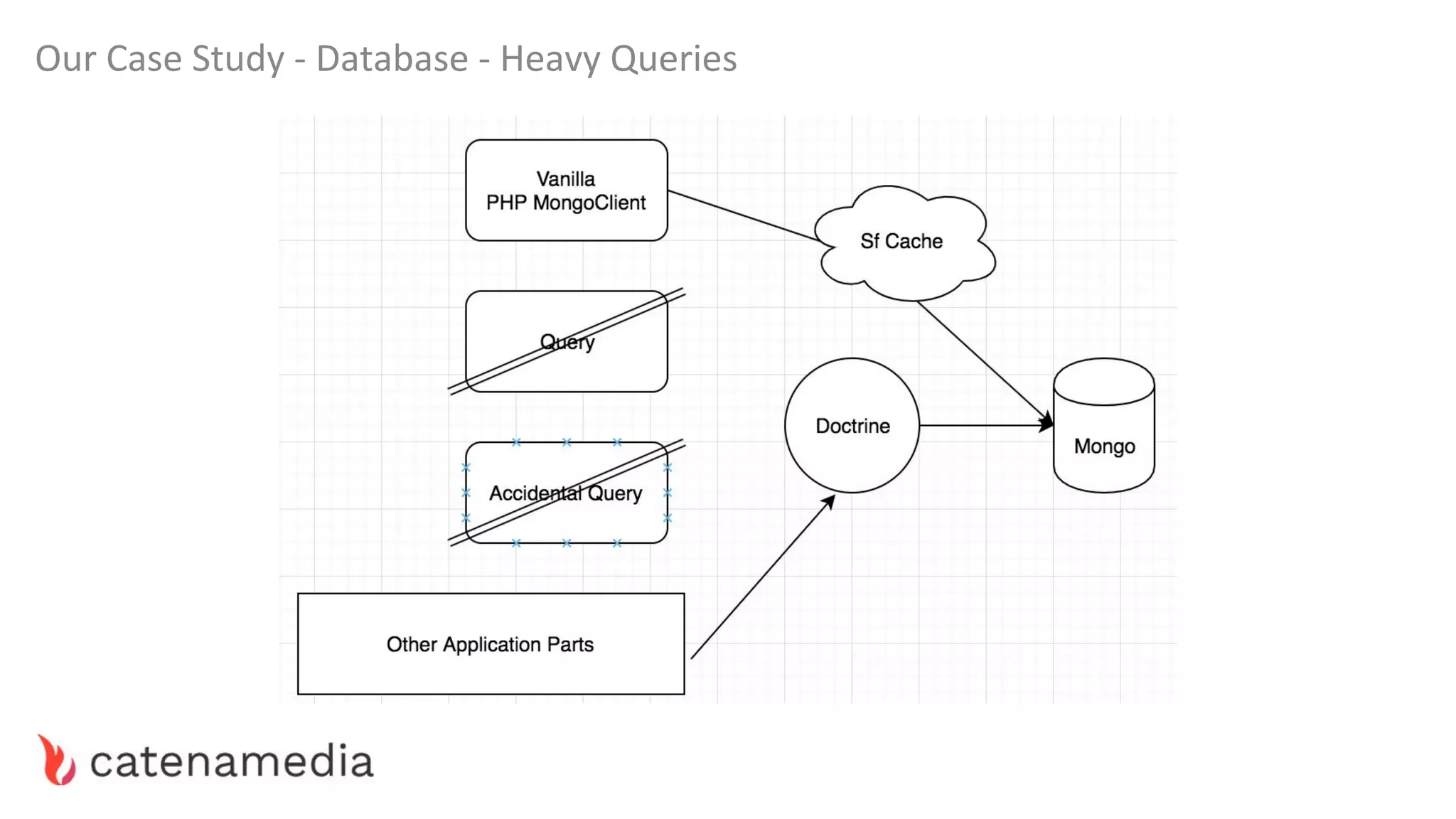
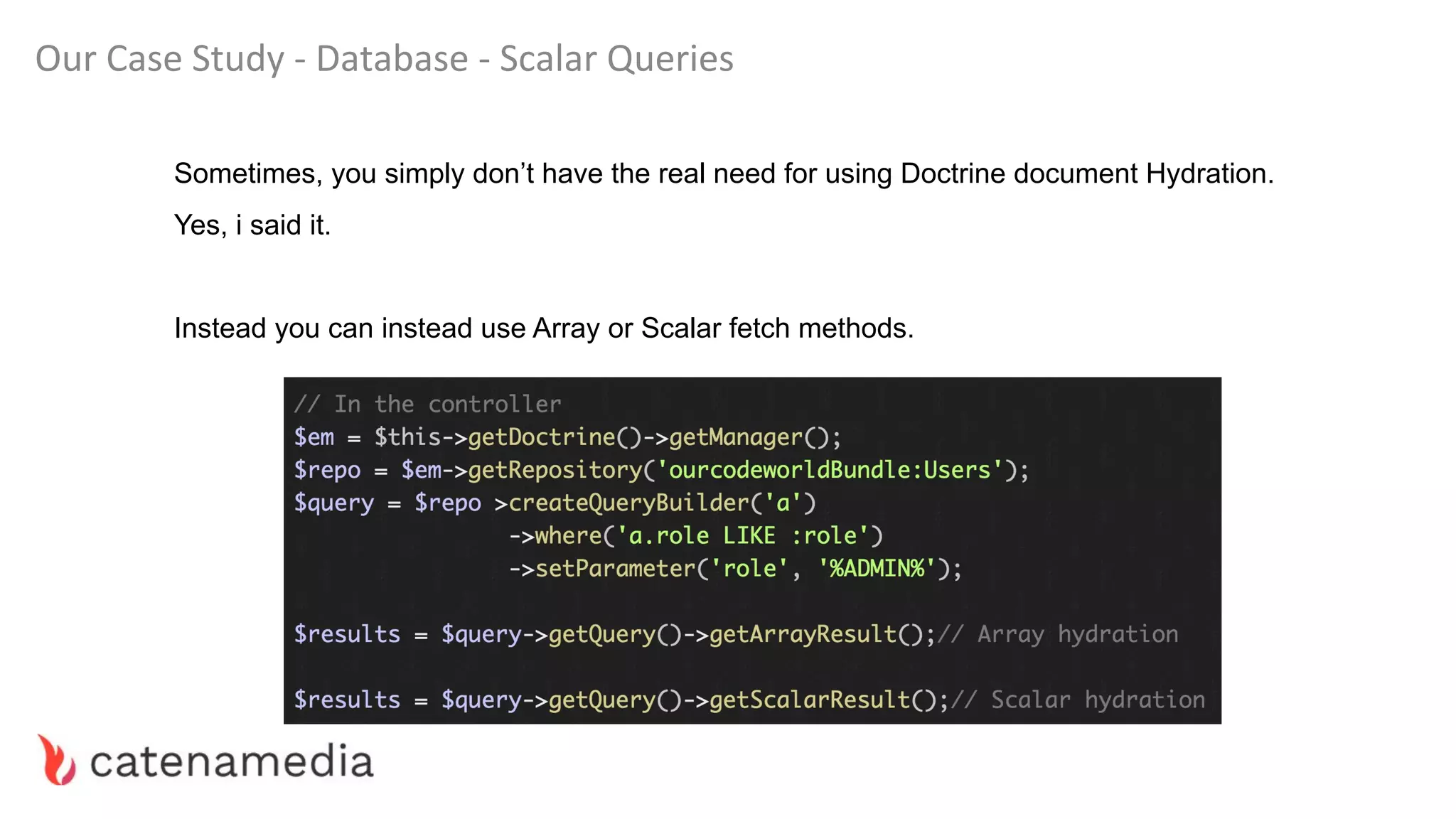
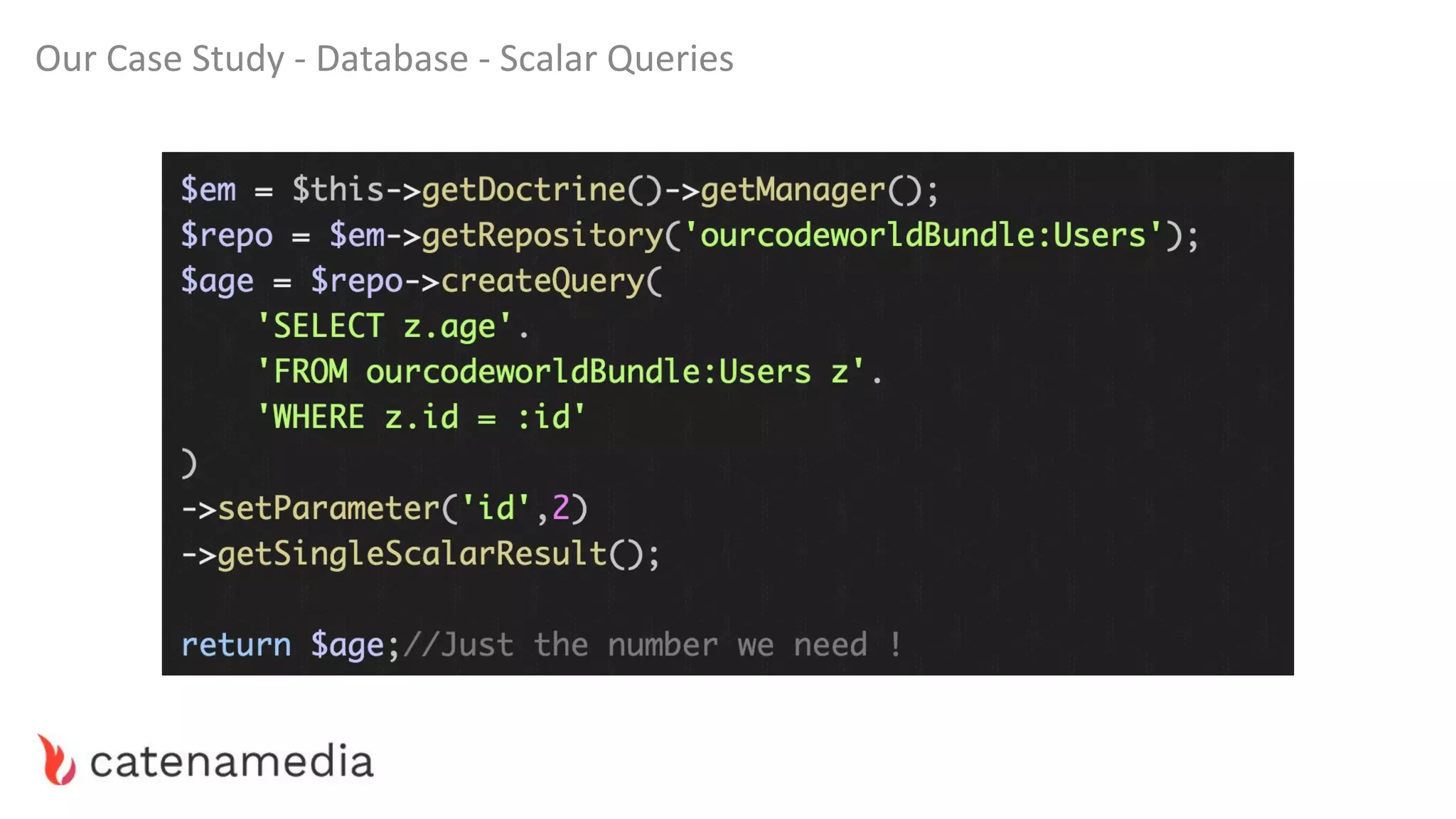
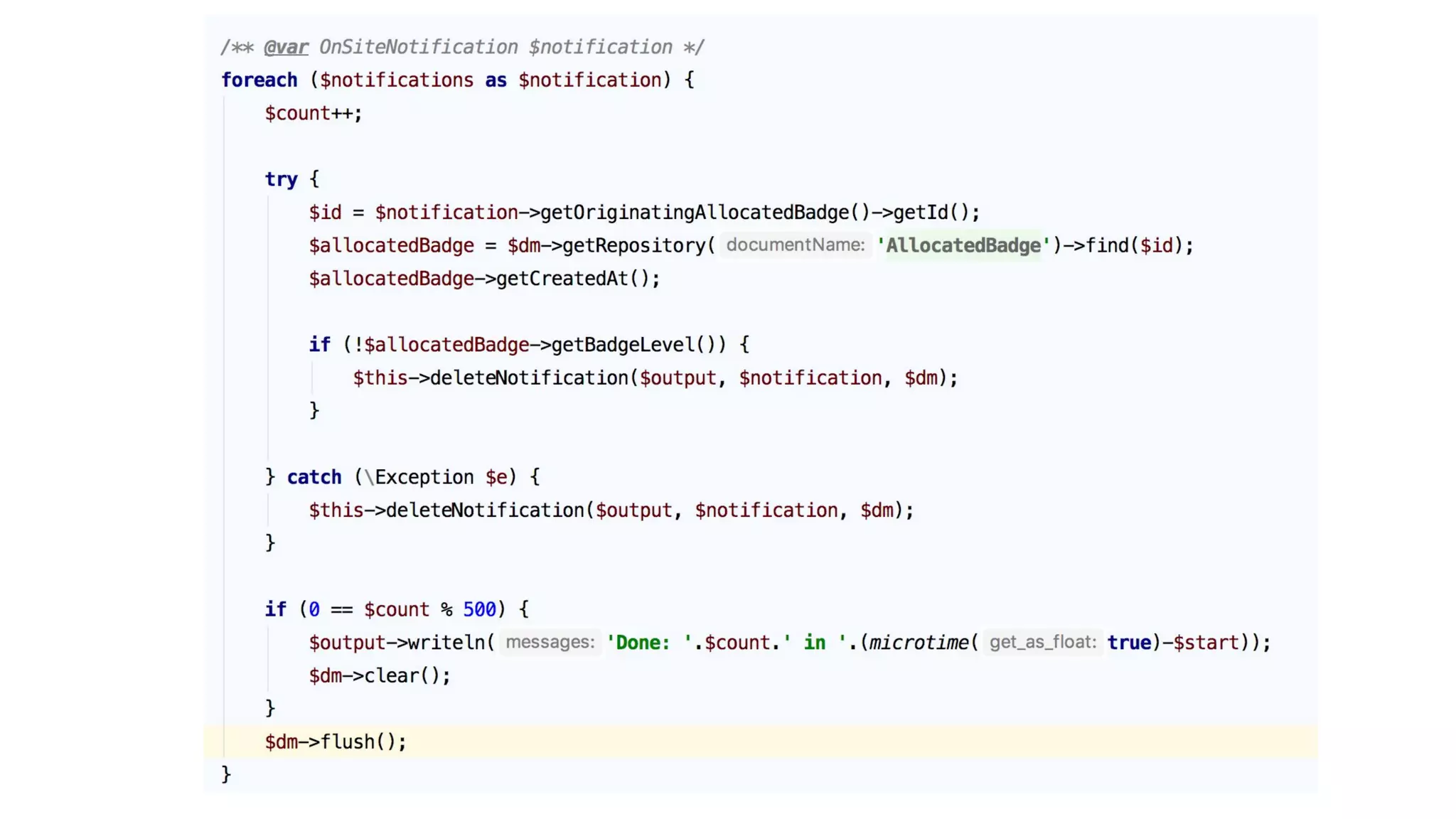
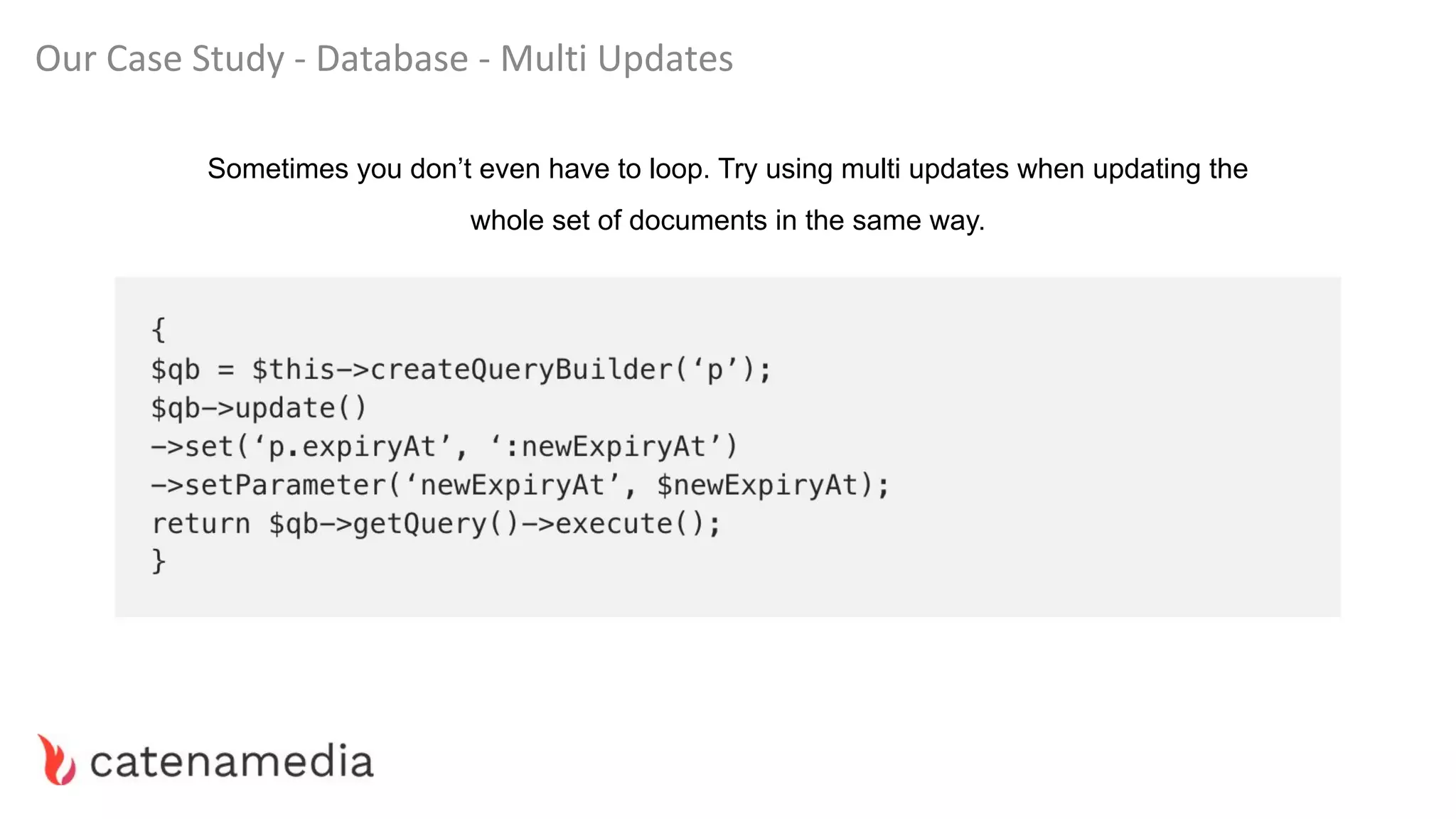
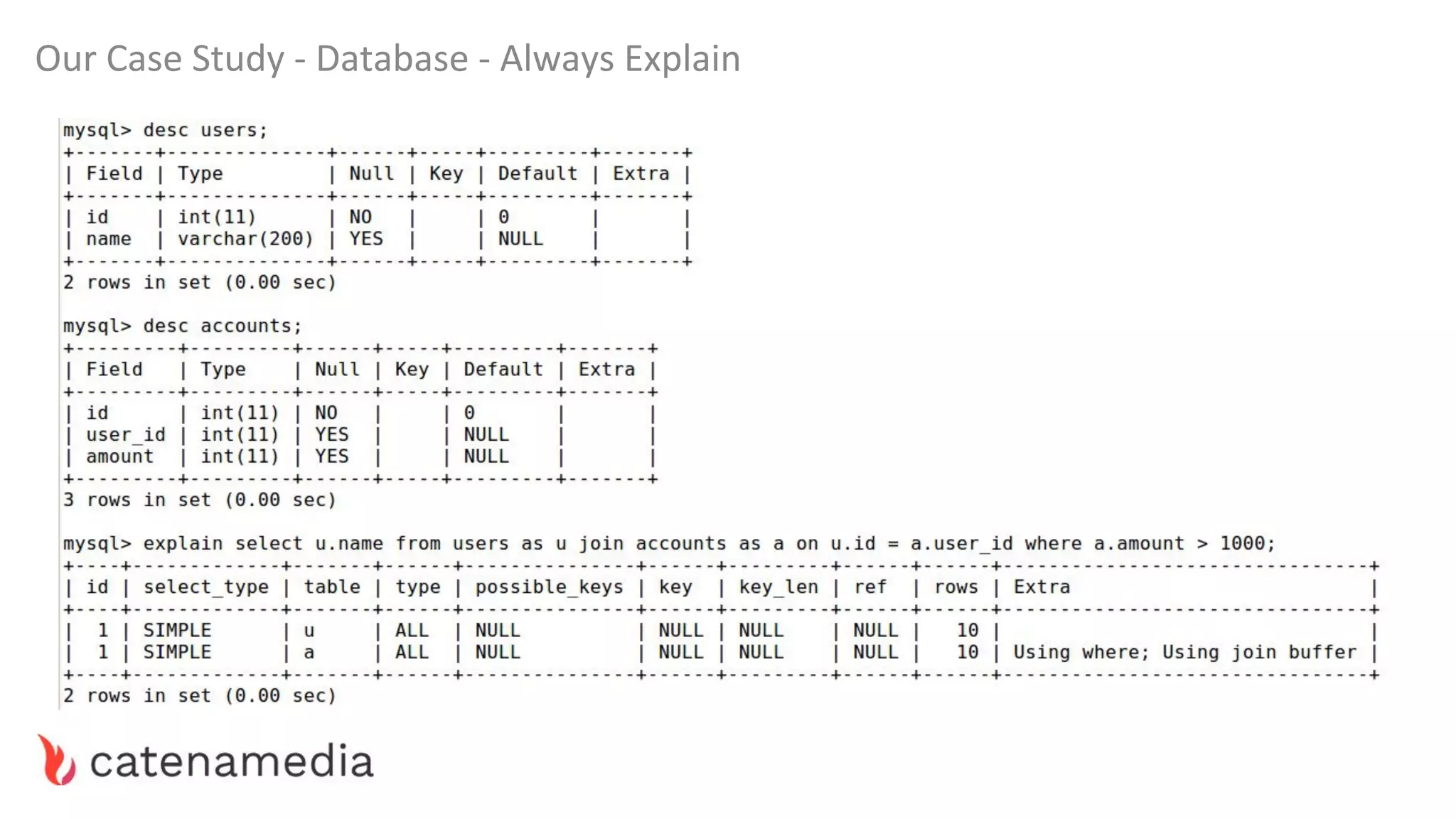
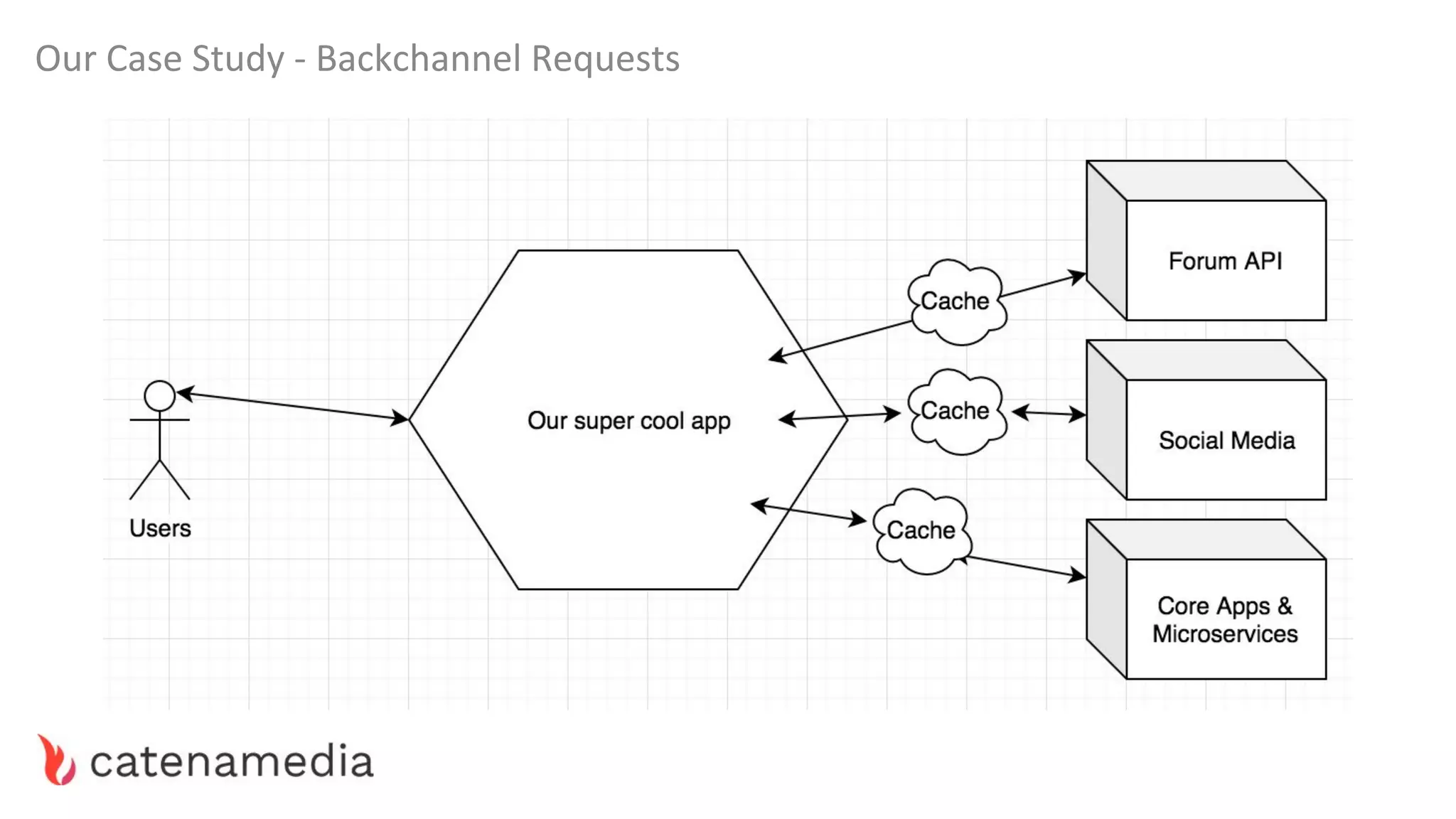
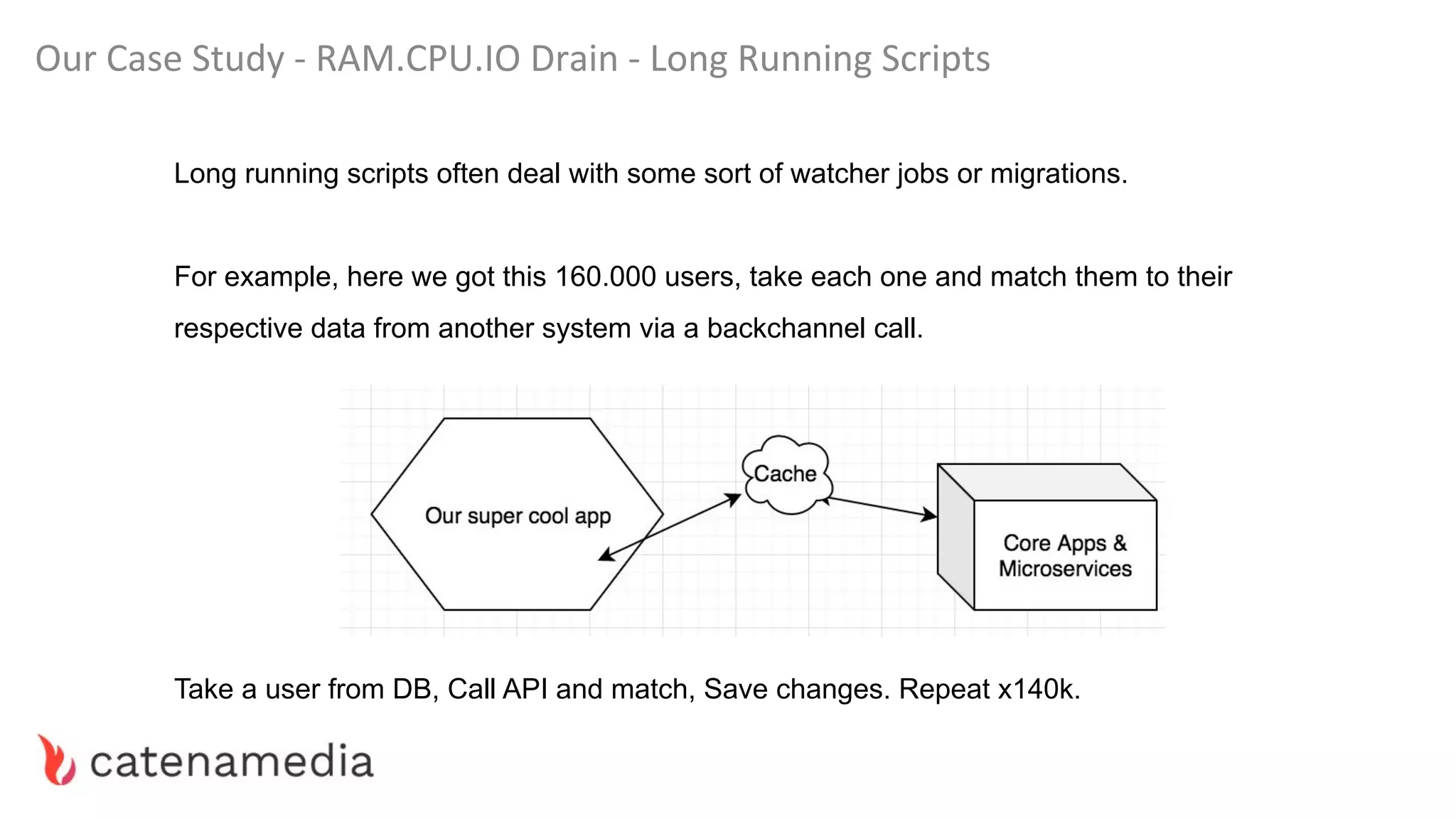
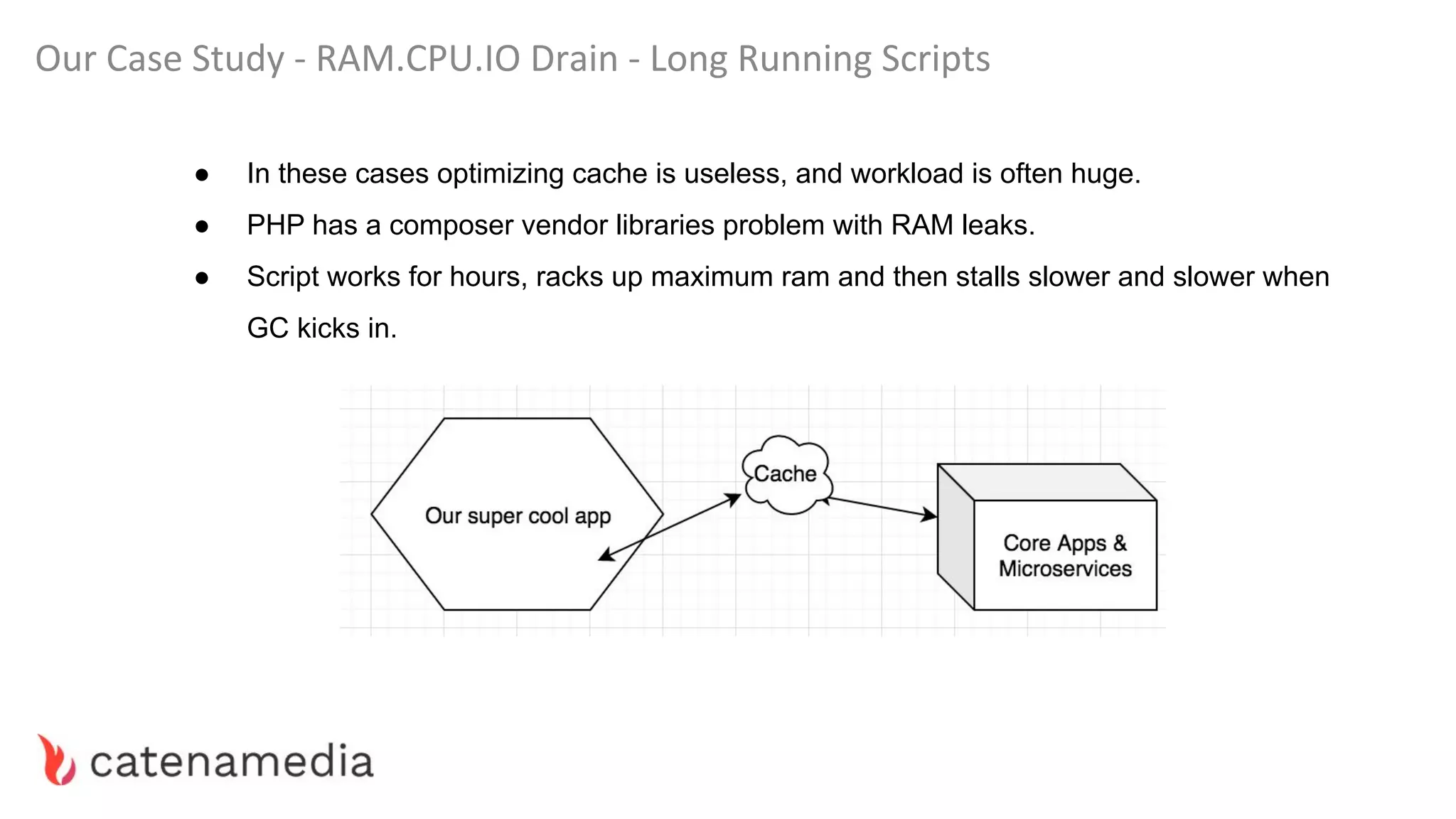
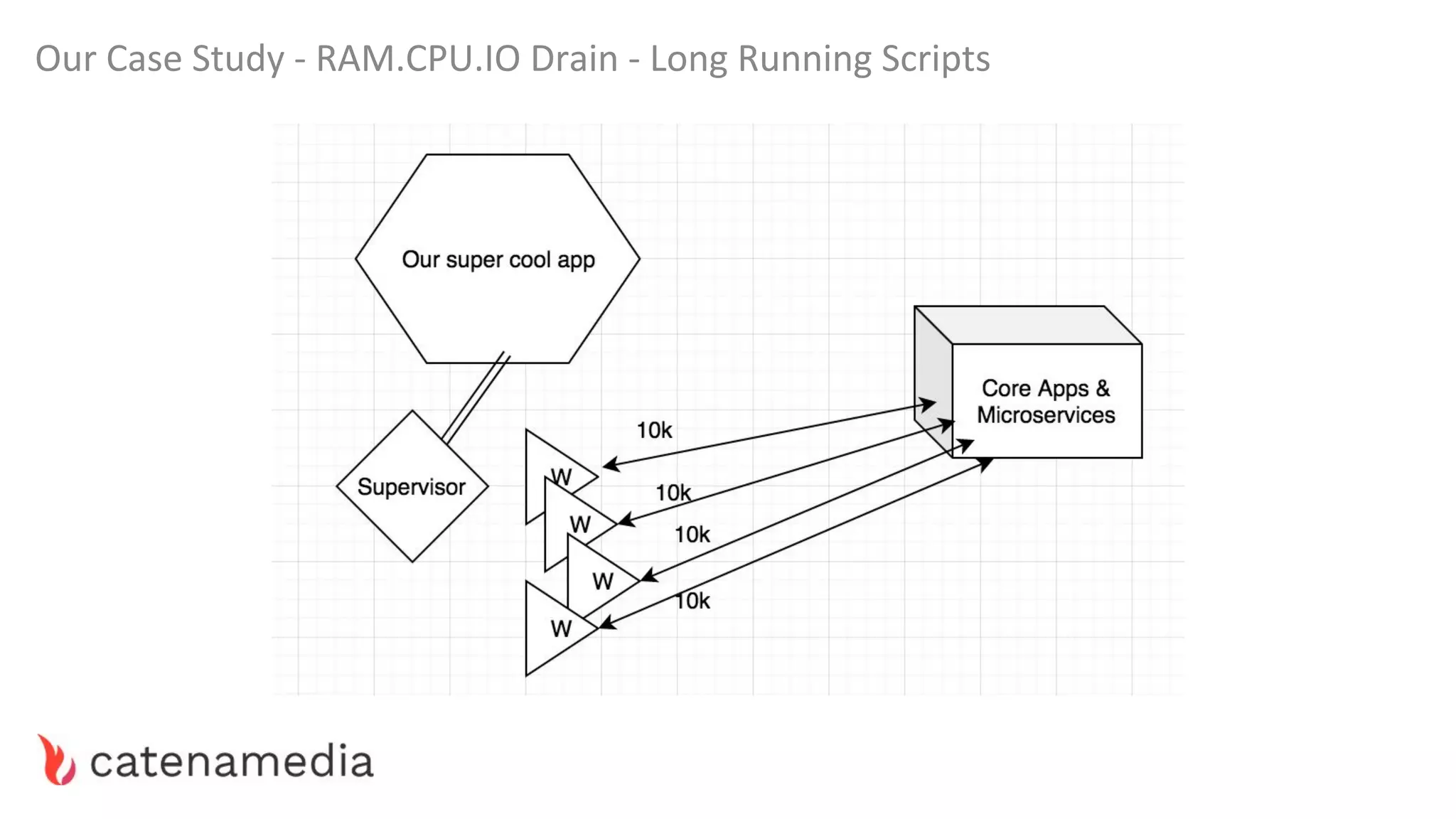
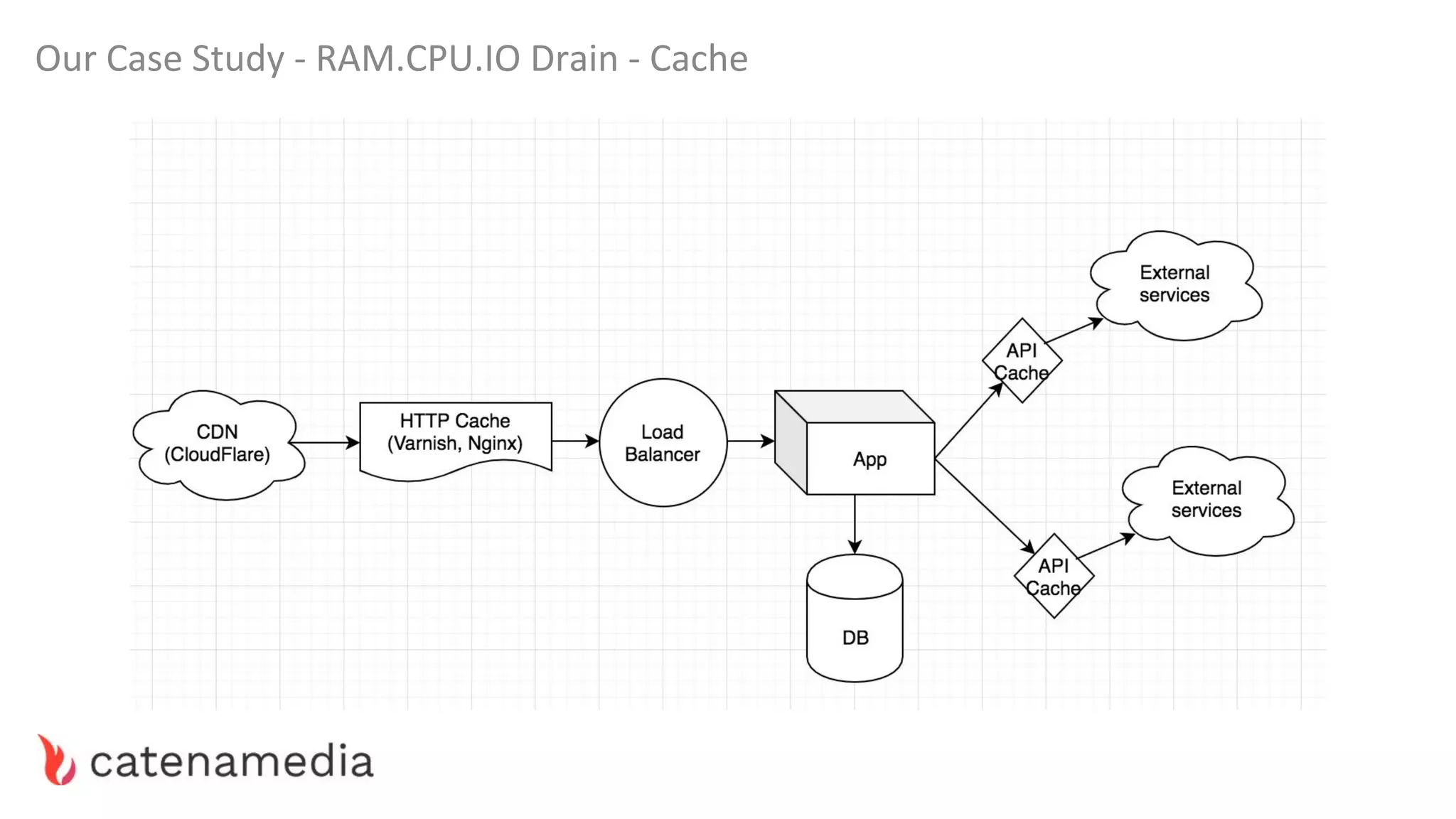
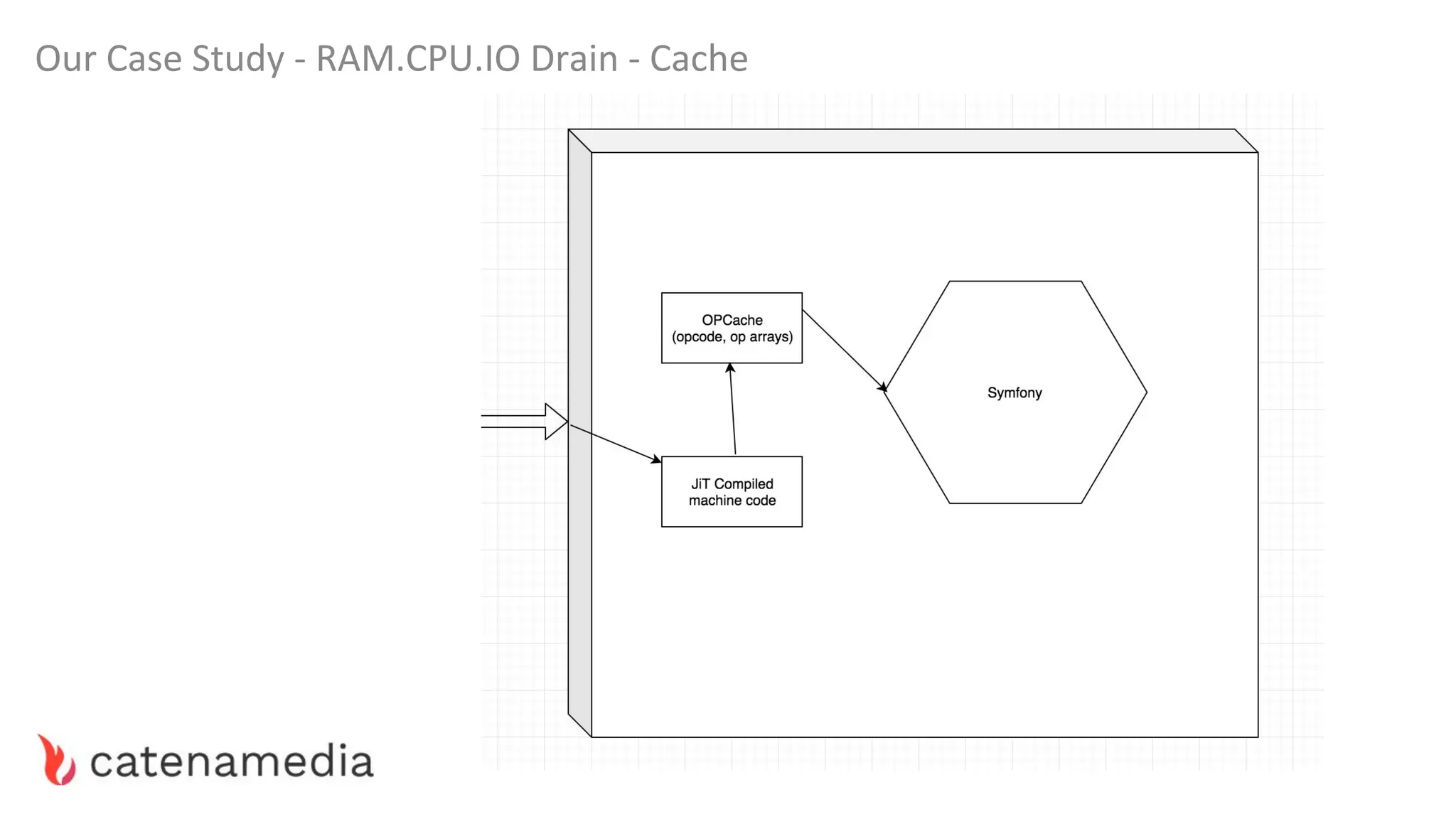
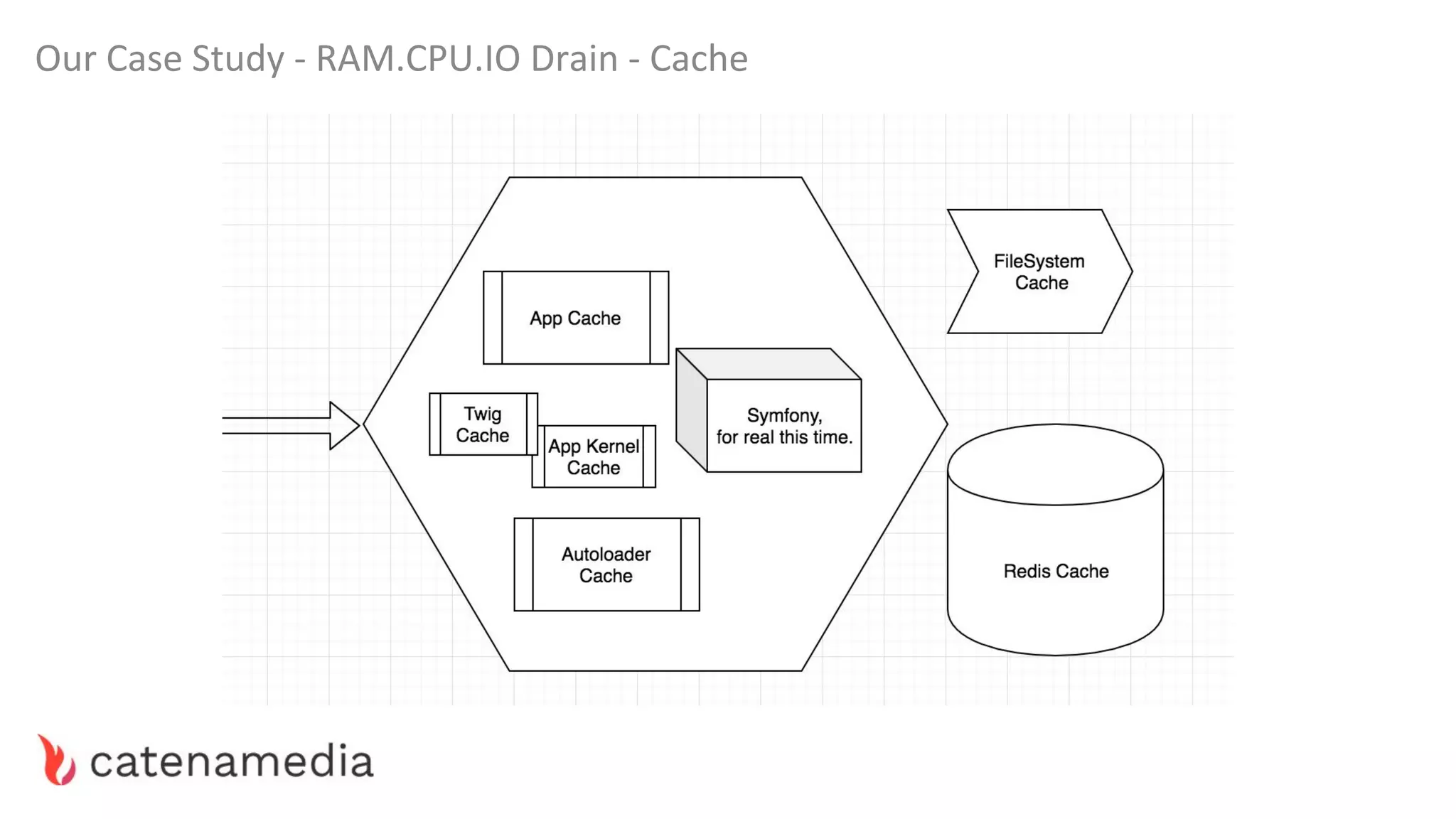
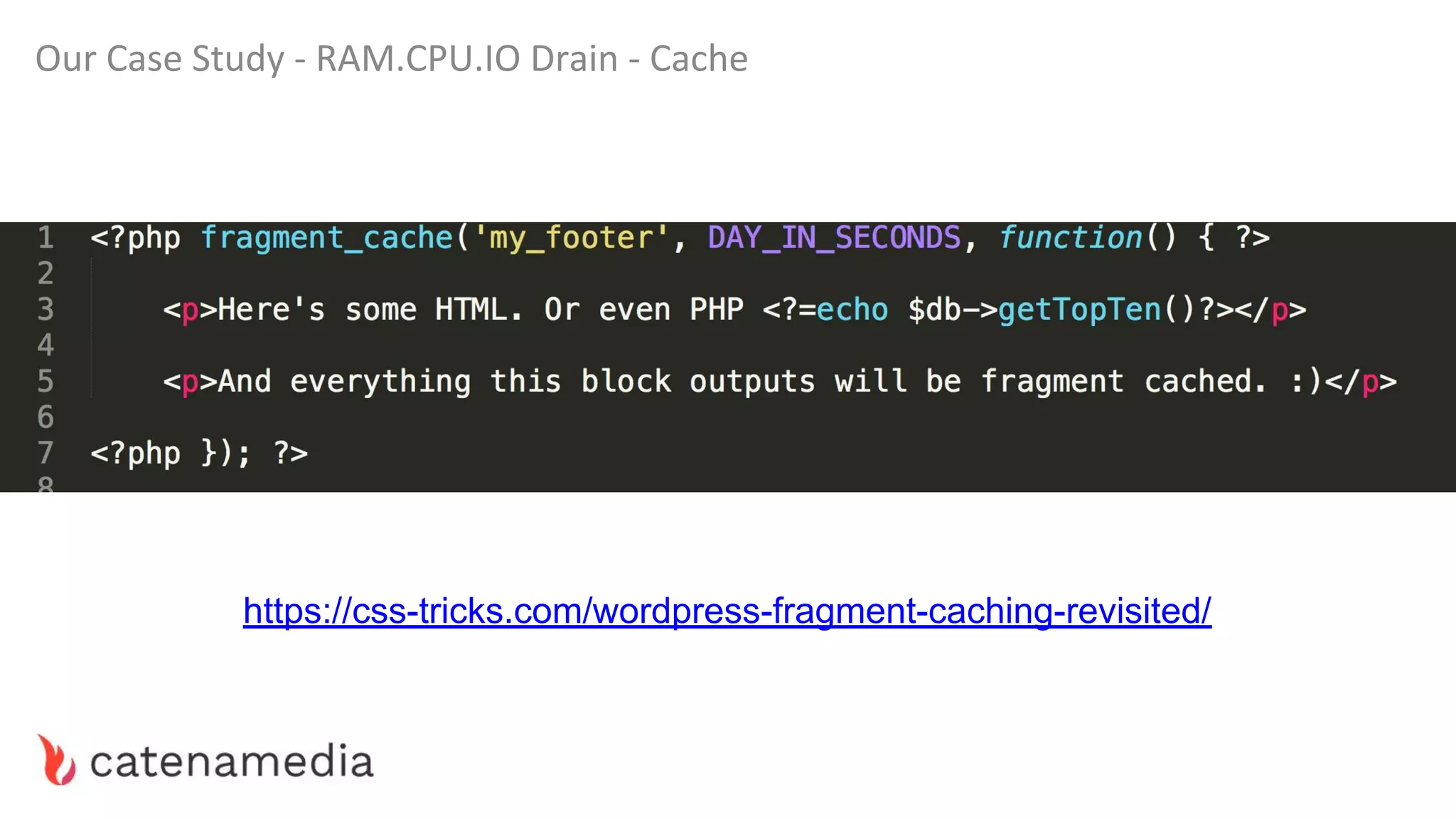
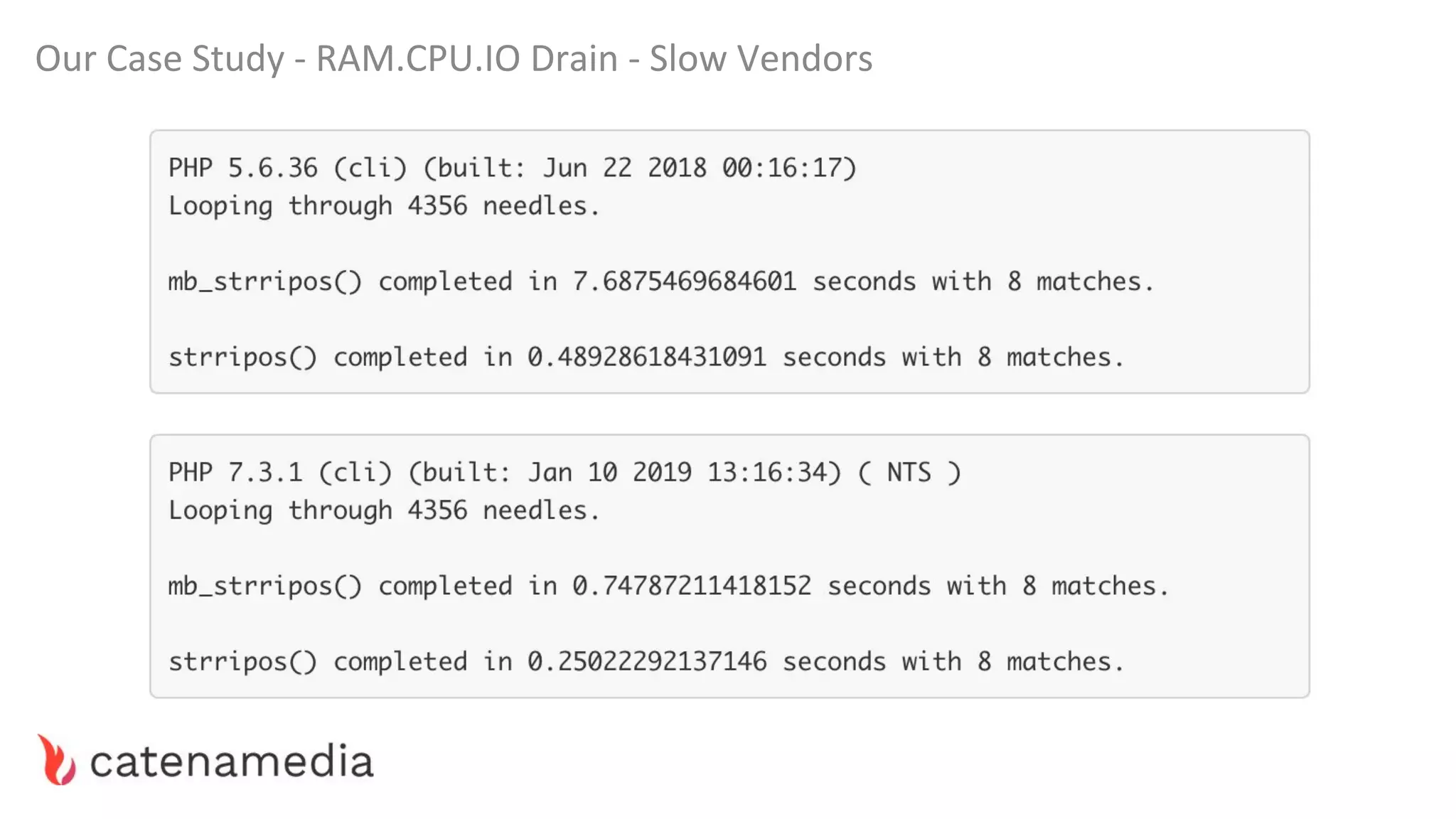
The document provides a comprehensive workshop on optimizing performance using Blackfire, led by Marko Mitranić, Alekxandar Ilić, and Bojana Kovačević. It covers project setup prerequisites, performance testing tools, and methodologies for profiling applications to identify bottlenecks, alongside detailed case studies on optimizing database queries and long-running scripts. Emphasis is placed on understanding performance issues before optimizing to avoid premature optimization pitfalls.