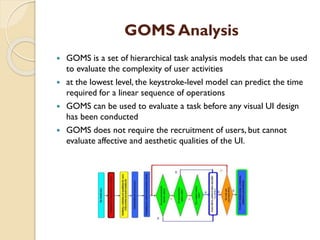
This document introduces a design charrette that will use four UX methods - heuristic review, eye tracking, GOMS analysis, and edge case brainstorming - to evaluate OneNote. Each method is briefly described, including strengths and weaknesses. Heuristic review involves inspecting a system using design rules to identify user experience issues. Eye tracking monitors users' eye movements during tasks to see where they focus visually. GOMS analysis predicts task times without users by modeling operations. Edge case brainstorming explores unique challenges through creative discussion. The results of applying each method to OneNote will be summarized and compared to understand their value when used together.