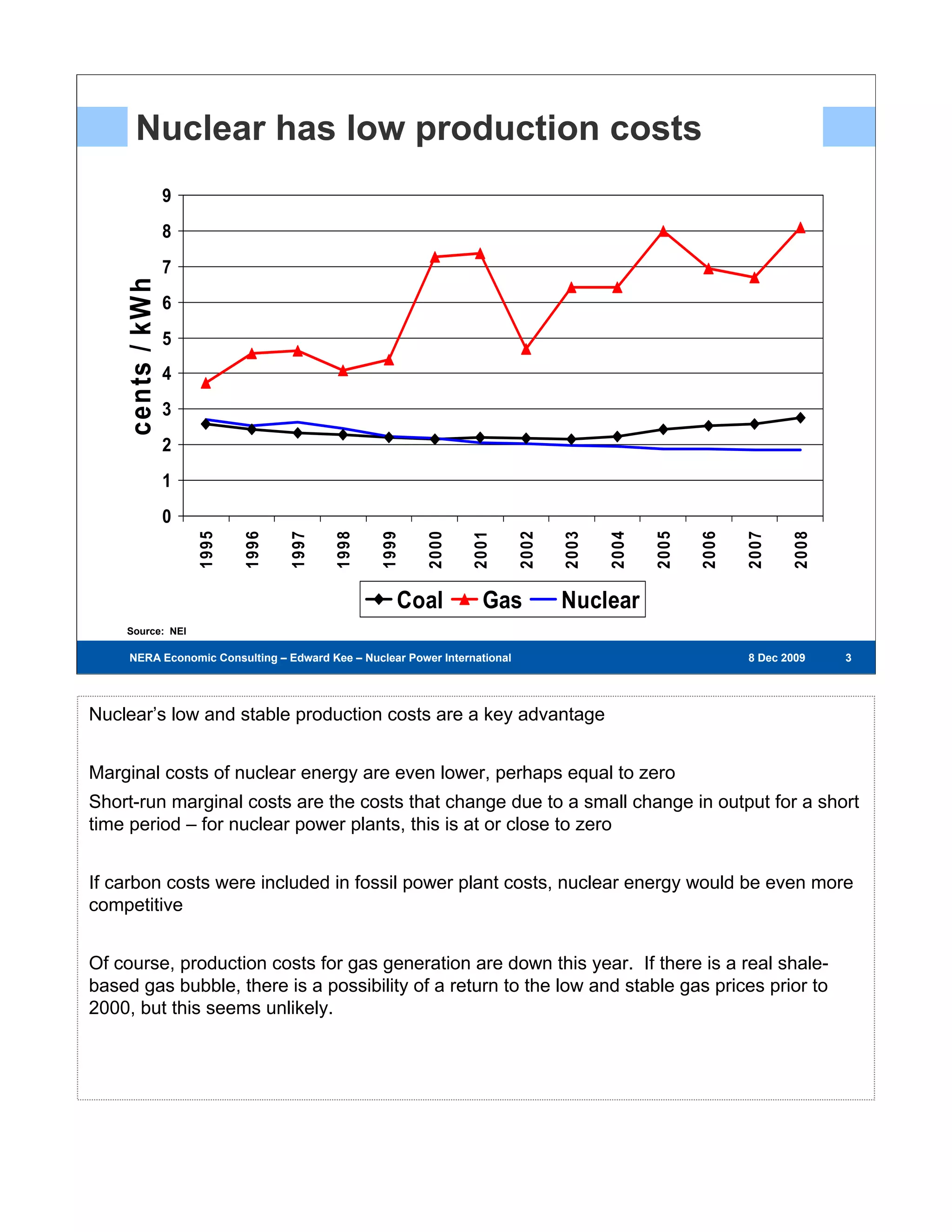
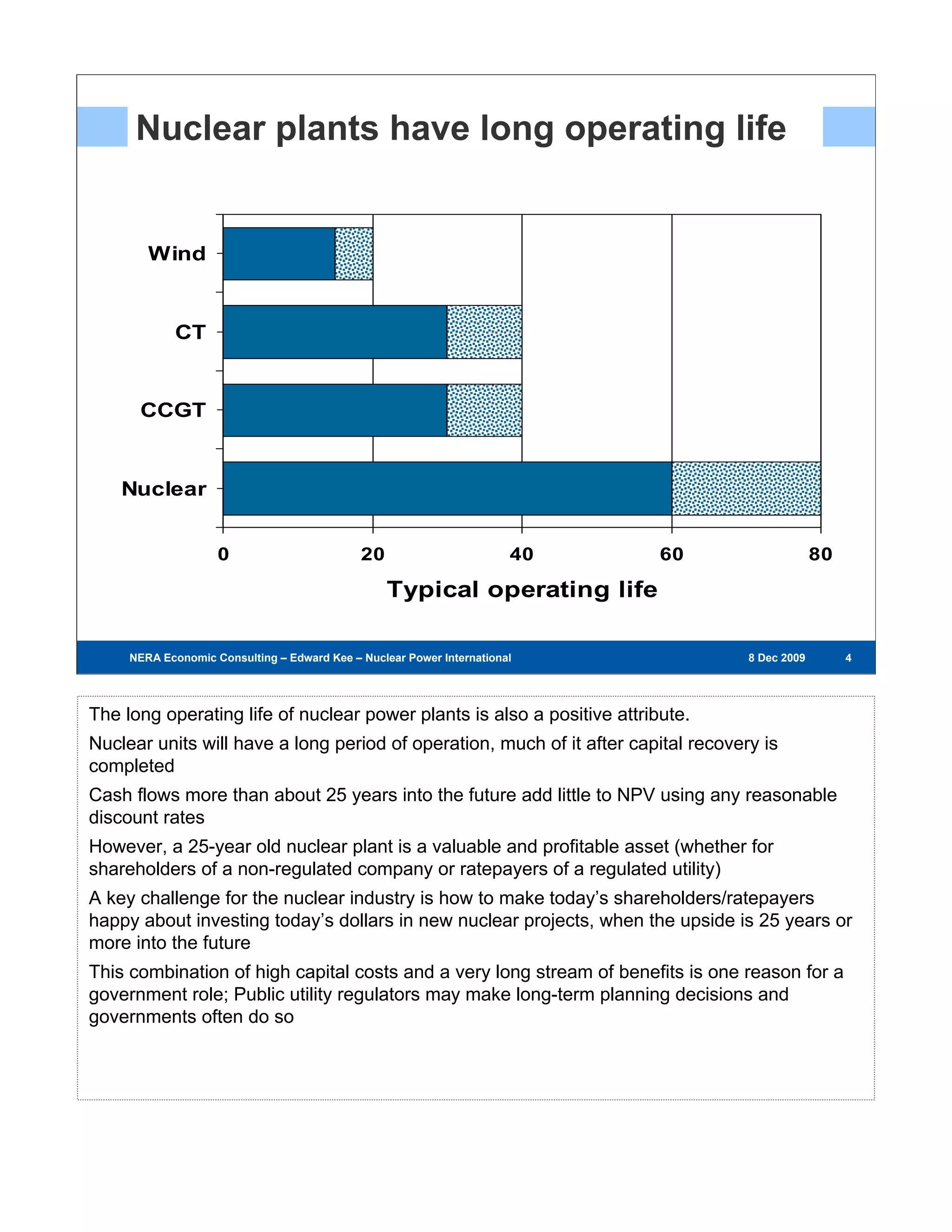
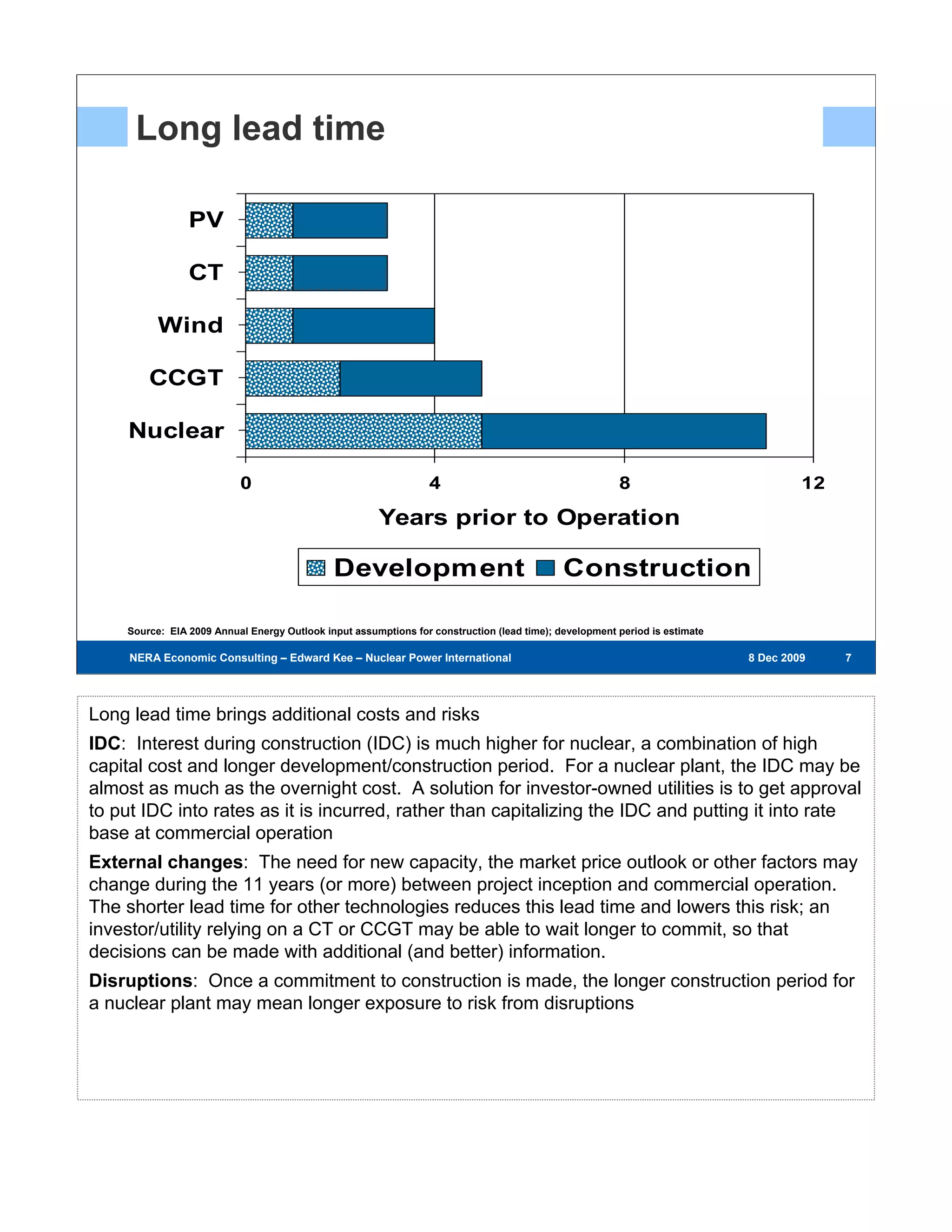
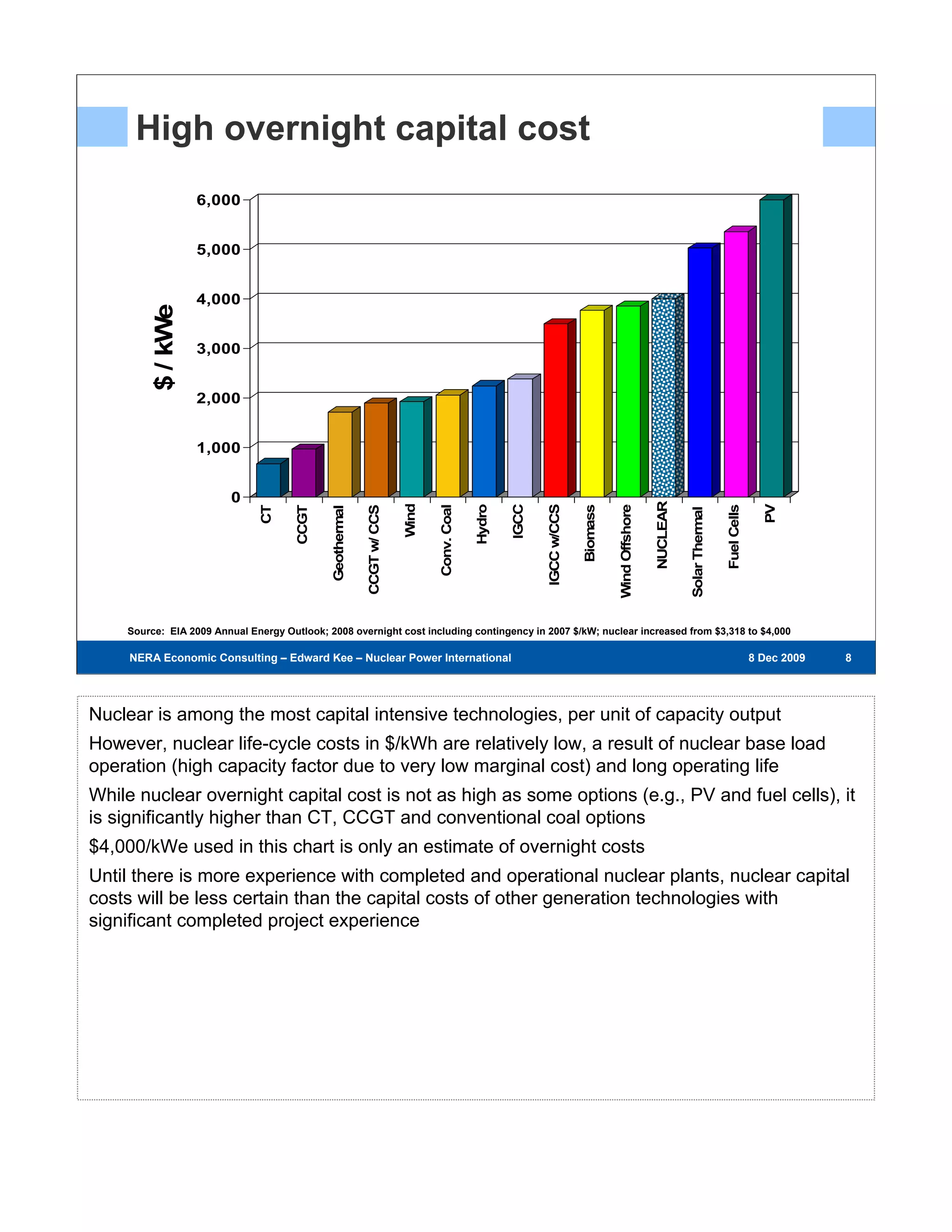
Existing nuclear power plants are valuable resources that provide zero-carbon, low-cost energy. However, building new nuclear power plants faces challenges due to high capital costs, long construction timelines, and regulatory hurdles. The first new nuclear power plants will test regulatory and project development processes and help reduce risks and costs for future plants. Government support through policies like loan guarantees may be needed to encourage investment in new nuclear energy.