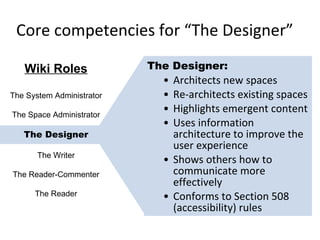
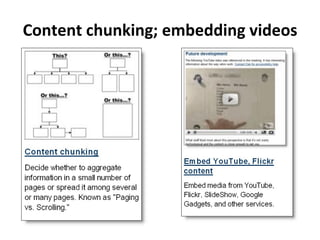
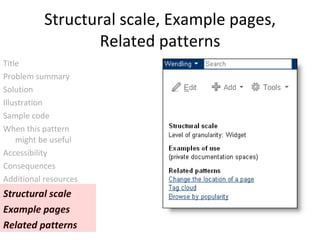
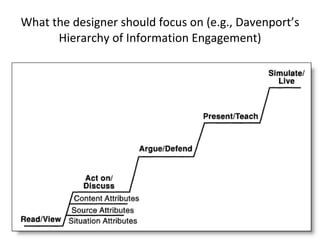
This document summarizes a presentation about creating a Confluence Design Pattern Library to support wiki designers. It describes core competencies for wiki designers and different wiki roles. It provides details on the structure and components of design patterns in the library, including a title, design problem, solution, illustration, sample code, usage guidance, accessibility notes, consequences, resources, examples, and related patterns. Examples of patterns like PageTree are shown with their various components. Reasons for implementing a design pattern library are given, focusing on user experience, structure, collaboration and reuse.
![Supporting wiki designers with a Confluence Design Pattern Library Dan Wendling, [email_address] National Library of Medicine Presentation for the Wiki Pecha Kucha, 5/14/2009, http://wiki.sla.org/display/CEWIKI/2009+05+14+~+Sharing+our+Stories+about+Wikis+the+Pecha+Kucha+Way](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20090514wendlingdanpechakuchawikis-090520053200-phpapp01/75/20090514-Wendling-Dan-Pecha-Kucha-Wikis-1-2048.jpg)